Abstract
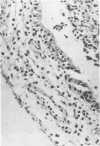
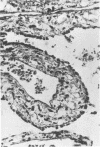
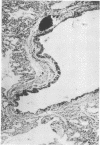
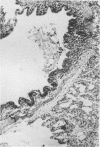
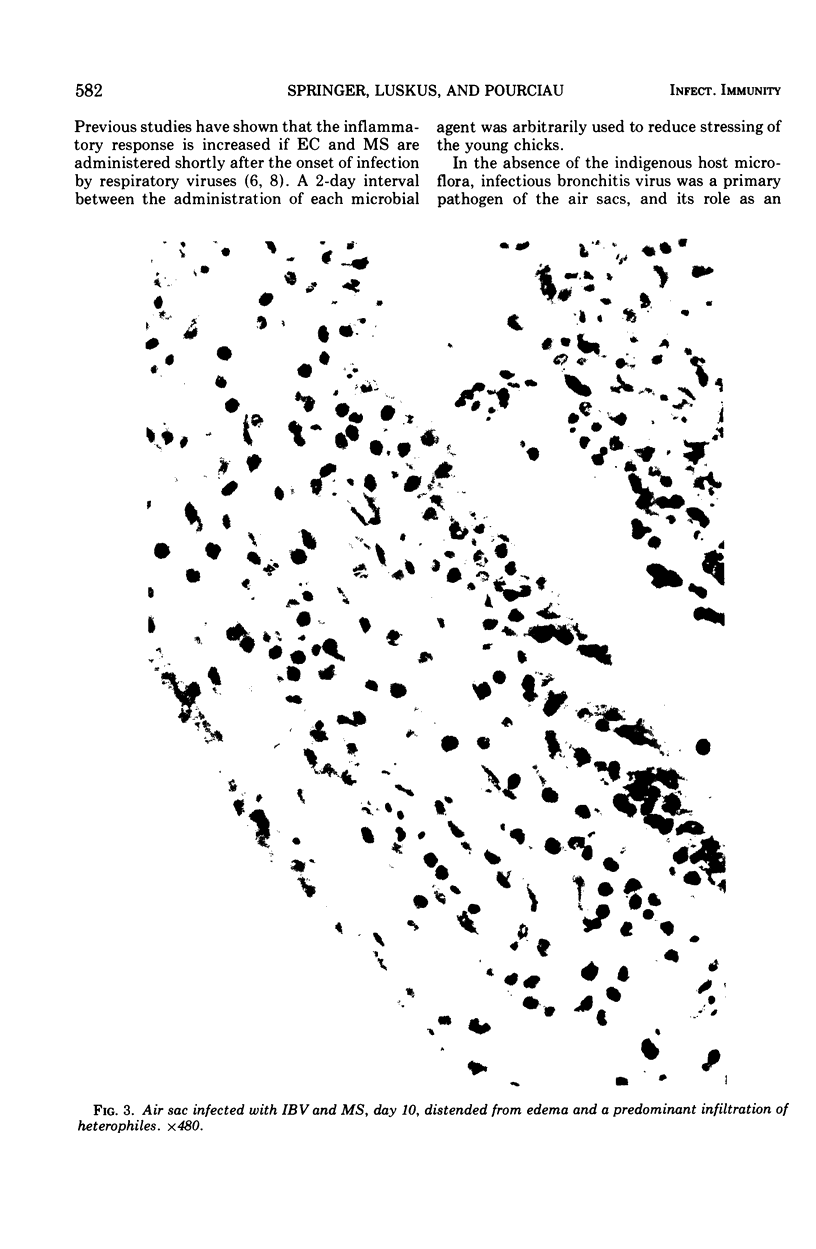
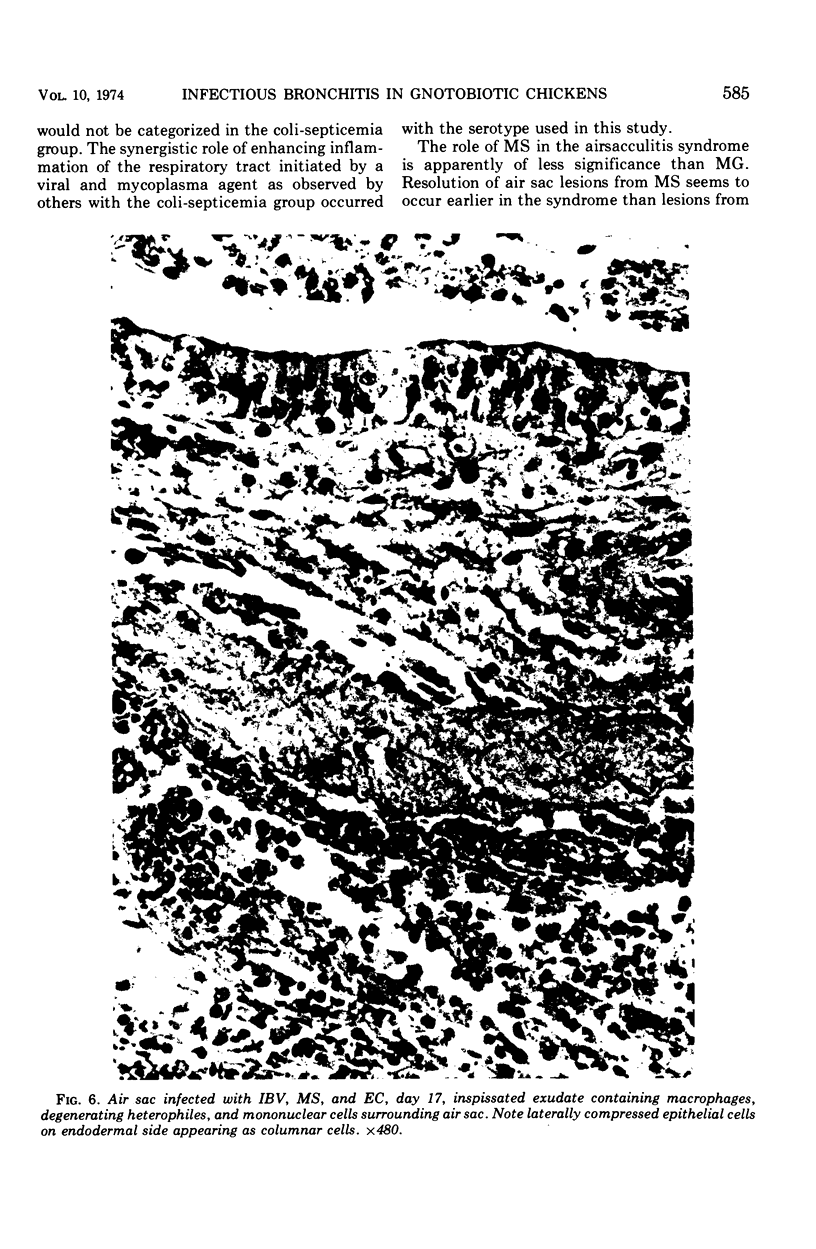
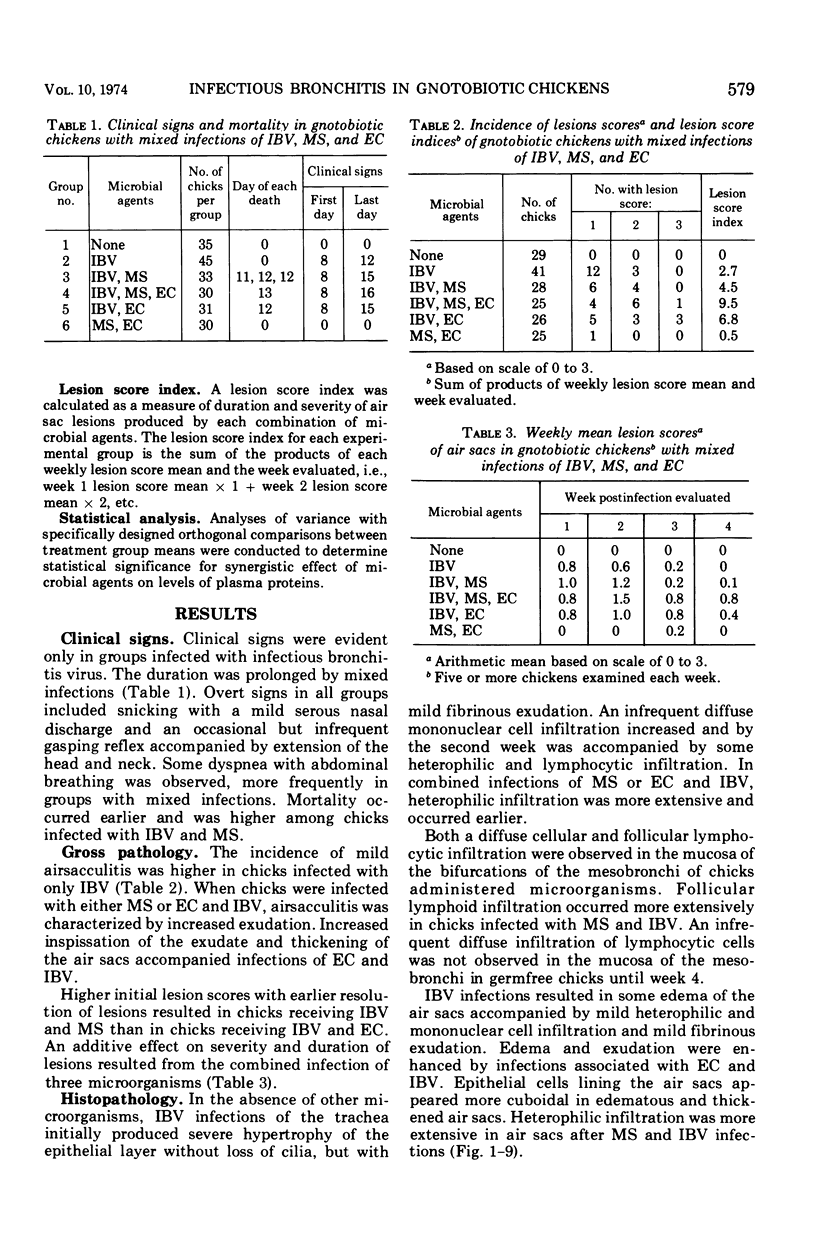
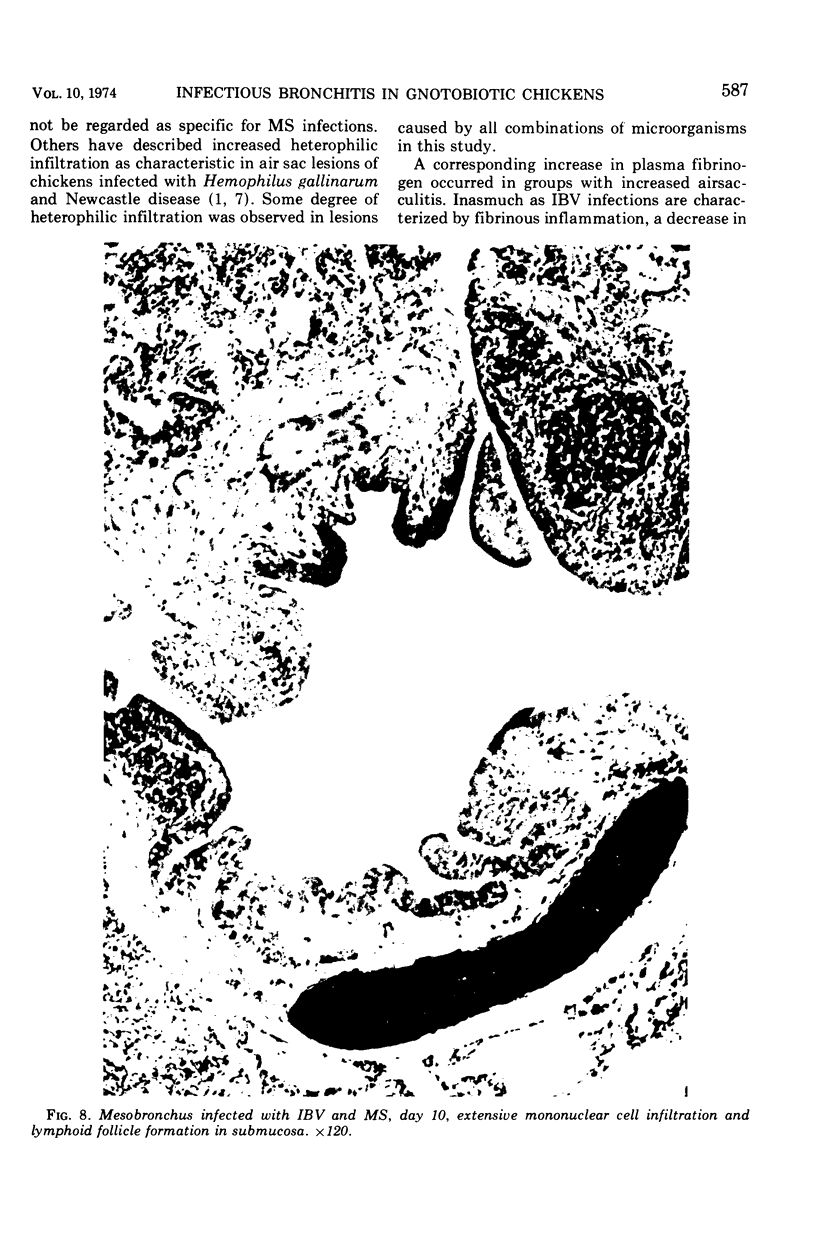
The synergistic role of infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) and mixed infections of Mycoplasma synoviae (MS) and Escherichia coli (EC) in the airsacculitis syndrome was evaluated in gnotobiotic chickens. Relative air sac lesion score indexes, in descending order of severity, from various combinations of organisms were: 9.5—IBV, MS, EC; 6.8—IBV, EC; 4.5—IBV, MS; 2.7—IBV; and 0.5—MS, EC. Infectious bronchitis virus caused a mild fibrinous inflammation. M. synoviae combined with IBV increased heterophilic and follicular lymphoid infiltration and mortality. E. coli combined with IBV increased exudation and prolonged airsacculitis. Concentrations of fibrinogen, gamma globulin, and total plasma proteins were elevated significantly by combined infections of IBV, MS, and EC (P < 0.01).
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIDDLE E. S., COVER M. S. The bacterial flora of the respiratory tract of chickens affected with chronic respiratory disease. Am J Vet Res. 1957 Apr;18(67):405–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleven S. H., King D. D., Anderson D. P. Airsacculitis in broilers from Mycoplasma synoviae: effect on air-sac lesions of vaccinating with infectious bronchitis and Newcastle virus. Avian Dis. 1972 Jul-Sep;16(4):915–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. L., Horton R. E., McCullough N. B. Mycoplasma gallisepticum infection in germfree and conventional chickens: experimental studies with a culture of low virulence. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Mar;28(123):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagi M. S., Mathey W. J. Interaction of Escherichia coli and Eimeria brunetti in chickens. Avian Dis. 1972 Jul-Sep;16(4):864–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS B. P., WOLFE P. A., BARTGIS I. L. Studies on the ameba-bacteria relationship in amebiasis. II. Some concepts on the etiology of the disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Jul;7(4):392–399. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. T., Johnson J., Reid W. M. Histomoniasis in gnotobiotic chickens and turkeys: biological aspects of the role of bacteria in the etiology. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. T., Schmittle S. C. Avian encephalomyelitis: a chronological study of the histopathogenesis in selected tissues. Avian Dis. 1968 May;12(2):229–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardaman T. H., Landreth K., Whatley S., Dreesen L. J., Glick B. Resistance to Mycoplasma synoviae is bursal dependent. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):674–676. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.674-676.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardaman T. H., Reece F. N., Deaton J. W. Effect of Mycoplasma synoviae on broiler performance. Poult Sci. 1973 Sep;52(5):1909–1912. doi: 10.3382/ps.0521909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn K. W., Eidson C. S. Changes in concentration of plasma proteins associated with Marek's disease. Poult Sci. 1970 May;49(3):784–793. doi: 10.3382/ps.0490784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]