Abstract
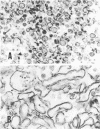
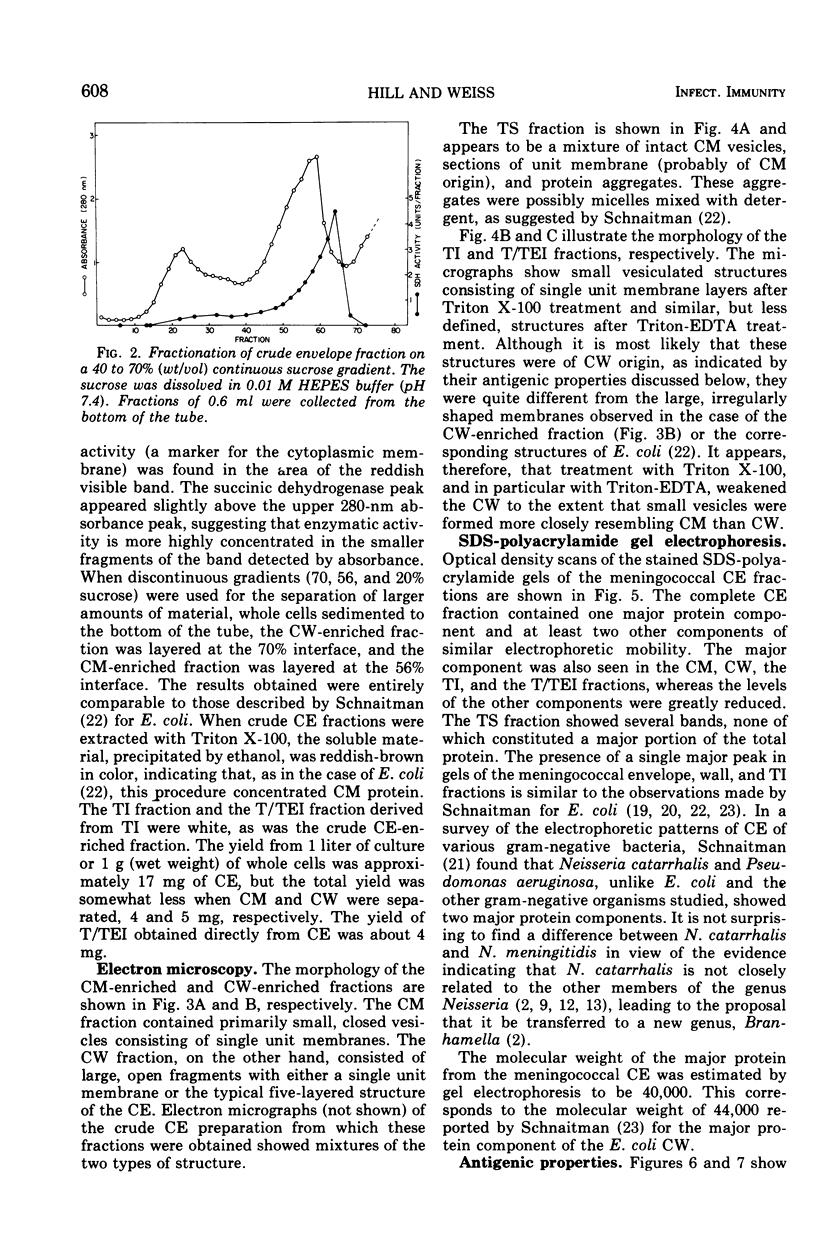
Several fractions were extracted from the cell envelope (CE) of Neisseria meningitidis group B and characterized with regard to their morphology, antigenicity, protein composition, and toxicity. Whole bacterial cells were suspended in a medium of low ionic strength and disrupted in a French pressure cell. The crude CE thus obtained were separated into cell membrane (CM) enriched and cell wall (CW) enriched fractions on sucrose density gradients. In addition, CM and CW fractions were separated from CE on the basis of differential solubility in the nonionic detergent, Triton X-100. The Triton-insoluble fraction, containing primarily CW components, was further treated with a mixture of Triton and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, which was shown to remove additional protein and most of the lipopolysaccharide. Electron microscope examination of the various fractions revealed typical unit membrane structures in the case of CM, or large, open segments in the case of CW. The Triton-insoluble and especially the Triton-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-insoluble fractions consisted of small vesicular structures. All fractions, except the Triton-soluble fraction, when assayed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, were shown to contain one major protein component accounting for more than 50% of the total. Sera from rabbits immunized with the various fractions formed precipitin lines in immunodiffusion tests against the homologous and some of the heterologous fractions. High-titer bactericidal antibodies were also demonstrated in these sera when tested against the homologous strains. Toxicity studies in rats sensitized with lead acetate indicate that the level of contamination of Triton-insoluble/Triton-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-insoluble fractions with lipopolysaccharide was significantly smaller than that of the other fractions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Purification and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):113–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.113-118.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. 3. Application of a new bactericidal-inhibition technique to distribution of serotypes among cases and carriers. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):149–154. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. I. Serological typing by a microbactericidal method. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):98–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.98-102.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. IV. Preliminary chemical studies on the nature of the serotype antigen. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):674–681. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.674-681.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Nachbar M. S., Salton M. R. Immunological properties of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):86–92. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.86-92.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Wyle F. A. New Classification of Neisseria meningitidis by Means of Bactericidal Reactions. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):479–484. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.479-484.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. C. Effect of glutamate on exogenous citrate catabolism of Neisseria meningitidis and of other species of Neisseria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):819–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.819-823.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. C., Peterson N. R., Weiss E. Characterization of spheroplast membranes of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):612–621. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.612-621.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. B., Wise J. L., Kiesow L. A. Failure of methylprednisolone to protect lead-sensitized rats against endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):683–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.683-684.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T. Deoxyribonucleic acid homologies among species of the genus Neisseria. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):870–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.870-874.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Brenner D. J. Thermal stability of interspecies Neisseria DNA duplexes. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Feb;55(2):201–208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr Acrylamide-gel electrophorograms by mechanical fractionation: radioactive adenovirus proteins. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Purification and properties of the colicin E3 receptor of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Comparison of the envelope protein compositions of several gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1404–1405. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1404-1405.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Examination of the protein composition of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.882-889.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]