Abstract
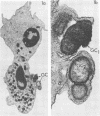
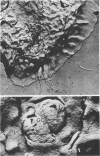
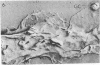
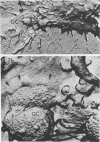
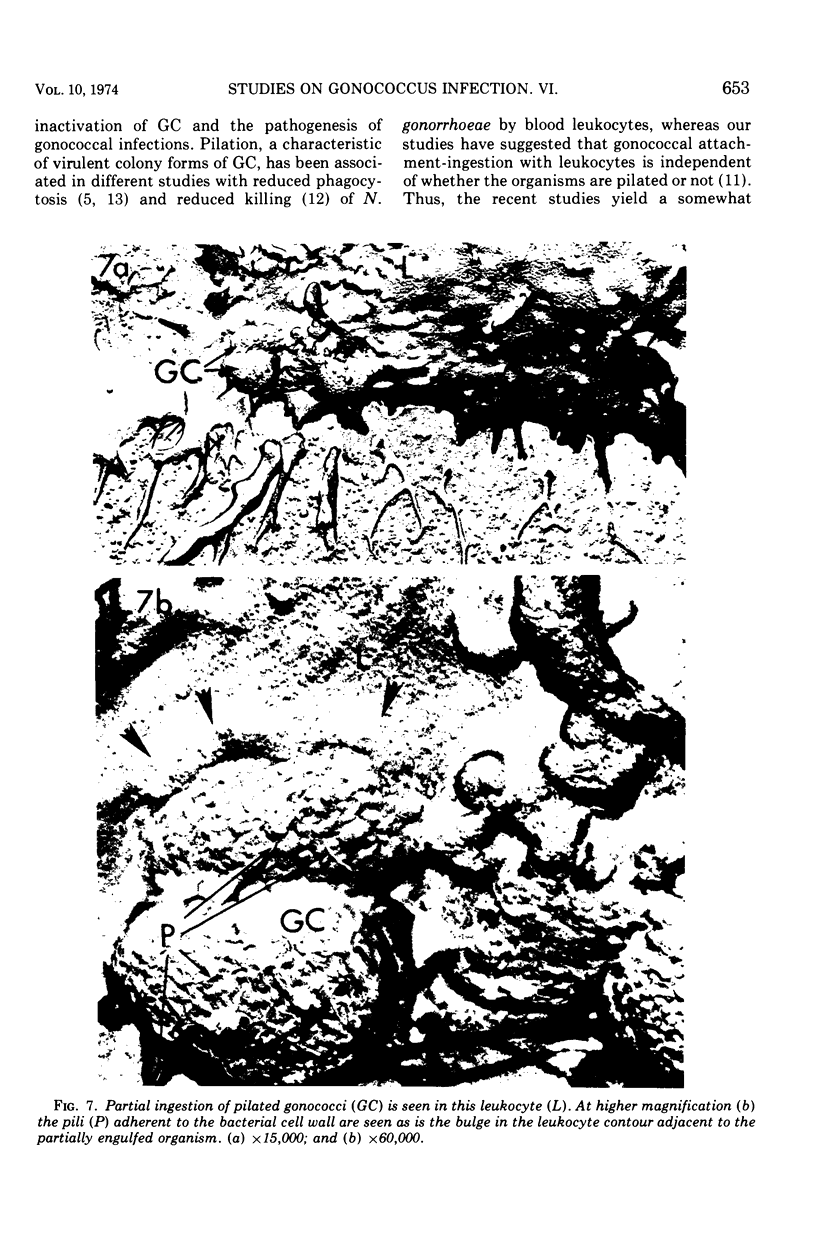
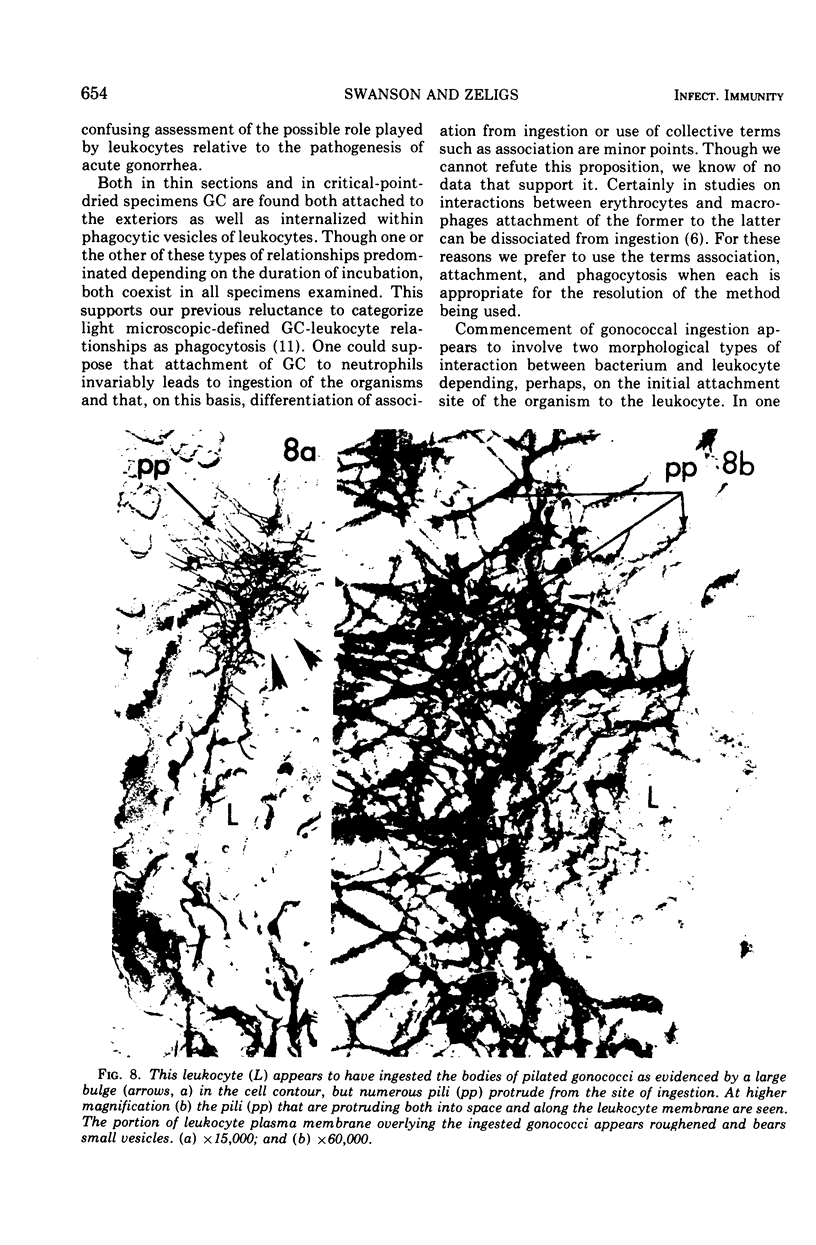
The ingestion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by isolated human leukocytes in vitro has been studied by electron microscopy. Use of the modified critical-point drying method allows clear visualization of progressive ingestion of both pilated and nonpilated gonococci by leukocytes. Incomplete ingestion of pilated gonococci with protrusion of tangled masses of pili from sites of phagocytosis are also found.
Full text
PDF

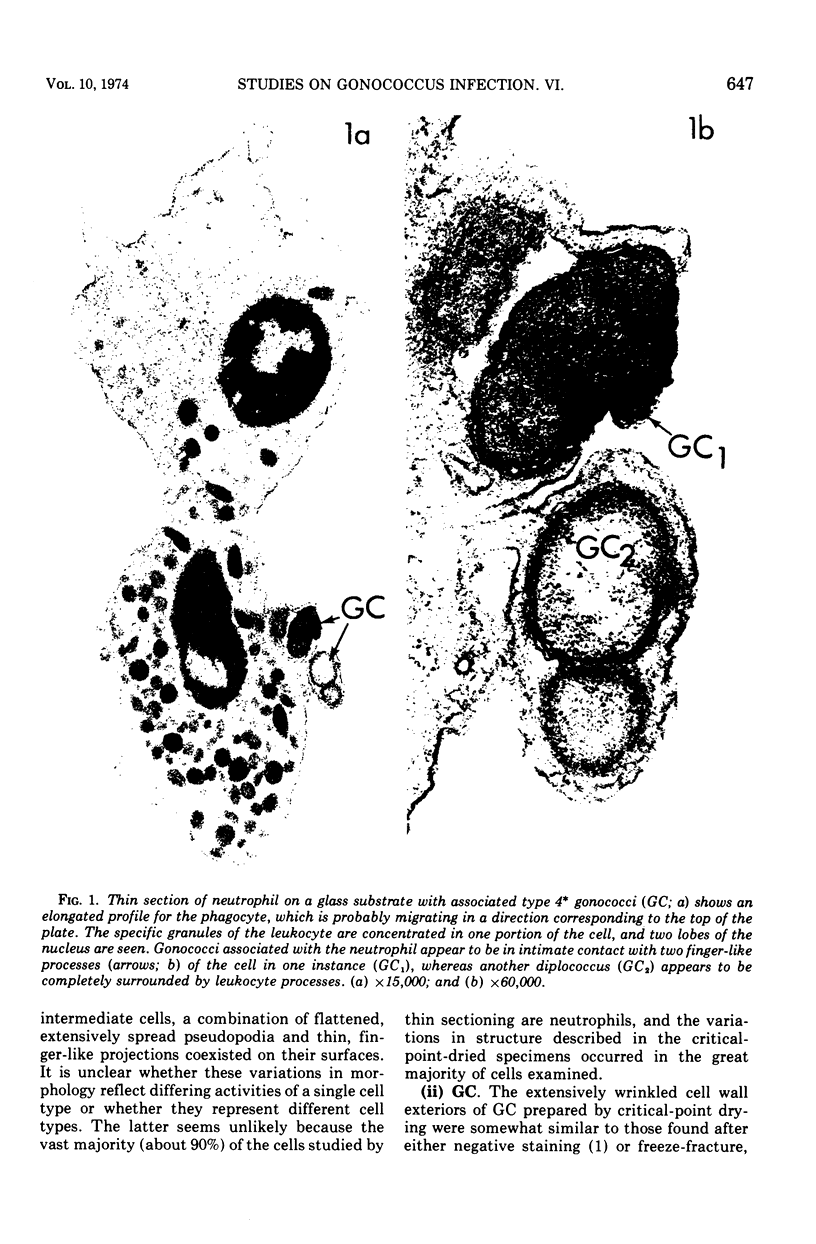

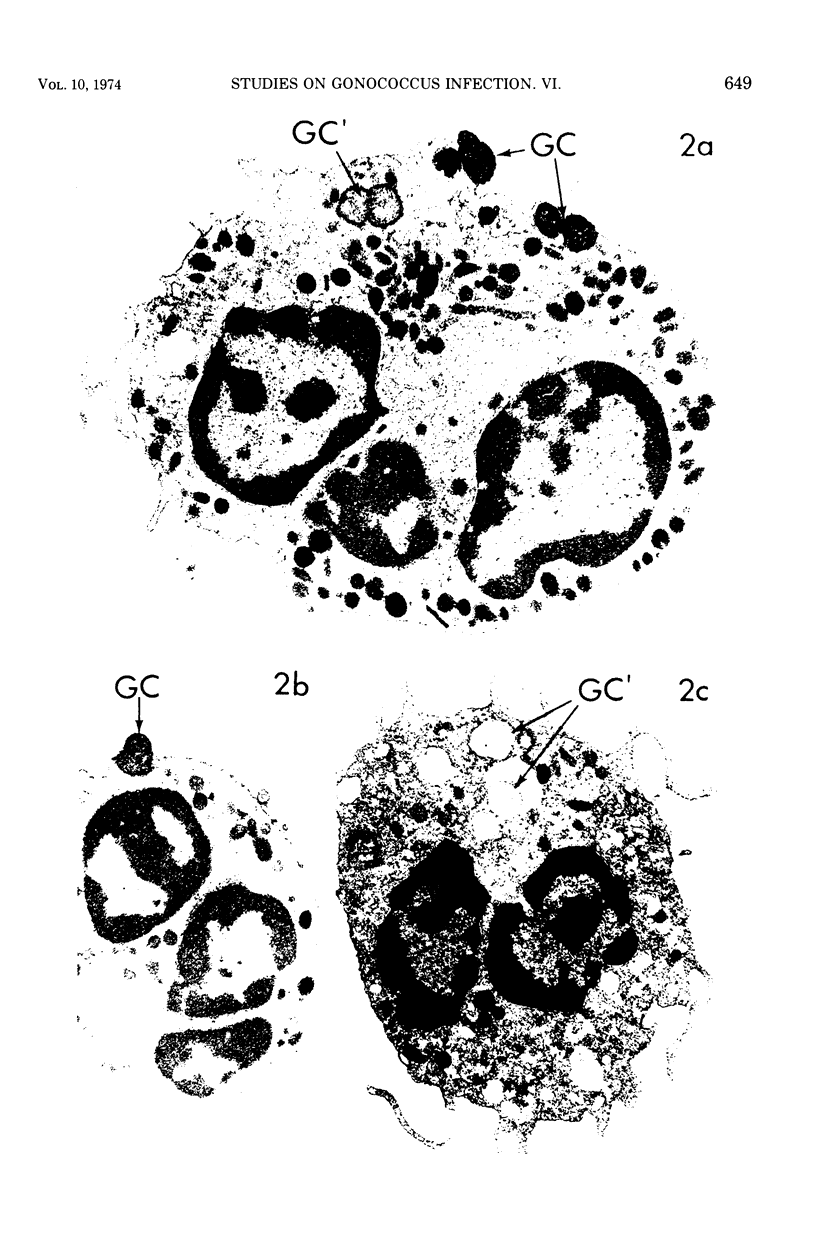

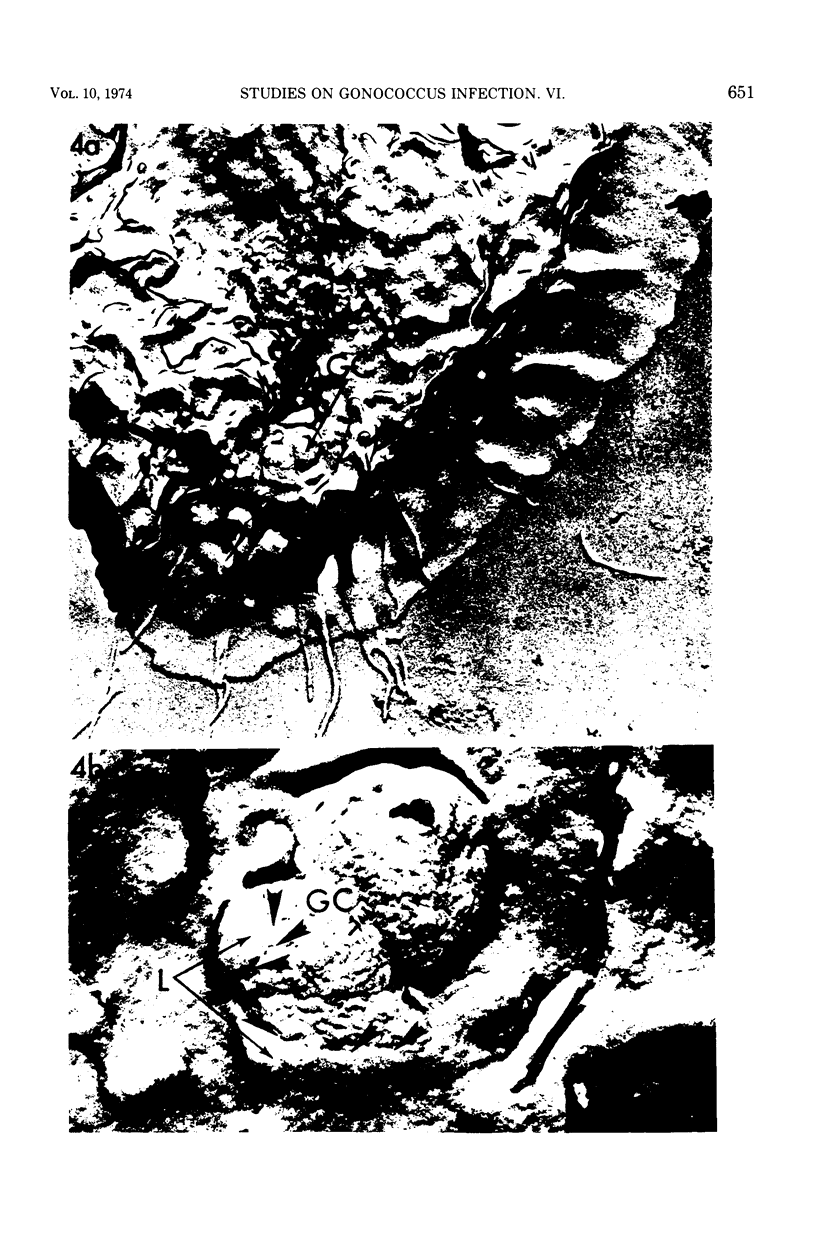



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLADEN H. A., MERGENHAGEN S. E. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF VEILLONELLA AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATION OF AN OUTER MEMBRANE WITH PARTICLES ASSOCIATED WITH ENDOTOXIC ACTIVITY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1482–1492. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1482-1492.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. The dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Zeligs B., Siam M. A., Parrott C. Studies on gonococcus infection. V. Observations on in vitro interactions of gonococci and human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):633–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.633-644.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. II. Freeze-fracture, freeze-etch studies on gonocci. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1258–1271. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Hill J. C., Tyeryar F. J., Jr Interaction of gonococci with phagocytic leukocytes from men and mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.98-104.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]