Abstract
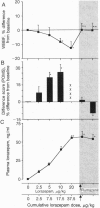
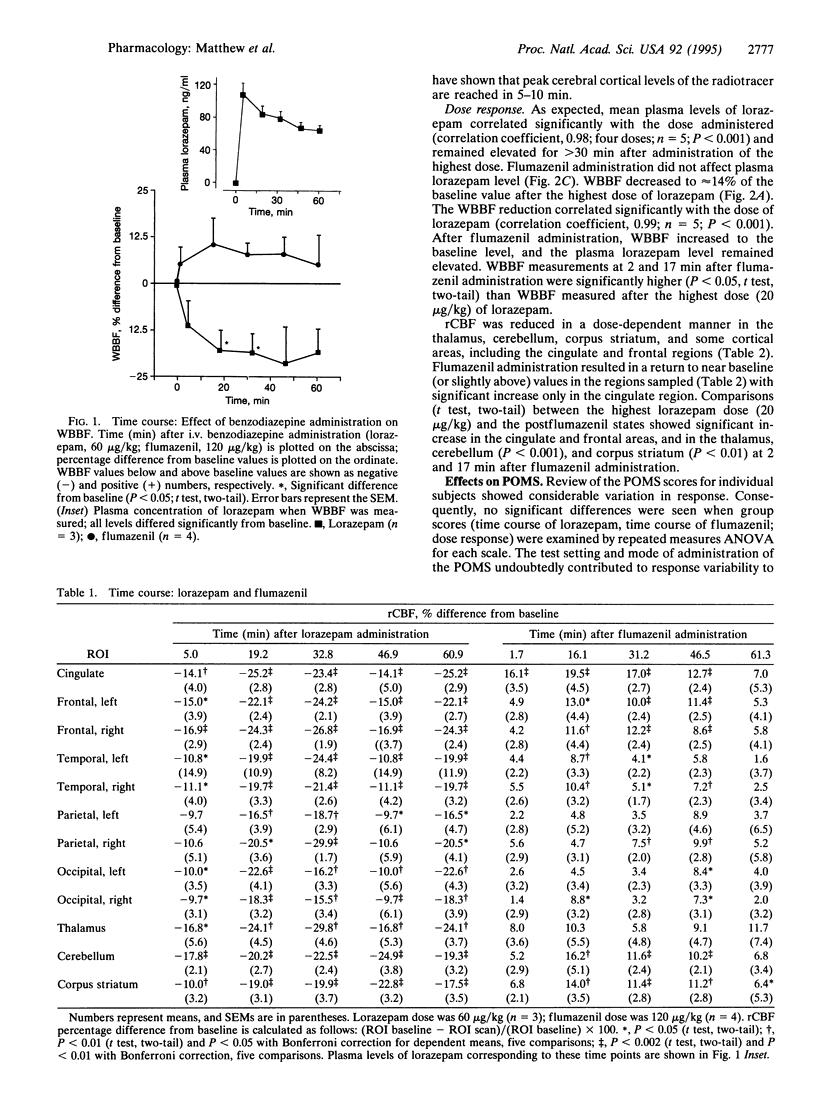
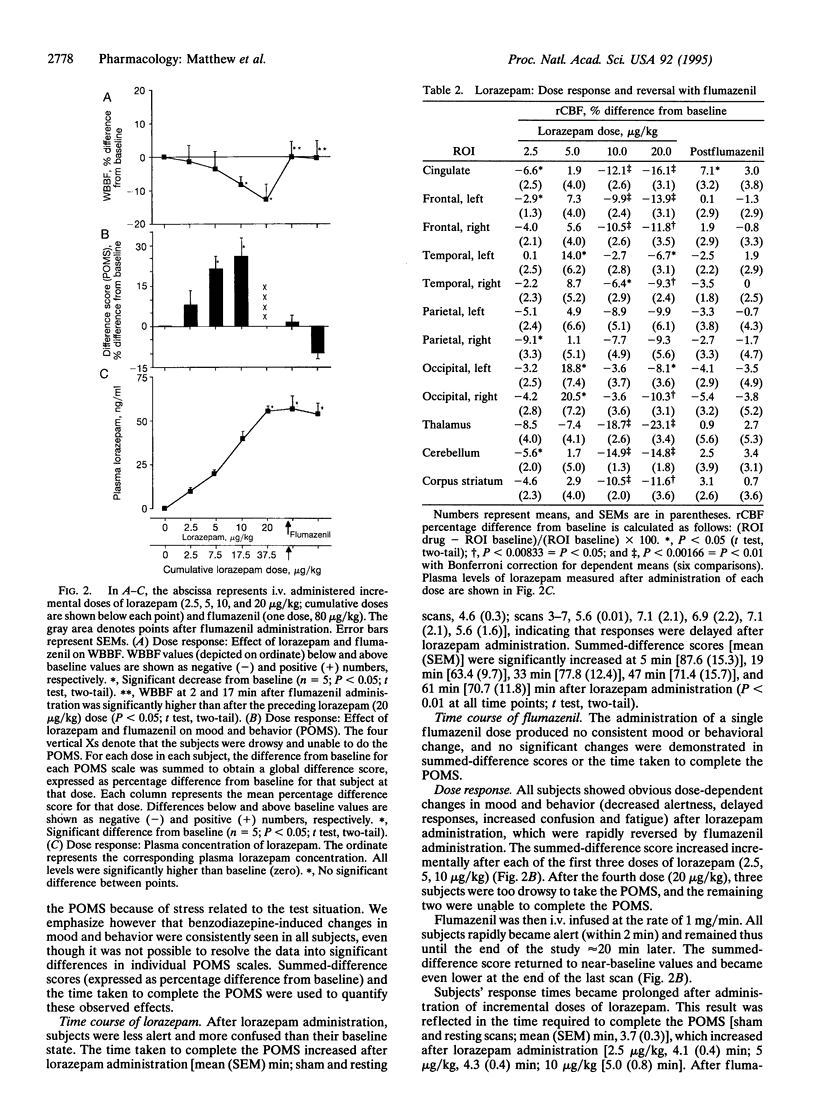
We studied the effects of a high-affinity gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-benzodiazepine-receptor agonist (lorazepam) and an antagonist (flumazenil) in humans, using H2(15)O positron-emission tomography. Administration of lorazepam to healthy volunteers caused time- and dose-dependent reductions in regional cerebral blood flow and self-reported alterations in behavioral/mood parameters. Flumazenil administration reversed these changes. These observations indicated that benzodiazepine-induced effects on regional cerebral blood flow and mood/behavior are mediated at some level through GABA-benzodiazepine receptors, although the specific mechanism remains unclear. The approach described here provides a method for quantifying GABA-benzodiazepine-receptor-mediated neurotransmission in the living human brain and may be useful for studying the role of these receptors in a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomqvist G., Pauli S., Farde L., Eriksson L., Persson A., Halldin C. Maps of receptor binding parameters in the human brain--a kinetic analysis of PET measurements. Eur J Nucl Med. 1990;16(4-6):257–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00842777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonetti E. P., Pieri L., Cumin R., Schaffner R., Pieri M., Gamzu E. R., Müller R. K., Haefely W. Benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788: neurological and behavioral effects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1982;78(1):8–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00470579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Albrechtsen R., Squires R. F. High densities of benzodiazepine receptors in human cortical areas. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):702–704. doi: 10.1038/269702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchsbaum M. S., Wu J., Haier R., Hazlett E., Ball R., Katz M., Sokolski K., Lagunas-Solar M., Langer D. Positron emission tomography assessment of effects of benzodiazepines on regional glucose metabolic rate in patients with anxiety disorder. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 22;40(25):2393–2400. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90753-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A., Juge O., Louis M., Nahory A. Effects of a specific benzodiazepine antagonist (RO 15-1788) on cerebral blood flow. Anesth Analg. 1987 Apr;66(4):309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. L., VanDerSpek A. F., Aldrich M. S., Berent S., Hichwa R. H., Sackellares J. C., Gilman S., Agranoff B. W. The effect of diazepam sedation on cerebral glucose metabolism in Alzheimer's disease as measured using positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Aug;7(4):415–420. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasby P. M., Friston K. J., Bench C. J., Frith C. D., Paulesu E., Cowen P. J., Liddle P. F., Frackowiak R. S., Dolan R. The effect of apomorphine and buspirone on regional cerebral blood flow during the performance of a cognitive task-measuring neuromodulatory effects of psychotropic drugs in man. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(12):1203–1212. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Franke K., Shader R. I. Analysis of lorazepam and its glucuronide metabolite by electron-capture gas--liquid chromatography. Use in pharmacokinetic studies of lorazepam. J Chromatogr. 1978 Sep 1;146(2):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Ford I., McCulloch J. The effect of diazepam upon local cerebral glucose use in the conscious rat. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., McCulloch J. Effects of the putative GABAergic agonists, muscimol and THIP, upon local cerebral glucose utilisation. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):613–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R. J., Wilson W. H., Daniel D. G. The effect of nonsedating doses of diazepam on regional cerebral blood flow. Biol Psychiatry. 1985 Oct;20(10):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(85)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R. J., Wilson W. H. Evaluation of the effects of diazepam and an experimental anti-anxiety drug on regional cerebral blood flow. Psychiatry Res. 1991 Oct;40(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0925-4927(91)90004-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew E., Andreason P., Carson R. E., Herscovitch P., Pettigrew K., Cohen R., King C., Johanson C. E., Paul S. M. Reproducibility of resting cerebral blood flow measurements with H2(15)O positron emission tomography in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 Sep;13(5):748–754. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt D. J., Glue P., Lawson C., Wilson S. Flumazenil provocation of panic attacks. Evidence for altered benzodiazepine receptor sensitivity in panic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990 Oct;47(10):917–925. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1990.01810220033004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. Drug interactions at the GABA receptor-ionophore complex. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:245–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Kuhar M. J., Rapoport S. I., London E. D. Increases and decreases in local cerebral glucose utilization in response to GABA agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 May 8;71(2-3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappata S., Samson Y., Chavoix C., Prenant C., Mazière M., Baron J. C. Regional specific binding of [11C]RO 15 1788 to central type benzodiazepine receptors in human brain: quantitative evaluation by PET. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Jun;8(3):304–313. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockoff M. A., Naughton K. V., Shapiro H. M., Ingvar M., Ray K. F., Gagnon R. L., Marshall L. F. Cerebral circulatory and metabolic responses to intravenously administered lorazepam. Anesthesiology. 1980 Sep;53(3):215–218. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198009000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. D., Garland W., Puia G., Guidotti A., Weber R. J., Costa E. Purification and characterization of naturally occurring benzodiazepine receptor ligands in rat and human brain. J Neurochem. 1992 Jun;58(6):2102–2115. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savic I., Persson A., Roland P., Pauli S., Sedvall G., Widén L. In-vivo demonstration of reduced benzodiazepine receptor binding in human epileptic foci. Lancet. 1988 Oct 15;2(8616):863–866. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L. Relationships among local functional activity, energy metabolism, and blood flow in the central nervous system. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2311–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow N. D., Wang G. J., Hitzemann R., Fowler J. S., Wolf A. P., Pappas N., Biegon A., Dewey S. L. Decreased cerebral response to inhibitory neurotransmission in alcoholics. Am J Psychiatry. 1993 Mar;150(3):417–422. doi: 10.1176/ajp.150.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wit H., Metz J., Wagner N., Cooper M. Effects of diazepam on cerebral metabolism and mood in normal volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1991 Aug;5(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]