Abstract
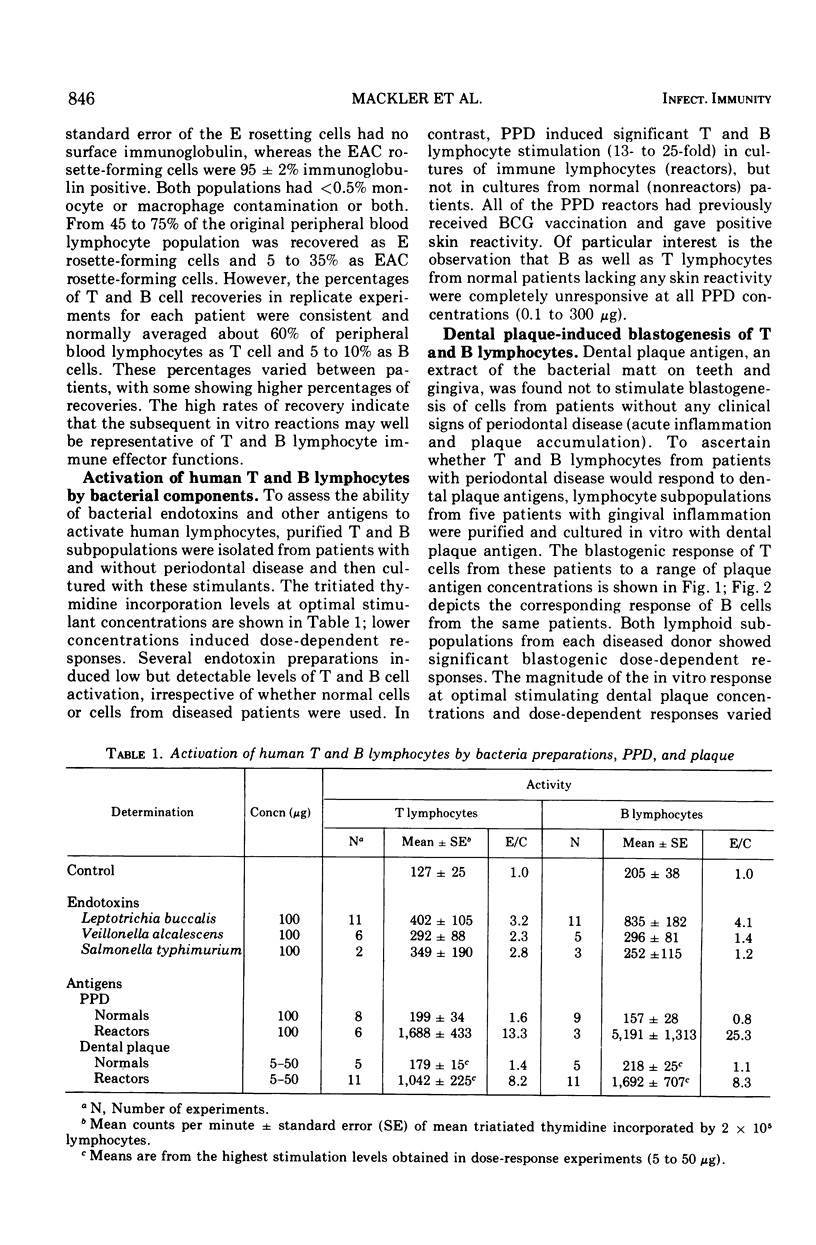
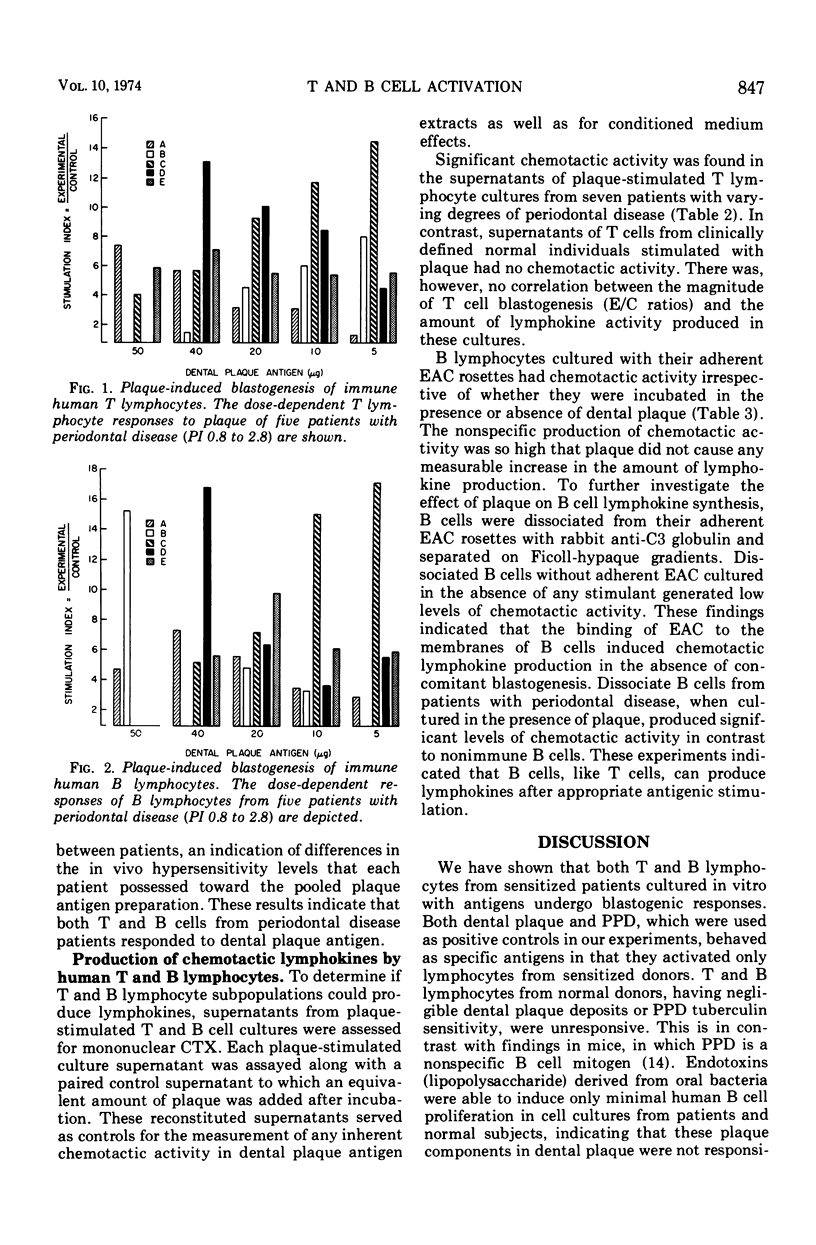
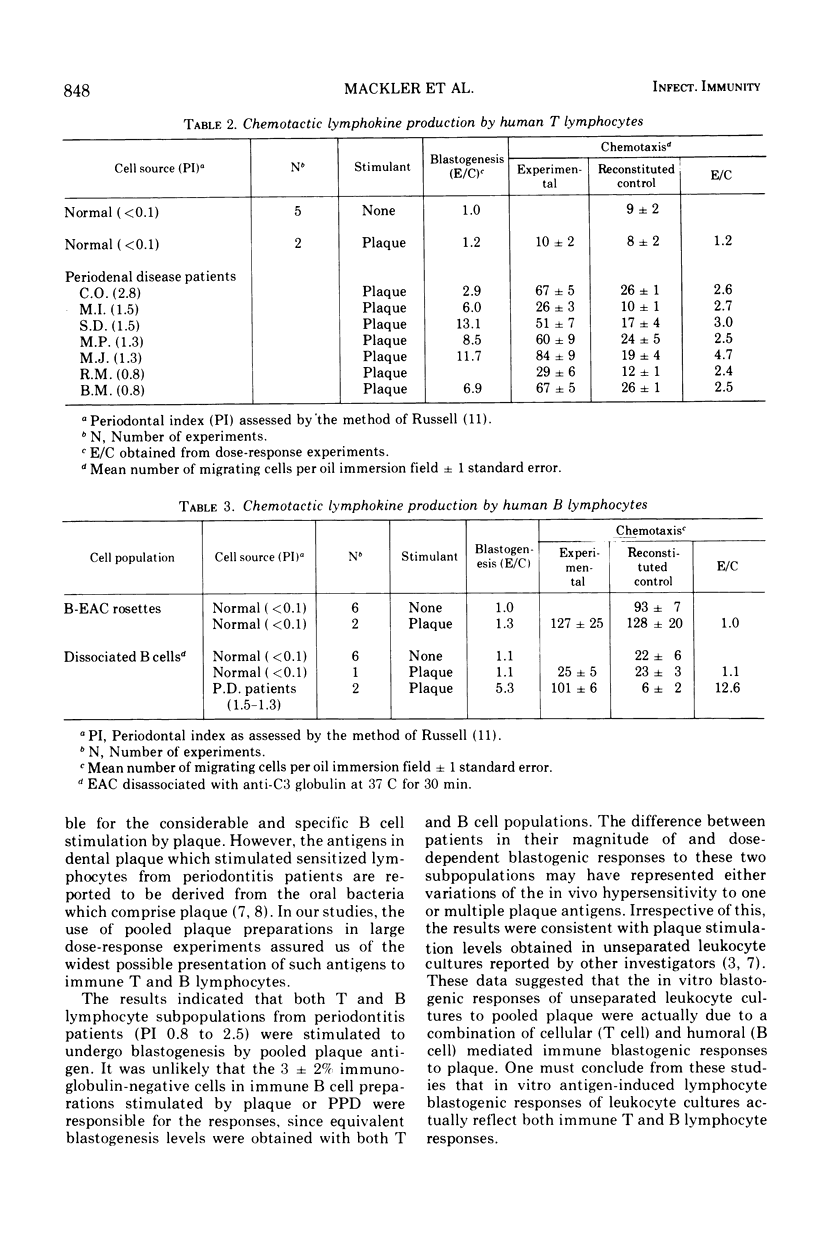
Thymus-derived (T) and bone marrow-derived (B) lymphocytes were isolated from human peripheral blood and cultured with various mitogens and antigens. Purified protein derivative of tuberculin stimulated both purified T and B cells from patients with positive skin reactivity to purified protein derivative but did not stimulate nonimmune lymphocytes. Similarly, both T and B lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease were stimulated to proliferate when incubated with dental plaque, whereas cells from normal individuals without gingivitis were unresponsive. In contrast, one component of plaque, bacterial endotoxins (lipopolysaccharide), minimally stimulated B lymphocytes from both normal or gingivitis patients. T lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease were also stimulated by plaque antigen to produce chemotactic lymphokine activity (CTX) for human monocytes. B cells purified by the EAC rosetting method nonspecifically produced CTX without concomitant blastogenesis; however, after dissociation of adherent EAC these immune B cells did not spontaneously produce CTX. Lymphokine synthesis by B cells was not dependent on concomitant blastogenesis. Dissociated B cells from periodontitis patients also produced CTX activity after stimulation with dental plaque antigen. Therefore, both T and B lymphocytes, after stimulation with nonendotoxin antigenic components of plaque, proliferated and produced lymphokines, which are presumed to contribute to the pathogenesis of periodontal disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Rosen F. S., Merler E. Unresponsiveness of human B lymphocytes to phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1974 Mar 29;248(447):426–428. doi: 10.1038/248426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Leikin S., Oppenheim J. J. Human lymphoproliferative reaction to saliva and dental plaque-deposits: an in vitro correlation with periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1972 Sep;43(9):522–527. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.9.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Elaboration of lymphotoxin by cultured human peripheral blood leucocytes stimulated with dental-plaque deposits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Mar;13(3):383–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972 Sep 1;177(4051):793–795. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4051.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Challacombe S. J., Lehner T. The specificity of serum factors in lymphocyte transformation in periodontal disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Aug;14(4):491–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by bacterial antigens in patients with periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. The significance of serum factors in stimulation of lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease by Veillonella alcalescens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(4):620–627. doi: 10.1159/000230554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Wilton J. M., Lehner T. Cell-mediated immunity in periodontal disease; cytotoxicity, migration inhibition and lymphocyte transformation studies. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):141–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler B. F., Altman L. C., Rosenstreich D. L., Oppenheim J. J. Induction of lymphokine production by EAC and of blastogenesis by soluble mitogens during human B-cell activation. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):834–837. doi: 10.1038/249834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL A. L. A system of classification and scoring for prevalence surveys of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1956 Jun;35(3):350–359. doi: 10.1177/00220345560350030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossberg A., Ferrigno P. D. A histological study of the incidence of plasma cells and lymphocytes in human gingival tissues. J Oral Med. 1971 Dec;26(3):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Nilsson B. S. PPD tuberculin--a B-cell mitogen. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):198–200. doi: 10.1038/newbio240198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


