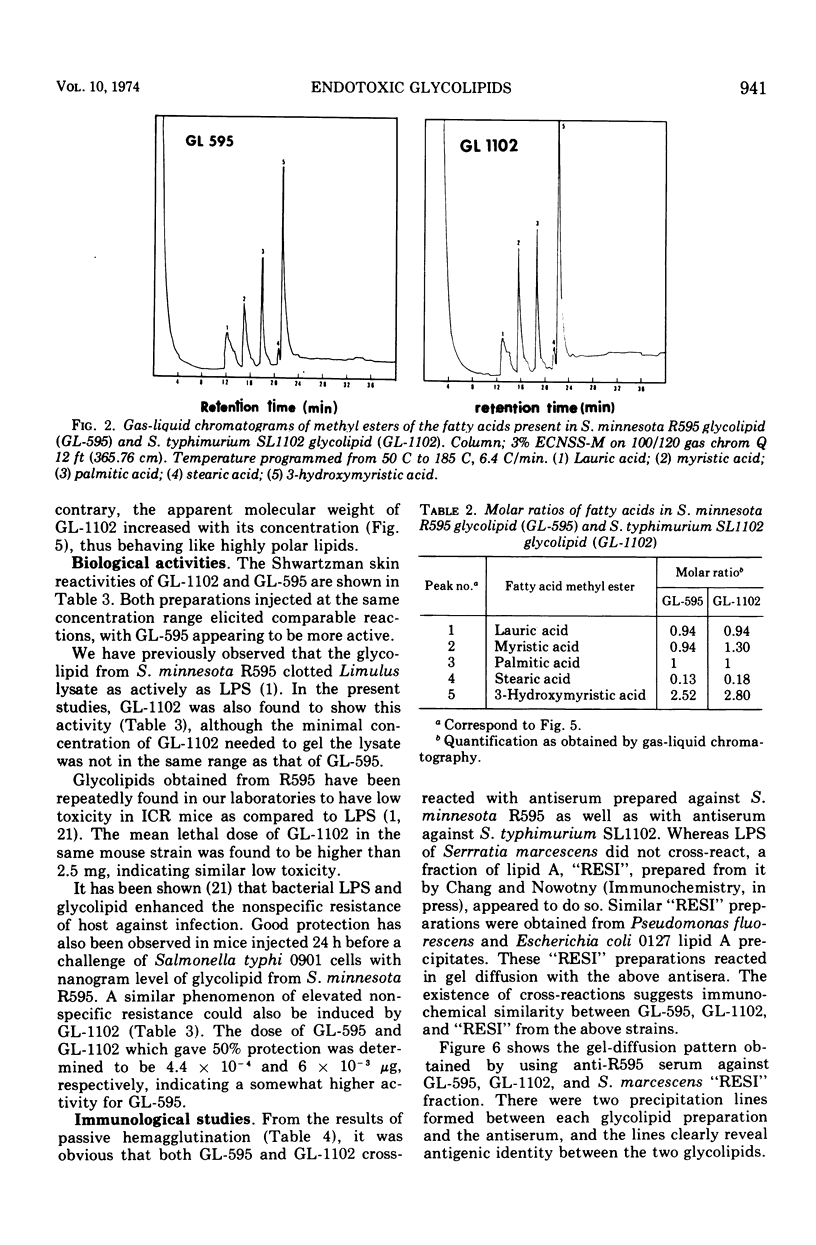
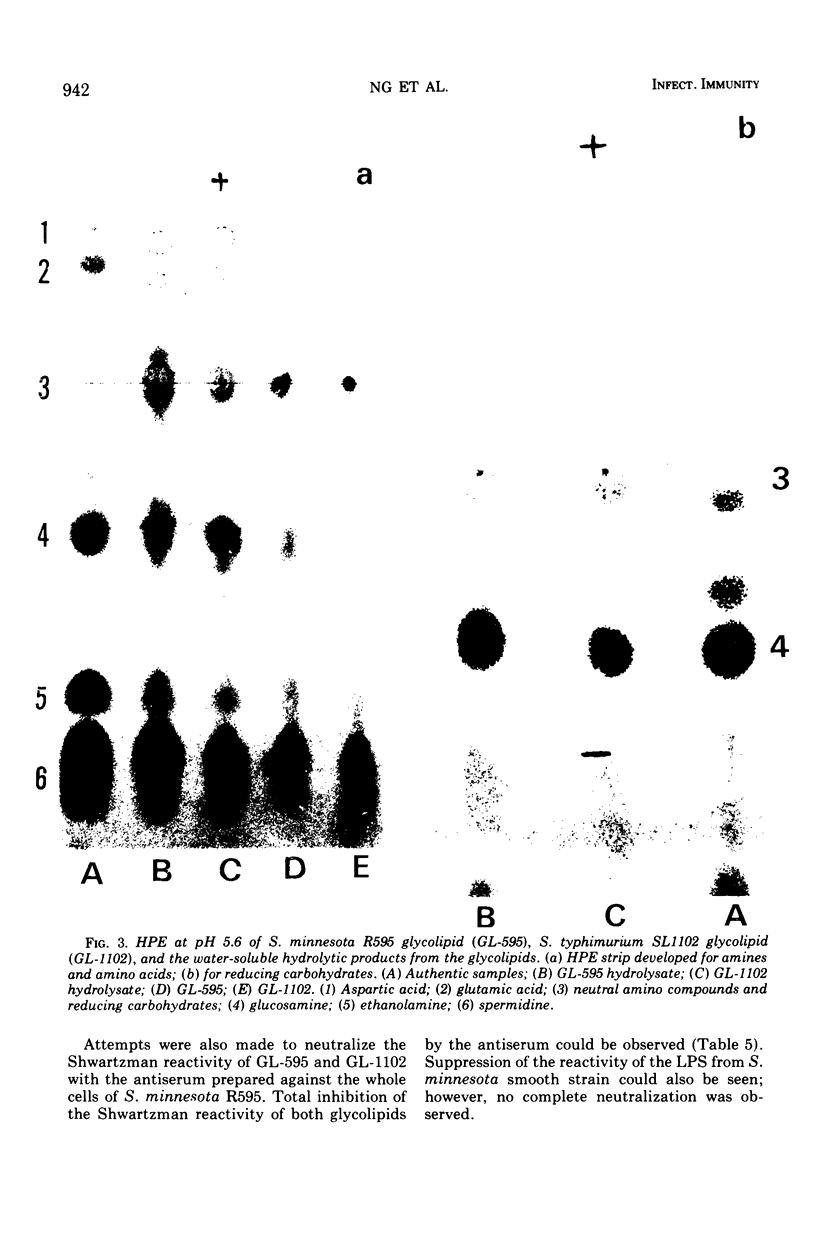
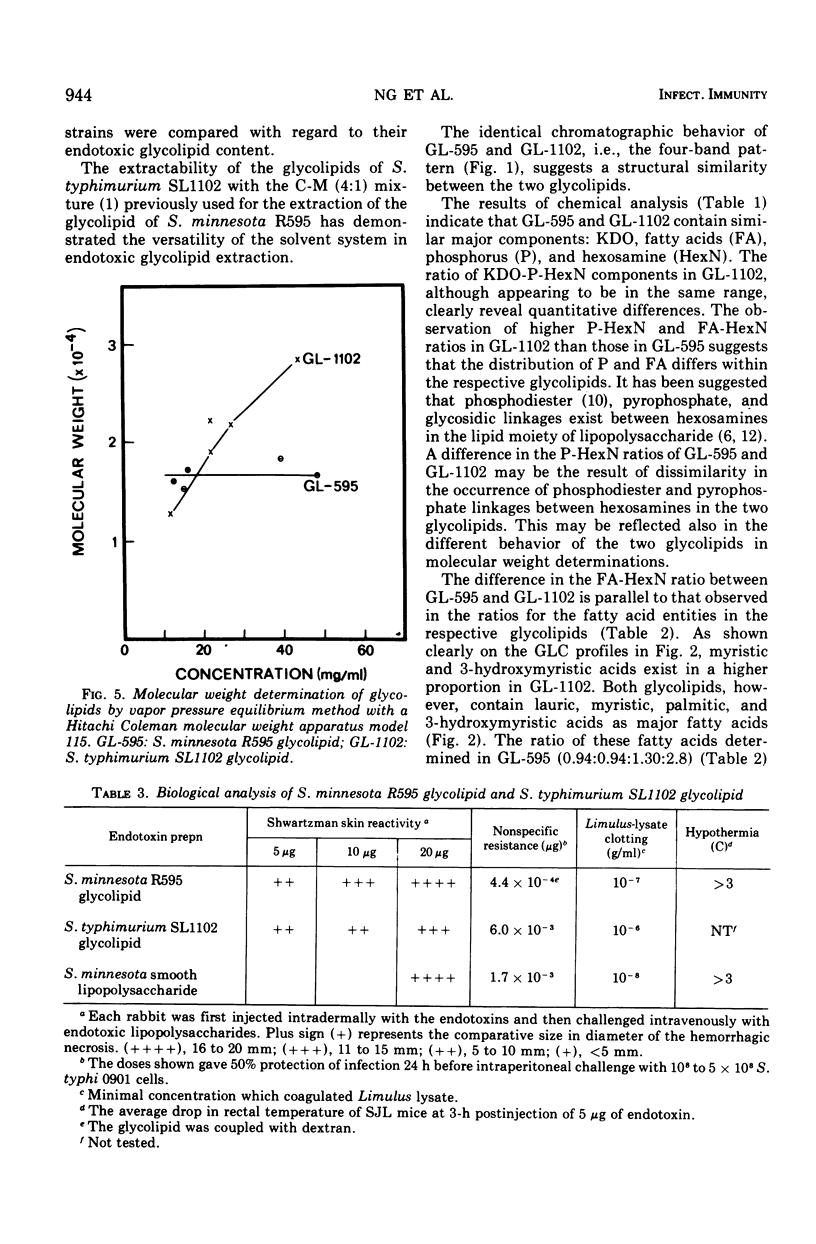
Abstract
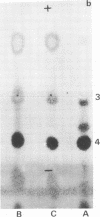
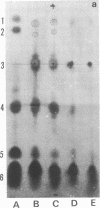
It has been assumed in the past that the lipid moieties of endotoxic lipopolysaccharides are quite similar if not identical. This has been tested in the reported work here, where the chemical composition and biological activities of the glycolipids of two heptoseless Re mutants, Salmonella minnesota R595 and Salmonella typhimurium SL1102, have been studied and compared. The two glycolipids, extracted with chloroform-methanol (4:1), showed identical thin-layer chromatographic patterns. The molar ratios for hexosamine, fatty acids, phosphorus, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate, total amines, and total nitrogen of the purified glycolipids were in the same range, but small differences could be established. Both glycolipids contained the same major fatty acids, i.e., lauric, myristic, palmitic, and 3-hydroxymyristic acids, in similar but not identical ratios. On paper electrophoresis, the acid hydrolysates of the two glycolipids showed analogous components. In the determination of molecular weight, whereas S. minnesota R595 glycolipid did not show concentration dependence, the molecular weight measured for S. typhimurium SL1102 increased with its concentration. The molecular weight of the fully endotoxic R595 glycolipid has been found to be 17,000 ± 1,500. Both glycolipids showed similar activities in the Shwartzman skin reaction, Limulus-lysate clotting assay, mouse lethality, and enhancement of nonspecific resistance, but the R595 preparation appeared to be more active on a weight basis in some parameters than SL1102. Using passive hemagglutination, we observed cross-reactivity between the glycolipids. In the gel-diffusion test, they revealed clear identity. The antiserum against S. minnesota R595 neutralized the Shwartzman skin reactivity not only of R595 but also of SL1102 glycolipid. These results confirm that there are identical immunodeterminant group(s) in the two glycolipids. On the other hand, chemical analytical data for two glycolipids showed only similarities, indicating that although both glycolipids are of comparable chemical nature, differences between them exist.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hannecart-Pokorni E., Dekegel D., Depuydt F. Macromolecular structure of lipopolysaccharides from gram-negative bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):6–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N., Nowotny A. Endotoxic glycolipid from a heptoseless mutant of Salmonella minnesota. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1824–1836. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1824-1836.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biologically active endotoxins from Salmonella mutants deficient in O- and R-polysaccharides and heptose. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1320–1326. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1320-1326.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Poore T. E., Zauber N. P., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in the blood of patients with sepsis due to gran-negative bacteria. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 10;283(24):1313–1316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012102832404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Risse H. J., Ruschmann E., Schlecht S., Schmidt G., Schulte-Holthausen H., Wheat R., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Structural relationship of Salmonella O and R antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):349–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of S. Minnesota. I. Protection against challenge with heterologous gram-negative bacilli. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):601–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Radvany R., Neale N. E. Neutralization of toxic bacterial O-antigens with O-antibodies while maintaining their stimulus on non-specific resistance. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(10):1107–1114. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A. Relationship of structure and biological activity of bacterial endotoxins. Naturwissenschaften. 1971 Aug;58(8):397–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00591520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radvany R., Neale N. L., Nowotny A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. VI. Neutralization of endotoxic O-antigens by homologous O-antibody. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):763–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Galanos C., Tanaka A., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biological activities of chemically modified endotoxins. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 24;22(2):218–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Gottert H., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in the lipid-A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse H. J., Dröge W., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Eine neue Gruppe von Salmonella R-Mutanten. Serologische und biochemische Analyse des Heptosekerns von Lipopolysacchariden aus Salmonella minnesota- und Salmonella ruiru-Mutanten. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Apr;1(2):216–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A., Goldfine H. Isolation and characterization of 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate-lipid A from a heptose-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):531–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.531-541.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G., Jann B., Jann K. Immunochemistry of R lipopolysaccharides of Escherichia coli. Studies on R mutants with an incomplete core, derived from E. coli O8:K27. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Oct;16(2):382–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman S. J. In vitro susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(Suppl):543–p. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_3.s543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi D., Nowotny A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. V. Nature of active sites in endotoxic lipopolysaccharides of Serratia marcescens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):604–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. C., Boorman L., Reid R. Assay of endotoxin by the hypothermic response of mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Apr;52(2):198–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]