Abstract
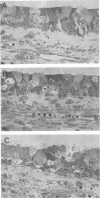
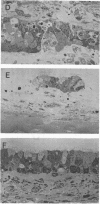
The effect of diphtheria toxin on guinea pig trachea in organ culture was examined to measure the susceptibility of respiratory epithelial cells to toxin action. Exposure of individual tracheal rings to toxin resulted in cessation of protein synthesis as well as the development of cytopathology within a few hours. Continued incubation led to further inhibition of protein synthesis and extensive disorganization of the epithelial layer. Other inhibitors of protein synthesis were monitored for their effect on the structural integrity of tracheal cells but were found incapable of eliciting similar histopathology. Early after its addition, toxin at minute concentrations possessed cytotoxic properties as well as the ability to inhibit protein synthesis. Interpretation of these data is correlated with current information on the structure and activity of diphtheria toxin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARSKI G., KOURILSKY R., CORNEFERT F. Resistance of respiratory ciliated epithelium to action of polio and adeno viruses in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Nov;96(2):386–391. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M., Harper A. A. Action of diphtheria toxin in the guinea pig. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1138–1152. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Imhoff J. G. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. I. Protein synthesis in guinea pig tissues. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1107–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Saelinger C. B. Inhibition of protein synthesis after intravenous or intramuscular challenge with diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):418–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.418-421.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. V. Protein metabolism in a guinea pig model simulating chronic diphtheritic toxemia. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):556–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.556-560.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Effect of diphtheria toxin on protein synthesis: inactivation of one of the transfer factors. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. Observations on the structure of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1485–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Baseman J. B. Studies on transferase II using diphtheria toxin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:595–602. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T. Diphtheria toxin, protein synthesis, and the cell. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M., Kuchler R. J., Solotorovsky M. The response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. I. Amino acid transport, accumulation, and incorporation in normal and intoxicated sensitive cells. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):407–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. II. Kinetic studies on intoxication of HeLa cells by diphtheria toxin and related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3845–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]