Abstract
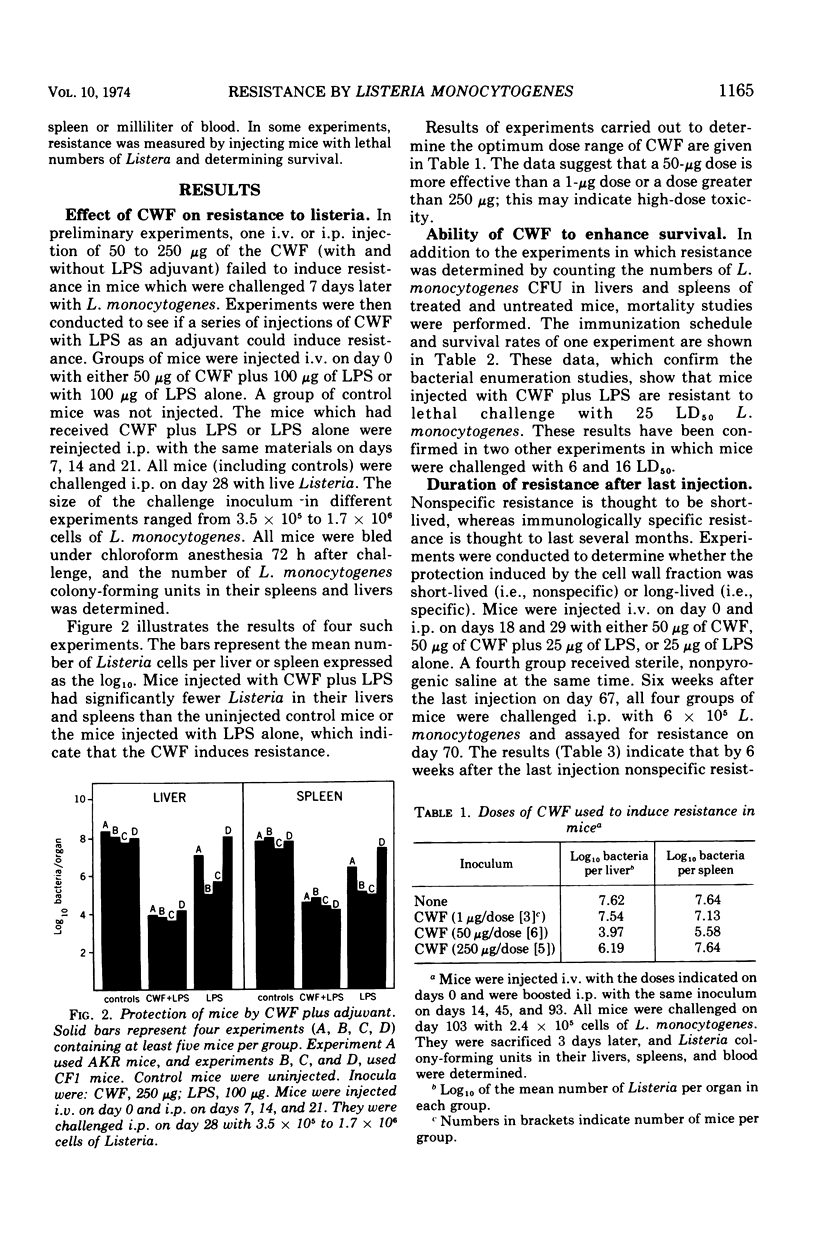
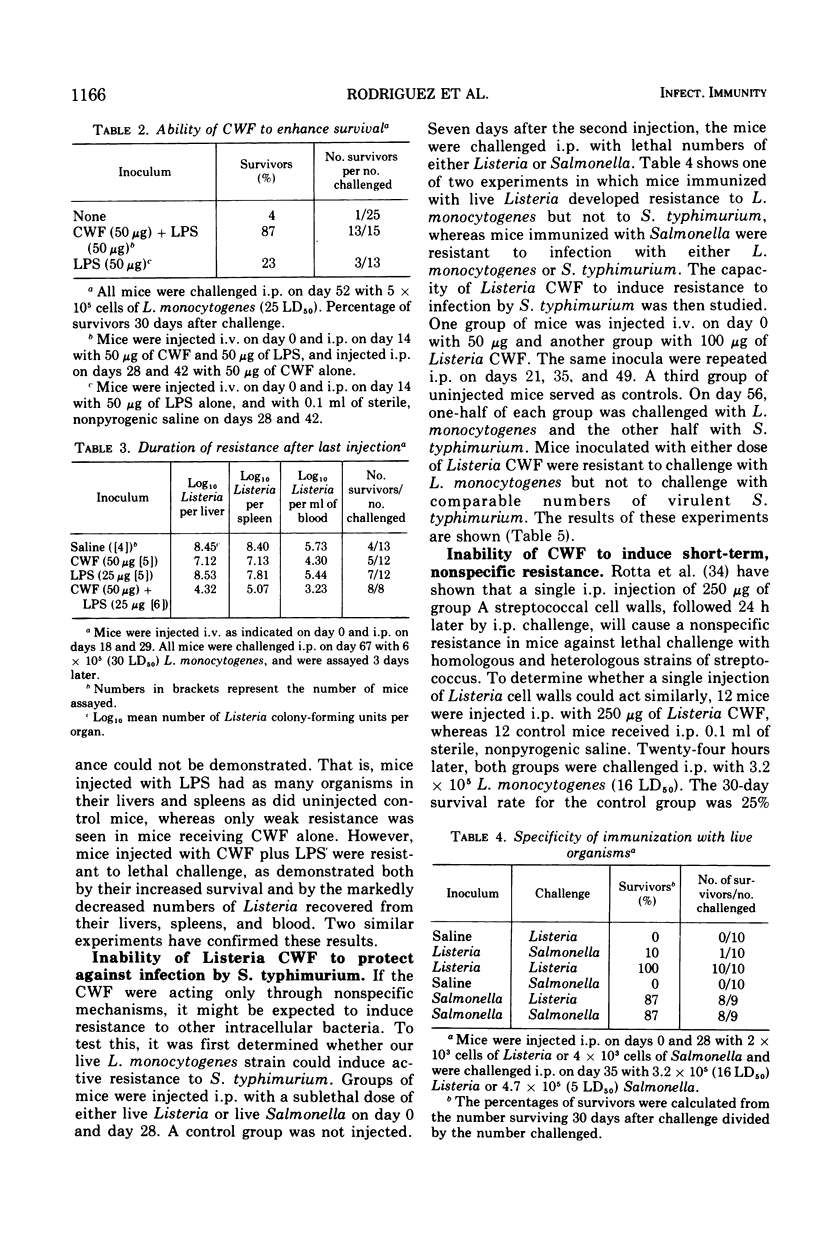
A crude cell wall fraction of Listeria monocytogenes was prepared by sonic disruption and differential centrifugation of viable, washed cultures. When injected into mice, this sterile, crude cell wall fraction protected mice against an intraperitoneal challenge with 18 to 85 50% mean lethal dose of L. monocytogenes. Resistance was greatly enhanced when bacterial endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) was injected along with the cell wall fraction. Resistance was measured both by enumerating the bacteria in the livers and spleens of vaccinated and control mice and by survival studies. Two major lines of evidence suggest that the resistance induced by cell wall fraction is at least in part specific. Unlike non-specific resistance, the cell wall fraction-induced resistance was relatively long-lived, (i.e., it was demonstrable 6 weeks after the last injection of cell wall fraction and lipopolysaccharide). In addition, cell wall fraction protected against challenge with L. monocytogenes, but not against challenge with S. typhimurium.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG A. S., SWORD C. P. CELLULAR RESISTANCE IN LISTERIOSIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:258–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUZINS I., ROWLEY D. On the question of the specificity of cellular immunity. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1962 Aug;40:283–291. doi: 10.1038/icb.1962.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander P., Evans R. Endotoxin and double stranded RNA render macrophages cytotoxic. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):76–78. doi: 10.1038/newbio232076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlema H. C., Braunius R. Studies on vaccination against Listeria infections. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(2):261–262. doi: 10.1007/BF02218493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. A., Martens B. L., Cooper H. R., McClatchy J. K. Requirement for bone marrow-derived cells in resistance to Listeria. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1407–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Boros D. L., Warren K. S. The effect of Schistosoma mansoni infection on the response of mice to Salmonella enteritidis and Listeria monocytogenes. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):249–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of Acquired Resistance Produced by Immunization with Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria Fractions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.121-126.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of the anamnestic response produced by Listeria monocytogenes or Mycobacterium tuberculosis to challenge with Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):127–133. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.127-133.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., SCHAEDLER R. W. Reversible changes in the susceptibility of mice to bacterial infections. I. Changes brought about by injection of pertussis vaccine or of bacterial endotoxins. J Exp Med. 1956 Jul 1;104(1):53–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., KARAKAWA W. W. Immunization of mice against Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Nov;74(5):584–586. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.5.584-586.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G., BIOZZI G., HALPERN B. N., STIFFEL C., MOUTON D. The effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (BCG) infection on the resistance of mice to bacterial endotoxin and Salmonella enteritidis infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Jun;40(3):281–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida T., Tajima M. Stimulation of non-specific resistance by heterologous endotoxins and experimental immunity to Bordetella pertussis in mice. Immunology. 1971 Aug;21(2):313–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D., AUZINS I. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. I. THE CARRIER STATE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:215–228. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasky S., Pickett M. J. Immunogenicity and specificity of Listeria monocytogenes cell walls. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):65–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKI K., MACKANESS G. B. THE PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:93–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Cellular immunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:89–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. Resistance to intracellular infection. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):439–445. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON C., Jr, COOK R. H., BAGDONAS V. An attempt to immunize sheep during an outbreak of listeriosis. Am J Vet Res. 1951 Oct;12(45):306–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSEBOLD J. W., SAWYER M. T. Immunization studies on listeriosis in mice. J Immunol. 1957 Apr;78(4):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATOCKA F., MARA M., SCHINDLER J. Studies on the pathogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes. II. Influence of substances isolated from cells of Listeria monocytogenes on experimental listeriosis in white mice. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1959 Apr;174(7-8):586–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATOCKA F., SCHINDLER J., MARA M. Studies on the pathogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes. I. Protein substance isolated from cells of Listeria monocytogenes enhancing listeric infection. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1959 Apr;174(7-8):573–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. Rapidly induced changes in the level of non-specific immunity in laboratory animals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):223–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D., TURNER K. J., JENKIN C. R. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. 3. CELL-BOUND ANTIBODY. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:237–248. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Synthetic polyanions protect mice against intracellular bacterial infection. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):361–363. doi: 10.1038/226361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Prendergast T. J., Karakawa W. W., Harmon C. K., Krause R. M. Enhanced resistance to streptococcal infection induced in mice by cell wall mucopeptide. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):877–890. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin J., McIntosh J., Remington J. S. Studies on the mechanisms of resistance to phylogenetically diverse intracellular organisms. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):252–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin J., Remington J. S. Resistance to intracellular infection in mice immunized with Toxoplasma vaccine and adjuvant. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 May;9(5):465–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBECKE G. J., BENACERRAF B. The reticulo-endothelial system and immunological phenomena. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:559–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER K. J., JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. 2. ANTIBODY FORMATION DURING THE CARRIER STATE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:229–236. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



