Abstract
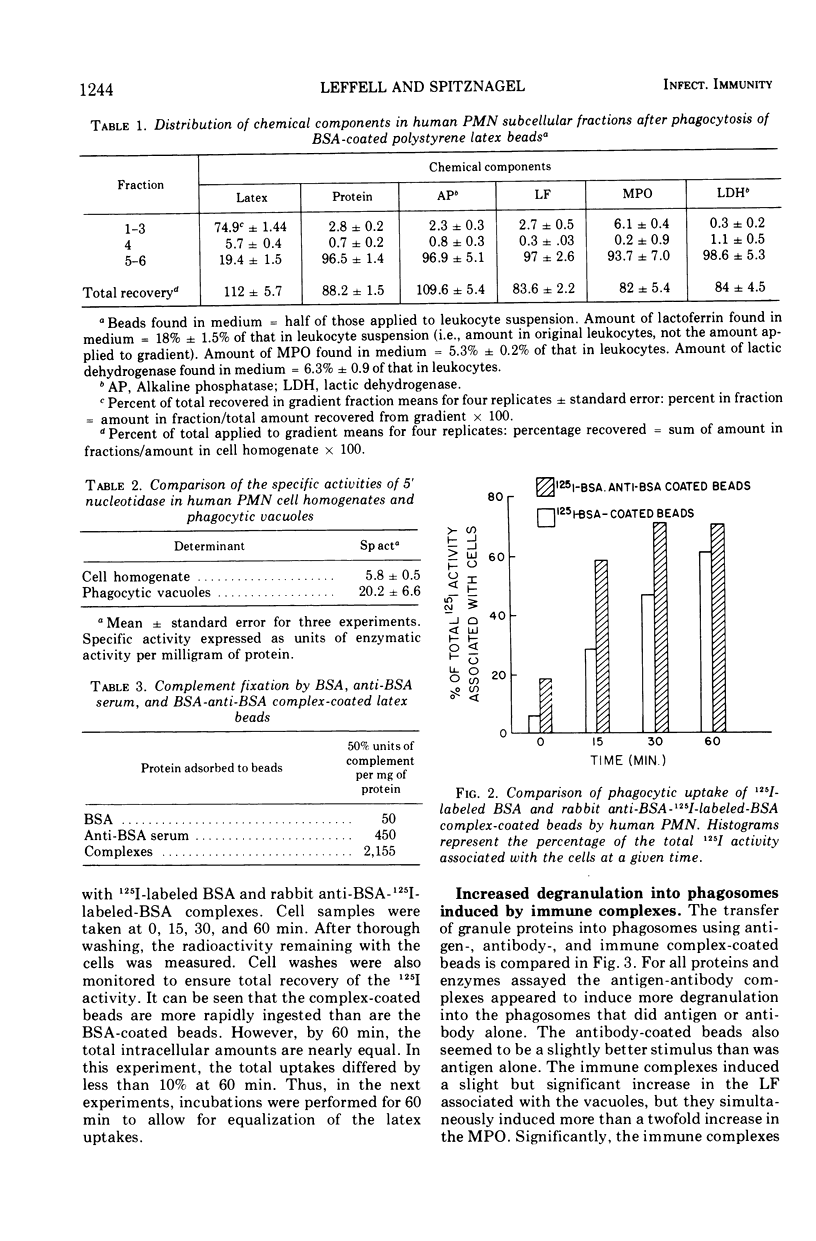
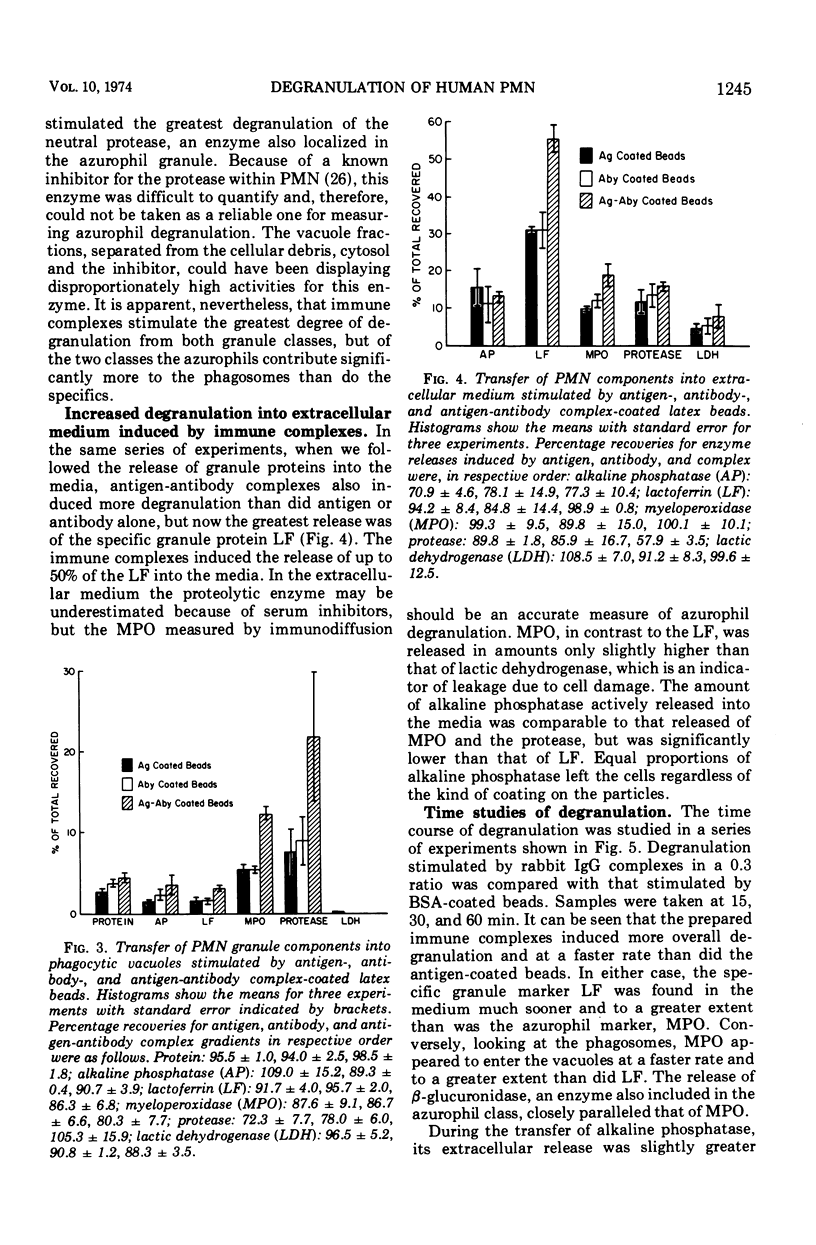
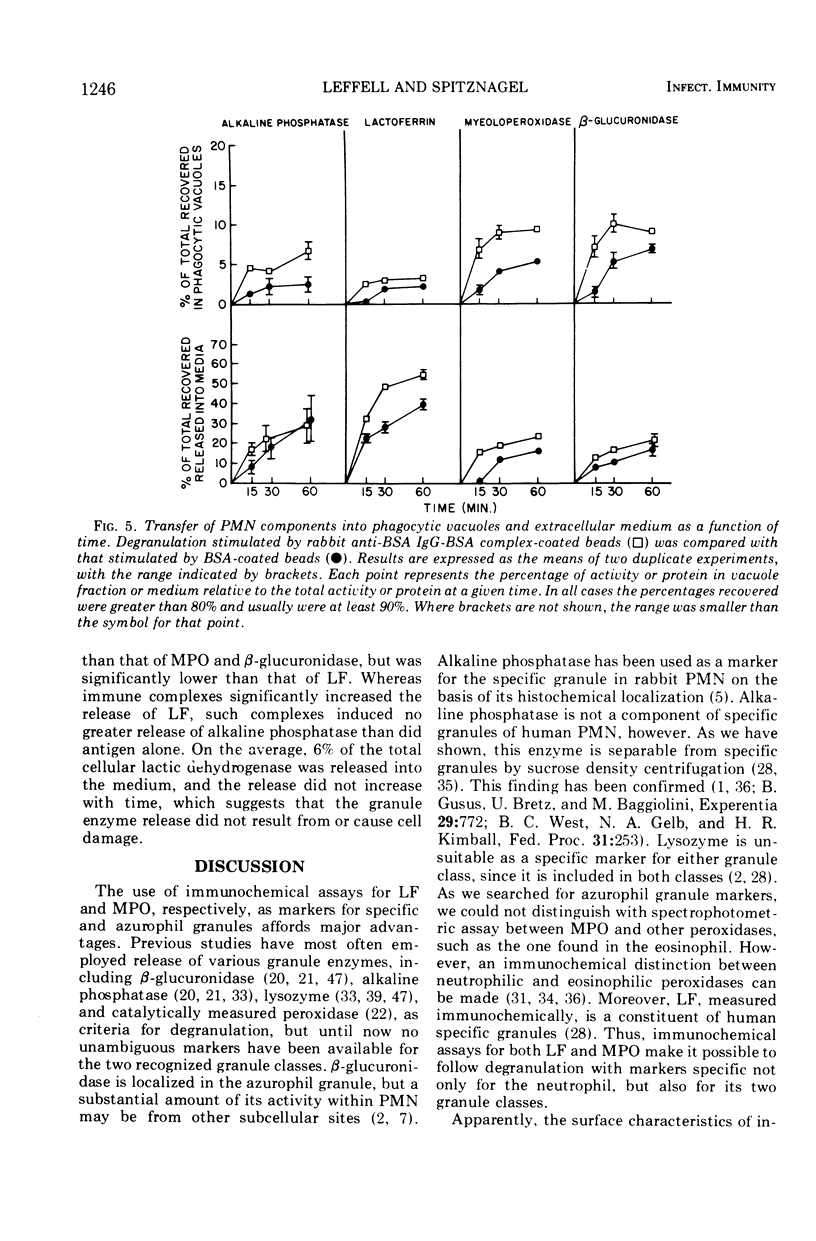
The nature of the phagocytic stimulus determines the degree of degranulation. Specifically, immune complexes induced more degranulation than did antigen or antibody alone. The release of constituents from the two granule classes represented independent phenomena. Relatively more of the specific granule proteins were released into the medium during phagocytosis, whereas more of the azurophil proteins were associated with the phagosomes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Bretz U., Gusus B. Biochemical characterization of azurophil and specific granules from human and rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1974 Jan 26;104(4):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Hirsch J. G., De Duve C. Resolution of granules from rabbit heterophil leukocytes into distinct populations by zonal sedimentation. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):529–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. II. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy of bone marrow cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):299–317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Origin of granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Two types derived from opposite faces of the Golgi complex in developing granulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):277–301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F. Sequential degranulation of the two types of polymorphonuclear leukocyte granules during phagocytosis of microorganisms. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):249–264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Ullyot J. L., Farquhar M. G. The development of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes in human bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):907–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J. Leukocyte function in inflammation: the ingestion, killing, and digestion of microorganisms. Ser Haematol. 1970;3(2):3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G. Immunologic tissue injury mediated by neutrophilic leukocytes. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:97–162. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:259–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., White J. G., Holmes B. Specific degranulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1974 Mar 22;248(446):347–348. doi: 10.1038/248347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALLON H. J., FREI E., 3rd, DAVIDSON J. D., TRIER J. S., BURK D. Leukocyte preparations from human blood: evaluation of their morphologic and metabolic state. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:779–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Nelson R. A., Jr Complement dependent immune phagocytosis. I. Requirements for C'1, C'4, C'2, C'3. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jul;51(1):45–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Brai M., Osler A. G., Weissmann G. Lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: mediation by the alternate pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D., Peeters S. The response of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to immune complexes in vitro. Lab Invest. 1971 Jun;24(6):483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Interaction of cells with immune complexes: adherence, release of constituents, and tissue injury. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):114s–135s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. I. The role of antibody and complement on nonphagocytosable surfaces or phagocytosable particles. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1535–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. II. Mechanisms of release during phagocytosis, and adherence to nonphagocytosable surfaces. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1547–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelhoch S. R., Evans W. H., Mage M. G., Peterson E. A. Purification of myeloperoxidases from the bone marrow of the guinea pig. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):914–921. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., Blondin J. Further studies on an esterase inhibitor in human leukocyte cytosol. Lab Invest. 1971 Dec;25(6):565–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Neutrophil proteases in inflammation. Annu Rev Med. 1972;23:177–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase: contribution to the microbicidal activity of intact leukocytes. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffell M. S., Spitznagel J. K. Association of lactoferrin with lysozyme in granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.761-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., Evans W. H., Himmelhoch S. R., McHugh L. Immunological identification and quantifications of guinea pig heterophil and eosinophil peroxidases. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Mar;9(3):201–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon S. E., Cline M. J., Schultz J., Lehrer R. I. Myeloperoxidase deficiency. Immunologic study of a genetic leukocyte defect. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 29;282(5):250–253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001292820505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Dalldorf F. G., Leffell M. S., Folds J. D., Welsh I. R., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E. Character of azurophil and specific granules purified from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):774–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Pollard T. D., Mason R. J., Vaughan M. Isolation and properties of phagocytic vesicles from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1745–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI106664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Pruzanski W., Ranadive N. S. Release of intracellular constituents from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes exposed to soluble and insoluble immune complexes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;43(2):182–195. doi: 10.1159/000230836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Singer J. M. The binding of immune globulins and other proteins by polystyrene latex particles. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1966 May;3(1):29–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser L., Blout E. R. The use of p-nitrophenyl N-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-L-alaninate as substrate for elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 7;268(1):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Spieler P. J., Goldstein I. M. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from leukocytes exposed to immune complexes and other particles. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):149s–165s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Cohn Z. A. Plasma membrane synthesis in the macrophage following phagocytosis of polystyrene latex particles. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2439–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel M. G., Korn E. D. Phagocytosis of latex beads by Acahamoeba castellanii (Neff). 3. Isolation of the phagocytic vesicles and their membranes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):90–104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Unkeless J. C. Partial purification of a lipoprotein with 5'-nucleotidase activity from membranes of rat liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1050–1057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Malawista S. E. The mobilization and extracellular release of granular enzymes from human leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):788–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Arginine-rich proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. Antimicrobial specificity and biochemical heterogeneity. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):927–941. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


