Abstract
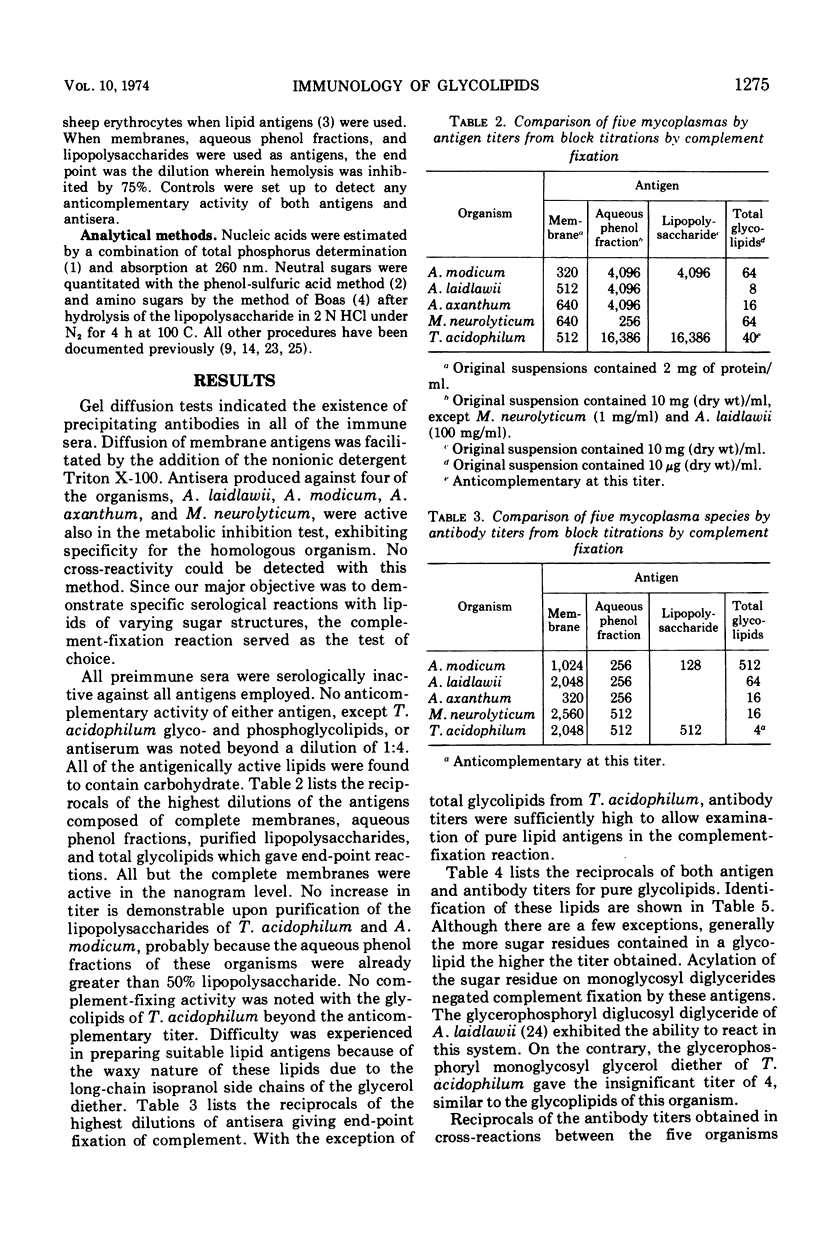
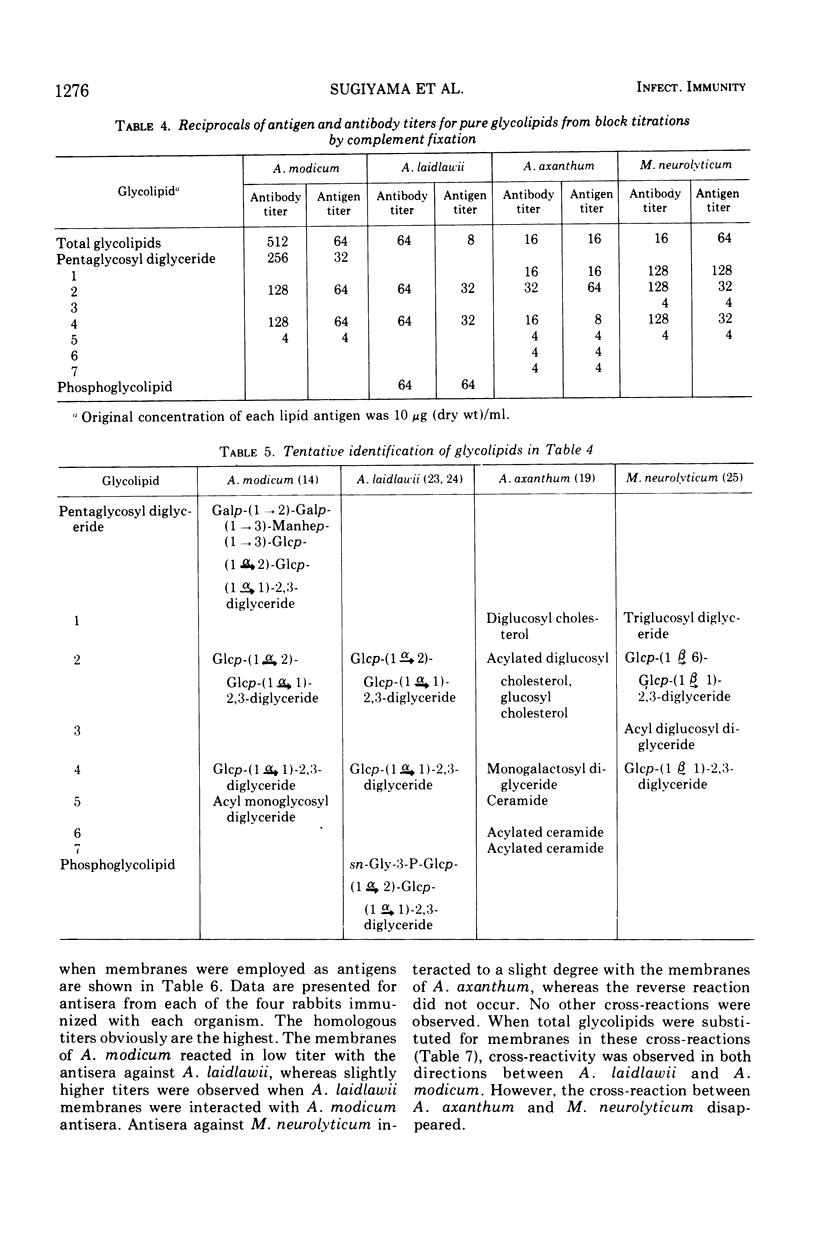
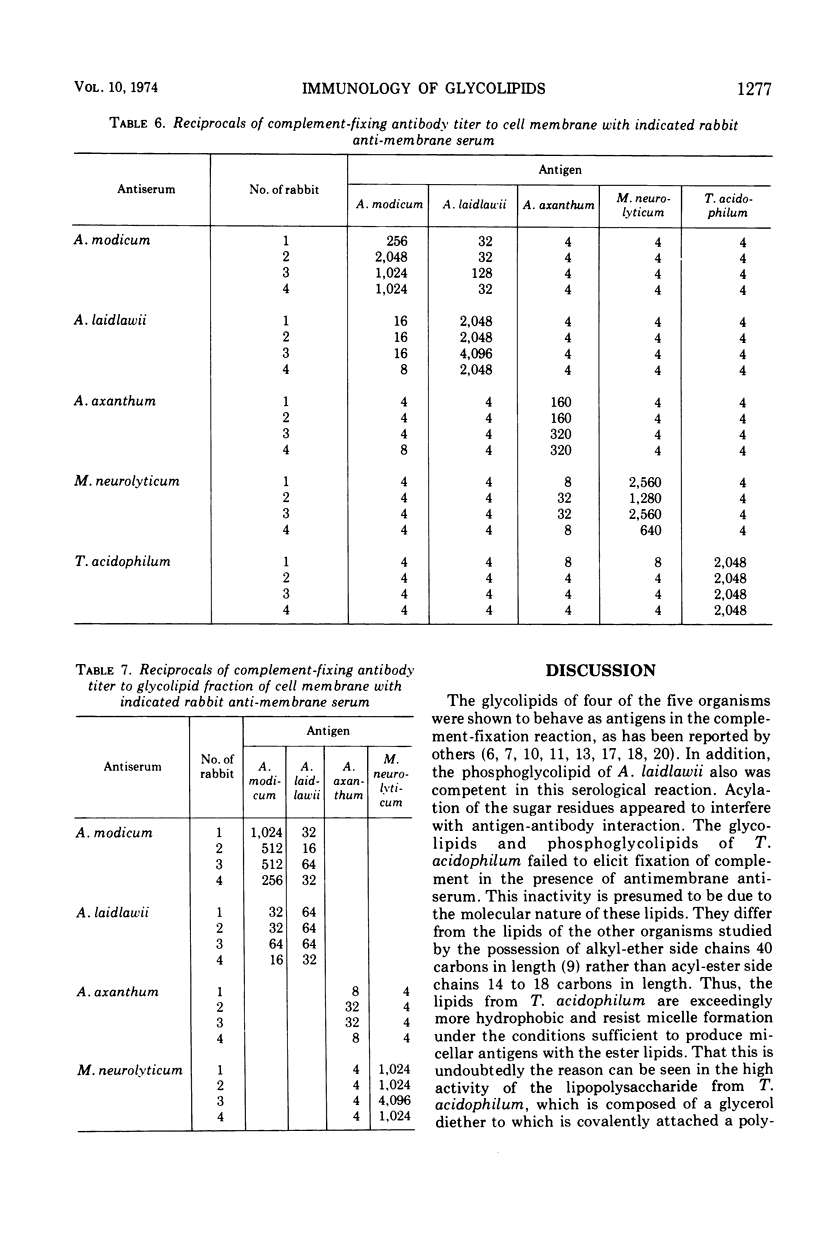
The lipids and lipopolysaccharides of five mycoplasmas were examined for complement-fixing activity to antimembrane rabbit sera. Total glycolipid fractions and the aqueous phenol fractions (lipopolysaccharides) from the membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii, A. modicum, A. axanthum, and Mycoplasma neurolyticum exhibited significant antigenic activity. The glycolipids and phosphoglycolipids from Thermoplasma acidophilum were either anticomplementary or did not react due to their extreme hydrophobic nature. High activity was found using the lipopolysaccharide of T. acidophilum. The pure glycolipids and phosphoglycolipids of the Acholeplasma and Mycoplasma species also exhibited significant complement-fixing activity. Acylation of the sugar residues of these lipids reduced or negated complement-fixing activity. Double cross-reactions between the glycolipids of A. laidlawii and A. modicum appeared to be due to mono- and diglucosyl diglycerides of identical structure. Specificity of glycolipid structure was noted by the absence of cross-reactions between A. laidlawii and M. neurolyticum, the glycolipids of which differ only in the nature of the glucose linkages. The existence of lipopolysaccharides in the membranes of mycoplasmas and their complement-fixing activity in the presence of antimembrane sera suggest their possible importance as specific antigenic determinants.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOAS N. F. Method for the determination of hexosamines in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):553–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman B. L., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical analysis of serologically active lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1171-1180.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterizion of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. II. Basis for differentiation of antigenic subtypes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1425–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1425-1429.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Serological cross-reaction between lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma neurolyticum. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):149–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.149-153.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Smith P. F., Mayberry W. R. Lipids of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1193-1200.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Marmion B. P., Plackett P. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):691–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Plackett P., Shaw E. J., Marmion B. P. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 2. Properties of chloroform-methanol extract from M. pneumoniae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Apr;46(2):123–139. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn R. J. The immune response of rabbits to various strains of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):654–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmion B. P., Plackett P., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 1. Methods of extraction and reaction of fractions from M. pneumoniae and from M. mycoides with homologous antisera and with antisera against Streptococcus MG. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):163–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Langworthy T. A., MAyberry W. R., Smith P. F. A new class of lipopolysaccharide from Thermoplasma acidophilum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 22;360(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A. Heptose-containing pentaglycosyl diglyceride among the lipids of Acholeplasma modicum. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):898–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.898-904.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Plackett P. Identification of the amide-linked fatty acids of Acholeplasma axanthum S743 as D(-)3-hydroxyhexadecanoate and its homologues. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1091-1095.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Marmion B. P., Shaw E. J., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 3. Separation and chemical identification of serologically active lipids. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Apr;47(2):171–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Shaw E. J. Glucolipids from Mycoplasma laidlawii and Streptococcus MG. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):61C–62C. doi: 10.1042/bj1040061c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Smith P. F., Mayberry W. R. Lipids of a sterol-nonrequiring Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):798–807. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.798-807.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Prescott B., Caldes G., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Role of Glycolipids and Phosphatidylglycerol in the Serological Activity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):408–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.408-416.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Prescott B., James W. D., Caldes G., Valdesuso J., Chanock R. M. Production and Properties of Antisera to Membrane Glycolipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):420–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.420-423.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Smith P. F., Koostra W. L. The lipid composition of Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):329–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1070329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Smith P. F., Verheij H. M. The structure of a glycerylphosphoryldiglucosyl diglyceride from the lipids of Acholeplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):167–173. doi: 10.1042/bj1290167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Koostra W. L., Mayberry W. R. Observations on membranes of Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1166–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1166-1174.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Langworth T. A., Mayberry W. R., Houghland A. E. Characterization of the membranes of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1019–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1019-1028.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Lipid composition of Mycoplasma neurolyticum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):554–558. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.554-558.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



