Abstract
The initial interaction between HIV-1 and the host occurs at the mucosa during sexual intercourse. In cervical mucosa, HIV-1 exists both as free and opsonized virions and this might influence initial infection. We used cervical explants to study HIV-1 transmission, the effects of opsonization on infectivity, and how infection can be prevented. Complement opsonization enhanced HIV-1 infection of dendritic cells (DCs) compared with that by free HIV-1, but this increased infection was not observed with CD4+ T cells. Blockage of the α4-, β7-, and β1-integrins significantly inhibited HIV-1 infection of both DCs and CD4+ T cells. We found a greater impairment of HIV-1 infection in DCs for complement-opsonized virions compared with that of free virions when αM/β2- and α4-integrins were blocked. Blocking the C-type lectin receptor macrophage mannose receptor (MMR) inhibited infection of emigrating DCs but had no effect on CD4+ T-cell infection. We show that blocking of integrins decreases the HIV-1 infection of both mucosal DCs and CD4+ T cells emigrating from the cervical tissues. These findings may provide the basis of novel microbicidal strategies that may help limit or prevent initial infection of the cervical mucosa, thereby reducing or averting systemic HIV-1 infection.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells, Complement system, DCs, HIV, Integrins
Introduction
The most common route of HIV-1 transmission is by hetero-sexual intercourse, with women accounting for more than half of the newly HIV-1-infected individuals 1. During sexual transmission, the first interactions between HIV-1 and the host occur at mucosal sites, such as genital and rectal mucosa. Within hours of initial exposure, the virions can reach the submucosa and local events that contribute to the establishment of a systemic infection are set in motion 2, leading to high levels of infection and destruction of CD4+ T effector memory cells, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract 3. While immune cells can be found at sites of inflammation throughout the female genital tract, in the absence of such inflammation, immune cells are found most frequently in the cervical transformation zone and surrounding tissues and are likely sites for HIV infection 4,5.
Studies in macaques inoculated with SIV, to model vaginal transmission of HIV, have shown that SIV virions cross the single layer mucosal barrier of the endocervix, however, virus has also been shown to enter through the stratified epithelium 6, especially at sites of preexisting inflammation. Sexually transmitted diseases and genital infections increase the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection due to disturbed epithelial layer and increased availability of target cells in the mucosa; moreover, the production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, is associated with an enhanced HIV-1 replication 7.
Another potential mechanism available to the virus to penetrate the mucosa is by exploiting dendritic cells (DCs) and Langerhans cells (LCs) localized in the stratified epithelium, where these cells can pick up HIV-1 and transfer the virus to the submucosa 8. When HIV-1 has reached the submucosa, the primary target cells for the virions are CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and DCs. In addition to binding to CD4 and the coreceptor CCR5/CXCR4 9, HIV-1 can be captured by DCs via an array of cell surface receptors, such as heparin sulfate proteoglycans, C-type lectins, and integrins 9–11. As soon as 24 h postexposure, DCs with captured virions can reach draining LNs where they can transfer infectious HIV-1 to surrounding cells 2,12. In macaques challenged vaginally with SIV, small founder populations of productively infected cells are demonstrable in the cervical mucosa 3 to 4 days postexposure. The founder populations normally consist of resting CD4+ T cells with a receptor pattern and functionality that support a productive infection 13,14, i.e. CD4+ T cells with high expression of CCR5 and α4β7-integrins 15. After local amplification, the infection spreads to draining and then distant lymphoid tissues, resulting in a disseminated infection 6,13.
The mucosal epithelium is not a simple passive barrier; it also mediates host defenses by secreting mucus, defensins, and complement proteins 16. HIV-1 can activate the different complement cascade pathways, which all converge at the cleavage of C3, but HIV-1 can escape complement-mediated lysis as the virions incorporate host proteins that will cleave activated C3 into inactivated iC3b 17. The iC3b fragments are covalently attached to the viral protein gp120 and can interact with complement receptor 3 (CR3: CD11b/CD18, αMβ2 integrin). After seroconversion, virions are covered with both specific antibodies and complement 17. In addition, seroconversion enhances complement activation and increases the amount of C3 cleavage products on the surface of HIV-1 18.
Complement-opsonized virions already exist at the mucosal surface during the initial phase of infection 18. We have shown earlier that complement-opsonized HIV-1 is internalized more efficiently by DCs than free HIV-1 9. Complement opsonization of HIV-1 has also been shown to enhance in vitro infectivity for cultured monocytes 19 and immature DCs 20–22. Given the potential impact of opsonization of HIV-1 on both the acute and chronic phases of infection, it is important to understand the effects of opsonization on the ability of HIV-1 to interact with cells and to infect them. The aim of this study was to investigate the initial HIV-1 infection of cervical mucosa, using an ex vivo cervical tissue explant model, comparing free and opsonized virions. The degree of infection of mucosal DCs and CD4+ T cells, and the receptors involved in the initial infection were analyzed.
Complement opsonization of virions resulted in a higher level of infection in DCs emigrating from explant tissues in culture compared with that of free HIV-1, whereas the effect on infection of emigrating CD4+ T cells was the opposite with decreased infection for opsonized HIV-1. Blocking of CD4, and integrins β1, β2, α4, and β7 all resulted in significantly decreased infection of DCs and CD4+ T cells. We found a higher impairment in HIV-1 infection in emigrating DCs for complement-opsonized virions when interactions with αM/β2- and α4-integrins were blocked than for free virions. Blockade of integrins decreased both the infection of DCs and CD4+ T cells emigrating from the cervical explant tissues, suggesting novel approaches for microbicidal strategies to limit or prevent vaginal transmission of HIV.
Results
Complement opsonization of HIV-1 enhances infec-tion of DCs emigrating from cervical mucosa tissue
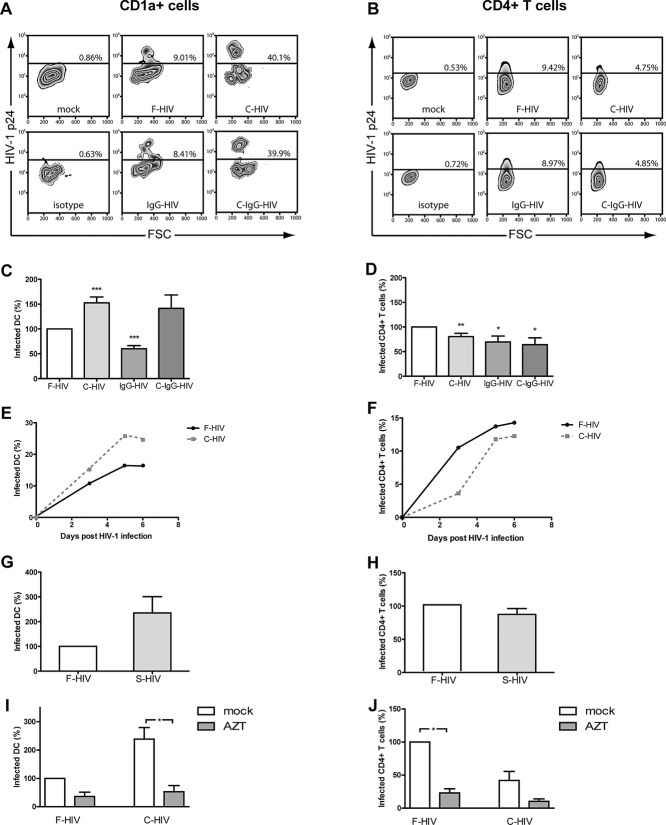
We studied the initial phase of HIV-1 infection in cervical mucosa. Cervical tissues were challenged with HIV-1BaL in different forms: free HIV-1 (F-HIV); complement opsonized HIV-1 (C-HIV), immune complexed HIV-1 with a mixture of unspecific, and HIV-1 specific neutralizing IgG (IgG-HIV); or HIV-1 opsonized with both complement and a mixture of unspecific and HIV-1 specific neutralizing IgG (C-IgG-HIV) and infection was measured on day 3–6. The level of HIV-1 infection of emigrating DCs was highest for C-HIV and C-IgG-HIV (Fig. 1A), whereas F-HIV gave the highest level of infection in CD4+ T cells (Fig. 1B). Compared with F-HIV, normalized as 100% value for infection, both C-HIV (151%: p < 0.005) and C-IgG-HIV (141%) showed enhanced infection of DCs emigrating from cervical explants (Fig. 1C), while infection using IgG-HIV was significantly decreased (60%; p < 0.005) (Fig. 1C). However, HIV-1 infection of mucosal CD4+ T cells emigrating from explant cultures was significantly decreased when exposed to opsonized forms of virions (C-HIV (80%, p = 0.01), IgG-HIV (70%, p = 0.025), or C-IgG-HIV (64%, p = 0.026) compared with F-HIV (normalized to 100%) (Fig. 1D). The infection profile was the same for endocervix and ectocervix (Supporting Information Fig. 1A and B).
Figure 1.
Complement opsonization of HIV-1 enhances infection of DCs but decreases infection of CD4+ T cells. The cervical tissue biopsies were infected with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV), complement opsonized (C-HIV), antibody opsonized (IgG-HIV), virions opsonized by a cocktail of complement and antibodies (C-Ig-HIV) or mock-treated, by spinning the cultures for 2 h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to six-well plates and cultured for 3–6 days. (A, B) The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with (A) anti-CD1a and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs, and (B) anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and the level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry. (C, D) The level of HIV-1 infection in the different (C) DC (N = 10–32) or (D) T-cell (N = 11–32) experiments was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. (E, F) The kinetics of HIV-1 infection of emigrating (E) DCs and (F) CD4+ T cells were measured day 3–6. (G, H) The level of HIV-1 infection of emigrating (G) DCs and (H) T cells (N = 4–5) exposed to F-HIV or HIV-1 opsonized with seminal fluid was also assessed. (I, J) The level of HIV-1 infection of emigrating (I) DCs and (J) T cells from cervical tissue biopsies (N = 3) pre-exposed to mock or AZT followed by infection with F-HIV or C-HIV was measured on day 4. Mock or AZT was present throughout the whole 6-day culture. Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Data are shown as mean + SEM of the indicated number of samples, each assessed in its own experiment.
The infection profiles were similar, independently of whether cultures were harvested at day 3, 5, or 6 (Fig. 1E and F) with the greatest difference in the level of infection in DCs using F-HIV versus C-HIV seen at day 5 (Fig. 1E). Impairment of T-cell infection by virion opsonization was more pronounced at day 3 than at day 6 (Fig. 1F). To assess the infection at a later time point than day 3–6, it was necessary to add exogenous GM-CSF and IL-2 to the culture to maintain cell viability. We found the same profile but enhanced infection at day 8 in both DCs and T cells compared with day 3–6 (Supporting Information Fig. 1C).
To further enhance the potential in vivo relevance, we performed similar studies using fresh seminal fluid as the opsonizing agent. The seminal fluid gave similar results as the fresh blood serum with an increased infection of DCs (211%) and a decreased infection of T cells (74%) for opsonized versus nonopsonized virions (Fig. 1G and H). Infection of cervical tissues was also assessed with two additional HIV-1 strains, the CXCR4 tropic HIV-MN and CCR5 tropic HIV-ADA, but these viruses gave very low or no infection (Supporting Information Fig. 1D) and this is in accordance with findings by Greenhead et al. 23. To distinguish between productive infection of the DCs and CD4+ T cells and p24 immunostaining of internalized virions without productive infection, experiments were performed where the reverse transcriptase inhibitor azidothymidine (AZT) was present throughout the whole course of culture. Tissues exposed to AZT had decreased levels p24 gag positive cells compared to untreated HIV-1-infected cells (Fig. 1I and J) confirming that most of the p24 signal was attributable to productive infection. To further characterize HIV infection of cervical mucosa, we assessed the levels of HIV-1 p24 in the supernatants at day 4 and we found that C-HIV gave a higher infection compared with the level obtained with F-HIV (Supporting Information Fig. 1E).
Characterization of C-type lectin and integrin expression on cervical mucosa DCs and T cells
To better understand the establishment of HIV-1 infection in the cervical mucosa, we characterized the expression of an array of receptors, and the location of DCs and T cells. The expression and both cellular and anatomic localization of the C-type lectin receptors MMR (CD206), DC-SIGN (CD209), and Langerin (CD207), and integrins β1, β2, β7, α4, and αM were assessed by flow cyto-metry (for emigrating cell populations) and fluorescence microscopy (for cervical tissues). Expression of Langerin was detected almost exclusively on LCs located in the epithelium (Fig. 2A). The vast majority of CD3+ T cells were located within the lamina propria (LP), but a few T cells could be found in the epithelium (Fig. 2B). CD1a expression was detected both on the LCs in the epithelial layer and on submucosal DCs in the LP (Fig. 2C). MMR expression was only detected in cells in the LP, presumably on submucosal DCs and macrophages (Fig. 2D). Cells expressing αM/β2-intergrins were located both in the epithelium and LP, and likely consist of LCs in the epithelial layer and submucosal DCs and macrophages in LP (Fig. 2E). β1-integrin expression was found on cells in LP and on the basement membrane (Fig. 2F), while cells expressing the β7-integrin were detected in the LP (Fig. 2G). The specificity of all positive staining was verified by use of isotype control antibodies (Fig. 2H and I). Emigrating DCs and T cells were assessed for expression of C-type lectin receptors MMR, DC-SIGN, and Langerin, and integrins β1, β2, β7, α4, and αM. Expression of C-type lectin receptors MMR, DC-SIGN, or Langerin was detected on DCs (Fig. 2J) but not on T cells (our unpublished observation). β1, β2, β7, α4, and αM integrins were expressed by DCs (Fig. 2J), whereas CD4+ T cells only expressed β1, β7, and α4 (our unpublished observation).
Figure 2.
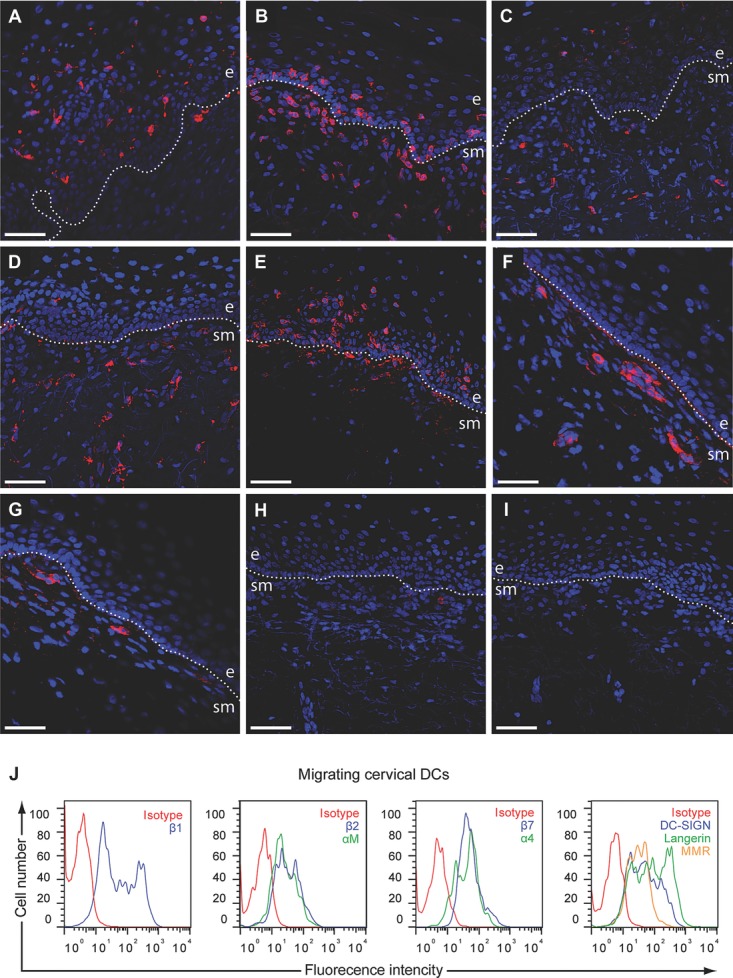
Expression of C-type lectins and integrins in cervical mucosa tissue and on emigrating immune cells. (A–I) Cryopreserved cervical mucosa tissue sections were stained with (A) anti-Langerin, (B) anti-CD3, (C) anti-CD1a, (D) anti-MMR, (E) anti-CD11b/CD18, (F) anti-β1, (G) anti-β7, or (H, I) isotype control. The primary antibody was visualized by an sAb conjugated to Rhodamin Red-X. The sections were mounted using mounting medium for fluorescence containing DAPI. Receptor expression is shown in red in the cervical mucosa, scale bar, 50 μm. (J) DCs emigrating from cervical mucosa tissue were labeled with anti-Langerin, anti-CD3 anti-DC-SIGN anti-MMR, anti-CD11b, anti-β1, anti-β7, anti-α4, or isotype control followed by goat-anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 and analyzed by flow cytometry. e = epithelium, sm = submucosa. Data shown are representative of three to five stainings performed on different tissue samples.
Blockage of CD4 binding abolishes infection of DCs and CD4+ T cells by free and opsonized HIV-1
We investigated the infection in DCs and CD4+ T cells after blocking CD4 with the mAb b12, a neutralizing antibody that specifically targets the CD4 binding site on gp120, and CCR5 with the inhibitor TAK779. We mostly used the b12 experiment to establish the level of inhibition reached in this model by a known blocker of HIV-1 infection 24. b12 significantly decreased the infection of migrating DCs to 45% of unblocked control for F-HIV (p = 0.019) and to 62% of control for C-HIV (p = 0.028) (Fig. 3A). When b12 was used, infection of CD4+ T cells emigrating from cervical explants was decreased by 85% (p < 0.0001) for F-HIV and by 74% (p < 0.0001) for C-HIV (Fig. 3B). The CCR5 inhibitor TAK799 decreased the HIV-1 infection of emigrating DCs by 41% (p = 0.037) for F-HIV and 66% for C-HIV (p = 0.06) and of CD4+ T cells by 48% (p = 0.02) for F-HIV and 68% (p = 0.01) for C-HIV (Fig. 3C and D).
Figure 3.
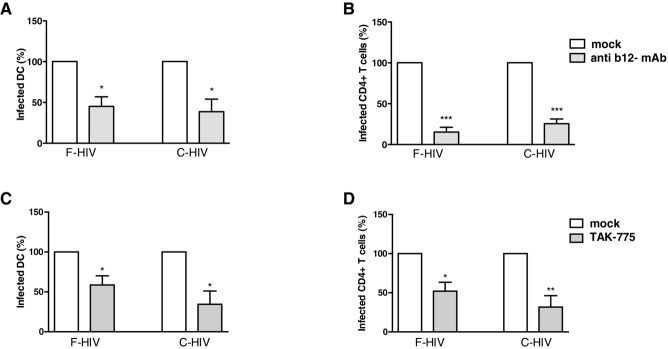
Blockade of CD4 and CCR5 decreases the infection of emigrating cervical mucosa DCs and T cells. Cervical tissue biopsies were infected with HIV-1BaL, either as free virions (F-HIV) or complement opsonized virions (C-HIV) that had been mock treated or incubated with b12 mAb, for 2 h at 37°C.The cervical tissue biopsies were pretreated for 30 min at 37°C with TAK779 followed by infection with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV) or complement opsonized (C-HIV), for 2 h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to six-well plates and cultured for 3–6 days in the absence or continuous presence of b12 mAb or TAK779. The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry for HIV-1 p24 expression. (A, B) The level of HIV-1 infection after mock treatment or treatment with b12 in the different (A) DCs (N = 4–6) or (B) T cells (N = 4–7) was normalized with mock-treated F-HIV set as 100%. (C, D) The level of HIV-1 infection after mock or TAK779 treatment in the different (C) DC or (D) T-cell experiments was normalized with F-HIV set as 100% (N = 3–4). Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Data are shown as mean + SEM of the indicated number of samples, each assessed in its own experiment.
Preventing HIV-1 binding to MMR inhibits infection in emigrating cervical DCs
To study the impact of C-type lectins on infection in DCs and CD4+ T cells, we exposed cervical mucosa to the mannose polymer mannan, a competing ligand for C-type lectins, before challenging the tissues with HIV-1. Infection was decreased for both F-HIV (46%, p = 0.005) and C-HIV (40%, p = 0.023) in emigrating DCs after blocking C-type lectins located in the cervical mucosa (Fig. 4A). In contrast, no effect on the infection of emigrating CD4+ T cells was observed (Fig. 4B). DCs emigrating from cervical tissues have been shown to express MMR 24. Blocking this C-type lectin using anti-MMR mAb gave similar results as when C-type lectins were blocked using mannan with a 51% (p = 0.006) decrease in F-HIV infection in DCs (Fig. 4C). When the cervical tissue was challenged with C-HIV, the corresponding decrease in DC infection was 43% (p = 0.029) (Fig. 4C). As expected, infection of CD4+ T cells was not affected by blocking MMR in the cervical mucosa (Fig. 4D). Blocking of MMR had a slightly higher effect on DC infection with F-HIV than with C-HIV.
Figure 4.
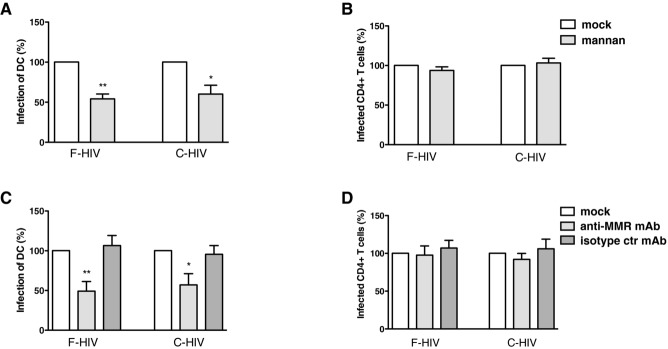
Blockade of the C-type lectin MMR decreases the infection of DCs emigrating out from cervical tissues. The cervical tissue biopsies were pretreated for 30 min at min 37°C with mock, mannan, anti-MMR mAb, or isotype control mAb followed by infection with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV) or complement opsonized (C-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2 h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to six-well plates and cultured for 3–6 days with mock, mannan, anti-MMR mAb, or isotype control mAb. The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry. (A, B) The level of HIV-1 infection in (A) DCs (N = 4–5) or (B) T cells (N = 3) in the different experiments treated with mock or mannan was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. (C, D) The level of HIV-1 infection in (C) DCs (N = 4–7) or (D) T cells (N = 4–9) in the different experiments treated with mock, anti-MMR mAb, or isotype control mAb was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Data are shown as mean + SEM of the indicated number of samples, each assessed in its own experiment.
Blockade of integrins decreases HIV-1 infection in emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells
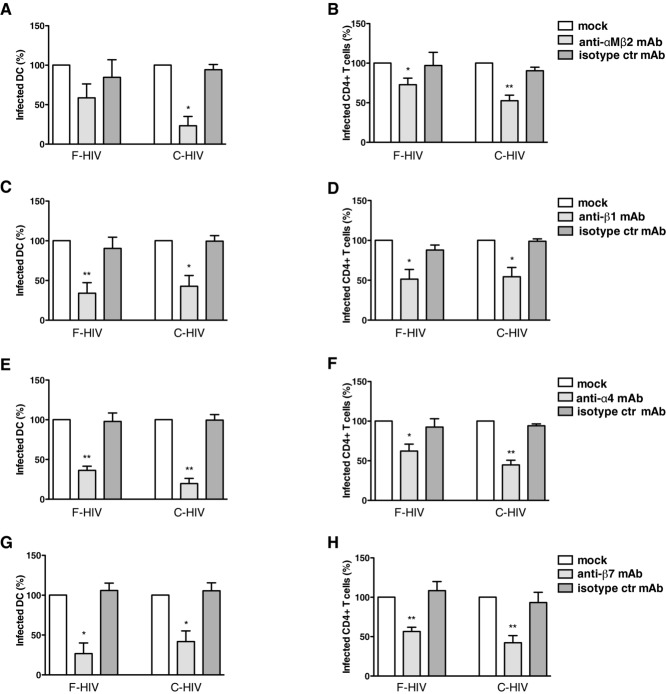
Integrins are used by different viruses to attach or infect host cells 25. Many integrins are expressed by DCs and T cells and we investigated the role of the αM (CD11b) and β2 (CD18) integrins, i.e. CR3, expressed on both DCs and LCs, in the establishment of HIV-1 infection. Cervical mucosa was incubated with anti-αM integrin and anti-β2 integrin mAbs to block CR3 before adding F-HIV or C-HIV. Upon blockade of CR3, the infection of emigrating DCs was decreased by 54% for F-HIV and 82% for C-HIV (p = 0.023) (Fig. 5A). The infection in emigrating CD4+ cells was also decreased but to a lesser extent. Blocking CR3 inhibited infection in the CD4+ T-cell population for F-HIV with 38% (p = 0.021) and C-HIV with 54% (p = 0.001) (Fig. 5B).
Figure 5.
Blockade of integrins decreases the infection of DCs and CD4+ T cells emigrating from cervical mucosa tissues. Cervical tissue biopsies were pretreated for 30 min at 37°C with mock, anti-CD11b/CD18 mAbs, anti-β1 mAb, anti-α4 mAb, anti-β7 mAb, or isotype control mAbs followed by infection with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV) or complement opsonized (C-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2 h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to six-well plates and cultured for 3–6 days with mock, anti-CD11b/CD18 mAbs, anti-β1 mAb, anti-α4 mAb, anti-β7 mAb, or isotype control mAbs. The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry (A, B) The level of HIV-1 infection in (A) DCs (N = 3) or (B) T cells (N = 6) in experiments treated with mock, anti-CD11b/CD18 mAbs, or isotype control mAbs was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. (C, D) The level of HIV-1 infection in (C) DCs (N = 5) or (D) T cells (N = 6) in the different experiments treated with mock, anti-β1 mAb, or isotype control mAbs was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. (E, F) The level of HIV-1 infection in (E) DCs (N = 3–4) or (F) T cells (N = 4) in the different experiments treated with mock, anti-α4 mAb, or isotype control mAbs was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. (G, H) The level of HIV-1 infection in (G) DCs (N = 3–4) or (H) T cells (N = 4) in the different experiments treated with mock, anti-β7 mAb, or isotype control mAbs was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Data are shown as mean + SEM of the indicated number of samples, each assessed in its own experiment.
α4- (CD49d), β1- (CD29), and β7-integrins are expressed by DCs (Fig. 2) and T cells in the cervical mucosa in different heterodimeric complexes, and α4β7-, αEβ7-, and α4β1-integrins are expressed on T cells 26, while αEβ7- and α4β1-integrins are expressed on DCs. We investigated whether blocking β1-integrins would affect the infection of emigrating immune cells from cervical tissue after exposure to free or complement opsonized HIV-1. Pretreatment of the cervical mucosa with anti-β1 integrin mAb inhibited infection in both emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells. Infection of DCs was inhibited by 66% (p = 0.008) for F-HIV and by 57% for C-HIV (p = 0.013) (Fig. 5C). In CD4+ T cells, the blocking of β1-integrins gave a 49% decrease in infection for F-HIV (p = 0.01) and a 46% decrease for C-HIV (p = 0.01) (Fig. 5D). HIV-1 gp120 binds to α4β7-integrins expressed on T cells and facilitates the formation of virological synapses and spread of the virus via LFA-1 26, whereas the effects of virion interaction with α4 and β7 on DCs remain unknown. Targeting the integrins α4 or β7 in the cervical mucosa with specific blocking antibodies 27–29 resulted in a decreased infection in both emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells (Fig. 5E–H). Blocking the α4 integrin decreased the infection in DCs by F-HIV by 62% (p = 0.006) and by C-HIV by 80% (p = 0.006) (Fig. 5E). In the CD4+ T-cell population, infection was decreased by 38% (p = 0.022) for F-HIV and 55% (p = 0.0025) for C-HIV (Fig. 5F). The blocking of β7-integrins in the cervical tissue also decreased infection in the emigrating DCs by 49% (p = 0.012) for F-HIV and 66% (p = 0.001) for C-HIV (Fig. 5G). The infection of CD4+ T cells was inhibited by 44% (p = 0.004) for F-HIV and by 58% (p = 0.004) for C-HIV (Fig. 5H). We found the same level of inhibition of infection when a lower concentration (5 μg/mL compared with 20 μg/mL) of the anti-β7 integrin or anti-α4 integrin antibodies was used (Supporting Information Fig. 2).
Of note, areas positive for HIV-1 p24 were detected in the submucosa tissues in all cervical tissues infected with F-HIV or C-HIV, whereas these areas were rarely or not found when the use of α4 and β7-integrins had been inhibited (our unpublished observation).
Discussion
It is important to gain a better understanding regarding the initial events in HIV-1 infection in the female genital tract in order to develop new strategies that prevent the initial infection or target the first week of local infection, with the ability to block the development of systemic infection. When studying the first steps of HIV-1 infection, there are many layers of interactions occurring within the mucosal microenvironment to take into account, e.g. cervical secretions, complement components, epithelial cell barrier, hormones, and immune cells 16. We used a tissue explant culture system to measure the HIV-1 infection of emigrating cervical DCs and CD4+ T cells after challenging the cervical explants with different forms of opsonized HIV-1 that are potentially relevant in vivo, i.e. virions covered in complement fragments or/and antibodies. Virions opsonized with complement produced higher levels of infection in the emigrating DCs than free HIV-1. In contrast, infection of emigrating CD4+ T cells was decreased when the virions were opsonized. The differential effects of complement-opsonized HIV could be due to the fact that only a few T cells express CR3 30 and the coating of HIV with iC3b affects the ability of the viral protein gp120 to interact with the CD4 receptor on the cell surface. DCs on the other hand typically express CR3 and this receptor enhances the binding and uptake of C-HIV 9 and is involved in the enhanced HIV-1 infection 21. Blockade of CD4, and the integrins β1, β2, αM, α4, and β7, and the C-type lectin MMR resulted in significantly decreased infection of DCs. For emigrating CD4+ T cells, the highest impairment of infection was seen when HIV-1 ability to bind to the CD4 receptor was neutralized but blocking the integrins β1, β2, α4, and β7 also decreased the infection. Blockade of the αM/β2- and α4-integrins inhibited infection of emigrating DCs by complement-opsonized virions more than it inhibited infection by free virions.
Within the cervix, T cells and APCs are most frequently found in the cervical transformation zone and surrounding tissues 5. Several different types of DCs exist in the cervical mucosa including myeloid DCs, with the LCs located in the epithelial layer and DCs in the submucosa, and a small number of plasmacytoid DCs 31. In human explant cultures, HIV-1 can rapidly reach both LCs and CD4+ T cells located in the cervical epithelial layer 8, although DCs have been implicated in vaginal SIV transmission and dissemination to draining LNs in macaques 32.
We have previously demonstrated that complement opsonization of HIV-1 increased binding and uptake by both immature and mature DCs compared with free virions 9. Furthermore, in other studies, infection of DCs, monocytes, and epithelial cells was enhanced when HIV-1 virions were complement opsonized 19,20,33. This study shows for the first time that complement opsonization of HIV-1 significantly increases the infection of DCs/LCs emigrating from the cervical mucosa and decreases the infection of CD4+ T cells. This was observed when HIV-1 was opsonized not only with fresh human sera but also when HIV-1 was opsonized in seminal fluid, despite the tenfold lower amount of C3 fragments in semen 33.
Exposing the cervical tissue to the neutralizing mAb b12 decreased the infection of both F-HIV and C-HIV in emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells, which is consistent with prior observations on the usage of the CD4 receptor for infection of cervical mucosal DCs and T cells 24. Neutralization of HIV-1 with b12 blocked both local infection of the cervical mucosa explants and viral dissemination of free HIV-1BaL to emigrating immune cells 24, findings consistent with the observation that b12 inhibited HIV-1 replication in the vaginal mucosa in macaques when the antibody was given in high doses 34. However, previous studies have shown that HIV-1 can mutate to escape neutralization, potentially limiting the protective activity ability of b12 and other neutralizing antibodies. We clearly demonstrate that other receptors besides the CD4 receptor and coreceptor, i.e. integrins, can be of importance for the interactions between virus and potential target cells and for infection of CD4+ T cells in the cervical mucosa, possibly by aiding viral attachment to the cell surface and/or facilitating viral synapse formation 26 and dissemination of HIV-1.
MMR is expressed by DCs located in cervical tissues and on DCs emigrating from cervical explants 24. HIV-1 uptake via MMR into macrophages and via Langerin into LCs can guide the virions away from the route leading to productive infection 35,36. We established that C-type lectins were involved in events leading to infection of emigrating DCs as mannan and anti-MMR mAb decreased the infection. Although the effect of mannan on HIV-1 infection of cervical tissue explants and the ability of emigrating cells to cross-infect target cells has been shown previously 24, our data show direct infection of emigrating DCs from the cervical explants. However, no protection against SIV infection was seen for mannan in a macaque model 37. Consequently, blocking of C-type lectins may not give the desired outcome as the viral interactions with these receptors are complex and may affect infection in different ways depending on the cell type.
Integrins bind to various cell surface and extracellular proteins to mediate cell-to-cell matrix adhesion and are involved in multiple important biological functions. Many viruses have been shown to use integrins to interact with host cells in order to facilitate or mediate infection 25. For example, the integrin β1 (CD29) is expressed by almost all cells and has been shown to be involved in rotavirus internalization and reovirus cell entry and infection 25. In the cervical mucosa, β1-integrin is expressed on the basal membrane of epithelial cells and on immune cells, with strongest expression at the basal membrane layer 38. A previous study showed that blocking β1-integrins on cervical mucosa epithelia diminished attachment of HIV-1 virions 38. The blocking of HIV-1 usage of this receptor in the cervical mucosa decreased infection of both DCs and T cells emigrating out of the tissues and this could be an effect of direct interaction of HIV-1 with β1-integrins expressed on the immune cells or an indirect effect of viral binding to epithelial cells and the basal membrane expressing integrin β1.
α4β7 is the submucosal homing receptor expressed by T cells and DCs located in the gut and genital mucosa 26. HIV-1 gp120 binds to an activated form of α4β7, and on T cells this binding leads to activation of LFA-1, facilitating efficient spread of virus to other cells via virological synapses 26. A variety of observations suggest that interactions between gp120 and α4β7 may play a role in mucosal transmission and/or early mucosal replication of HIV-1 15,39. Of note, blocking α4β7-integrin by intravenous administration during acute SIV infection leads to decreased viral load in infected rhesus macaques 40. Blocking of α4- and β7-integrins significantly diminished HIV-1 infection of DCs and T cells emigrating from cervical tissue explants, possibly reflecting involvement of α4β7 in complex with CD4 on the DCs and T cells in direct infection and/or the formation of virological synapses and dissemination of virions between immune cells.
Following vaginal SIV mucosal challenge of macaques, small populations of infected cells are established, which undergo a local expansion before disseminating to establish systemic infection 13. These small founder populations must be sustained at a basic reproductive ratio (R0) > 1 to give rise to systemic infection, otherwise the infection will be aborted 13,14. The inhibition seen in infection of mucosal CD4+ T cells and DCs when blocking integrins may substantially decrease the founder populations in the cervical mucosa. These findings suggest that compounds targeting integrins might be successful in preventing the establishment of HIV-1 infection. However, there could be negative effects of blocking integrins on the mucosa and immune cells’ ability to form immunological synapse and this needs to be assessed in animal models as these factors play important roles in modulating immune responses. Recent trials with microbicides and vaccines have shown some ability to prevent HIV-1 transmission but the efficacy has been low. A deeper understanding of how HIV-1 interacts with the immune cells in the cervicovaginal mucosa is necessary to prevent transmission and HIV infection in the future. New molecules to target for the use in new vaccines and microbicides are of great interest and our results suggest that integrins, such as α4 and β7, may be promising microbicide candidates.
Materials and methods
Cervical tissue samples Ethics statement
This study was approved by Linköping Ethical Review Board (Ethical permit EPN M206-06) and informed consent of all participating subjects was obtained. Normal cervical tissue samples (N = 42) were obtained mainly from women who underwent prolapse surgery and from a few women who underwent hysterectomy for benign conditions comprising menstrual bleeding disorders and myomas at the Gynecology Clinic in Linköping, Sweden. All women had normal Pap smears prior to surgery and showed cytologically and clinically no signs of infection/inflammation at surgery.
Virus propagation
HIV-1BaL/SUPT1-CCR5 CL.30 (Lot #P4143: Biological Products Core/AIDS and Cancer Virus Program, SAIC-Frederick, Inc., NCI Frederick) was produced using chronically infected cultures of ACVP/BPC cell line (No. 204). Virus was purified by continuous flow centrifugation for 30 min after sample loading. Virus containing fractions were pooled and diluted to <20% sucrose, and virus pelleted at approximately 100 000 × g for 1 h. The virus pellet was resuspended and aliquots were frozen in liquid N2 vapor. All virus preparations were assayed for infectivity.
Opsonization of HIV-1
We used different preparations of HIV-1; F-HIV, HIV-1 opsonized with complement (C-HIV), HIV opsonized with a mixture of unspecific and HIV-1-specific IgG (IgG-HIV), or HIV-1 opsonized with a combination of both complement and IgG (C-IgG-HIV). C-HIV was obtained by incubation of HIV-1BaL (30 μg/mL p24 equivalent) with an equal volume of human serum (HS) or seminal plasma containing 25% Veronal buffer 33. To obtain C-IgG-HIV, 0.20 μg/mL neutralizing HIV-specific IgG (SMI, Stockholm, Sweden) and 20 μg/mL gamma globulin (Pharmacia, Stockholm, Sweden) were added besides the HS containing Veronal buffer, whereas IgG-HIV was obtained by adding only the antibodies. F-HIV was treated with media alone. All groups were incubated for 1 h at 37°C. As a negative control, human sera were heat-inactivated for 30 min at 56°C, incubated with HIV-1 and prepared under the same conditions as the other groups.
Cervical tissue samples and virus inoculations
The cervical tissues were kept on ice and processed within 30 min after resection. The epithelial layer and lamina propria were separated from underlying stroma and the tissue explants (8 mm2) were placed in cell culturing plates containing RPMI 1640, 20 μg/mL Gentamicin, 10 mM HEPES (Fisher Scientific, Gothenburg, Sweden), and 5% pooled HS (Fisher Scientific). Cervical explants were preincubated for 30 min at 37°C for mock treatment or with different inhibitors. The following inhibitors were used: 10 mg/mL mannan, 10 μM AZT (SIGMA-Aldrich), 5 mg/mL EDTA (SIGMA-Aldrich), mAb against the CD4 binding site on gp120 (b12, a kind gift from Professor D. Burton), anti-αM integrin mAb (CD11b: ICRF44, Ancell Corp., Bayport, NY, USA), anti-αM integrin mAb (KIM75), and anti-β2 integrin mAb (CD18: clone 6.5) (kind gifts from M. Robinson, Celltech, UCB group), anti-MMR mAb (CD206: clone 15-2, Biosite), anti-α4 integrin mAb (clone P1H4, Abcam), anti-β7 integrin mAb (clone F1B504, Biosite), and anti-β1 integrin (CD29) (clone JB1A, Millipore); matching isotype controls were used.
Tissue samples were challenged with HIV-1BaL (250 ng/mL), spinocculated for 2 hours at 37°C, washed four times, transferred to six-well tissue culture plates, and cultured. After 3–6 days the emigrating cervical cells were collected and stained for flow cytometry. The infected cervical explants were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and stored for later immunohistochemisty and/or immunofluorescence staining. To compare results obtained from separate experiments, using cervical explants derived from different donors, the F-HIV and C-HIV infection of emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells in absence of inhibitors was normalized to 100% for each experiment.
Flow cytometry
Emigrated cells were harvested on day 3–6 from cervix cultures and stained with the following anti-human mAbs; CD4-allophycocyanin (BD Biosciences), CD3-PerCP (BD Biosciences), and CD1a-PE (BD Biosciences). For detection of HIV-1, the cells were fixed in 4% PFA, permeabilized in 0.2% saponin, and incubated with the anti-HIV-1 mAb (KC57, clone FH190-1-1) and the corresponding isotype control (BD PharMingen, SanDiego, CA, USA) for 45 min. The stained cells were assessed by flow cytometry (FACS Calibur) and acquired data were analyzed by FlowJo (Treestar, Ashland, OR, USA). In addition, the emigrating immune cells were stained with mAbs against Langerin (CloneDCGM4/122D5 Biosite), MMR, DC-SIGN, α4, αM, β1, β7, α4, or β7 followed by sAb conjugated with FITC for 1 h followed by CD1a-PE or CD3-PerCP staining.
Immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy
Cryopreserved cervical tissue explants were sectioned and the sections were fixed in 4% PFA, quenched, and stained with the following mAbs: CD1a (HI149, BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA), Langerin, MMR, α4, β7, α4β7, αVβ5, and β1. The slides were incubated with antibodies over night at 4°C, washed three times, and stained with a secondary mAb (Rhodamine Red-X conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG, Jackson ImmunoResearch, Baltimore, PA, USA) for 1 h at room temperature. The sections were then washed and mounted using mounting medium containing DAPI (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA). The samples were analyzed using an LSM 510 META confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss AB, Stockholm, Sweden) and LSM 510 software.
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used for statistical analysis. Results were tested for statistical significance using a two-sided paired t-test and p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. In all figures, N denotes the number of times each experiment was replicated, using cervical explants derived from different women.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Biological Products Core of the AIDS and Cancer Virus Program, SAIC Frederick, Inc., National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD, USA for providing infectious and AT-2 inactivated HIV-1. This work was supported by grants through: Marie Larsson: AI52731, The Swedish Research Council, The Swedish, Physicians Against AIDS research Foundation, The Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency; SIDA SARC, VINNMER for Vinnova, Linköping University hospital research Fund, C ALF, and The Swedish Society of Medicine, and in part with federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under contract HHSN261200800001E (J.L.).
Glossary
- AZT
azidothymidine
- C-HIV
complement opsonized HIV-1
- F-HIV
free HIV-1
- HS
human serum
- LC
Langerhans cell
- LP
lamina propria
- PFA
paraformaldehyde
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Additional supporting information may be found in the online version of this article at the publisher's web-site
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
Supporting Figure 1: HIV-1 infection of ectocervical and endocervical mucosa tissue explants Endocervical and ectocervical tissue biopsies were infected with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV), complement opsonized (C-HIV), or virions opsonized by a cocktail of complement and antibodies (C-Ig-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to 6-well plates and cultured for 4 days. The emigrating cells from endocervix (A) and ectocervix (B) were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs, and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and the level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry (N=4) (A and B). The levels of HIV-1 infection of emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells were assessed at day 4 and day 8 from the same donors (C). The level of HIV-1 infection of emigrating DCs and T cells from cervical tissue biopsies (N=2) infected with HIV-1BaL, HIV-MN, or HIV-ADA was assessed day 4 (D). The level of HIV infection of cervical mucosa was assessed by measuring HIV-1 in the tissue culture supernatant at day 4 with a p24 ELISA (N=8) (E). Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test and p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.001.
Supporting Figure 2: Block of α4 and β7 integrins decreased the infection of DCs and CD4+ T cells emigrating from cervical mucosa tissue Cervical tissue biopsies were pretreated for 30min at 37°C with 5μg/ml mock, anti-α4mAb, anti-β7 mAb or isotype control mAb followed by infection with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV), or complement opsonized (C-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2h at 37°C. The biopsies were washed and transferred to 6 well plates and cultured for 4 days with 5μg/ml mock, anti-α4 mAb, anti-β7 mAb, or isotype control mAb. The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and the level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry. The level of HIV-1 infection in DCs or T cells was normalized with F-HIV as 100%. (N=1).
References
- Merbah M, Introini A, Fitzgerald W, Grivel JC, Lisco A, Vanpouille C. Margolis L. Cervico-vaginal tissue ex vivo as a model to study early events in HIV-1 infection. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011;65:268–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J, Gardner MB. Miller CJ. Simian immunodeficiency virus rapidly penetrates the cervicovaginal mucosa after intravaginal inoculation and infects intraepithelial dendritic cells. J. Virol. 2000;74:6087–6095. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.6087-6095.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley JM. Douek DC. HIV infection and the gastrointestinal immune system. Mucosal Immunol. 2008;1:23–30. doi: 10.1038/mi.2007.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan J, Singer A, Jones H. Shafi M. The Cervix. 2nd ed. Wiley Blackwell Press; 2006. (Eds.) [Google Scholar]
- Pudney J, Quayle AJ. Anderson DJ. Immunological microenvironments in the human vagina and cervix: mediators of cellular immunity are concentrated in the cervical transformation zone. Biol. Reprod. 2005;73:1253–1263. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.105.043133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase AT. Early events in sexual transmission of HIV and SIV and opportunities for interventions. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011;62:127–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-080709-124959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong MA, de Witte L, Oudhoff MJ, Gringhuis SI, Gallay P. Geijtenbeek TB. TNF-alpha and TLR agonists increase susceptibility to HIV-1 transmission by human Langerhans cells ex vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118:3440–3452. doi: 10.1172/JCI34721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladik F, Sakchalathorn P, Ballweber L, Lentz G, Fialkow M, Eschenbach D. McElrath MJ. Initial events in establishing vaginal entry and infection by human immunodeficiency virus type-1. Immunity. 2007;26:257–270. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjomsland V, Ellegard R, Che K, Hinkula J, Lifson JD. Larsson M. Complement opsonization of HIV-1 enhances the uptake by dendritic cells and involves the endocytic lectin and integrin receptor families. PLoS One. 2011;6:e23542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turville SG, Arthos J, Donald KM, Lynch G, Naif H, Clark G, Hart D, et al. HIV gp120 receptors on human dendritic cells. Blood. 2001;98:2482–2488. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.8.2482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Witte L, Bobardt M, Chatterji U, Degeest G, David G, Geijtenbeek TB. Gallay P. Syndecan-3 is a dendritic cell-specific attachment receptor for HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:19464–19469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703747104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet V. Steinman RM. The interaction of HIV with dendritic cells: outcomes and pathways. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:503–510. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.07.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller CJ, Li Q, Abel K, Kim EY, Ma ZM, Wietgrefe S, La Franco-Scheuch L, et al. Propagation and dissemination of infection after vaginal transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 2005;79:9217–9227. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.14.9217-9227.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Schuler T, Zupancic M, Wietgrefe S, Staskus KA, Reimann KA, Reinhart TA, et al. Sexual transmission and propagation of SIV and HIV in resting and activated CD4+ T cells. Science. 1999;286:1353–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5443.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz F, Cicala C, Van Ryk D, Block KE, Jelicic K, McNally JP, Ogundare O, et al. The genotype of early-transmitting HIV gp120s promotes alpha (4) beta(7)-reactivity, revealing alpha (4) beta(7) +/CD4 +T cells as key targets in mucosal transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1001301. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase AT. Targeting early infection to prevent HIV-1 mucosal transmission. Nature. 2010;464:217–223. doi: 10.1038/nature08757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoiber H, Pruenster M, Ammann CG. Dierich MP. Complement-opsonized HIV: the free rider on its way to infection. Mol. Immunol. 2005;42:153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoiber H, Banki Z, Wilflingseder D. Dierich MP. Complement-HIV interactions during all steps of viral pathogenesis. Vaccine. 2008;26:3046–3054. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieblemont N, Delibrias C, Fischer E, Weiss L, Kazatchkine MD. Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Complement enhancement of HIV infection is mediated by complement receptors. Immunopharmacology. 1993;25:87–93. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(93)90012-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajtay Z, Speth C, Erdei A. Dierich MP. Cutting edge: productive HIV-1 infection of dendritic cells via complement receptor type 3 (CR3, CD11b/CD18) J. Immunol. 2004;173:4775–4778. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.8.4775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhlal H, Chomont N, Requena M, Nasreddine N, Saidi H, Legoff J, Kazatchkine MD, et al. Opsonization of HIV with complement enhances infection of dendritic cells and viral transfer to CD4 T cells in a CR3 and DC-SIGN-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 2007;178:1086–1095. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.2.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilflingseder D, Banki Z, Garcia E, Pruenster M, Pfister G, Muellauer B, Nikolic DS, et al. IgG opsonization of HIV impedes provirus formation in and infection of dendritic cells and subsequent long-term transfer to T cells. J. Immunol. 2007;178:7840–7848. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.7840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhead P, Hayes P, Watts PS, Laing KG, Griffin GE. Shattock RJ. Parameters of human immunodeficiency virus infection of human cervical tissue and inhibition by vaginal virucides. J. Virol. 2000;74:5577–5586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.12.5577-5586.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q, Frank I, Williams V, Santos JJ, Watts P, Griffin GE, Moore JP, et al. Blockade of attachment and fusion receptors inhibits HIV-1 infection of human cervical tissue. J. Exp. Med. 2004;199:1065–1075. doi: 10.1084/jem.20022212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart PL. Nemerow GR. Cell integrins: commonly used receptors for diverse viral pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2007;15:500–507. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthos J, Cicala C, Martinelli E, Macleod K, Van Ryk D, Wei D, Xiao Z, et al. HIV-1 envelope protein binds to and signals through integrin alpha4beta7, the gut mucosal homing receptor for peripheral T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008;9:301–309. doi: 10.1038/ni1566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Nieves J, Olson T, Bamias G, Bruce A, Solga M, Knight RF, Hoang S, et al. L-selectin, alpha 4 beta 1, and alpha 4 beta 7 integrins participate in CD4+ T cell recruitment to chronically inflamed small intestine. J. Immunol. 2005;174:2343–2352. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.4.2343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danussi C, Petrucco A, Wassermann B, Pivetta E, Modica TM, Del Bel Belluz L, Colombatti A, et al. EMILIN1-alpha4/alpha9 integrin interaction inhibits dermal fibroblast and keratinocyte proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 195:131–145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201008013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garmy-Susini B, Jin H, Zhu Y, Sung RJ, Hwang R. Varner J. Integrin alpha4beta1-VCAM-1-mediated adhesion between endothelial and mural cells is required for blood vessel maturation. J. Clin. Invest. 2005;115:1542–1551. doi: 10.1172/JCI23445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S, Vetvicka V. Ross GD. CR3 (CD11b/CD18) expressed by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells is upregulated in a manner similar to neutrophil CR3 following stimulation with various activating agents. J. Clin. Immunol. 1993;13:175–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00919970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirbod T, Kaldensjo T, Lopalco L, Klareskog E, Andersson S, Uberti-Foppa C, Ferrari D, et al. Abundant and superficial expression of C-type lectin receptors in ectocervix of women at risk of HIV infection. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2009;51:239–247. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181a74f89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller CJ. Lu FX. Anti-HIV and -SIV immunity in the vagina. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2003;22:65–76. doi: 10.1080/08830180305230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhlal H, Chomont N, Haeffner-Cavaillon N, Kazatchkine MD, Belec L. Hocini H. Opsonization of HIV-1 by semen complement enhances infection of human epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2002;169:3301–3306. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.6.3301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessell AJ, Rakasz EG, Poignard P, Hangartner L, Landucci G, Forthal DN, Koff WC, et al. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000433. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Witte L, Nabatov A, Pion M, Fluitsma D, de Jong MA, de Gruijl T, Piguet V, et al. Langerin is a natural barrier to HIV-1 transmission by Langerhans cells. Nat. Med. 2007;13:367–371. doi: 10.1038/nm1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo JR, Rogers R, Molina RM, Dangond F, McLane MF, Essex M. Brain JD. Noninfectious entry of HIV-1 into peripheral and brain macrophages mediated by the mannose receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:5097–5102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611263104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veazey RS, Klasse PJ, Schader SM, Hu Q, Ketas TJ, Lu M, Marx PA, et al. Protection of macaques from vaginal SHIV challenge by vaginally delivered inhibitors of virus-cell fusion. Nature. 2005;438:99–102. doi: 10.1038/nature04055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher D, Wu X, Schacker T, Horbul J. Southern P. HIV binding, penetration, and primary infection in human cervicovaginal tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:11504–11509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500848102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicala C, Martinelli E, McNally JP, Goode DJ, Gopaul R, Hiatt J, Jelicic K, et al. The integrin alpha4beta7 forms a complex with cell-surface CD4 and defines a T-cell subset that is highly susceptible to infection by HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:20877–20882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911796106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari AA, Reimann KA, Mayne AE, Takahashi Y, Stephenson ST, Wang R, Wang X, et al. Blocking of alpha4beta7 gut-homing integrin during acute infection leads to decreased plasma and gastrointestinal tissue viral loads in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques. J. Immunol. 2011;186:1044–1059. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting Figure 1: HIV-1 infection of ectocervical and endocervical mucosa tissue explants Endocervical and ectocervical tissue biopsies were infected with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV), complement opsonized (C-HIV), or virions opsonized by a cocktail of complement and antibodies (C-Ig-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to 6-well plates and cultured for 4 days. The emigrating cells from endocervix (A) and ectocervix (B) were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs, and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and the level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry (N=4) (A and B). The levels of HIV-1 infection of emigrating DCs and CD4+ T cells were assessed at day 4 and day 8 from the same donors (C). The level of HIV-1 infection of emigrating DCs and T cells from cervical tissue biopsies (N=2) infected with HIV-1BaL, HIV-MN, or HIV-ADA was assessed day 4 (D). The level of HIV infection of cervical mucosa was assessed by measuring HIV-1 in the tissue culture supernatant at day 4 with a p24 ELISA (N=8) (E). Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test and p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.001.
Supporting Figure 2: Block of α4 and β7 integrins decreased the infection of DCs and CD4+ T cells emigrating from cervical mucosa tissue Cervical tissue biopsies were pretreated for 30min at 37°C with 5μg/ml mock, anti-α4mAb, anti-β7 mAb or isotype control mAb followed by infection with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV), or complement opsonized (C-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2h at 37°C. The biopsies were washed and transferred to 6 well plates and cultured for 4 days with 5μg/ml mock, anti-α4 mAb, anti-β7 mAb, or isotype control mAb. The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and the level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry. The level of HIV-1 infection in DCs or T cells was normalized with F-HIV as 100%. (N=1).