Abstract
The first total synthesis of the lipid mediator MaR1n-3 DPA (5) has been achieved in 12% overall yield over 11 steps. The stereoselective preparation of 5 was based on a Pd-catalyzed sp3-sp3 Negishi cross-coupling reaction and a stereo controlled Evans-Nagao acetate aldol reaction. LC-MS/MS results with synthetic material matched the biologically product 5. This novel lipid mediator displayed potent pro-resolving properties stimulating macrophage efferocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils.
Keywords: sp3-sp3 cross-coupling, total synthesis, palladium, natural products, inflammation
The critical role of inflammatory processes in health and diseases has long been recognized.[1] The detailed molecular mechanisms and biological events that regulate the progression and resolution of inflammation have recently emerged.[2,3] These studies have established that the resolution of inflammation is a biosynthetically active process, where stereospecific di- and trihydroxy-containing polyunsaturated fatty acids derived lipid mediators, named specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), resolve inflammation, protect organs, stimulate resolution and induce tissue regeneration.[3] The resolvins, [4] protectins [4–10] and maresins [10,11] are examples of different families of SPMs. Among the many SPMs identified,[2] those derived from the dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have attracted significant interest from biomedical researchers.[3] Examples of this class of SPMs includes resolvin D1 (1), resolvin D2 (2), protectin D1 (3) and maresin 1 (MaR1, 4) (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
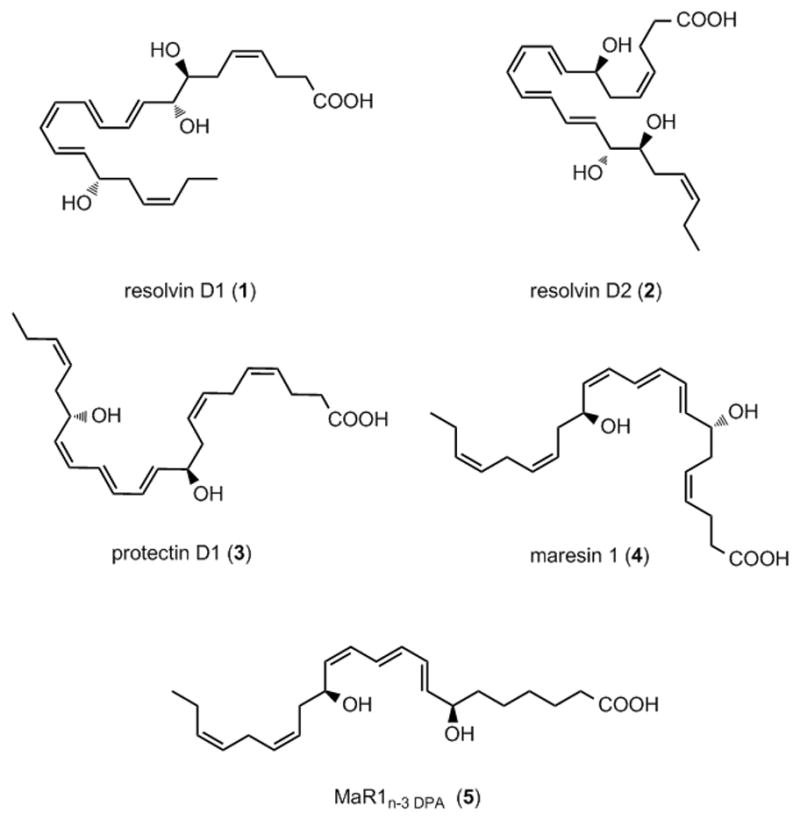
SPMs exhibiting potent anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving actions.
These stereospecific tri- or di-hydroxylated polyunsaturated natural products exhibit very potent agonist activities, most often in the low nanomolar range, in a wide range of in vivo animal inflammation models. The precise molecular understanding and stereoselective mode of action of resolution of inflammation has been explained with these local mediators as pharmacological agents.[3] Several SPMs have entered clinical development programs.[2,3]
In 2013 Dalli et al. reported that n-3 docosapentaenoic acid (n-3 DPA) was converted biosynthetically in both human and murine leukocytes to several new SPMs.[10] One of the products identified was denoted MaR1n-3 DPA (5), given its relation to maresin 1 (4) (Figure 1). This SPM was produced in pico- to nanogram amounts in vivo. The initial structural assignment of MaR1n-3 DPA (5) was based on biosynthetic results and LC-MS/MS fragmentation data.[10] The exact stereochemical determination of the double bond geometry in the conjugated triene system and the absolute configurations of the C-7 and C-14 groups remained to be established. Hence, total synthesis became necessary for exact structural determination of 5, but also for providing sufficient material for confirmation and further biological studies.
The sensitive E, E, Z-triene connected to either one or two secondary allylic alcohols is a common feature found in several of the SPMs.[2] In our retrosynthetic analysis of 5 a palladium catalyzed sp3-sp3 coupling reaction[12] is a key step leading back to alkyne 6, alcohol 7 and 4-ethoxy-4-oxobutylzinc bromide (8) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
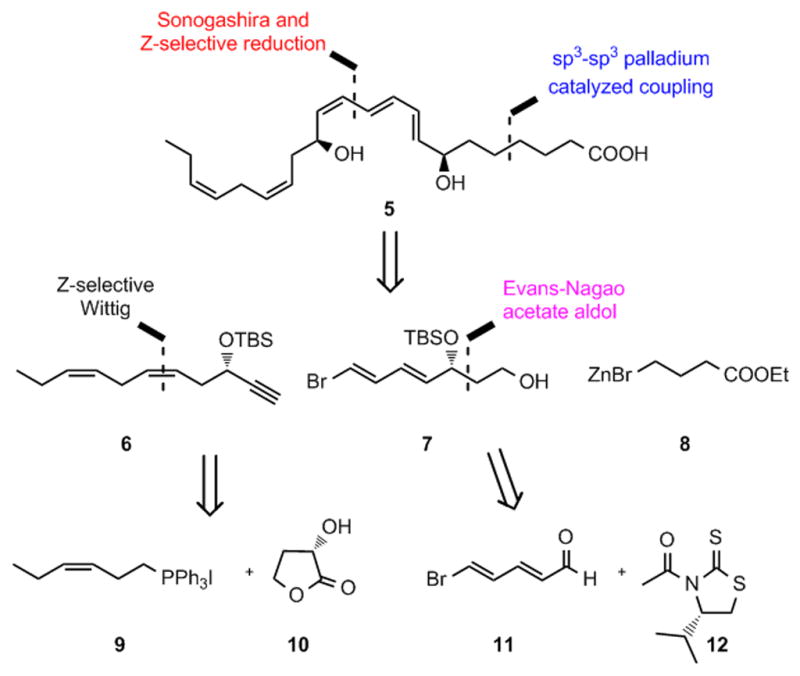
Retrosynthetic analysis of MaR1n-3 DPA (5).
The reliability of this type of coupling reaction under transition metal catalysis has recently been considerably improved due to the work of Organ and co-workers.[13] As of today, no examples of palladium catalyzed Negishi sp3-sp3 coupling reactions, using alkylzinc reagents, have been applied to the total synthesis of natural products.[14] So far, most protocols have been based on magnesium-[15] or copper-reagents[16] in the presence of nickel-complexes.[17] We were tempted by this disconnection since intermediate 7 can easily be prepared employing a stereoselective Evans-Nagao acetate aldol reaction[18,19] between aldehyde 11[20] and the chiral auxiliary 12.
Our synthesis of 5 started with the preparation of alkyne 6 using an efficient protocol. First, (S)-(−)-α-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone (10) was TBS-protected to 13, which was reduced to the corresponding lactol that was converted to the alkyne 14 in a Colvin rearrangement. A Swern oxidation of 14 produced multi-grams of TBS-protected 3-hydroxy-4-pentynal (15) in overall 47% yield (Scheme 1). The Wittig-salt 9 was prepared from cis-3-hexen-1-ol (16) in 90% yield using a literature procedure,[21] see Scheme 1. Then a Z-selective Wittig reaction between 9 and aldehyde 15 afforded alkyne 6 in 83% yield after purification by chromatography. The stereochemical purity of 6 was determined by GC and 1H NMR analyses. Overall, TBS-protected alkyne 6 was efficiently synthesized in 39% yield from 10.
Scheme 1.
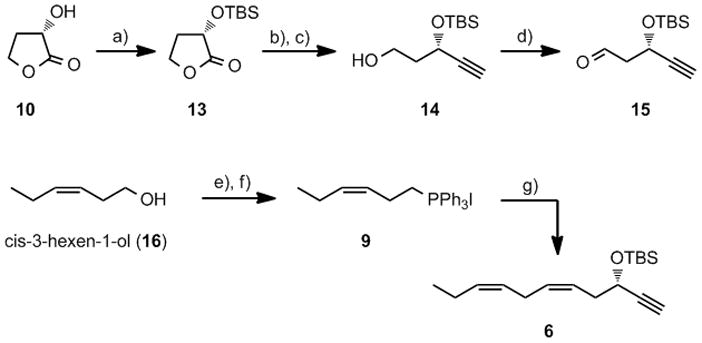
Reagents and conditions: a) TBSOTf, 2,6-lutidine, CH2Cl2, −78 °C, 97%; b) DIBAL-H, CH2Cl2, −78 °C; c) LDA, TMSCHN2, THF, −78 °C, 57%; d) (COCl)2, DMSO, Et3N, CH2Cl2, −78 °C, 85%; e) I2, PPh3, imidazole, CH2Cl2; f) PPh3, MeCN, Δ, 90%; g) NaHMDS, HMPA, THF, 15, −78 °C, 83%.
Next, commercially available pyridinium-1-sulfonate (17) was converted to (2E, 4E)-5-bromopenta-2,4-dienal (11) employing a two-step protocol.[22] Then 11 was reacted with 12 in an Evans-Nagao acetate aldol reaction under conditions developed by Olivo and co-workers.[23] This yielded a 15.3:1 ratio(HPLC analysis) of the desired diasteromer19.[23b] Protection (TBSOTf, 2,6-lutidine) and purification by chromatography afforded stereochemically pure 20 (HPLC and NMR analyses). Removal of the auxiliary in 20 was achieved with LiBH4 yielding primary alcohol 7 in 88% yield. Alcohol 7 and alkyne 9 were then coupled in a Sonogashira reaction at ambient temperature in the presence of catalytic amounts of Pd(PPh3)4 and CuI affording 21 in 68% yield. All attempts to improve this reaction were unsuccessful.[24] An Apple reaction afforded the primary bromide 22 in near quantitative yield from 21. This high yielding protocol allowed the preparation of 22 in 20% yield over seven steps (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2.
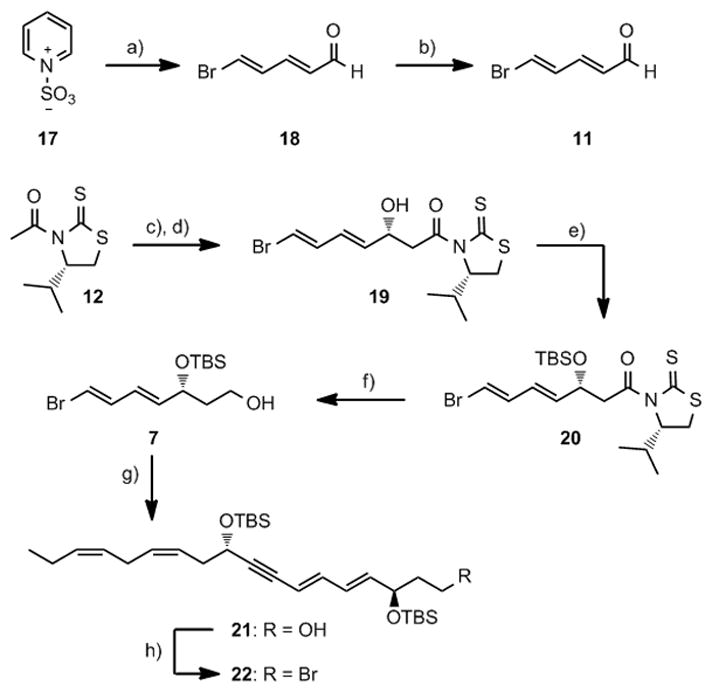
Reagents and conditions: a) KOH (aq.), −20 °C tort.; b) Br2, PPh3, CH2Cl2, 0 °C, 41%; c) (i-Pr)2NEt, TiCl4, CH2Cl2, −78 °C; d) aldehyde 11, 86%; e) TBSOTf, 2,6-lutidine, CH2Cl2, −78 °C, 97%; f) LiBH4, Et2O, MeOH, 88%; g) Pd(PPh3)4, CuI, 6, Et2NH, 68%; h) CBr4, PPh3, 2,6-lutidine, CH2Cl2, 97%.
Several sp3-sp3 cross-coupling reactions between the primary bromide 22 with methyl 3-(9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-9-yl) propanoate were explored.[25] Unfortunately, all efforts to accomplish this coupling were unsuccessful as only trace amounts of 23 was formed.[25d] To our delight, when the palladium-based PEPPSI™-IPr catalyst 24 was employed in the presence of bromide 22 and 4-ethoxy-4-oxobutylzinc bromide (8), the desired ethyl ester23 was formed consistently in 68–72% yield after chromatography. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported application of the sp3-sp3 palladium-catalysed cross-coupling protocol developed by Organ and co-workers in a synthesis of a natural product. Removal of the TBS-protection groups with tetra-n-butyl ammonium fluoride yielded 25 that wa as reduced employing a modified Lindlar procedure.[23b] This yielded ester 26 in 75% yield over the two steps (Scheme 3.) Basic hydrolysis of 26 afforded synthetic MaR1n-3 DPA (5) in 86% yield with UV-, MS- and NMR-data in accord with the structure. The chemical purity of synthetic 5 was determined to be >98% by HPLC analyses.
Scheme 3.
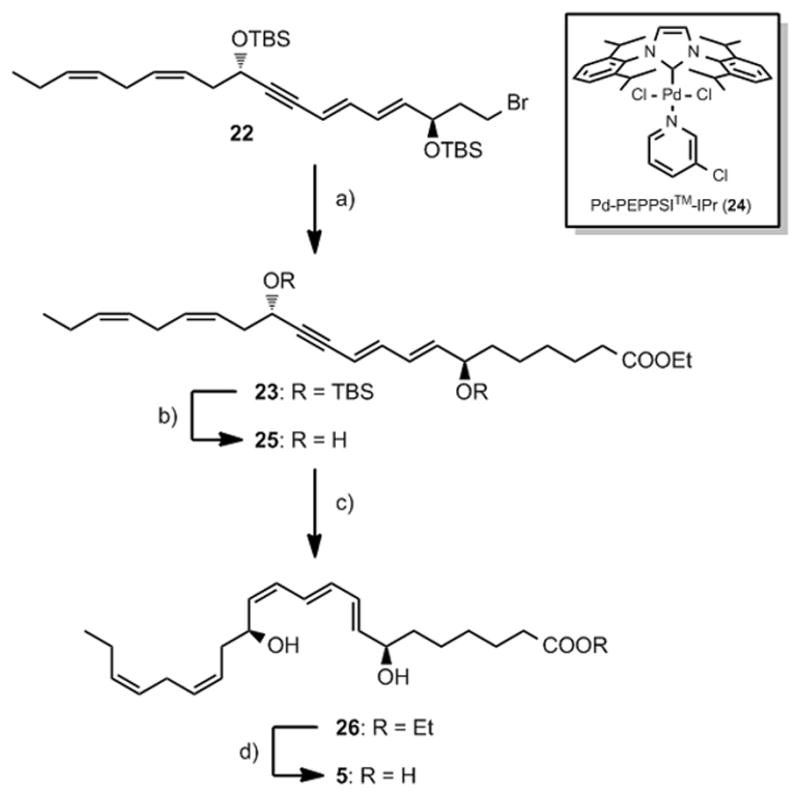
Reagents and conditions: a) Pd-PEPPSI™-IPr, LiCl, 8, THF, NMP, 68%; b) TBAF, THF, 0 °C, 97%; c) Lindlar, H2, EtOAc, pyridine, 1-octene, 77%, d) LiOH, THF, MeOH, 0 °C, 86%.
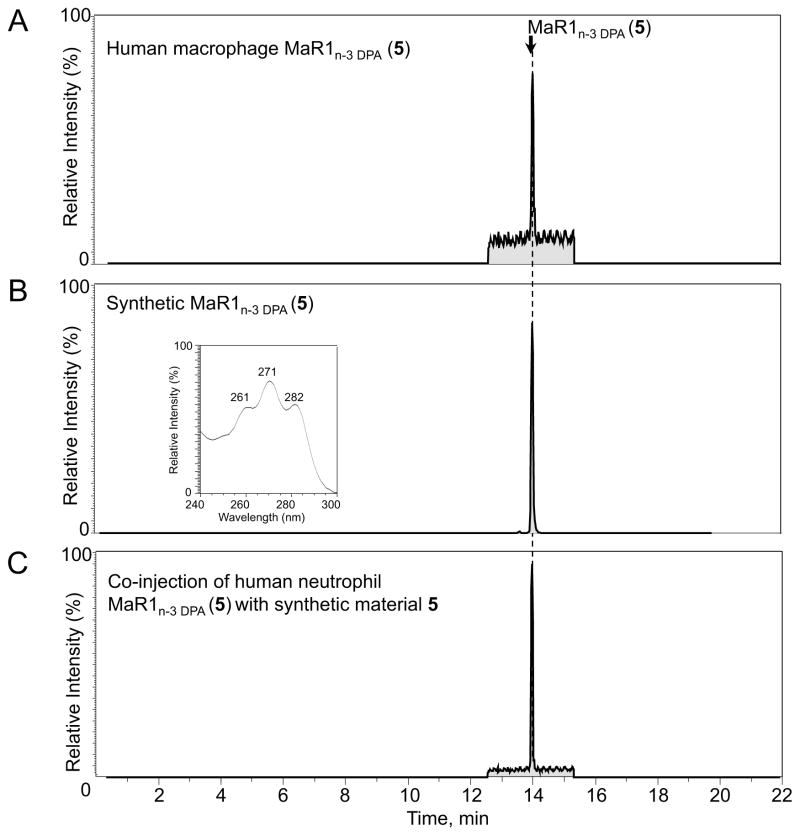
To determine if synthetic 5 matched authentic MaR1n-3 DPA (5), biologically formed 5 from human macrophages was employed.[10] Human macrophage induced formation of MaR1n-3 DPA (5) showed retention time (TR) of 14.1 min (Figure 3A). The retention time of synthetic 5 was identical (TR = 14.1 min) with biologically produced 5, see Figure 3B. Figure 3C depicts the co-injection of synthetic and biologically obtained material added at equal amounts. These experiments demonstrated that synthetic 5 co-elutes with natural occurring 5. In addition, the MS/MS spectra for both natural and synthetic 5 were essentially identical, see Supporting information, and in accord with literature.[10]
Figure 3.
Matching of synthetic 5 and authentic MaR1n-3 DPA (5). See Supporting information for details.
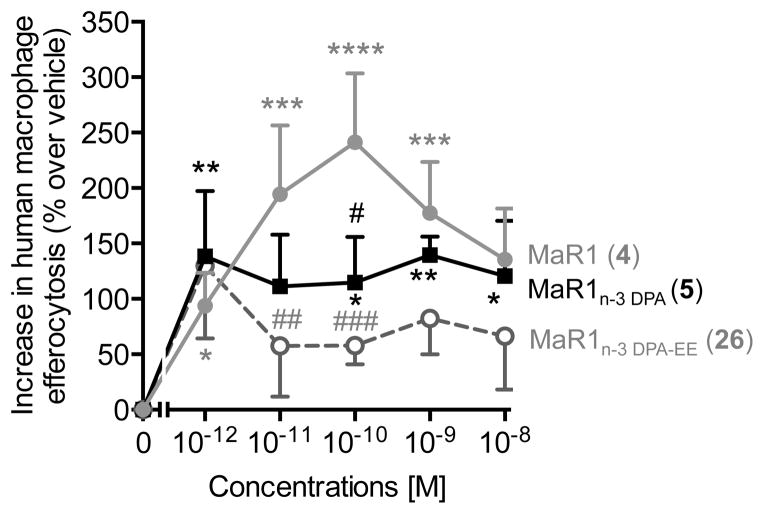
Next incubation of synthetic material 5 with human macrophages was performed; a very potent stimulation of macrophage efferocytosis of apoptotic human neutrophils was observed (Figure 4). This is a key step in the resolution of inflammation;[3] an action that was shared with the DHA derived MaR1 (4).[11,26] Of note, the ethyl ester 26 also stimulated macrophage efferocytosis of apoptotic human neutrophils albeit to a lower extent (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
MaR1n-3 DPA (5) enhances human macrophage efferocytosis. Results are percent increase over vehicle and expressed as mean ± s.e.m. n = 4 with 3 – 4 determinations for each. *P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001 and ****P <0.0001 vs. vehicle; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P <0.001 vs. maresin 1 (MaR1, 4). See Supporting information for details
In summary, multi mg of the potent anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving lipid mediator MaR1n-3 DPA (5) was stereoselectively prepared in 11 steps and 12% overall yield from cheap, commercially available salt 17. Our synthesis compares very favorable to those syntheses published of the maresin SPM class of natural products.[27] The palladium catalyzed sp3-sp3 cross-coupling reaction using the Pd-PEPPSI™-IPr catalyst 24was applied for the first time to the synthesis of a natural product. The synthetic material displayed identical chromatographic properties with biologically produced 5. These efforts confirmed the structure of the bioactive natural MaR1n-3 DPA (5) to be (7S, 8E, 10E, 12Z, 14S, 16Z, 19Z)-7,14-dihydroxydocosa-8, 10, 12, 16, 19-pentaenoic acid and its potent biological actions in human macrophage efferocytosis. The results presented for (5) will be useful for future developments towards new pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory agents.[28] Further biological studies with synthetic material are ongoing and will be reported.
Experimental Section
Experimental procedures and 1H-,13C-spectra data, HRMS and UV/VIS spectra, HPLC chromatograms of 1 and all intermediates as well as LC/MS-MS of authentic MaR1n-3DPA (1) are available in the Supporting Information. Blood was obtained from healthy human volunteers giving informed consent (protocol #199-P-001297 approved by the Partners Human Research Committee).
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
The School of Pharmacy, University of Oslo and The Norwegian Research Council (KOSK II), are gratefully acknowledged for Ph.D.-scholarships to J.E.T. and M.A., respectively. C.N.S., J.D. and H.A. are supported by the National Institutes of Health USA Grant PO1GM095467 (C.N.S.).
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://
Contributor Information
Jørn Eivind Tungen, School of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, University of Oslo, PO Box 1068 Blindern, N-0316 Oslo (Norway).
Dr. Marius Aursnes, School of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, University of Oslo, PO Box 1068 Blindern, N-0316 Oslo (Norway)
Dr. Jesmond Dalli, Center for Experimental Therapeutics and Reperfusion Injury, Department of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, Harvard Institutes of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, 02115(USA)
Dr. Hildur Arnardottir, Center for Experimental Therapeutics and Reperfusion Injury, Department of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, Harvard Institutes of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, 02115(USA)
Prof. Dr. Charles Nicholas Serhan, Center for Experimental Therapeutics and Reperfusion Injury, Department of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, Harvard Institutes of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, 02115(USA)
Prof. Dr. Trond Vidar Hansen, Email: t.v.hansen@farmasi.uio.no, School of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, University of Oslo, PO Box 1068 Blindern, N-0316 Oslo (Norway)
References
- 1.Tabas I, Glass CK. Science. 2013;339:166. doi: 10.1126/science.1230720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Serhan CN, Petasis NA. Chem Rev. 2011;111:5922. doi: 10.1021/cr100396c. and references cited therein. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Serhan CN, Chiang N. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13:632. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.05.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Serhan CN, Clish CB, Brannon J, Colgan SP, Chiang N, Gronert KJ. Exp Med. 2000;192:1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.8.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Serhan CN, Hong S, Gronert K, Colgan SP, Devchand PR, Mirick G, Moussignac RL. J Exp Med. 2002;196:1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hong S, Gronert K, Devchand PR, Moussignac RL, Serhan CN. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:14677. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300218200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mukherjee PK, Marcheselli VL, Serhan CN, Bazan NG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:8491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402531101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ariel A, Pin-Lan L, Wang W, Tang WX, Fredman G, Hong S, Gotlinger KH, Serhan CN. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:43079. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509796200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aursnes M, Tungen JE, Vik A, Collas R, Cheng CY, Dalli J, Serhan CN, Hansen TV. J Nat Prod Chem. 2014;77:910. doi: 10.1021/np4009865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dalli J, Colas RA, Serhan CN. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1940. doi: 10.1038/srep01940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Serhan CN, Yang R, Martinod K, Kasuga K, Pillai PS, Porter TF, Oh SF, Spite M. J Exp Med. 2009;206:15. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Negishi E. In: Handbook of Organo palladium Chemistry for Organic Synthesis. Negishi E, editor. Wiley; New York: 2002. [Google Scholar]; (b) Devasagayaraj A, Stüdemann T, Knochel P. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1996;34:2723. [Google Scholar]; (c) Giovannini R, Stüdemann T, Dussin G, Knochel P. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1998;37:2387. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980918)37:17<2387::AID-ANIE2387>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Zhou J, Fu GC. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:12527. doi: 10.1021/ja0363258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Arp FO, Fu GC. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:10482. doi: 10.1021/ja053751f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Hadei N, Kantchev EAB, O’Brien CJ, Organ MG. Org Lett. 2005;7:3805. doi: 10.1021/ol0514909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Valente C, Belowich ME, Hadei N, Organ MG. Eur J Org Chem. 2010:4343. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Geist E, Kirschning A, Schmidt T. Nat Prod Rep. 2014;31:441. doi: 10.1039/c3np70108e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Brand GJ, Studte C, Breit B. Org Lett. 2009;11:4668. doi: 10.1021/ol901944b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Schmidt T, Kirschning A. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2012;51:1063. doi: 10.1002/anie.201106762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.(a) Yang CT, Zhang ZQ, Liang J, Liu JH, Lu XY, Chen HH, Liu L. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:11124. doi: 10.1021/ja304848n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Garcia PMP, Di Franco T, Orsino A, Ren P, Hu X. Org Lett. 2012;14:4286. doi: 10.1021/ol302067b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.(a) Smith SW, Fu GC. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2008;47:9334. doi: 10.1002/anie.200802784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Son S, Fu GC. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:2756. doi: 10.1021/ja800103z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Evans DA, Bartroli J, Shih TL. J Am Chem Soc. 1981;103:2127. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nagao Y, Dai WM, Ochiai M, Tsukagoshi S, Fujita E. J Org Chem. 1989;54:5211. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Becher J. Org Synth. 1979;59:79. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Detterbeck R, Guggisberg A, Popaj K, Hesse M. Helv Chim Acta. 2002;85:1742. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Soullez D, Ple G, Duhamel L, Duhamel P. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1. 1997;11:1639. [Google Scholar]
- 23.(a) Tello-Aburto R, Ochoa-Teran A, Olivo HF. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006;47:5915. [Google Scholar]; (b) Aursnes M, Tungen JE, Vik A, Dalli J, Hansen TV. Org Biomol Chem. 2014;12:432. doi: 10.1039/c3ob41902a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Tungen JE, Aursnes M, Hansen TV. Tetrahedron. 2014;70:3793. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Altering the concentrations of 7 and 9 or the amount of Cu(I) and Pd(PPh3)4 did not improve the yield of 21.
- 25.Keaton KA, Phillips AJ. Org Lett. 2007;9:2717. doi: 10.1021/ol0710111.Ishiyama T, Abe S, Miyaura N, Suzuki A. Chem Lett. 1992:691.Netherton MR, Dai C, Neuschütz K, Fu GC. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:10099. doi: 10.1021/ja011306o.(d) Despite great care being exercised to use meticulously purified coupling components, solvents and reagents of high quality, as well as carefully excluding oxygen to the best of our ability, we were never able to obtain the cross-coupled product 23 in good yield or purity. Only trace amounts of the desired coupled product were observed. Using either Pd(PCy3)2 or Pd(PCy3)2Cl2 did not alter the outcome. The bromide 22 was also converted into the corresponding iodide that was employed using the aforementioned experiments and conditions. Again, no formation of 23 was observed.
- 26.Serhan CN, Dalli J, Karamnov S, Choi A, Park CK, Xu ZZ, Ji RR, Zhu M, Petasis NA. FASEB J. 2012:1755. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-201442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.(a) Sasaki K, Urab D, Arai H, Arita M, Inoue M. Chem Asian J. 2011;6:534. doi: 10.1002/asia.201000494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rodriguez AR, Spur BW. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012;53:4169. [Google Scholar]; (c) Ogawa N, Tojo T, Kobayashi Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014;55:2738. [Google Scholar]; (d) Zhu M. PhD Thesis. University of Southern California; Los Angeles, CA: 2013. Total Synthesis of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators and Their Analogs. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Serhan CN. Nature. 2014;510:92. doi: 10.1038/nature13479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.