Abstract
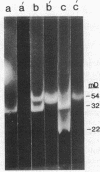
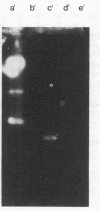
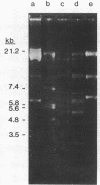
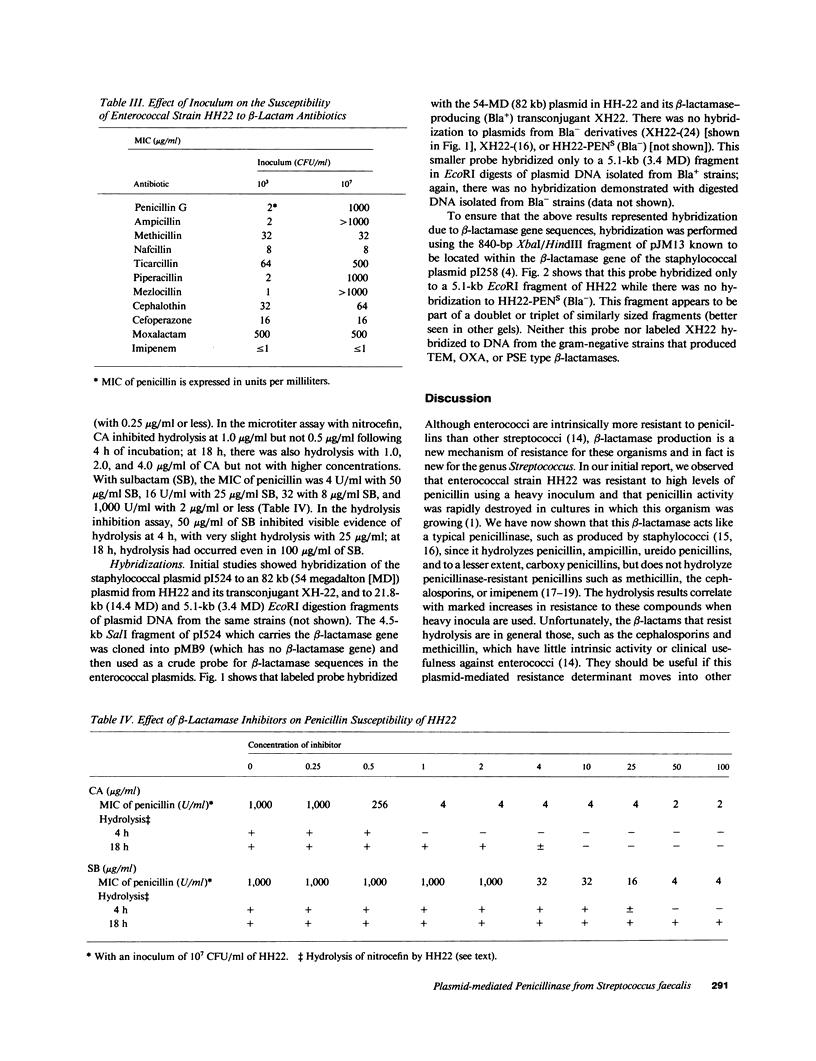
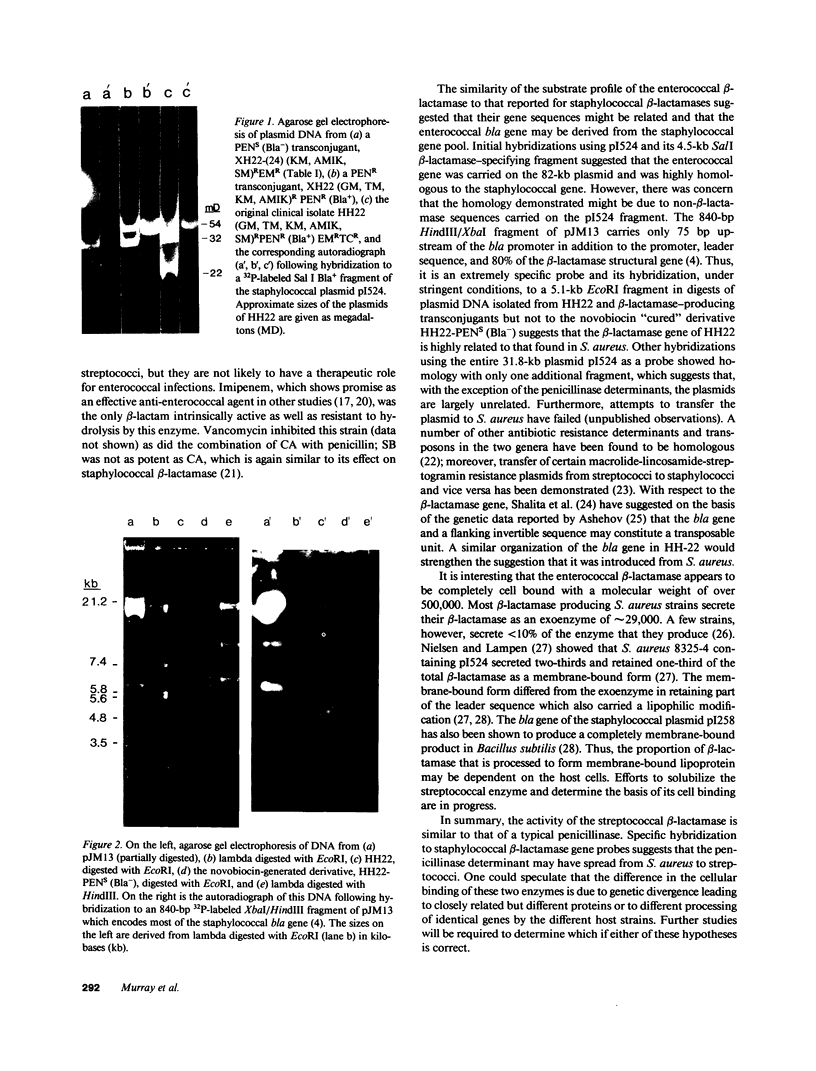
A strain of Streptococcus faecalis with plasmid-mediated penicillinase production was studied further. Partially purified penicillinase from the S. faecalis strain hydrolyzed penicillin, ampicillin, and ureido-penicillins but not penicillinase-resistant semisynthetic penicillins, cephalosporins, or imipenem; hydrolysis was inhibited by clavulanic acid. Hydrolysis of a given antibiotic correlated with a marked increase in the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of that drug when a high inoculum was used. As with most enterococci, the MICs of cephalosporins and penicillinase-resistant semisynthetic penicillins were too high for clinical usefulness, although these agents did not show an inoculum effect. Based upon hybridization under stringent conditions of plasmid DNA from the S. faecalis strain to cloned penicillinase genes from Staphylococcus aureus, it appears that these resistance determinants are highly homologous and suggests that this enzyme was introduced into streptococci from staphylococci.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Citri N., Pollock M. R. The biochemistry and function of beta-lactamase (penicillinase). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:237–323. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Moellering R. C., Jr Susceptibility of enterococci and Listeria monocytogenes to N-Formimidoyl thienamycin alone and in combination with an aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):789–793. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Girard A. E., Lynch J. E., Barth W. E. CP-45,899, a beta-lactamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of beta-lactams: initial bacteriological characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Azlocillin and mezlocillin: new ureido penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):930–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Lee L. N. Characterization of two tetracycline resistance determinants in Streptococcus faecalis JH1. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):835–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.835-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas T. J. An evaluation of 12 methods for the demonstration of penicillinase. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):1061–1065. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W. Analytical isoelectric focusing of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):713–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.713-718.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Hedges R. W., Jacoby G. A. Spread of a "Pseudomonas-specific" beta-lactamase to plasmids of enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.700-707.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Novick R. P. Physical mapping of Staphylococcus aureus penicillinase plasmid pI524: characterization of an invertible region. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):19–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00267851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mederski-Samaroj B. Transferable beta-lactamase. A new mechanism for in vitro penicillin resistance in Streptococcus faecalis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1168–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI111042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Membrane-bound penicillinases in Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4490–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Muggleton P. W., Ross G. W. Effects of beta-lactamase from gram-negative organisms on cephalosporins and penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE EXOPENICILLINASE FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:452–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0880452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy R. P., Murray B. E. Evidence for an epidemic trimethoprim-resistance plasmid in fecal isolates of Escherichia coli from citizens of the United States studying in Mexico. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):25–29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders C. W., Schmidt B. J., Mirot M. S., Thompson L. D., Guyer M. S. Use of chromosomal integration in the establishment and expression of blaZ, a Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene, in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):718–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.718-726.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Clewell D. B., Glatzer L. Conjugative transfer of R-plasmids from Streptococcus faecalis to Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):204–207. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalita Z., Murphy E., Novick R. P. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus: structural and evolutionary relationships. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):291–311. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Nordström K. Microiodometric determination of beta-lactamase activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):94–99. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of group D streptococcus (enterococcus) to 21 antibiotics in vitro, with special reference to species differences. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):416–430. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]