Abstract
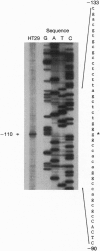
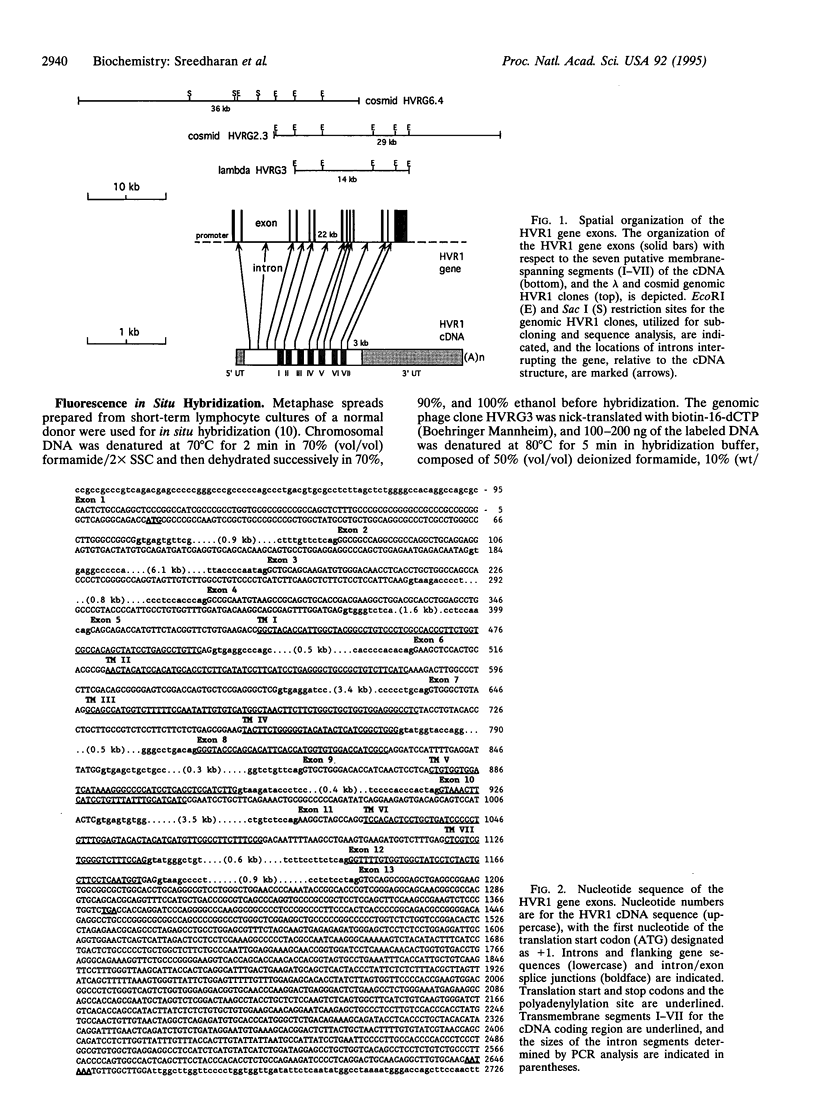
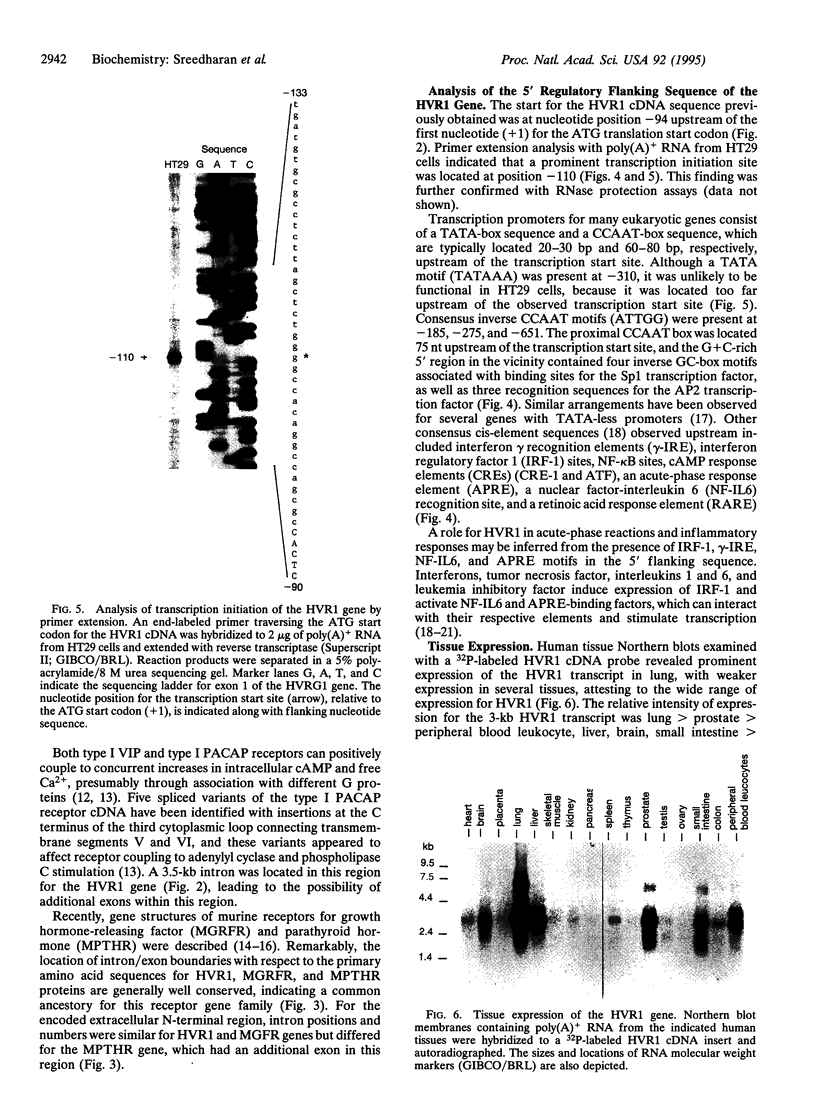
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and other members of the pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) and secretin neuroendocrine peptide family are recognized with specificity by related G protein-coupled receptors. We report here the cloning, characterization, and chromosomal location of the gene encoding the human type I VIP receptor (HVR1), also termed the type II PACAP receptor. The gene spans approximately 22 kb and is composed of 13 exons ranging from 42 to 1400 bp and 12 introns ranging from 0.3 to 6.1 kb. Primer extension analysis with poly(A)+ RNA from human HT29 colonic adenocarcinoma cells indicated that the transcription initiation site is located at position -110 upstream of the first nucleotide (+1) of the translation start codon, and 75 nt downstream of a consensus CCAAT-box motif. The G+C-rich 5' flanking region contains potential binding sites for several nuclear factors, including Sp1, AP2, ATF, interferon regulatory factor 1, NF-IL6, acute-phase response factor, and NF-kappa B. The HVR1 gene is expressed selectively in human tissues with a relative prevalence of lung > prostate > peripheral blood leukocytes, liver, brain, small intestine > colon, heart, spleen > placenta, kidney, thymus, testis. Fluorescence in situ hybridization localized the HVR1 gene to the short arm of human chromosome 3 (3p22), in a region associated with small-cell lung cancer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Reis L. F., Watanabe N., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Induction of the transcription factor IRF-1 and interferon-beta mRNAs by cytokines and activators of second-messenger pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9936–9940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozes I., Brenneman D. E. VIP: molecular biology and neurobiological function. Mol Neurobiol. 1989 Winter;3(4):201–236. doi: 10.1007/BF02740606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto H., Ishihara T., Shigemoto R., Mori K., Nagata S. Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of a receptor for pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90188-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki N., Yoshida H., Mizuta M., Mizuno N., Fujii Y., Gonoi T., Miyazaki J., Seino S. Cloning and functional characterization of a third pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptor subtype expressed in insulin-secreting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Wolf M. E., Giambernardi T. A., Naylor S. L. Definition of a tumor suppressor locus within human chromosome 3p21-p22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10877–10881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong X. F., Schipani E., Lanske B., Joun H., Karperien M., Defize L. H., Jüppner H., Potts J. T., Jr, Segre G. V., Kronenberg H. M. The rat, mouse and human genes encoding the receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide are highly homologous. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1290–1299. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. C., Lin C. R., Gukovsky I., Lusis A. J., Sawchenko P. E., Rosenfeld M. G. Molecular basis of the little mouse phenotype and implications for cell type-specific growth. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):208–213. doi: 10.1038/364208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz E. M., Sheward W. J., West K. M., Morrow J. A., Fink G., Harmar A. J. The VIP2 receptor: molecular characterisation of a cDNA encoding a novel receptor for vasoactive intestinal peptide. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 8;334(1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81668-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCuaig K. A., Clarke J. C., White J. H. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the mouse parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Johnson B. E., Minna J. D., Sakaguchi A. Y. Loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 3p markers in small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):451–454. doi: 10.1038/329451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal A., Patil N., Chao M. A constitutive promoter directs expression of the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3160–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler D., Waeber C., Pantaloni C., Holsboer F., Bockaert J., Seeburg P. H., Journot L. Differential signal transduction by five splice variants of the PACAP receptor. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):170–175. doi: 10.1038/365170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S. P., Patel D. R., Huang J. X., Goetzl E. J. Cloning and functional expression of a human neuroendocrine vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 15;193(2):546–553. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S. P., Patel D. R., Xia M., Ichikawa S., Goetzl E. J. Human vasoactive intestinal peptide1 receptors expressed by stable transfectants couple to two distinct signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 30;203(1):141–148. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Sugawara M., Ponath P. D., Wessendorf L., Banerji J., Li Y., Strominger J. L. Interferon gamma response region in the promoter of the human DPA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9226–9230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]