Figure 1. The chromodomain helicase DNA binding family of chromatin remodelers.
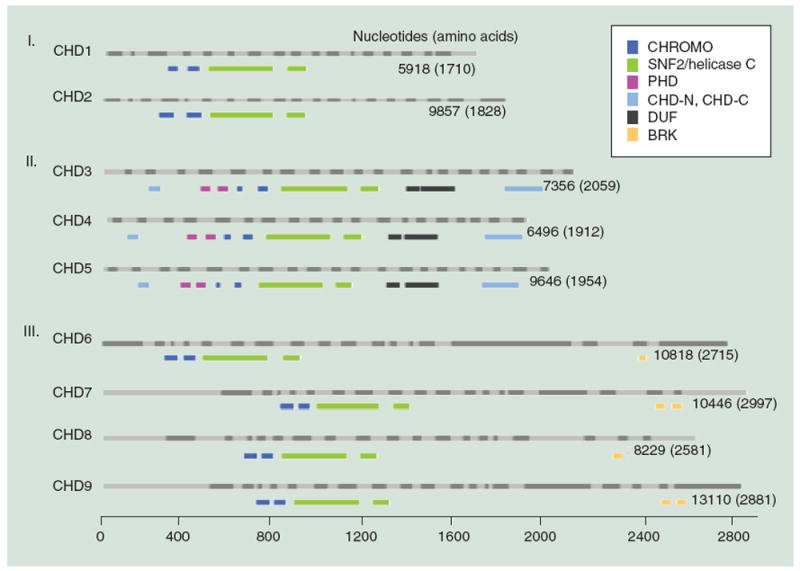
CHD proteins are classified into three subfamilies (Roman numerals) based on their functional motifs (see legend). The human CHD family based on ensemble is drawn to scale, with light and dark gray bars depicting alternating exons (above) and the functional motifs from PFAM (a database of protein families of multiple sequence alignments generated using hidden Markov models) shown in color (below) for each CHD member. The number of nucleotides and amino acid residues for the CHD transcript and protein, respectively, are shown.
BRK: Brahma and Kismet domains; CHD: chromodomain helicase DNA binding; CHROMO: Chromodomain; CHD-N, CHD-C: CHD_N and CHD_C are shown in upstream and downstream region, respectively; DUF: Domain of unknown function; PHD: Plant homeodomain; SNF2/helicase C: SNF2_N and helicase_C are shown in upstream and downstream region, respectively.
