Abstract
Metabolic acidosis is associated with enhanced renal ammonia-genesis which is regulated, in part, by glucocorticoids. The interaction between glucocorticoids and chronic metabolic acidosis on nitrogen utilization and muscle protein metabolism is unknown. In rats pair-fed by gavage, we found that chronic acidosis stunted growth and caused a 43% increase in urinary nitrogen and an 87% increase in urinary corticosterone. Net protein degradation in incubated epitrochlearis muscles from chronically acidotic rats was stimulated at all concentrations of insulin from 0 to 10(4) microU/ml. This effect of acidosis persisted despite supplementation of the media with amino acids with or without insulin, indomethacin, and inhibitors of lysosomal thiol cathepsins. Acidosis did not change protein synthesis; hence, the increase in net protein degradation was caused by stimulation of proteolysis. Acidosis did not increase glutamine production in muscle. The protein catabolic effect of acidosis required glucocorticoids; protein degradation was stimulated in muscle of acidotic, adrenalectomized rats only if they were treated with dexamethasone. Moreover, when nonacidotic animals were given 3 micrograms/100 g of body weight dexamethasone twice a day, muscle protein degradation was increased if the muscles were simply incubated in acidified media. We conclude that chronic metabolic acidosis depresses nitrogen utilization and increases glucocorticoid production. The combination of increased glucocorticoids and acidosis stimulates muscle proteolysis but does not affect protein synthesis. These changes in muscle protein metabolism may play a role in the defense against acidosis by providing amino acid nitrogen to support the glutamine production necessary for renal ammoniagenesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addae S. K., Lotspeich W. D. Relation between glutamine utilization and production in metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1968 Aug;215(2):269–277. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. M., Goldthorp R., Watts R. W. Fluorimetric measurement of the phenylalanine content of human granulocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Feb 12;43(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
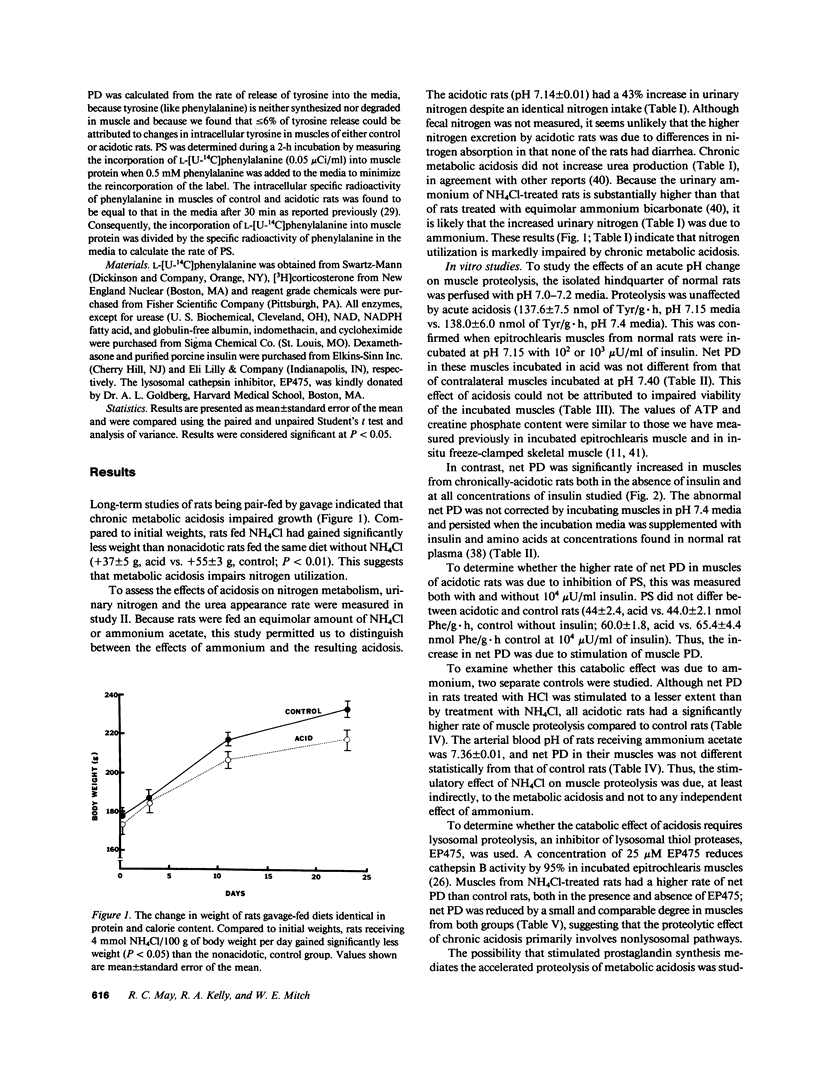
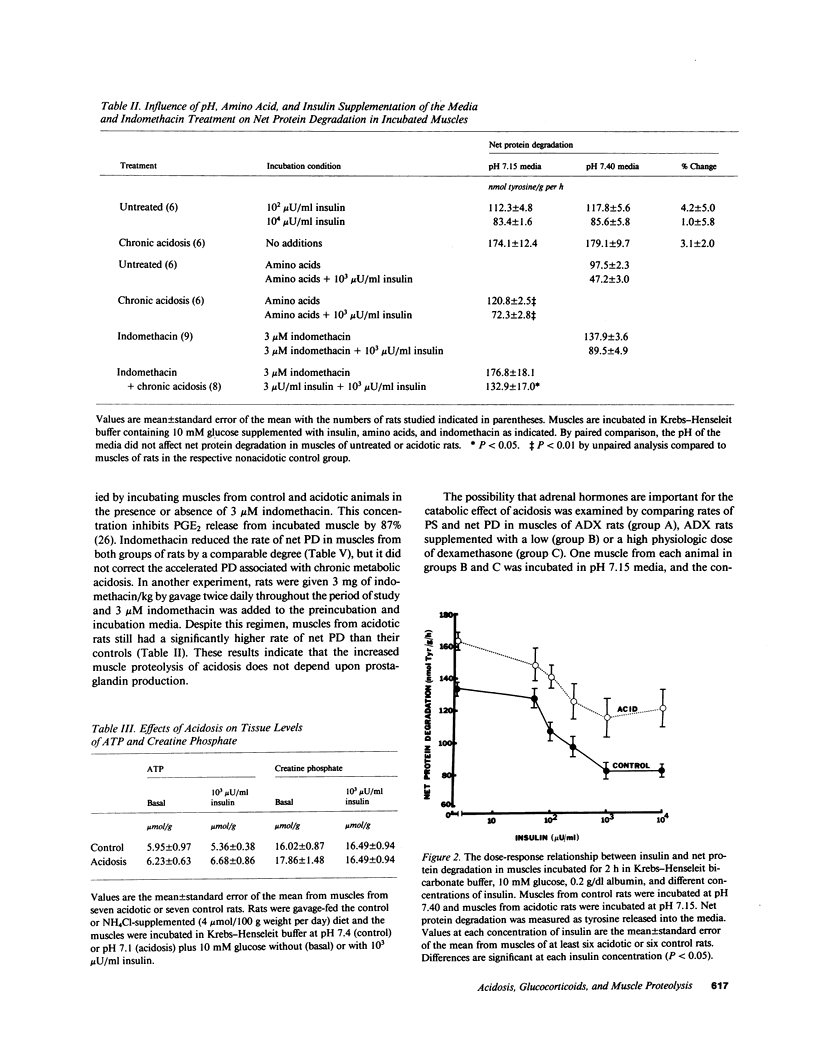
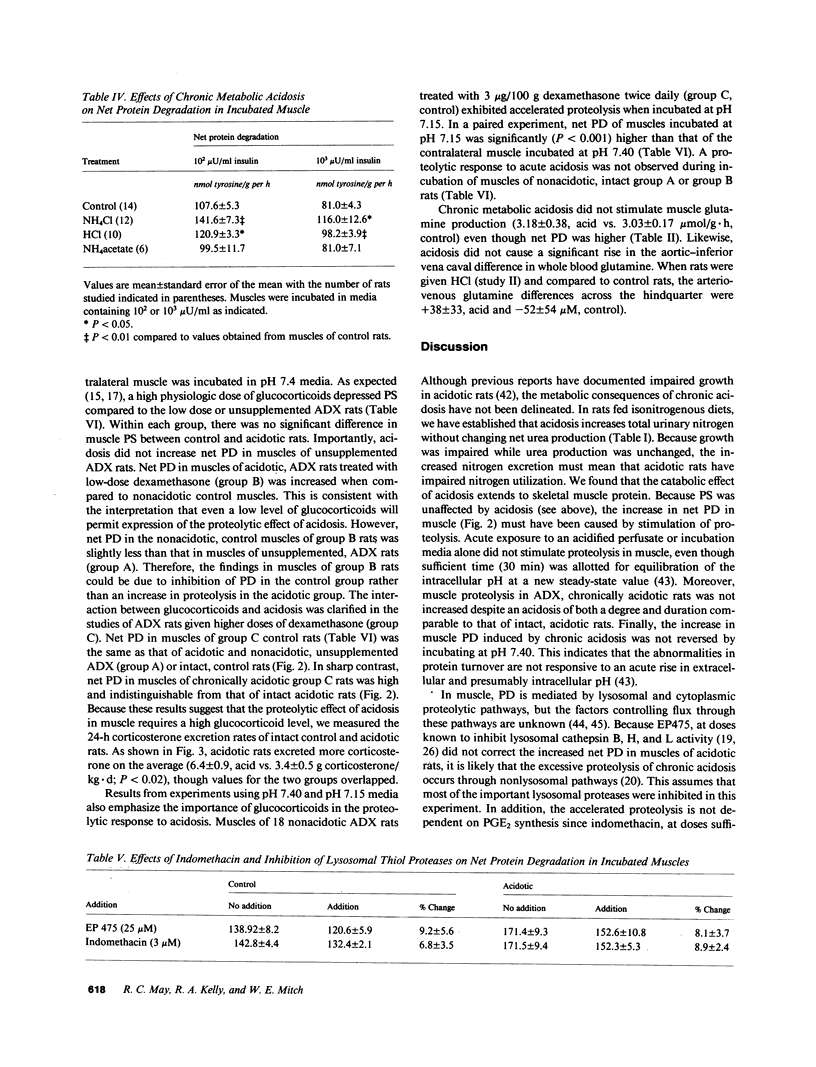
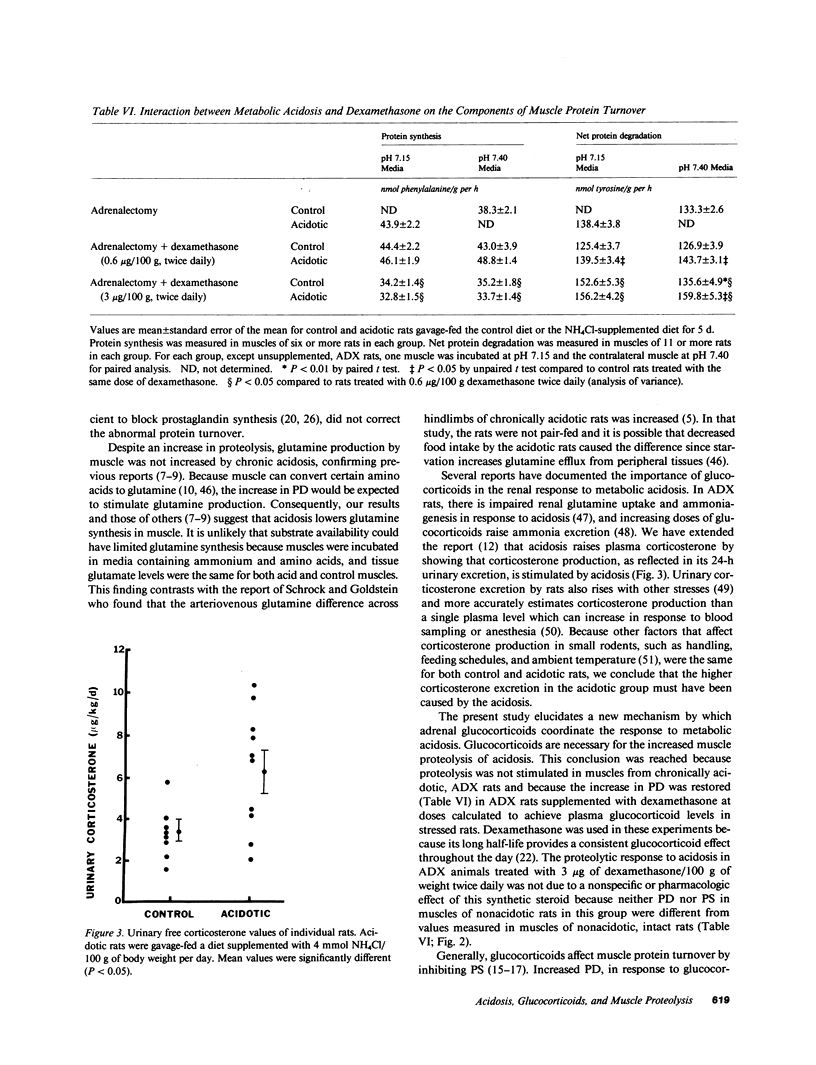
- COOKE R. E., BOYDEN D. G., HALLER E. The relationship of acidosis and growth retardation. J Pediatr. 1960 Sep;57:326–337. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney J. A., Walker B. L. Mode of killing and plasma corticosterone concentrations in the rat. Lab Anim Sci. 1973 Oct;23(5):675–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Goldberg A. L. The metabolic fates of amino acids and the formation of glutamine in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3685–3693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. S., Kelly R. A., Mitch W. E. Systemic response to thermal injury in rats. Accelerated protein degradation and altered glucose utilization in muscle. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):888–897. doi: 10.1172/JCI111506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. S., Mitch W. E. Comparison of protein synthesis and degradation in incubated and perfused muscle. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):649–653. doi: 10.1042/bj2120649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. S., Mitch W. E. Muscle protein turnover and glucose uptake in acutely uremic rats. Effects of insulin and the duration of renal insufficiency. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):836–845. doi: 10.1172/JCI111054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubrovsky A. H., Nair R. C., Byers M. K., Levine D. Z. Renal net acid excretion in the adrenalectomized rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Apr;19(4):516–528. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel-Link R. M., Salusky I. B., Jones M. R., Kopple J. D. Protein and amino acid metabolism in posterior hemicorpus of acutely uremic rats. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):E615–E623. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.6.E615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Karl I. E., Kipnis D. M. Alanine and glutamine synthesis and release from skeletal muscle. I. Glycolysis and amino acid release. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):826–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L. Protein turnover in skeletal muscle. II. Effects of denervation and cortisone on protein catabolism in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3223–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Tischler M., DeMartino G., Griffin G. Hormonal regulation of protein degradation and synthesis in skeletal muscle. Fed Proc. 1980 Jan;39(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannaford M. C., Goldstein M. B., Josse R. G., Halperin M. L. Role of acidosis in the protein wasting of fasting in the rat and the rabbit. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;60(3):331–334. doi: 10.1139/y82-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannaford M. C., Leiter L. A., Josse R. G., Goldstein M. B., Marliss E. B., Halperin M. L. Protein wasting due to acidosis of prolonged fasting. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):E251–E256. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.3.E251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. J., Parsons S. Metabolism and transport of glutamine and glucose in vascularly perfused small intestine rat. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):509–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1660509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughey R. P., Rankin B. B., Curthoys N. P. Acute acidosis and renal arteriovenous differences of glutamine in normal and adrenalectomized rats. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):F199–F204. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.3.F199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Gerok W., Sies H. Regulation of flux through glutaminase and glutamine synthetase in isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 25;755(2):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. R., Beck T. R., Kapoor S., Shay R., Narins R. G. Prostaglandins inhibit renal ammoniagenesis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):992–1002. doi: 10.1172/JCI111520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlen D. M., Bourke E. Effects of chronic metabolic acidosis on glutamine turnover and urea production in the perfused rat liver. Ir J Med Sci. 1975 Dec;144(12):453–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kley H. K., Elsässer W., Dehnen H., Krüskemper H. L. Evaluation of adrenal function in rats by the measurement of urinary free corticosterone, free aldosterone and free 11-deoxycorticosterone. Steroids. 1978 Sep;32(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(78)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux G., Watford M., Vinay P., Gougoux A. Metabolic changes in skeletal muscle during chronic metabolic acidosis. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(1-2):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueck J. D., Miller L. L. The effect of perfusate pH on glutamine metabolism in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5491–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May R. C., Clark A. S., Goheer M. A., Mitch W. E. Specific defects in insulin-mediated muscle metabolism in acute uremia. Kidney Int. 1985 Sep;28(3):490–497. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane Anderson N., Bennett F. I., Alleyne G. A. Ammonia production by the small intestine of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 23;437(1):238–243. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitch W. E. Amino acid release from the hindquarter and urea appearance in acute uremia. Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):E415–E419. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.241.6.E415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitch W. E., Clark A. S. Muscle protein turnover in uremia. Kidney Int Suppl. 1983 Dec;16:S2–S8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash M. A., Torrado A. D., Greifer I., Spitzer A., Edelmann C. M., Jr Renal tubular acidosis in infants and children. Clinical course, response to treatment, and prognosis. J Pediatr. 1972 May;80(5):738–748. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiso T., Iwaki M., Tamaki E. Disposition, intestinal absorption and drug metabolizing enzyme activities after multiple doses of indomethacin in rat and effect of antacid and dicyclomine on the parameters. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1982 Oct;5(10):760–770. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.5.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J., Bourke E. Adaptations in urea ammonium excretion in metabolic acidosis in the rat: a reinterpretation. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1975 Jun;48(6):515–510. doi: 10.1042/cs0480515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadoyannakis N. J., Stefanidis C. J., McGeown M. The effect of the correction of metabolic acidosis on nitrogen and potassium balance of patients with chronic renal failure. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Sep;40(3):623–627. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/40.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus L. M., Windmueller H. G. Phosphate-dependent glutaminase of small intestine: localization and role in intestinal glutamine metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):506–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINGLER I., WEST K., DULIN W. E., BOLAND E. W. BIOLOGICAL POTENCIES OF CHEMICALLY MODIFIED ADRENOCORTICOSTEROIDS IN RAT AND MAN. Metabolism. 1964 Jan;13:37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels S. R., Jefferson L. S. Effects of glucocorticoids on muscle protein turnover in perfused rat hemicorpus. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):E564–E572. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.6.E564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann H. P., Goldberg A. L. Arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha influence rates of protein turnover in skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann H. P., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. The stimulation of protein degradation in muscle by Ca2+ is mediated by prostaglandin E2 and does not require the calcium-activated protease. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8716–8723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Berger M. The formation of glutamine and alanine in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5500–5506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Houghton C. R., Hems R. Evaluation of the isolated perfused rat hindquarter for the study of muscle metabolism. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(3):639–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1240639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARTORIUS O. W., CALHOON D., PITTS R. F. The capacity of the adrenalectomized rat to secrete hydrogen and ammonium ions. Endocrinology. 1952 Nov;51(5):444–450. doi: 10.1210/endo-51-5-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLUSHER M. A., ROBERTS S. Fate of adrenal ascorbic acid: relationship to corticosteroid secretion. Endocrinology. 1957 Jul;61(1):98–105. doi: 10.1210/endo-61-1-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröck H., Cha C. J., Goldstein L. Glutamine release from hindlimb and uptake by kidney in the acutely acidotic rat. Biochem J. 1980 May 15;188(2):557–560. doi: 10.1042/bj1880557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröck H., Goldstein L. Interorgan relationships for glutamine metabolism in normal and acidotic rats. Am J Physiol. 1981 May;240(5):E519–E525. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.5.E519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomas F. M., Munro H. N., Young V. R. Effect of glucocorticoid administration on the rate of muscle protein breakdown in vivo in rats, as measured by urinary excretion of N tau-methylhistidine. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):139–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1780139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomas F. M., Murray A. J., Jones L. M. Interactive effects of insulin and corticosterone on myofibrillar protein turnover in rats as determined by N tau-methylhistidine excretion. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):469–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2200469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAALKES T. P., UDENFRIEND S. A fluorometric method for the estimation of tyrosine in plasma and tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walser M. Determinants of ureagenesis, with particular reference to renal failure. Kidney Int. 1980 Jun;17(6):709–721. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welbourne T. C. Acidosis activation of the pituitary-adrenal-renal glutaminase I axis. Endocrinology. 1976 Oct;99(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-4-1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Cemerikic D. A., Giebisch G. Differential effects of acute mineralo- and glucocorticosteroid administration on renal acid elimination. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):546–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann E., Critchlow V. Effects of diurnal variation in plasma corticosterone levels on adrenocortical response to stress. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):658–663. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



