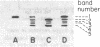Abstract
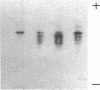
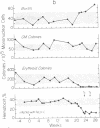
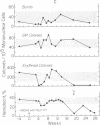
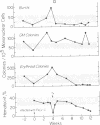
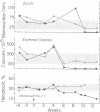
Neoplasms result from the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal or transformed cells. The early stages of this process are difficult to study because of the lack of sensitive and specific markers of clonal evolution in an experimental system. We have developed a cat model using cellular mosaicism for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD). Our findings confirm that the structural locus for feline G-6-PD is on the X-chromosome and demonstrate that it is randomly inactivated in somatic cells. Heterozygous cats have balanced ratios of G-6-PD enzyme types in peripheral blood cells and hematopoietic progenitors that remain stable over time. In our initial studies, we used the model to analyze the events surrounding marrow failure experimentally induced by selected strains of feline leukemia virus (FeLV). Two G-6-PD heterozygous cats, one F1 male hybrid and one domestic cat were infected with FeLV (C or KT) and developed pure red cell aplasia (PRCA). Colonies arising from the more mature erythroid colony-forming cell were not detected in marrow culture of anemic animals although erythroid bursts persisted, suggesting that the differentiation of early erythroid progenitors (BFU-E) was inhibited in vivo. The ratio of G-6-PD types in hematopoietic progenitors and peripheral blood cells from the heterozygous cats did not change when the animals developed PRCA. Thus, the anemia did not result from the clonal expansion of a transformed myeloid stem cell. With this experimental approach, one may prospectively assess clonal evolution and cellular interactions in other FeLV-induced diseases.
Full text
PDF


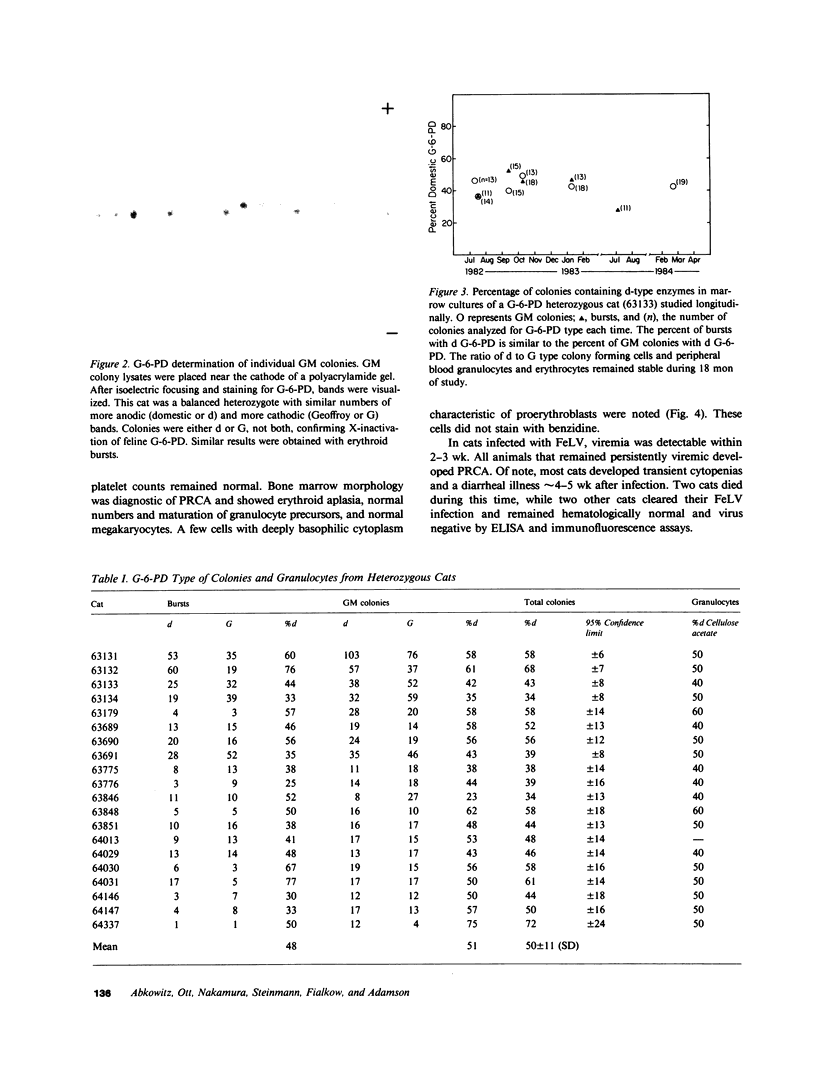
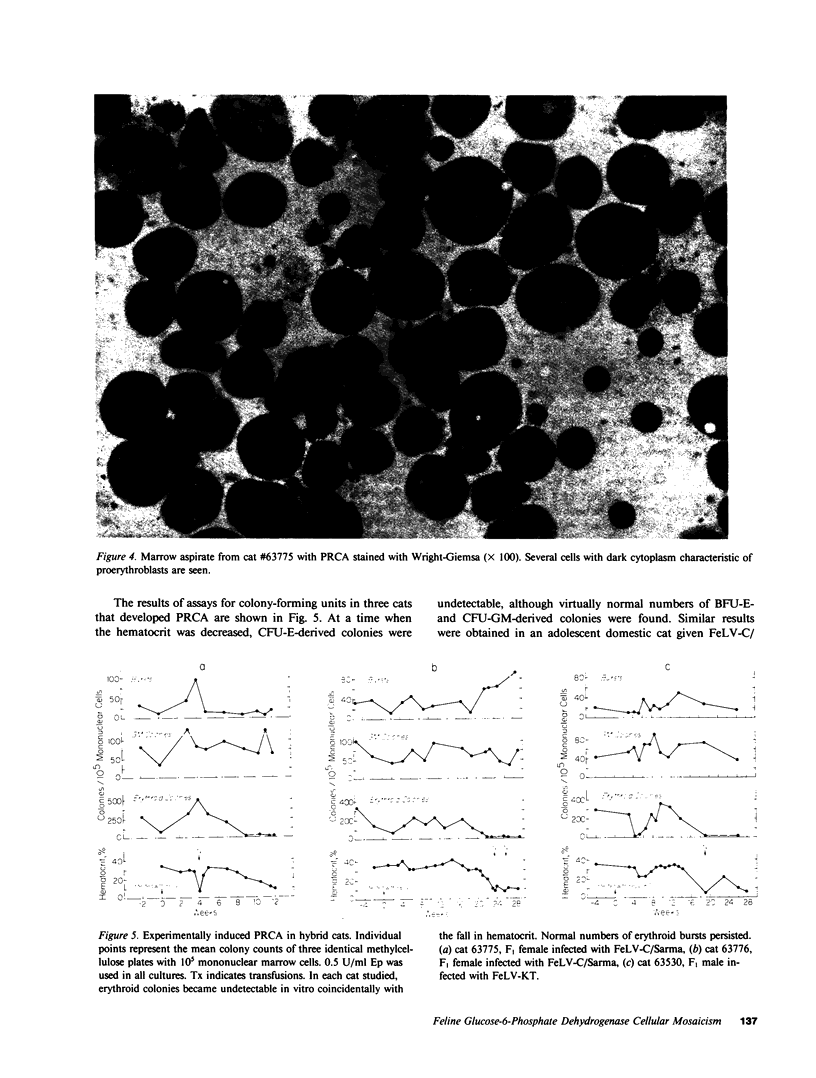
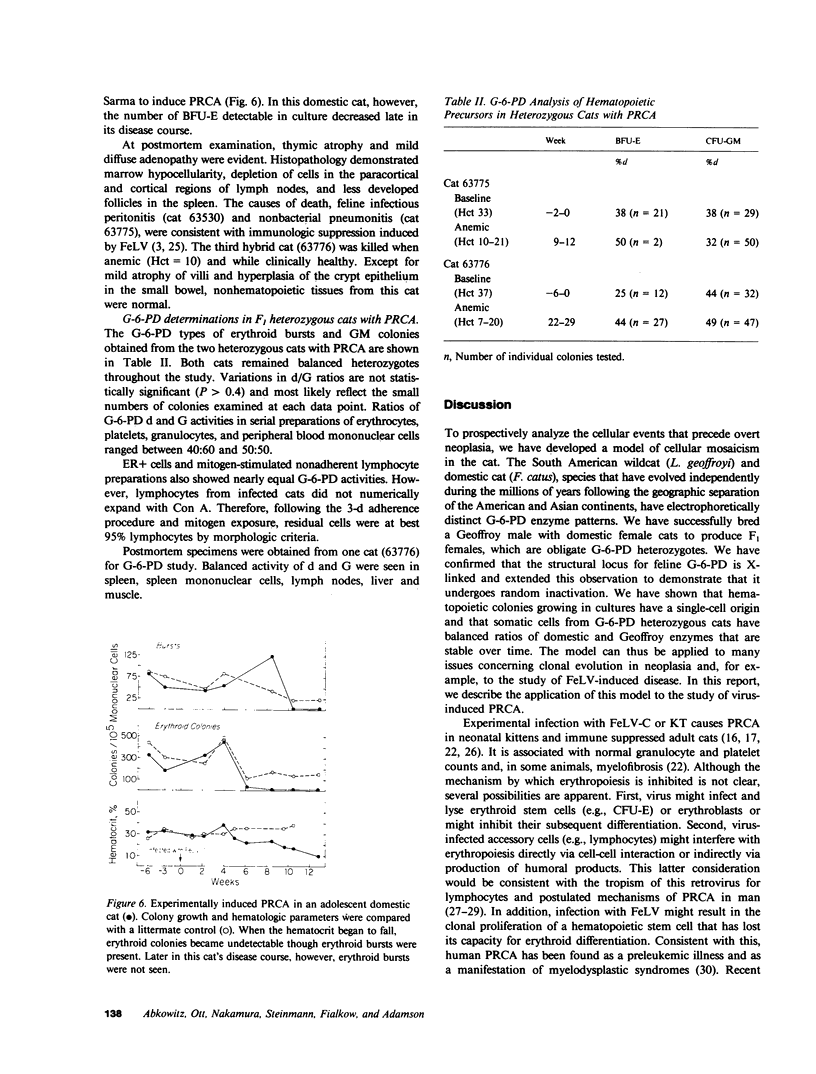


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abkowitz J. L., Fialkow P. J., Niebrugge D. J., Raskind W. H., Adamson J. W. Pancytopenia as a clonal disorder of a multipotent hematopoietic stem cell. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):258–261. doi: 10.1172/JCI111199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. A., Dessypris E. N., Krantz S. B. Studies on pure red cell aplasia. XI. Results of immunosuppressive treatment of 37 patients. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):277–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerell G. L., Hoover E. A., Krakowka S., Olsen R. G., Yohn D. S. Lymphocyte mitogen reactivity and enumeration of circulating B- and T-cells during feline leukemia virus infection in the cat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Nov;57(5):1095–1099. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.5.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Fialkow P. J. Clonal nature of mink cell focus-inducing virus-induced AKR leukemia: studies with X-chromosome inactivation cellular mosaicism. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Mar;70(3):529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. Clonal origin of human tumors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 12;458(3):283–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Singer J. W., Adamson J. W., Vaidya K., Dow L. W., Ochs J., Moohr J. W. Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia: heterogeneity of stem cell origin. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Blevins C. S., Nomura S. Simple, quantitative assay for both xenotropic murine leukemia and ecotropic feline leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):177–179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.177-179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. D., Jr, Hess P. W., MacEwen E. G., McClelland A. J., Zuckerman E. E., Essex M., Cotter S. M., Jarrett O. Biology of feline leukemia virus in the natural environment. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 2):582–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Kociba G. J., Hardy W. D., Jr, Yohn D. S. Erythroid hypoplasia in cats inoculated with feline leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Nov;53(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.5.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Olsen R. G., Mathes L. E., Schaller J. P. Relationship between feline leukemia virus antigen expression and viral infectivity in blood, bone marrow, and saliva of cats. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3707–3710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. T., Thomas W. A., Janakidevi K., Kroms M., Reiner J. M., Borg K. Y. Mosaicism in female hybrid hares heterozygous for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD). I. General properties of a hybrid hare model with special reference to atherogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Apr;34(2):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio L., Hoffman R., Cotter S. M., Dainiak N., Mooney S., Maffei L. A. Feline preleukemia: an animal model of human disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1978 Jul-Aug;51(4):469–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa T., Abe T., Nakagawa T. Pure red cell aplasia and hypogammaglobulinemia associated with Tr-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1025–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Hughes D., McFarlane R., Wilkie N. M., Onions D. E., Lees G., Jarrett O. Transduction and rearrangement of the myc gene by feline leukaemia virus in naturally occurring T-cell leukaemias. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):814–820. doi: 10.1038/308814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. T., Chapman V. M. Electrophoretic variation for x-chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase (pgk-1) in the mouse. Genetics. 1977 Oct;87(2):319–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Nash W. G. Genetic mapping in mammals: chromosome map of domestic cat. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):257–265. doi: 10.1126/science.7063884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Poole J., Gustavsson I. Sex-linkage of erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in two species of wild hares. Science. 1965 Dec 24;150(3704):1737–1738. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3704.1737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onions D., Jarrett O., Testa N., Frassoni F., Toth S. Selective effect of feline leukaemia virus on early erythroid precursors. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):156–158. doi: 10.1038/296156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy A. L., Fialkow P. J. Clonal development of lymphomas induced by Rauscher leukemia virus. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;31(1):107–109. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Log T. Subgroup classification of feline leukemia and sarcoma viruses by viral interference and neutralization tests. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. W., Adamson J. W., Ernst C., Lin N., Steinmann L., Murphy S., Fialkow P. J. Polycythemia vera. Physical separation of normal and neoplastic committed granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):730–735. doi: 10.1172/JCI109910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Baluda M. C., Townsend D. E. Cellulose acetate electrophoresis of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Mar;73(3):531–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D., Weinberg R. A. The integrated genome of murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D., Hokama Y., Perri S. F. Differentiating feline T and B lymphocytes by rosette formation. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):862–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa N. G., Onions D., Jarrett O., Frassoni F., Eliason J. F. Haemopoietic colony formation (BFU-E, GM-CFC) during the development of pure red cell hypoplasia induced in the cat by feline leukaemia virus. Leuk Res. 1983;7(2):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(83)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainin Z., Wernicke D., Ungar-Waron H., Essex M. Suppression of the humoral antibody response in natural retrovirus infections. Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):858–859. doi: 10.1126/science.6302837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Hahn B., Manzari V., Colombini S., Franchini G., Gelmann E. P., Gallo R. C. A survey of human leukaemias for sequences of a human retrovirus. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):626–628. doi: 10.1038/302626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]