Figure 3.
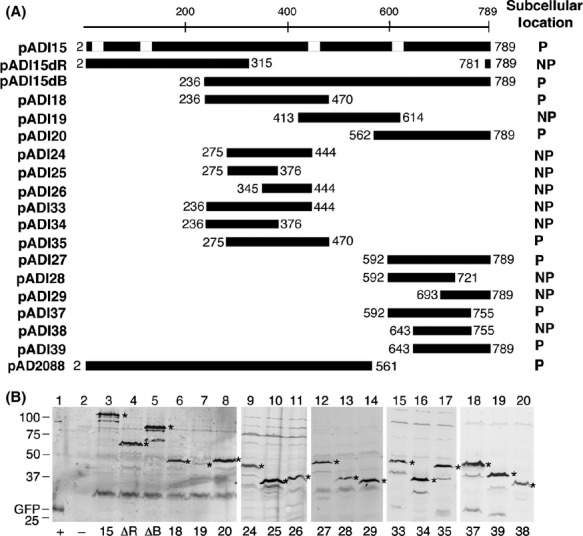
Identification of VirB4 polar localization domain. (A) GFP-VirB4 fusions constructed in this study and the subcellular locations of the fusion proteins are shown. The VirB4 region at the C-terminus of GFP is shown as a dark box. Numbers indicate the virB4 codons present in the fusion. The white boxes on the full-length VirB4 map (pADI15) indicate locations of the four hydrophobic regions that can function in membrane spanning (Dang and Christie 1997). P, polar; NP, nonpolar. (B) Expression of GFP-VirB4 fusion proteins. Accumulation of GFP-VirB4 and its derivatives were monitored as described in legend to Figure2B. The full-length fusion proteins are marked with an asterisk. Accumulation of degradation products migrating below the major band was noted in some samples (lanes 3, 5, 10, and 15–19). Numbers below the figure identify the pADI plasmid the strain harbors. ΔR, pADI15ΔR; ΔB, pADI15ΔB; +, bacteria expressing GFP alone; –, bacteria with no GFP. Numbers on left indicate the molecular mass (kDa) of marker proteins. Protein encoded by plasmid pADI19 (lane 7) accumulated at a low level.
