Abstract
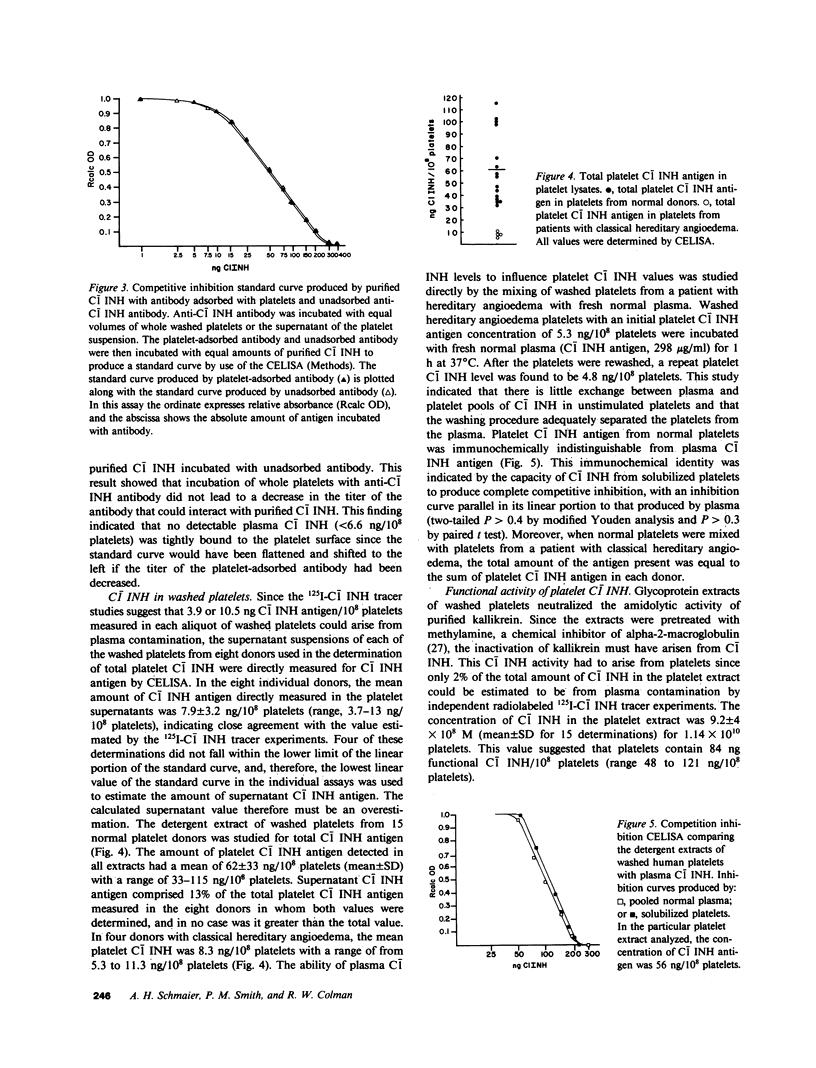
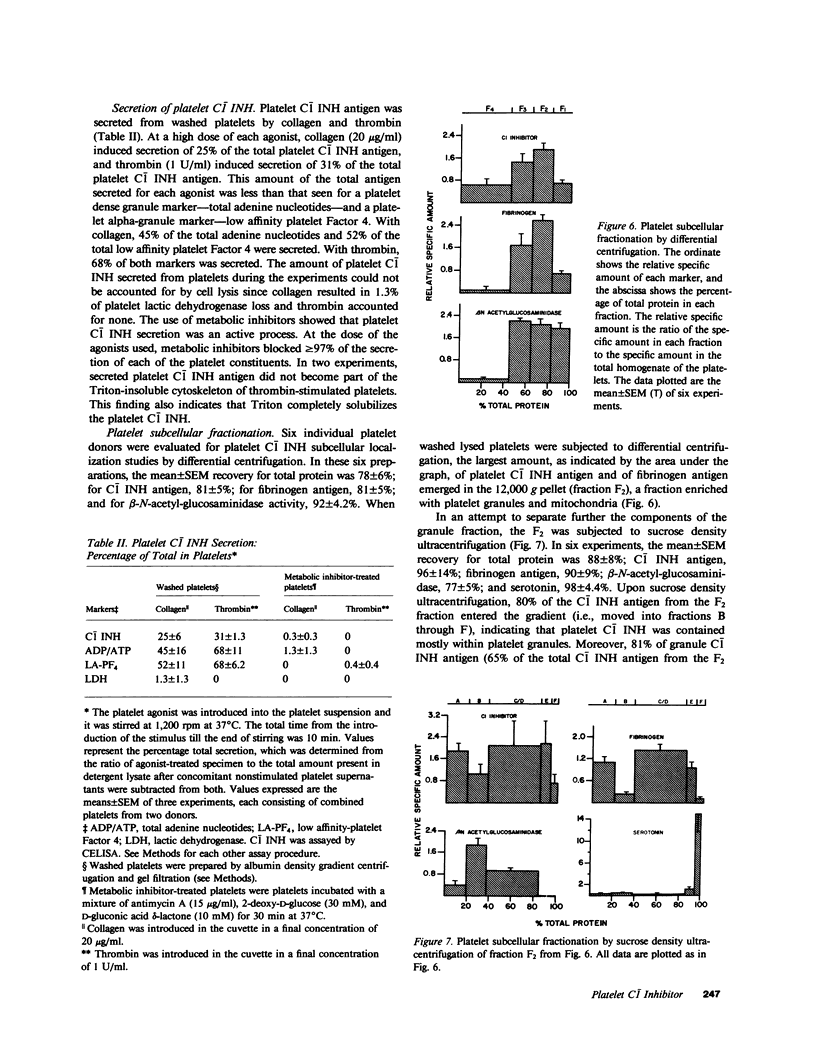
In order to characterize which proteins of the contact phase of coagulation interact with platelets, human platelets were studied immunochemically and functionally to determine if they contain C1- inhibitor. By means of monospecific antibody to C1- inhibitor, a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (CELISA) was developed to measure directly platelet C1- inhibitor. With the CELISA, from 33 to 115 ng of C1- inhibitor antigen per 10(8) platelets from 15 normal donors was quantified in lysates of washed human platelets solubilized in nonionic detergent. The mean concentration in 10(8) platelets was 62 +/- 33 ng (SD). Plasma C1- inhibitor either in the platelet suspension medium or on the surface of the platelets could account for only from 6.5 to 16% of the total antigen measured in the solubilized platelets. Upon functional studies, platelets contained 84 +/- 36 ng (SD) of C1- inhibitor activity in 10(8) platelets. As assessed by the CELISA, platelet C1- inhibitor antigen was immunochemically identical to plasma and purified C1- inhibitor. In contrast, the mean concentration of platelet C1- inhibitor antigen in platelets from four patients with classical hereditary angioedema was 8.3 ng/10(8) platelets (range, 5.3 to 11.3 ng/10(8) platelets). 25 and 31% of the total platelet C1- inhibitor was secreted without cell lysis from normal platelets after exposure to collagen (20 micrograms/ml) and thrombin (1 U/ml), respectively, and this secretion was blocked by metabolic inhibitors. Platelet subcellular fractionation showed that platelet C1- inhibitor resided mostly in alpha-granules, similar to the location of platelet fibrinogen. Thus, human platelets contained C1- inhibitor, which became available by platelet secretion. The identification of platelet C1- inhibitor suggests that platelets may modulate the activation of the proteins of early blood coagulation and the classical complement pathways.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian A., Colman R. W. Subcellular localization and purification of platelet alpha1-antitrypsin. Blood. 1978 Jan;51(1):139–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breederveld K., Giddings J. C., ten Cate J. W., Bloom A. L. The localization of factor V within normal human platelets and the demonstration of a platelet-factor V antigen in congenital factor V deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1975 Mar;29(3):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Handin R. I., Cohen P. Distribution of fibrinogen, and platelet factors 4 and XIII in subcellular fractions of human platelets. Br J Haematol. 1975 Sep;31(1):51–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canellas P. F., Karu A. E. Statistical package for analysis of competition ELISA results. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Pifer D., Colman R. W. Subcellular localization and secretion of factor V from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5180–5184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day H. J., Holmsen H., Hovig T. Subcellular particles of human platelets. A biochemical and electron microscopic study with particular reference to the influence of fractionation techniques. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1969;7:3–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endresen G. K. Immunological studies of plasma protease inhibitors associated with human blood platelets. Thromb Res. 1980 Jul 1;19(1-2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Bauer J. S., Stewart G. J., Salganicoff L. An improved method for the isolation of dense storage granules from human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):389–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly P. A low molecular weight antiplasmin of human blood platelets. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Jul;39(2):466–468. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Phillips D. R., Rao G. H., Plow E. F., Walz D. A., Ross R., Harker L. A., White J. G. Biochemical studies of two patients with the gray platelet syndrome. Selective deficiency of platelet alpha granules. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI109823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Randazzo B. P., Dunn J. T., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Mechanisms of activation of the classical pathway of complement by Hageman factor fragment. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1450–1456. doi: 10.1172/JCI110898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Activation of the classical pathway of complement by Hageman factor fragment. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):665–676. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Mason J. W., Colman R. W., Austen K. F. Interaction of plasma kallikrein with the C1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Painter R. G., Birdwell C., Plow E. F. The detection, immunofluorescent localization, and thrombin induced release of human platelet-associated fibronectin antigen. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(2):167–174. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Robkin L. Effects of antimycin A and 2-deoxyglucose on energy metabolism in washed human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Feb 29;42(5):1460–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Storm E., Day H. J. Determination of ATP and ADP in blood platelets: a modification of the firefly luciferase assay for plasma. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Lee L. T., Harboe A., Haukenes G. Immunochemical study of influenza virus and associated host tissue components. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):543–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joist J. H., Niewiarowski S., Nath N., Mustard J. F. Platelet antiplasmin: its extrusion during the release reaction, subcellular localization, characterization, and relationship to antiheparin in pig platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Lindhout M. J., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Factor Va-dependent binding of factor Xa to human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan J. P., Solum N. O. Quantitative studies on the release of platelet fibrinogen by thrombin. Br J Haematol. 1972 Oct;23(4):461–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutts J., Walsh P. N., Plow E. F., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Bouma B. N., Zimmerman T. S. Active release of human platelet factor VIII-related antigen by adenosine diphosphate, collagen, and thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1255–1263. doi: 10.1172/JCI109246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Johnson U., Mårtensson U., Sjöholm A. G. Formation of complexes composed of C1r, C1s, and C1 inactivator in human serum on activation of C1. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Dec;86C(6):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Pepper D. S., Cash J. D. The isolation and characterisation of a platelet-specific beta-globulin (beta-thromboglobulin) and the detection of antiurokinase and antiplasmin released from thrombin-aggregated washed human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):360–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mui P. T., James H. L., Ganguly P. Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight antiplasmin of human blood platelets and serum. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):627–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Harpel P. C. Platelet alpha2-macroglobulin and alpha1-antitrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4512–4521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A. Subcellular platelet factor VIII antigen and von Willebrand factor. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1101–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D. Immunologic studies of proteins associated with subcellular fractions of normal human platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):651–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I., Lavine K. K. Factor V activity of platelets: evidence for an activated factor V molecule and for a platelet activator. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):819–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Collen D. The presence and release of alpha 2-antiplasmin from human platelets. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1069–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucinski B., Niewiarowski S., James P., Walz D. A., Budzynski A. Z. Antiheparin proteins secreted by human platelets. purification, characterization, and radioimmunoassay. Blood. 1979 Jan;53(1):47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salganicoff L., Fukami M. H. Energy metabolism of blood platelets. I. Isolation and properties of platelet mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):726–735. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salganicoff L., Hebda P. A., Yandrasitz J., Fukami M. H. Subcellular fractionation of pig platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):394–411. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Protection of human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by C1 inhibitor and other protease inhibitors. The role of high molecular weight kininogen. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2738–2743. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. New and rapid functional assay for C1 inhibitor in human plasma. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):719–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Claypool W., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: recognition and purification of a timber rattlesnake platelet aggregating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1013–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: characterization of the timber rattlesnake platelet activating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1020–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Zuckerberg A., Silverman C., Kuchibhotla J., Tuszynski G. P., Colman R. W. High-molecular weight kininogen. A secreted platelet protein. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1477–1489. doi: 10.1172/JCI110901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Measurement of protein by spectrophotometry at 205 nm. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A. Preparation and properties of human C1 inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):43–54. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Bevacqua S. J., Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W., Walsh P. N. Factor XI antigen and activity in human platelets. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1148–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Walsh P. N., Piperno J. R., Koshy A. Association of coagulation factor V with the platelet cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4557–4563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicic W. J., Lages B., Weiss H. J. Release of human platelet factor V activity is induced by both collagen and ADP and is inhibited by aspirin. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):448–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH H., WAALKES T. P., UDENFRIEND S. A simplified method for measuring serotonin in tissues; simultaneous assay of both serotonin and histamine. J Biol Chem. 1958 Feb;230(2):865–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi K., Fujikawa K., Abe T. Some properties of an antiplasmin substance from rabbit platelets. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Oct 31;24(1):76–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Broekman M. J., Kaplan K. L. Factor VIII-related antigen in human blood platelets: localization and release by thrombin and collagen. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Nov;94(5):675–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Bouma B. N. Inactivation of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



