Abstract
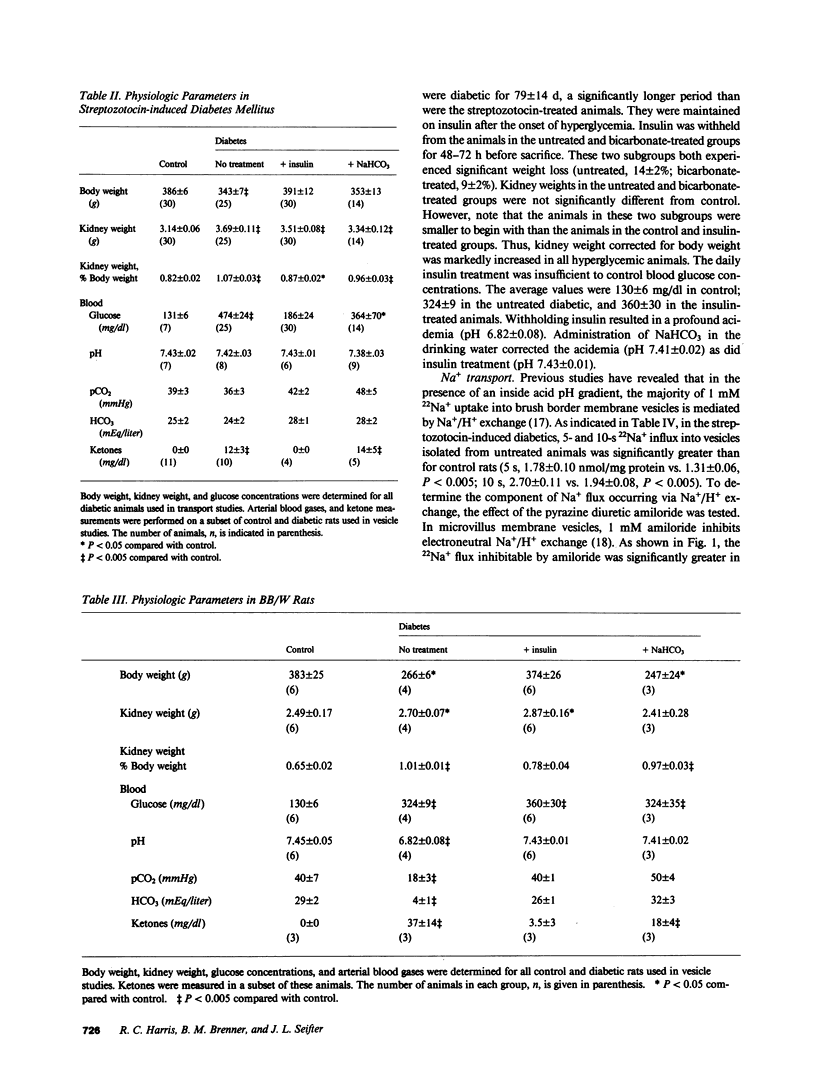
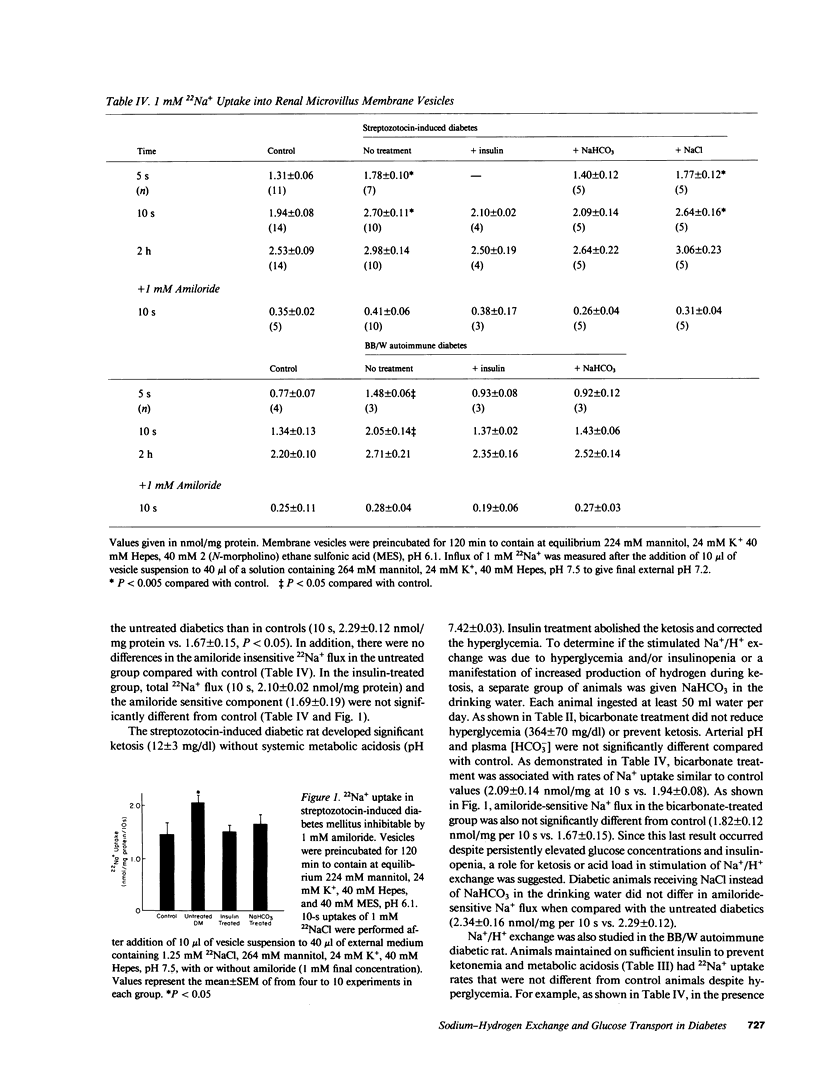
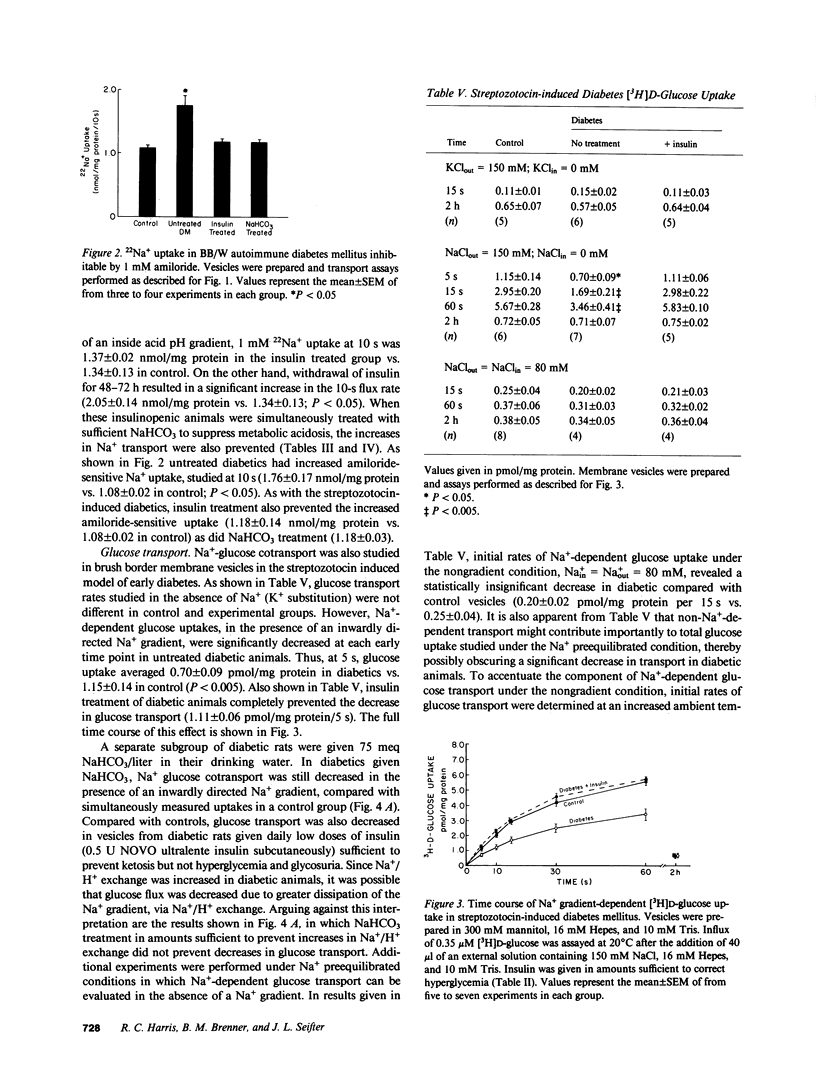
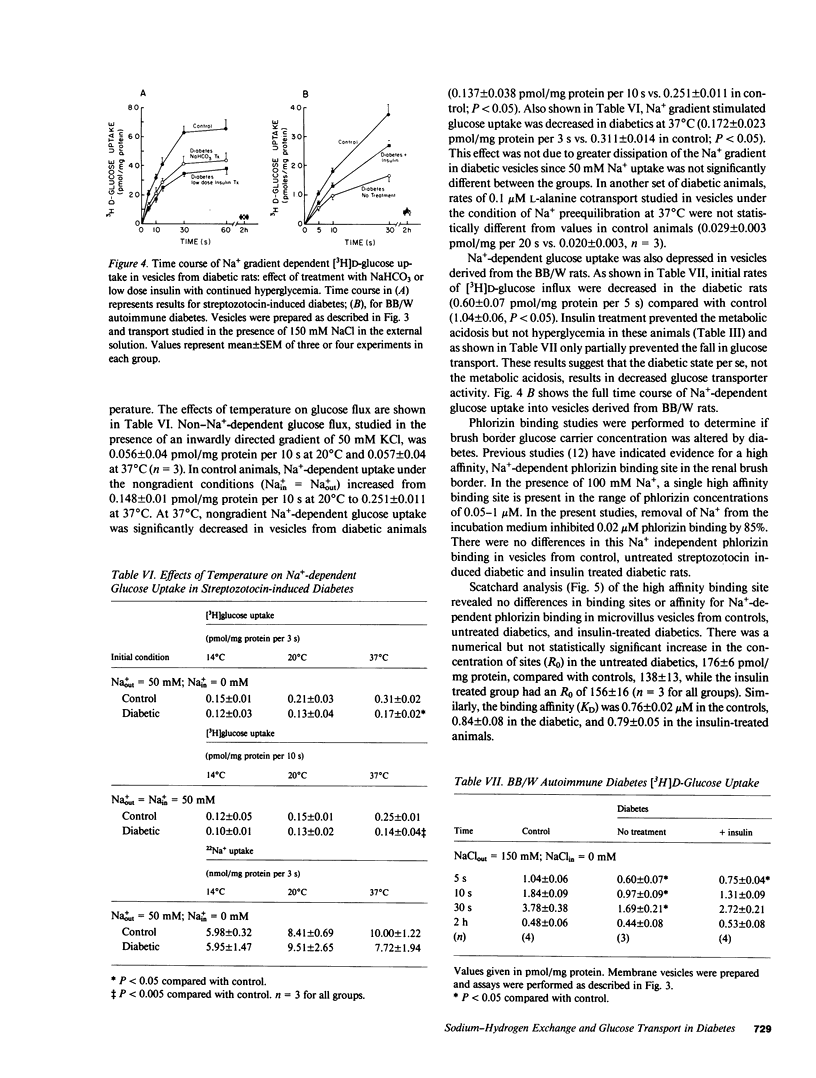
Diabetes mellitus is associated with important changes in renal hemodynamics and transport function. Disturbances in solute transport have also been characterized in nonrenal tissues during hyperglycemia and insulinopenia. The purpose of this study was to determine if diabetes is associated with adaptive changes in function of the brush-border membrane of the proximal tubule. We studied Na+ and glucose transport in rat microvillus membrane vesicles isolated from the renal cortex of streptozotocin-induced and BB/W autoimmune diabetic rats. Untreated diabetes was associated with an increase in pH-stimulated total and amiloride-sensitive 22Na+ uptake into vesicles. Insulin treatment returned vesicle 22Na+ uptake to control levels. The increased Na+/H+ exchange was shown to be a result of increased net renal acid production rather than a specific response to insulinopenia because treatment with NaHCO3 also returned 22Na+ uptake to control levels. On the other hand, Na+-glucose cotransport, which was depressed in vesicles from untreated diabetics, returned to control levels with insulin but not NaHCO3 administration. This decreased Na+-glucose cotransport was not secondary to reduction in transport sites in untreated diabetics. These results show that in diabetes mellitus, increased Na+/H+ exchange activity is not the direct result of insulinopenia. However, the diabetic state appears to alter the functioning of the luminal Na+-glucose cotransporter.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effects of extracellular fluid volume and plasma bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI110821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. Energy-dependence of phlorizin binding to isolated renal microvillus membranes. Evidence concerning the mechanism of coupling between the electrochemical Na+ gradient the sugar transport. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jul 21;42(1):81–98. doi: 10.1007/BF01870395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Sacktor B. The Na+ gradient-dependent transport of D-glucose in renal brush border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6032–6039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. Q., Aronson P. S. Glucose and alanine inhibition of phosphate transport in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1982 Feb;242(2):F126–F131. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.2.F126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasitus T. A., Schachter D., Mamouneas T. G. Functional interactions of lipids and proteins in rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4136–4144. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Cerami A. Nonenzymatic glycosylation and the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Oct;101(4):527–537. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-4-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. L., Wong N. L., Dirks J. H. Acute effects of streptozotocin diabetes on rat renal function. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jun;93(6):950–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. L., Hamel F. G., Queener S. F. Changes in renal phospholipid fatty acids in diabetes mellitus: correlation with changes in adenylate cyclase activity. Lipids. 1983 Oct;18(10):696–705. doi: 10.1007/BF02534536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Alpern R. J. Regulation of proximal bicarbonate reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 2):F387–F395. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.3.F387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. E., Hruska K. A., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Increased Na+-H+ exchange in brush border vesicles from dogs with renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):F293–F299. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.3.F293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. E., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Metabolic acidosis and parathyroidectomy increase Na+-H+ exchange in brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):F217–F222. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Smedt H., Kinne R. Temperature dependence of solute transport and enzyme activities in hog renal brush border membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 6;648(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Goldberg M., Agus Z. S. The effects of glucose and insulin on renal electrolyte transport. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):83–90. doi: 10.1172/JCI108463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjedde A., Crone C. Blood-brain glucose transfer: repression in chronic hyperglycemia. Science. 1981 Oct 23;214(4519):456–457. doi: 10.1126/science.7027439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Anderson C. E., Coleman D. L., Craighead J. E., Gerritsen G. C., Hansen C. T., Herberg L., Howard C. F., Jr, Lernmark A., Matschinsky F. M. Metabolic and underlying causes of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1982;31(Suppl 1 Pt 2):45–53. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.s45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman M. R., Rogers S., Hansen V. A., Gavin J. R., 3rd Insulin stimulates Pi transport in brush border vesicles from proximal tubular segments. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):E616–E624. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.5.E616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
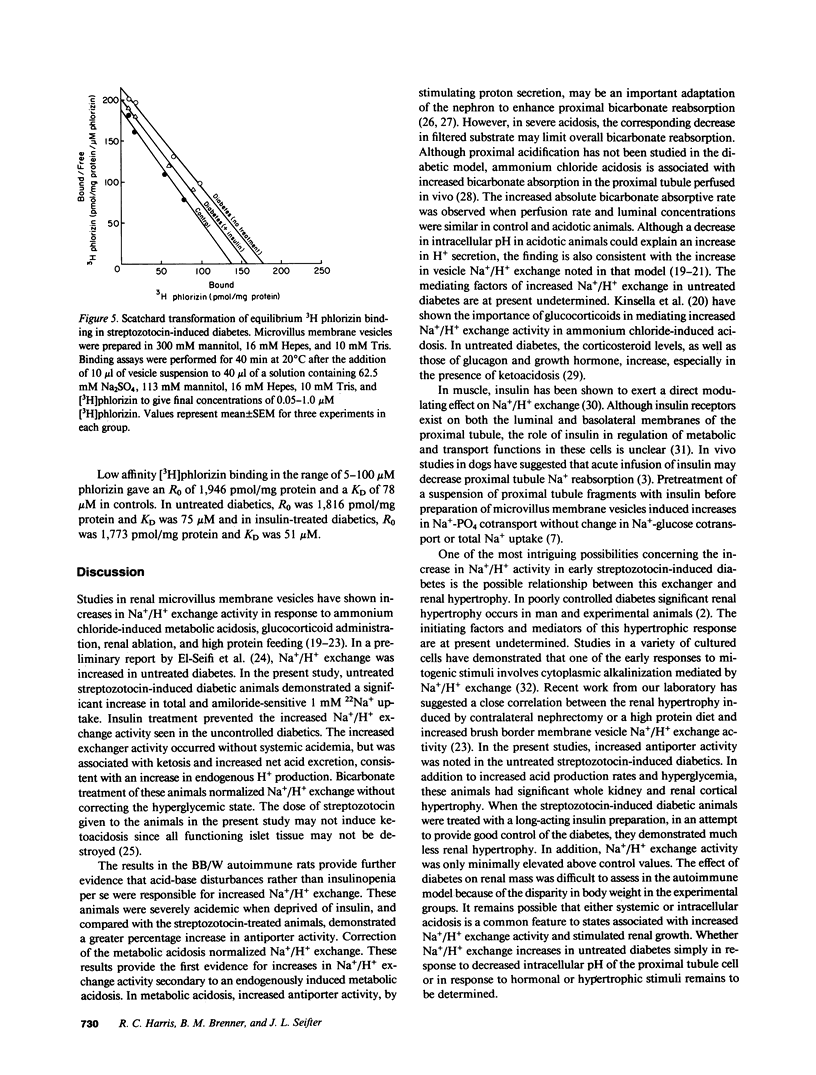
- Harris R. C., Seifter J. L., Brenner B. M. Adaptation of Na+-H+ exchange in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Role of dietary protein and uninephrectomy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1979–1987. doi: 10.1172/JCI111619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U. Diabetes mellitus: changes in the transport properties of isolated intestinal microvillous membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Glomerular hemodynamics in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1981 Mar;19(3):410–415. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska K. A., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Decreased luminal membrane transport of phosphate in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):F17–F22. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.1.F17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm D. E., Cahill G. F., Jr Effect of acid-base status on renal and hepatic gluconeogenesis in diabetes and fasting. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1207–1212. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):811–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI110318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Amiloride inhibition of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F374–F379. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Properties of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):F461–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.6.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Na+-H+ exchange activity in renal brush border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis: The role of glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramp R. A., Lorentz W. B. Glucose transport in chronically altered rat nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):F393–F403. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.4.F393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr, Hart J. I., Walker K. A. Effect of metabolic acidosis on proximal tubular total CO2 absorption. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 2):F62–F68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.1.F62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong T. F., Bennett C. M. Relationship between glomerular filtration rate and maximum tubular reabsorptive rate of glucose. Kidney Int. 1974 Jan;5(1):23–29. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Yarden Y., de Laat S. W., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces electrically silent Na+ influx in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8502–8506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D. Effects of insulin upon ion transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):1–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran A., Turner R. J., Handler J. S. Regulation of sodium-coupled glucose transport by glucose in a cultured epithelium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15087–15090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H. J., Hogan W. C., Hellman R. N., Klahr S. Mechanism of activation of renal Na+-K+-ATPase in the rat: effects of potassium loading. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):F315–F323. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.4.F315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostand S. G., Watkins J. B., Clements R. S., Jr The effect of insulin and of anti-insulin serum on handling of sodium by the isolated, perfused kidney of the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Diabetes. 1980 Sep;29(9):679–685. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.9.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze R. G., Berger H. The influence of GFR and saline expansion on TmG of the dog kidney. Kidney Int. 1973 May;3(5):291–297. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer-Hansen K. Renal hypertrophy in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1983 Apr;23(4):643–646. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talor Z., Emmanouel D. S., Katz A. I. Insulin binding and degradation by luminal and basolateral tubular membranes from rabbit kidney. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1136–1146. doi: 10.1172/JCI110549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. J., Ives H. E., Alpern R. J., Yee V. J., Warnock D. G., Rector F. C., Jr Increased Vmax for Na+/H+ antiporter activity in proximal tubule brush border vesicles from rabbits with metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F339–F343. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tune B. M., Burg M. B. Glucose transport by proximal renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):580–585. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Cemerikic D. A., Giebisch G. Differential effects of acute mineralo- and glucocorticosteroid administration on renal acid elimination. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):546–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



