Abstract
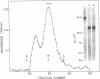
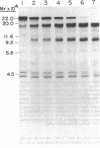
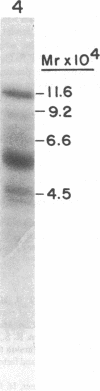
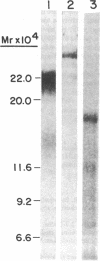
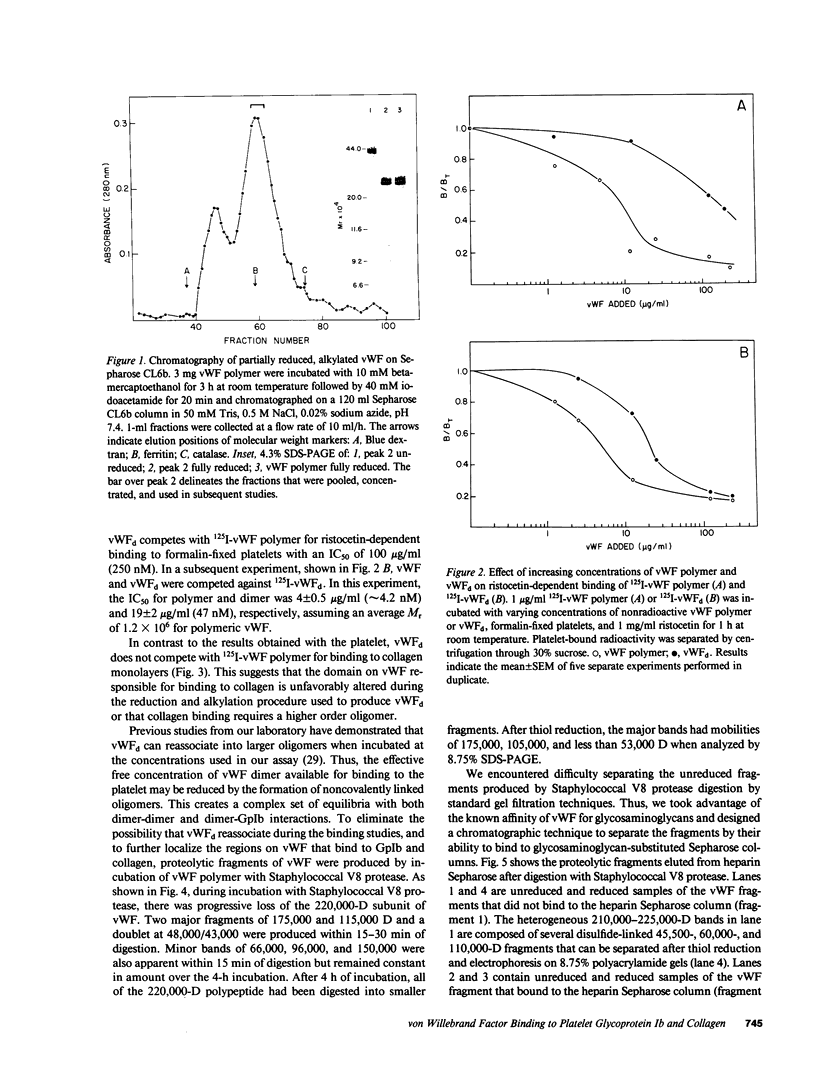
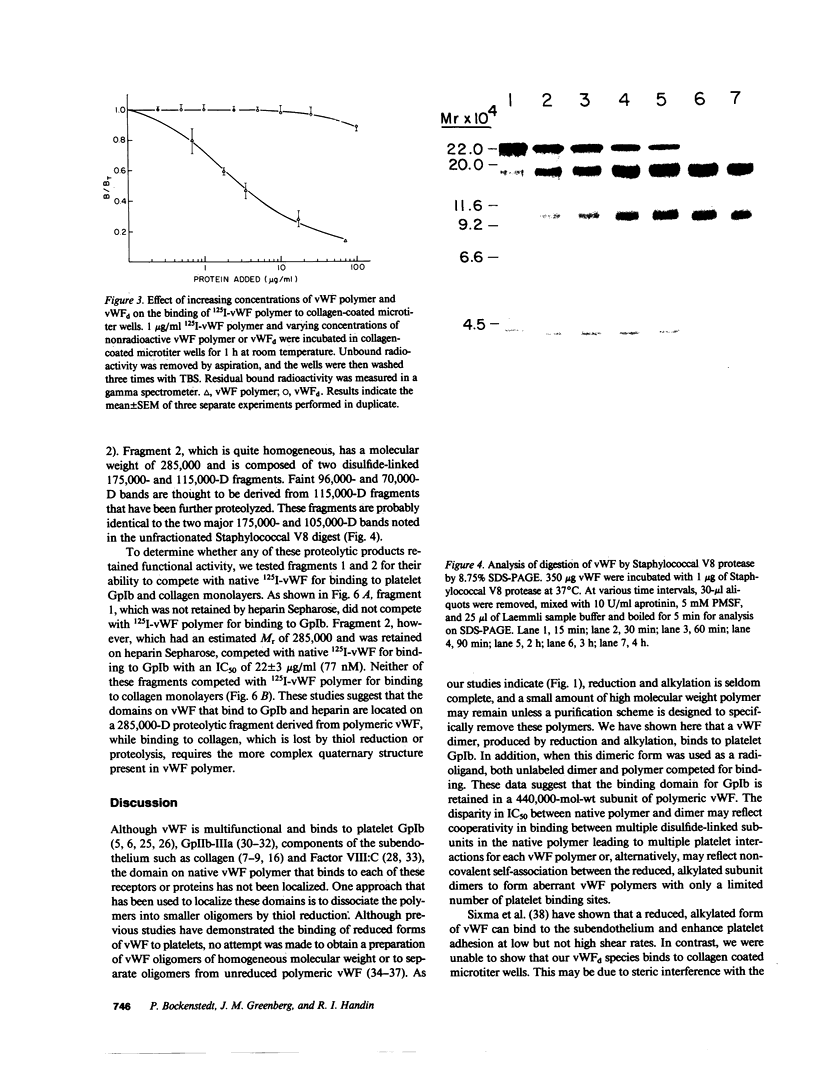
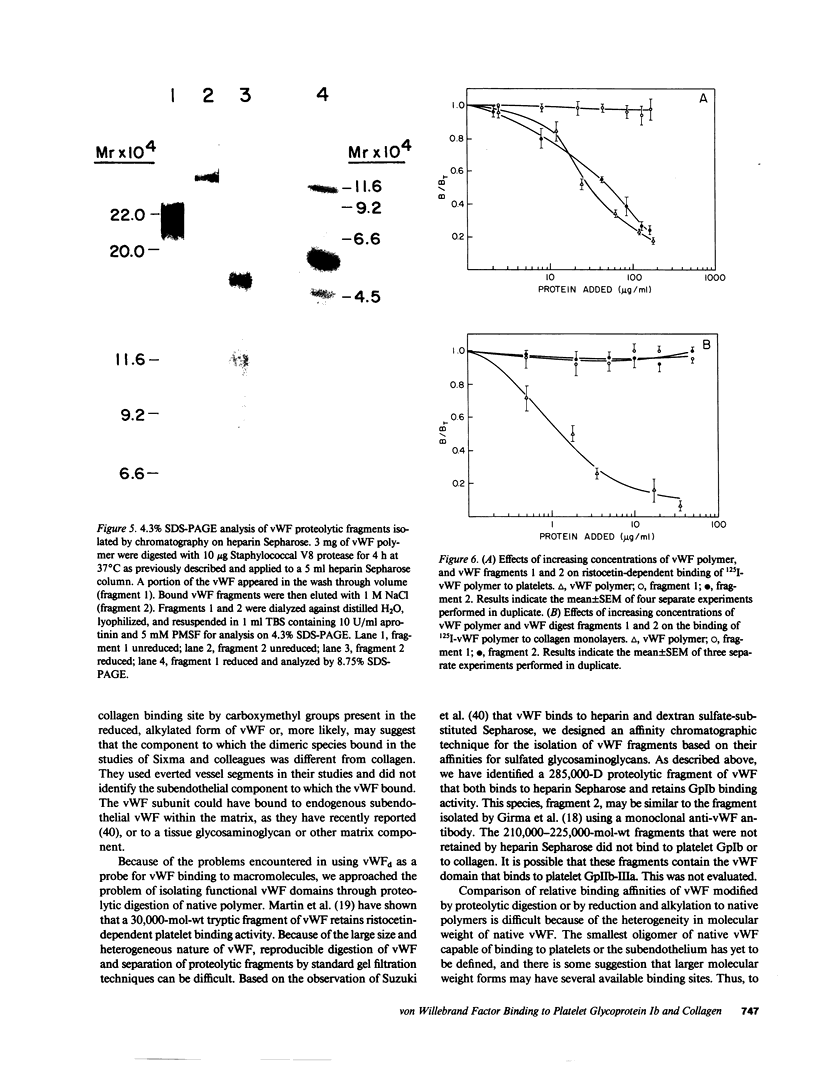
von Willebrand factor (vWF) is a large, multimeric glycoprotein that helps platelets adhere to vascular subendothelium. Although vWF binding to platelet receptors and connective tissue constituents is of fundamental importance in adhesion, there is little information regarding the nature of these vWF binding sites. In this paper, we have compared the structural requirements for vWF binding with platelet glycoprotein Ib (GpIb), heparin, and collagen and have shown that fragments derived from large vWF multimers retain biologic activity. We have shown that a 440,000-D subunit produced by disulfide reduction and alkylation of vWF polymer binds to platelet GpIb. When analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Sepharose CL6B chromatography, the 440,000-D vWF oligomer is a dimer of the 220,000 subunit of fully reduced native vWF. This vWF dimer competes with 125I-vWF for binding to GpIb with an IC50 of 100 micrograms/ml (227 nM). The GpIb binding domain on vWF was further localized by digestion of native vWF polymers with Staphylococcal V8 protease. A 285,000-D fragment of vWF multimer was separated from heterogeneous 210,000-225,000-D fragments by its ability to bind to heparin. The 285,000-D fragment that bound to heparin Sepharose was composed of two disulfide-linked 175,000- and 115,000-D polypeptides. The heterogeneous fragments contained disulfide-linked 96,000, 66,000, and 53,000-D polypeptides when analyzed on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The 285,000-D fragment competed with 125I-vWF for binding to GpIb with an IC50 of 22 micrograms/ml (77 nM), while the other fragments did not compete for binding. Neither the vWF dimer nor the proteolytic fragments competed with native 125I-vWF polymer for binding to collagen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Platelets fixed with paraformaldehyde: a new reagent for assay of von Willebrand factor and platelet aggregating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrani D. L., Mosesson M. W., Hoyer L. W. Distribution of plasma fibronectin (cold-insoluble globulin) and components of the factor VIII complex after heparin-induced precipitation of plasma. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):657–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Meyer D. Shear rate dependent inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation on collagenous surfaces by antibodies to human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jan;44(1):127–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Meyer D. Shear rate dependent inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation on collagenous surfaces by antibodies to human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jan;44(1):127–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V., Chan T. K. Characterization of factor VIII related protein synthesized by human endothelial cell: a study of structure and function. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Oct 29;48(2):177–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts R. B., Paskell S. L., Elgee S. K. Disulfide bonds and the quaternary structure of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):702–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI109178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso M., Cappelletti R., Viti M., Vannucchi S., Chiarugi V. Binding of the basement-membrane glycoprotein laminin to glycosaminoglycans. An affinity-chromatography study. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):699–704. doi: 10.1042/bj1990699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Hawiger J. Adenosine diphosphate induces binding of von Willebrand factor to human platelets. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):154–156. doi: 10.1038/297154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Fibrinogen competes with von Willebrand factor for binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex when platelets are stimulated with thrombin. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):797–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., Morisato D. K. Effect of multimeric structure of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein on binding to platelets. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):387–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. L., McKee P. A. Comparison of thrombin and ristocetin in the interaction between von Willebrand factor and platelets. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Nagai Y. Factors affecting the interactions of collagen molecules as observed by in vitro fibril formation. II. Effects of species and concentration of anions. J Biochem. 1973 Aug;74(2):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk W. P., Sakariassen K. S., Nievelstein P. F., Sixma J. J. Role of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor and fibronectin in the interaction of platelets in flowing blood with monomeric and fibrillar human collagen types I and III. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):531–540. doi: 10.1172/JCI111729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin--a new tool in the investigation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Hök M. Heparin enhances the rate of binding of fibronectin to collagen. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):521–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1870521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Demonstration and characterization of specific binding sites for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):656–664. doi: 10.1172/JCI109348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Platelet receptors for human Factor VIII/von Willebrand protein: functional correlation of receptor occupancy and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5317–5320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C. M., Floyd C. M., Rick M. E., Krizek D. M., Lee S. L., Gralnick H. R. Collagen-factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein interaction. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1291–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J., Handin R. I. Conformational domains and structural transitions of human von Willebrand protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3880–3886. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. C., Zimmerman T. S., Kirby E. P., Livingston D. M. Subunit composition of oligomeric human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12757–12760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. E., Marder V. J., Francis C. W., Loftus L. S., Barlow G. H. Enzymatic degradation of the factor-VIII-von-Willebrand protein: a unique tryptic fragment with ristocetin cofactor activity. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A. Observations on structure-function relationships of human antihemophilic/von Willebrand factor protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:210–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Baumgartner H. R. Role of von Willebrand factor in platelet adhesion to the subendothelium. Br J Haematol. 1983 May;54(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Olson J. D., Troll J. H., Tang S. S., Funicella T., Peterson D. M. Binding of radioiodinated human von Willebrand factor to Bernard-Soulier, thrombasthenic and von Willebrand's disease platelets. Thromb Res. 1980 Jul 1;19(1-2):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D. K., Gralnick H. R. Selective binding of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein to human platelets. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton L. F., Griffin B., Pepper D. S., Barnes M. J. The interaction between collagens and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor: investigation of the structural requirements for interaction. Thromb Res. 1983 Dec 15;32(6):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman D. Von Willebrand factor dependent platelet aggregation and adsorption of factor VIII related antigen by collagen. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura T., Jamieson G. A. Platelet glycocalicin. I. Orientation of glycoproteins of the human platelet surface. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5944–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. D., Brockway W. J., Fass D. N., Magnuson M. A., Bowie E. J. Evaluation of ristocetin-Willebrand factor assay and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Feb;63(2):210–218. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Complexing of fibronectin glycosaminoglycans and collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pekkala A., Engvall E. Effect of dextran sulfate on fibronectin-collagen interaction. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Bolhuis P. A., Sixma J. J. Human blood platelet adhesion to artery subendothelium is mediated by factor VIII-Von Willebrand factor bound to the subendothelium. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):636–638. doi: 10.1038/279636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schullek J., Jordan J., Montgomery R. R. Interaction of von Willebrand factor with human platelets in the plasma milieu. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):421–428. doi: 10.1172/JCI111228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. M., Griffin B., Pepper D. S., Barnes M. J. The binding of purified factor VIII/von Willebrand factor to collagens of differing type and form. Thromb Res. 1981 Dec 1;24(5-6):467–472. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Nelsestuen G. L. von Willebrand factor. A protein which binds at the cell surface interface between platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12327–12333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Sakariassen K. S., Beeser-Visser N. H., Ottenhof-Rovers M., Bolhuis P. A. Adhesion of platelets to human artery subendothelium: effect of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor of various multimeric composition. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):128–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Sakariassen K. S., Stel H. V., Houdijk W. P., In der Maur D. W., Hamer R. J., de Groot P. G., van Mourik J. A. Functional domains on von Willebrand factor. Recognition of discrete tryptic fragments by monoclonal antibodies that inhibit interaction of von Willebrand factor with platelets and with collagen. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):736–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI111489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nishioka J., Hashimoto S. Inhibition of factor VIII-associated platelet aggregation by heparin and dextran sulfate, and its mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 4;585(3):416–426. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nishioka J., Hashimoto S. The influence of 2-mercaptoethanol on von Willebrand factor and bovine platelet aggregating factor. Thromb Res. 1980 Feb 1;17(3-4):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp T. B., Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R. Decreased adhesion of platelets to subendothelium in von Willebrand's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):296–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turitto V. T., Weiss H. J., Zimmerman T. S., Sussman I. I. Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in subendothelium mediates platelet adhesion. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento M., Vartio T., Saraste M., von Bonsdorff C. H., Vaheri A. Spontaneous and polyamine-induced formation of filamentous polymers from soluble fibronectin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):33–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells. Identification of a large precursor polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2065–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Chute L. E. Two distinct forms of Factor VIII coagulant protein in human plasma. Cleavage by thrombin, and differences in coagulant activity and association with von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):307–316. doi: 10.1172/JCI111215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]