Abstract
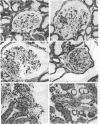
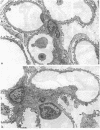
Micropuncture and/or morphologic studies were performed in intact Wistar-Kyoto rats (WKY) (group 0), intact spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) (groups 1 and 5), uninephrectomized (UNX) WKY (groups 2 and 6), and UNX SHR (groups 3 and 4, 7 and 8). UNX was performed when rats were 5 wk of age. Groups 0-4 were observed for 34 wk after which whole kidney clearance and morphologic studies were performed. Groups 5-8 underwent micropuncture study at 10 wk of age. Groups 4 and 8 were fed a diet containing 6% protein. All other rats ingested standard laboratory diet. 5 wk after UNX, normotensive group 6 had higher single nephron glomerular filtration rate (SNGFR) and initial glomerular plasma flow rate (QA) than intact, hypertensive group 5. Glomerular transcapillary hydraulic pressure difference (delta P) was similar in these two groups. Hypertensive group 7 exhibited less elevation in SNGFR and QA than group 6, but delta P was significantly increased. The presence of glomerular capillary hypertension in UNX SHR at 10 wk was associated with the development of significant proteinuria and an increased incidence of mesangial expansion and glomerular sclerosis at 7 mo (group 3) as compared with groups 0, 1, and 2. Protein restriction prevented the development of increased delta P in UNX SHR (group 8) and also conferred long-term protection from increased urinary protein excretion and glomerular injury (group 4). These studies suggest that glomerular capillary hypertension predisposes to glomerular injury in this model of hypertension with reduced renal mass.
Full text
PDF
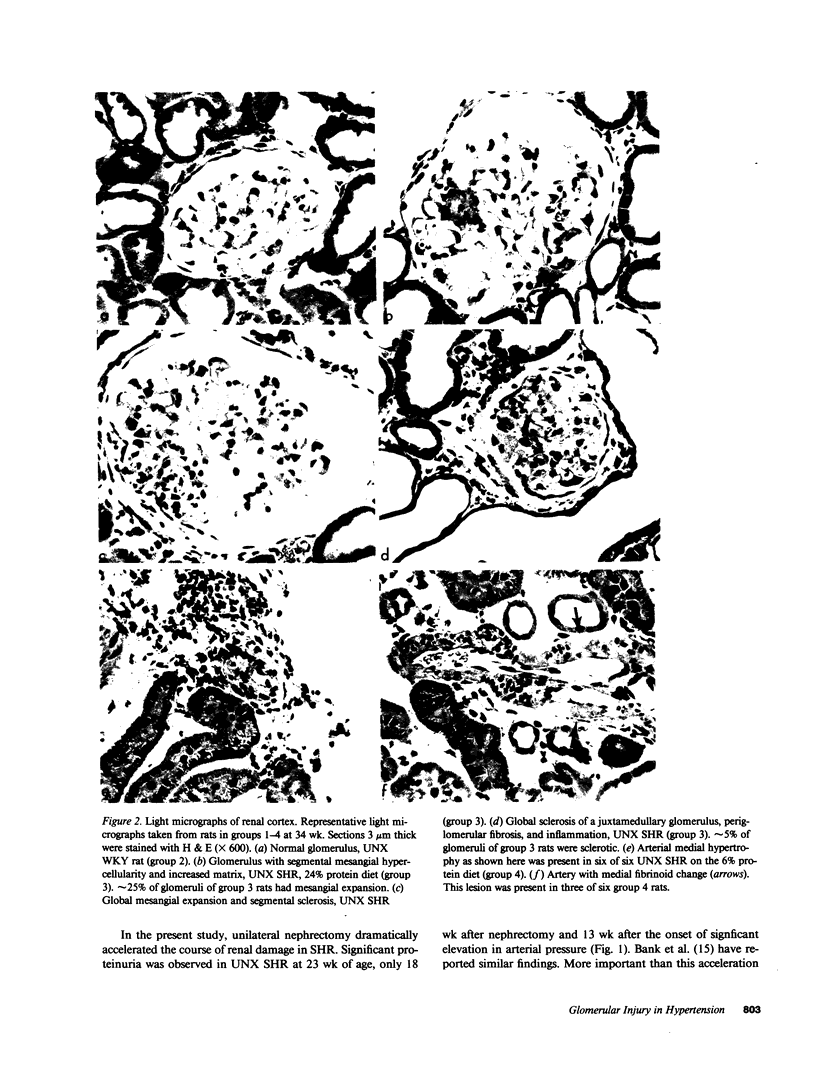





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. E., Lipham E. M., Gottschalk C. W. Hydrostatic pressure in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1972 Oct;223(4):975–983. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.4.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Control of glomerular hypertension limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):612–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI112013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendshorst W. J., Beierwaltes W. H. Renal and nephron hemodynamics in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):F246–F251. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.3.F246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azar S., Johnson M. A., Hertel B., Tobian L. Single-nephron pressures, flows, and resistances in hypertensive kidneys with nephrosclerosis. Kidney Int. 1977 Jul;12(1):28–40. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azar S., Johnson M. A., Scheinman J., Bruno L., Tobian L. Regulation of glomerular capillary pressure and filtration rate in young Kyoto hypertensive rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Mar;56(3):203–209. doi: 10.1042/cs0560203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank N., Alterman L., Aynedjian H. S. Selective deep nephron hyperfiltration in uninephrectomized spontaneously hypertensive rats. Kidney Int. 1983 Aug;24(2):185–191. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C., Deen W. M., Myers B. D., Brenner B. M. Effects of some vasodilator drugs on transcapillary fluid exchange in renal cortex. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1148–1158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. J., Brewer D. B., Hardwicke J. Urinary proteins and glomerular morphometry in protein overload proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1978 Mar;38(3):232–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Maddox D. A., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. VII. Response to reduced renal mass. Am J Physiol. 1974 Sep;227(3):556–562. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.3.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin L. D., Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Hemodynamic basis for glomerular injury in rats with desoxycorticosterone-salt hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1448–1461. doi: 10.1172/JCI111349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feld L. G., Van Liew J. B., Galaske R. G., Boylan J. W. Selectivity of renal injury and proteinuria in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Kidney Int. 1977 Nov;12(5):332–343. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. S., Fernandes G., Good R. A., Michael A. F., Yunis E. J. Dietary restrictions early and late: effects on the nephropathy of the NZB X NZW mouse. Lab Invest. 1978 Jun;38(6):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser R. J., Velosa J. A., Michael A. F. Experimental model of focal sclerosis. I. Relationship to protein excretion in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser R. J., Velosa J. A., Michael A. F. Experimental model of focal sclerosis. I. Relationship to protein excretion in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim R. M., Goldszer R. C., Brenner B. M. Hypertension and proteinuria: long-term sequelae of uninephrectomy in humans. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):930–936. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A., Brenner B. M. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F85–F93. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Purkerson M. L., Klahr S., Troy J. L., Martinez-Maldonado M., Brenner B. M. Mechanism of reduced glomerular filtration rate in chronic malnutrition. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):982–988. doi: 10.1172/JCI109784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlinsky M. L., Haut L., Buddington B., Schrier N. A., Alfrey A. C. Preservation of renal function in experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1980 Mar;17(3):293–302. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinknecht C., Salusky I., Broyer M., Gubler M. C. Effect of various protein diets on growth, renal function, and survival of uremic rats. Kidney Int. 1979 May;15(5):534–541. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalich J. J., Burkholder P. M., Paik W. C. Protein overload nephropathy in rats with unilateral nephrectomy. A correlative light immunogluorescence and electron microscopical analysis. Arch Pathol. 1975 Feb;99(2):72–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., HEIDER C., PEVEY K., FORD R. V. The effect of treatment on the vascular deterioration associated with hypertension, with particular emphasis on renal function. Am J Med. 1958 Feb;24(2):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maschio G., Oldrizzi L., Tessitore N., D'Angelo A., Valvo E., Lupo A., Loschiavo C., Fabris A., Gammaro L., Rugiu C. Effects of dietary protein and phosphorus restriction on the progression of early renal failure. Kidney Int. 1982 Oct;22(4):371–376. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitch W. E., Walser M., Steinman T. I., Hill S., Zeger S., Tungsanga K. The effect of a keto acid-amino acid supplement to a restricted diet on the progression of chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):623–629. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell H. C., Graham R. M., Pettinger W. A. Renal function during long-term treatment of hypertension with minoxidil: comparison of benign and malignant hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Nov;93(5):676–681. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-5-676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen C. K. Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent patients. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 12;311(2):89–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407123110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow in short-term and long-term juvenile diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;28(1):91–100. doi: 10.3109/00365517109090667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Long-term antihypertensive treatment inhibiting progression of diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Sep 11;285(6343):685–688. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6343.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugarten J., Feiner H. D., Schacht R. G., Baldwin D. S. Amelioration of experimental glomerulonephritis by dietary protein restriction. Kidney Int. 1983 Nov;24(5):595–601. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugarten J., Feiner H. D., Schacht R. G., Gallo G. R., Baldwin D. S. Aggravation of experimental glomerulonephritis by superimposed clip hypertension. Kidney Int. 1982 Sep;22(3):257–263. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. L., Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M., Venkatachalam M. A. Altered glomerular permselectivity and progressive sclerosis following extreme ablation of renal mass. Kidney Int. 1982 Aug;22(2):112–126. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. P., Gyntelberg F. Transcapillary escape rate of albumin and plasma volume in essential hypertension. Circ Res. 1973 May;32(5):643–651. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salusky I., Kleinknecht C., Broyer M., Gubler M. C. Prolonged renal survival and stunting, with protein-deficient diets in experimental uremia. Reversal of these effects by addition of essential amino acids. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Mechanisms of action of various hormones and vasoactive substances on glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):442–451. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Brown D. M., Mauer S. M. Diabetic glomerulopathy following unilateral nephrectomy in the rat. Diabetes. 1978 Jan;27(1):35–41. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen I., Fyhrquist F., Miettinen A., Törnroth T. Autologous immune complex nephritis and DOCA-NaCl load: a new model of hypertension. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1980 Jul;88(4):241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets J. W., Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Determination of serum protein concentration in nanoliter blood samples using fluorescamine or 9-phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Dupont J., Sassard J. Plasma renin activity as a function of age in two new strains of spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Feb;50(2):103–107. doi: 10.1042/cs0500103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel L. W., Cole L. J., Rosen V. J. X-ray-induced glomerulosclerosis in rats: modification of lesion by food restriction, uninephrectomy, and age. J Gerontol. 1966 Jul;21(3):442–448. doi: 10.1093/geronj/21.3.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]