Abstract
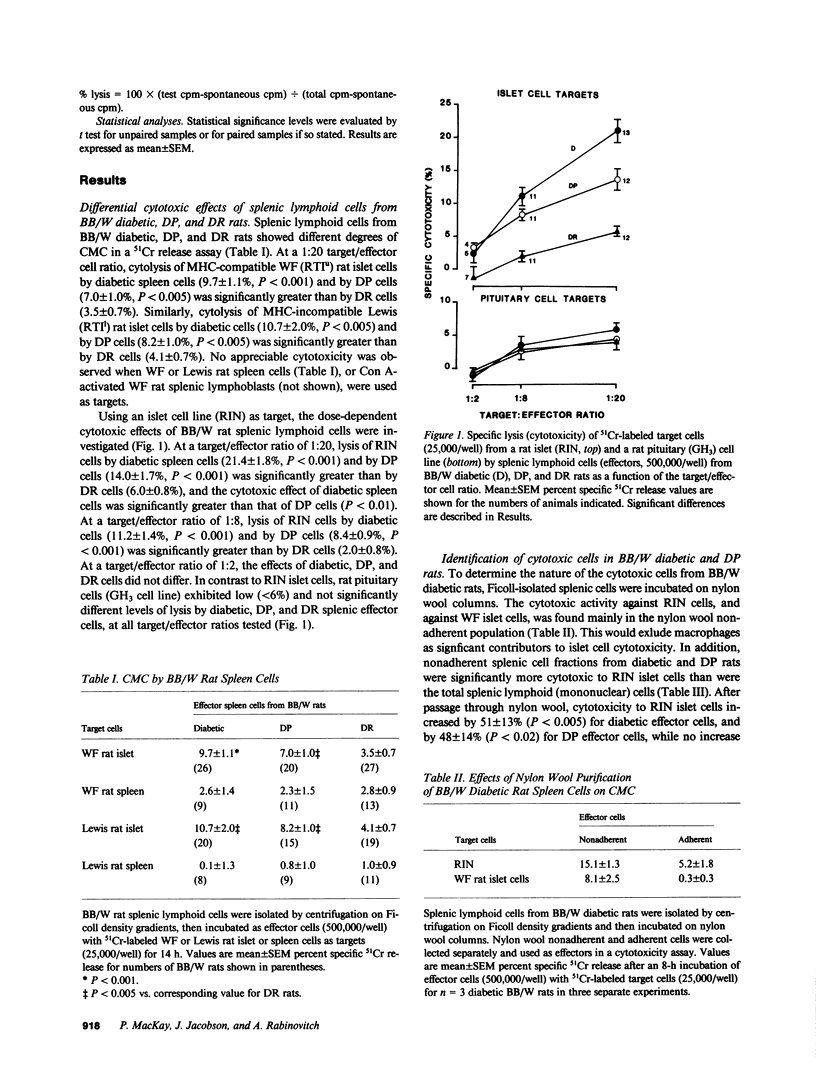
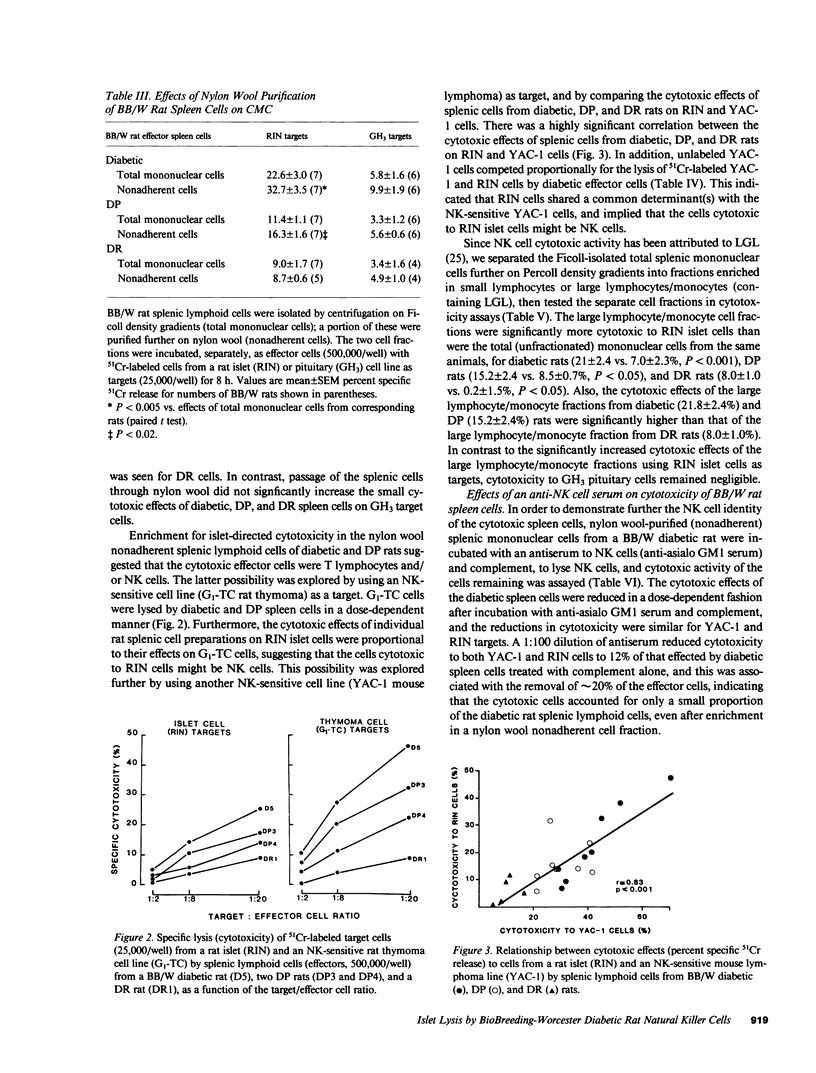
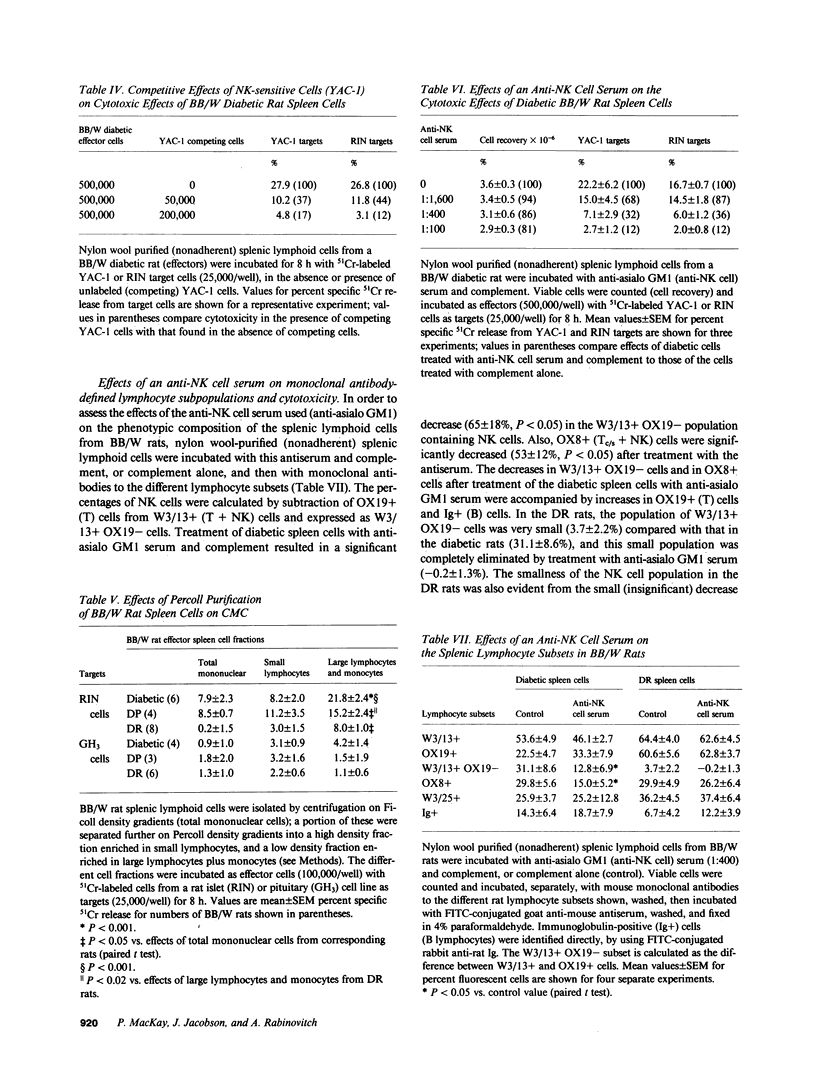
We sought direct evidence for anti-islet cellular cytotoxicity in diabetic Bio-Breeding/Worcester (BB/W) rats by comparing the effects of splenic lymphoid cells from BB/W diabetic (D), diabetes-prone (DP), and diabetes-resistant (DR) rats on the release of 51Cr from damaged islet cells in vitro. D and DP splenic lymphoid cells were cytotoxic to major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-compatible Wistar-Furth (WF) rat islet cells and also to MHC-incompatible Lewis rat islet cells and a rat islet cell line (RIN 5F), whereas WF and Lewis rat spleen cells and a rat pituitary cell line (GH3) were not lysed by lymphoid cells from D or DP rats. The cytotoxic cells were identified as natural killer (NK) cells since NK-sensitive cells (G1-TC and YAC-1 cell lines) were lysed by D and DP spleen cells, YAC-1 cells competed for the lysis of RIN islet cells by D spleen cells, lysis of RIN cells was increased by using D spleen cells from the low density fraction (large lymphocytes/monocytes) of a Percoll density gradient, and incubation of D spleen cells with an antiserum to NK cells (anti-asialo GM1 serum) and complement decreased monoclonal antibody-defined subsets containing NK cells (W3/13+ OX19- and OX8+), and this was accompanied by similar decreases in cytotoxicity to YAC-1, RIN, and WF islet cells. These studies demonstrate that NK cell activity is increased in BB/W diabetic and DP rats, and that islet cells can serve as targets for these NK cells. The findings suggest that NK cells may participate in the islet-directed cellular cytotoxic response leading to beta cell destruction and diabetes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alinaji, Silvers W. K., Bellgrau D., Anderson A. O., Plotkin S., Barker C. F. Prevention of diabetes in rats by bone marrow transplantation. Ann Surg. 1981 Sep;194(3):328–338. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198109000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alviggi L., Johnston C., Hoskins P. J., Tee D. E., Pyke D. A., Leslie R. D., Vergani D. Pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes: a role for activated T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1984 Jul 7;2(8393):4–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91994-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft F. C., Tashjian A. H., Jr Growth in suspension culture of rat pituitary cells which produce growth hormone and prolactin. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jan;64(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellgrau D., Naji A., Silvers W. K., Markmann J. F., Barker C. F. Spontaneous diabetes in BB rats: evidence for a T cell dependent immune response defect. Diabetologia. 1982 Oct;23(4):359–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00253745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Röpke C., Madsbad S., Mehlsen J., Rygaard J. T lymphocyte subsets in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: a prospective study. Diabetologia. 1983 Sep;25(3):247–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00279938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Robins R. A., Brooks C. G., Baldwin R. W. Phenotype of rat natural killer cells defined by monoclonal antibodies marking rat lymphocyte subsets. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):97–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Suzuki M., Waldeck N., Dodson L. E., Slater L., Ong K., Kershnar A., Buckingham B., Golden M. Immune islet killing mechanisms associated with insulin-dependent diabetes: in vitro expression of cellular and antibody-mediated islet cell cytotoxicity in humans. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1189–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder M. E., Maclaren N. K. Identification of profound peripheral T lymphocyte immunodeficiencies in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1723–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild R. S., Kyner J. L., Abdou N. I. Specific immunoregulation abnormality in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Feb;99(2):175–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S., Kaye R., Falkner B. Subpopulations of peripheral lymphocytes in juvenile diabetes. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):101–103. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Morris M. A., Haynes B. F., Eisenbarth G. S. Increased circulating Ia-antigen-bearing T cells in type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 1;306(13):785–788. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204013061305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky S. G., Nakamura I., Cudkowicz G. Genetic control of the natural killer cell activity in SJL and other strains of mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):665–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koevary S. B., Williams D. E., Williams R. M., Chick W. L. Passive transfer of diabetes from BB/W to Wistar-Furth rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1904–1907. doi: 10.1172/JCI111904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koevary S., Rossini A., Stoller W., Chick W., Williams R. M. Passive transfer of diabetes in the BB/W rat. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):727–728. doi: 10.1126/science.6836309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laupacis A., Stiller C. R., Gardell C., Keown P., Dupre J., Wallace A. C., Thibert P. Cyclosporin prevents diabetes in BB Wistar rats. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman M. M., Ellner J. J., Rodman H. M. Defective suppressor cell generation in juvenile onset diabetes. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2051–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Anthony M., Guberski D. L., Rossini A. A. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus in the BB/W rat. Effects of glucocorticoids, cyclosporin-A, and antiserum to rat lymphocytes. Diabetes. 1983 Apr;32(4):326–330. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.4.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Kislauskis E., Williams R. R., Rossini A. A. Neonatal thymectomy prevents spontaneous diabetes mellitus in the BB/W rat. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):644–646. doi: 10.1126/science.7041259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Rossini A. A., Guberski D. L., Appel M. C., Williams R. M. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus: reversal and prevention in the BB/W rat with antiserum to rat lymphocytes. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.388619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Weringer E. J., Holdash A., McGill P., Atkinson D., Rossini A. A. Adoptive transfer of autoimmune diabetes mellitus in biobreeding/Worcester (BB/W) inbred and hybrid rats. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1583–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetopoulos J., Valiquette N., Madura E., Cvet D. The onset and progression of pancreatic insulitis in the overt, spontaneously diabetic, young adult BB rat studied by pancreatic biopsy. Diabetes. 1984 Jan;33(1):33–36. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay P., Boulton A., Rabinovitch A. Lymphoid cells of BB/W diabetic rats are cytotoxic to islet beta cells in vitro. Diabetes. 1985 Jul;34(7):706–709. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.7.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Nakhooda A. F., Poussier P., Sima A. A. The diabetic syndrome of the 'BB' Wistar rat: possible relevance to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes in man. Diabetologia. 1982 Apr;22(4):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00281296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy R. C., Andersson J., Sandler S., Hellerström C. Multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the mouse. Evidence for stimulation of a cytotoxic cellular immune response against an insulin-producing beta cell line. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):715–722. doi: 10.1172/JCI111487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naji A., Silvers W. K., Kimura H., Bellgrau D., Markmann J. F., Barker C. F. Analytical and functional studies on the T cells of untreated and immunologically tolerant diabetes-prone BB rats. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2168–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler J. R., Lindsay L. R., Nunn M. E., Herberman R. B. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rats. I. Tissue and strain distribution, and demonstration of a membrance receptor for the Fc portion of IgG. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):204–209. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzilli P., Sensi M., Gorsuch A., Bottazzo G. F., Cudworth A. G. Evidence for raised K-cell levels in type-I diabetes. Lancet. 1979 Jul 28;2(8135):173–175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Russell T., Shienvold F., Noel J., Files N., Patel Y., Ingram M. Preparation of rat islet B-cell-enriched fractions by light-scatter flow cytometry. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):939–943. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Sharrow S. O., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Natural killer activity in the rat. II. Analysis of surface antigens on LGL by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2204–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Faustman D., Woda B. A., Like A. A., Szymanski I., Mordes J. P. Lymphocyte transfusions prevent diabetes in the Bio-Breeding/Worcester rat. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):39–46. doi: 10.1172/JCI111416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Mordes J. P., Pelletier A. M., Like A. A. Transfusions of whole blood prevent spontaneous diabetes mellitus in the BB/W rat. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):975–977. doi: 10.1126/science.6823559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Slavin S., Woda B. A., Geisberg M., Like A. A., Mordes J. P. Total lymphoid irradiation prevents diabetes mellitus in the Bio-Breeding/Worcester (BB/W) rat. Diabetes. 1984 Jun;33(6):543–547. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.6.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemayer T. A., Tannenbaum G. S., Goldman H., Colle E. Dynamic time course studies of the spontaneously diabetic BB Wistar rat. III. Light-microscopic and ultrastructural observations of pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Am J Pathol. 1982 Feb;106(2):237–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensi M., Pozzilli P., Gorsuch A. N., Bottazzo G. F., Cudworth A. G. Increased killer cell activity in insulin dependent (type 1) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1981 Feb;20(2):106–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00262010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue A., Mantovani A., Kilgallen M., Herberman R. B., McCoy J. L. Natural cytotoxicity of mouse monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2363–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vánky F., Klein E. Alloreactive cytotoxicity of interferon-triggered human lymphocytes detected with tumor biopsy targets. Immunogenetics. 1982 Jan;15(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00375500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weringer E. J., Like A. A. Immune attack on pancreatic islet transplants in the spontaneously diabetic BioBreeding/Worcester (BB/W) rat is not MHC restricted. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2383–2386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woda B. A., Like A. A., Padden C., McFadden M. L. Deficiency of phenotypic cytotoxic-suppressor T lymphocytes in the BB/W rat. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):856–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woda B. A., McFadden M. L., Welsh R. M., Bain K. M. Separation and isolation of rat natural killer (NK) cells from T cells with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2183–2184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yale J. F., Marliss E. B. Altered immunity and diabetes in the BB rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


