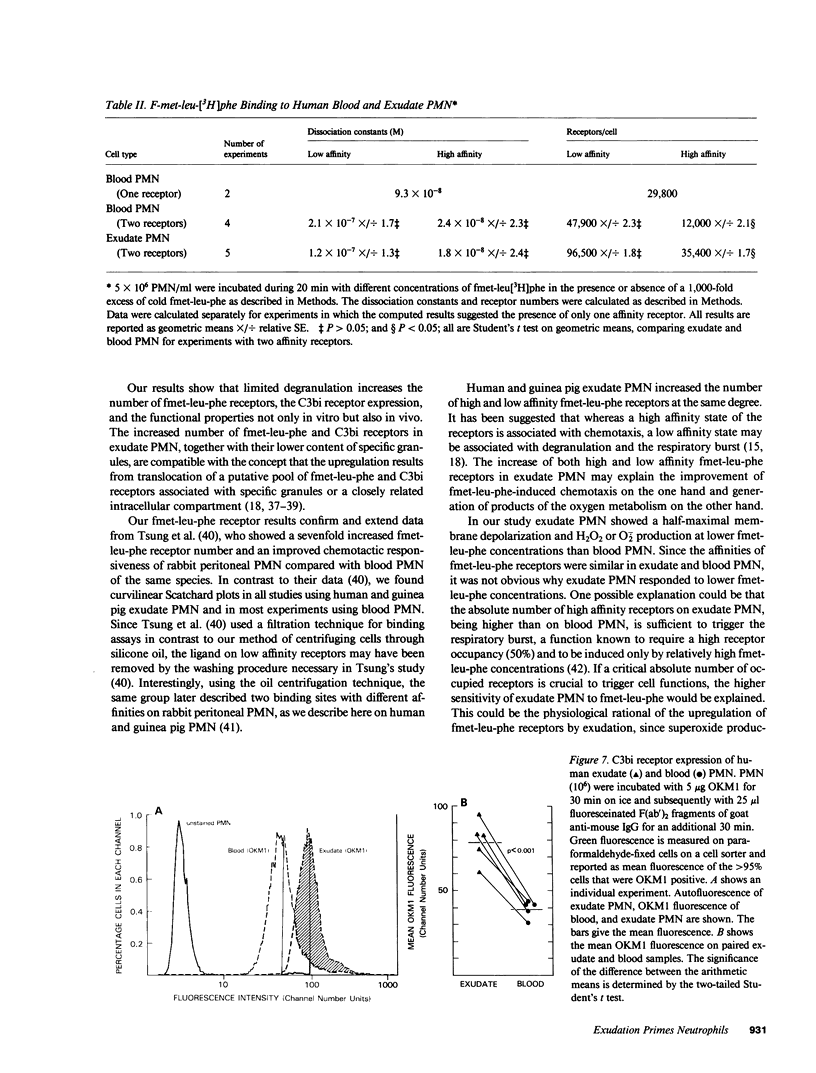
Abstract
After circulating in the vascular system a short time, polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) migrate to extravascular sites in response to chemotactic stimuli. Prestimulation of PMN in vitro by secretagogues has been shown to increase their number of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (fmet-leu-phe) and complement component C3bi (CR3) receptors. We investigated whether the same phenomenon occurred in vivo, comparing characteristics of human skin chamber and guinea pig peritoneal exudate and blood PMN. Exudate PMN of both species contained approximately 28% less of the specific granule marker vitamin B12-binding protein (P less than 0.01) but a similar amount of the azurophil granule marker beta-glucuronidase. The total number of fmet-leu-phe receptors was 5.9 times higher in guinea pig exudate than in blood PMN (P less than 0.01) and 2.9 times higher in human exudate than in blood PMN (P less than 0.02). All exudate PMN and most blood PMN preparations showed a high affinity receptor (Kd approximately 2.3 X 10(-8) M) and a low affinity receptor (approximately 1.5 X 10(-7) M). The upregulation of fmet-leu-phe receptors in exudate PMN correlated with an improved responsiveness to fmet-leu-phe induced membrane depolarization, oxidative metabolism, and chemotaxis. In addition, the concentration of fmet-leu-phe that produced a half-maximal response of chemotaxis, superoxide production, and membrane potential depolarization was 10-fold lower in exudate PMN than in blood PMN. Human exudate PMN had a twofold increased C3bi receptor expression compared with blood PMN. Thus, a preferential loss of specific granules is associated with increased number of high and low affinity fmet-leu-phe receptors and increased C3bi receptor expression not only in vitro, but also in vivo. The data indicate that exudation primes PMN for their subsequent responsiveness to fmet-leu-phe, a modification that may be crucial for efficient antimicrobial host defense.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A., Allen J. M., Davis J. Autooxidation as a basis for altered function by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Aug;50(2):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. G., McPhail L. C., Van Epps D. E. Exposure of human neutrophils to chemotactic factors potentiates activation of the respiratory burst enzyme. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2316–2323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., O'Shea J., Cross A. S., Folks T. M., Chused T. M., Brown E. J., Frank M. M. Human neutrophils increase expression of C3bi as well as C3b receptors upon activation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1566–1571. doi: 10.1172/JCI111572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT G. E., ATHENS J. W., WINTROBE M. M. THE KINETICS OF GRANULOPOIESIS IN NORMAL MAN. Blood. 1964 Dec;24:780–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H. Mitochondrial N-formylmethionyl proteins as chemoattractants for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):264–275. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon J. A., Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oliver C., Gallin J. I., Mergenhagen S. E. An in vitro study of neutrophils obtained from the normal gingival sulcus. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Nov;17(6):614–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Goodman M. G. The C5a receptor of neutrophils and macrophages. Agents Actions Suppl. 1983;12:252–273. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9352-7_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Whitin J. C., Chovaniec M. E., Tape E. H., Simons E. R. Is activation of the granulocyte by concanavalin-A a reversible process? Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M., Dineen P., Gallin J. I. Neutrophil degranulation and abnormal chemotaxis after thermal injury. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1467–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H., Gallin J. I. Deactivation of human neutrophil chemotaxis by chemoattractants: effect on receptors for the chemotactic factor f-Met-Leu-Phe. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):839–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Roloff J. S., Lukens J. N. Chemotactic factor enhancement of superoxide release from fluoride and phorbol myristate acetate stimulated neutrophils. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Roloff J. S., Lukens J. N. Regulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte superoxide release by cellular responses to chemotactic peptides. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):165–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli increase the availability of receptors on human neutrophils for the chemoattractant f-met-leu-phe. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1585–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Human neutrophils contain an intracellular pool of putative receptors for the chemoattractant N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):792–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Seligmann B. E., Gallin J. I. Correlation of human neutrophil secretion, chemoattractant receptor mobilization, and enhanced functional capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):941–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Durocher J. R., Kaplan A. P. Interaction of leukocyte chemotactic factors with the cell surface. I. Chemotactic factor-induced changes in human granulocyte surface charge. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):967–974. doi: 10.1172/JCI108026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Malech H. L., Davis J. M., Klempner M. S., Kirkpatrick C. H. Disorders of phagocyte chemotaxis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Apr;92(4):520–538. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-4-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Schiffmann E. Role of secretory events in modulating human neutrophil chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1364–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI109257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellum K. B., Solberg C. O. Human leucocyte migration: studies with an improved skin chamber technique. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Dec;85C(6):413–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. U., Cottier H. Comparison of locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesiveness of rabbit neutrophils from blood and peritoneal exudates. Blood Cells. 1984;10(1):45–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackin W. M., Huang C. K., Becker E. L. The formylpeptide chemotactic receptor on rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. I. Evidence for two binding sites with different affinities. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1608–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Feltner D. E., Ward P. A. Formyl peptide chemotaxis receptors on the rat neutrophil: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):359–375. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Phan S. H., Krutzsch H., Showell H. J., Feltner D. E., Nairn R., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5430–5439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Becker E. L. Anti-f Met-Leu-Phe: similarities in fine specificity with the formyl peptide chemotaxis receptor of the neutrophil. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Chenoweth D. E., Solomkin J. S., Solem L. D. Cytotaxin receptors on human neutrophils: modulation of C5a and peptide receptor number. Agents Actions Suppl. 1983;12:274–289. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9352-7_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Chovaniec M. E., Cohen H. J. Activity and activation of the granulocyte superoxide-generating system. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):85–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Adaptation of human neutrophil responsiveness to the chemoattractant N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine. Heterogeneity and/or negative cooperative interaction of receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6280–6286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Histamine modulation of human neutrophil oxidative metabolism, locomotion, degranulation, and membrane potential changes. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1902–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Gallin E. K., Martin D. L., Shain W., Gallin J. I. Interaction of chemotactic factors with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: studies using a membrane potential-sensitive cyanine dye. J Membr Biol. 1980;52(3):257–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01869194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Gallin J. I. Use of lipophilic probes of membrane potential to assess human neutrophil activation. Abnormality in chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):493–503. doi: 10.1172/JCI109880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B., Chused T. M., Gallin J. I. Differential binding of chemoattractant peptide to subpopulations of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2641–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G. Ligand/receptor internalization: a spectroscopic analysis and a comparison of ligand binding, cellular response, and internalization by human neutrophils. J Cell Biochem. 1982;20(2):193–202. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240200210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsung P. K., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Surface membrane enzyme, chemotactic peptide binding activities, and chemotactic responsiveness of rabbit peripheral and peritoneal neutrophils. Inflammation. 1980 Sep;4(3):271–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00915028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. A., Schumacher R., Myers A. R. Phagocytic function of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in rheumatic diseases. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1632–1635. doi: 10.1172/JCI107342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Garcia M. L. Enhancement of neutrophils function as a result of prior exposure to chemotactic factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):167–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI109841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton J. M., Renggli H. H., Lehner T. A functional comparison of blood and gingival inflammatory polymorphonuclear leucocytes in man. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):152–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Gallin J. I. Secretory responses of human neutrophils: exocytosis of specific (secondary) granules by human neutrophils during adherence in vitro and during exudation in vivo. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Cohen H. J., Waldvogel F. A. Comparative superoxide-generating system of granulocytes from blood and peritoneal exudates. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):625–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.625-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Waldvogel F. A. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection. Evidence for a local granulocyte defect. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1191–1200. doi: 10.1172/JCI111305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]