Abstract
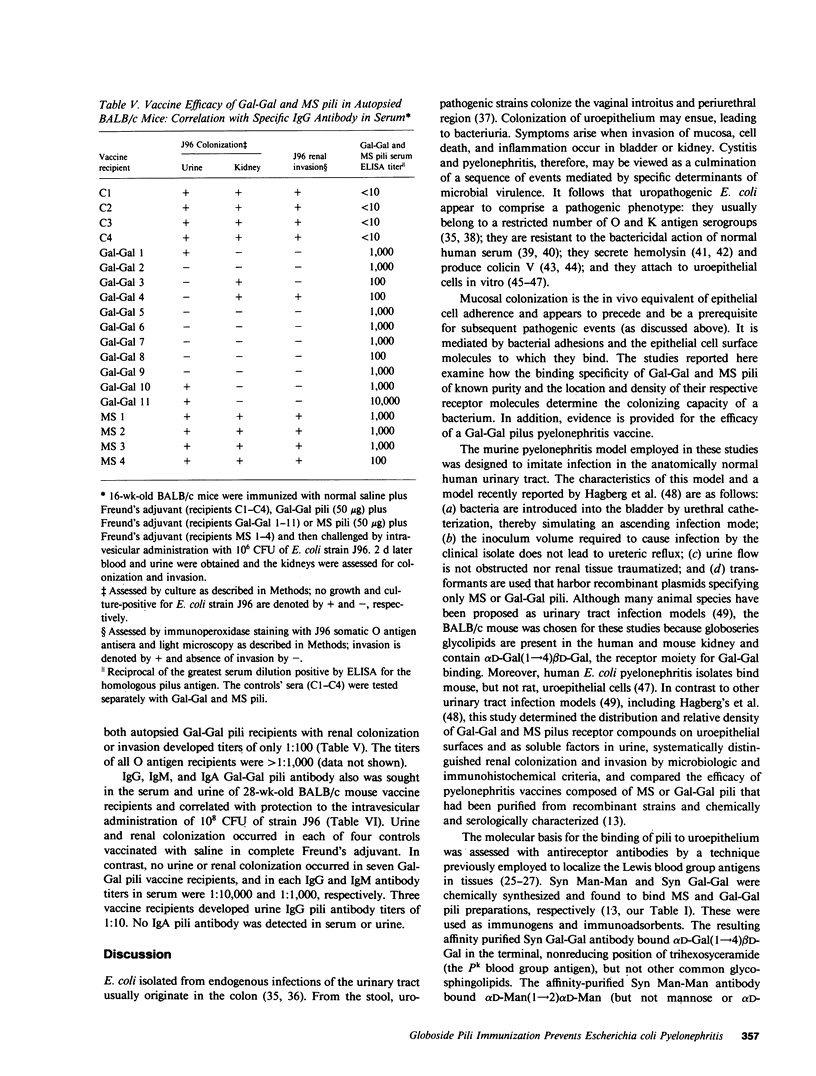
Most human pyelonephritis Escherichia coli isolates express both mannose (MS)- and globoside (Gal-Gal)-binding pili. An ascending E. coli urinary tract infection model was established in the 16-wk-old female BALB/c mouse to compare the pathogenic significance of MS and Gal-Gal pili and their efficacy as vaccines for the prevention of pyelonephritis. The distribution and density of pilus receptor compounds in urogenital tissues and as soluble compounds in urine were determined with antibodies to the synthetic receptor analogues, alpha D-Gal(1----4) beta D-Gal and alpha D-Man(1----2) alpha D-Man. Both carbohydrates were detected in vagina, bladder, ureter, and renal pelvis epithelium and in collecting duct and tubular cells. A pilus receptor compound also was detected in urine. It competitively inhibited the binding capacity of MS pili and was found to be physically, chemically, and immunologically related to Tamm-Horsfall uromucoid. Infectivity and invasiveness were quantitatively and histologically characterized for four E. coli strains: J96, a human pyelonephritis strain that expresses both MS and Gal-Gal pili; two recombinant strains prepared from J96 chromosomal DNA encoding MS pili or Gal-Gal pili; and the nonpiliated K12 recipient. Intravesicular administration of J96 (10(6) colony-forming units [CFU]) resulted in renal colonization and invasion in each of nine mice. The Gal-Gal clone (10(6) CFU) colonized the kidneys in each of 10 mice but did not invade. In contrast, the MS clone (10(6) CFU) did not colonize renal epithelium or invade. This effect was superceded when larger doses (greater than or equal to 10(10) CFU) of the MS clone were administered in volumes that cause acute vesicoureteric reflux. The efficacy was determined of vaccines composed of pure MS or Gal-Gal pili or the lipopolysaccharide containing O somatic antigen of the challenge strain, J96. The Gal-Gal pilus vaccine blocked renal colonization in 19 of 22 mice and renal invasion in 10 of 11 mice. Gal-Gal pili may be useful immunogens for the prevention of pyelonephritis in anatomically normal urinary tracts.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Kaijser B. Interaction of human serum and neutrophils with Escherichia coli strains: differences between strains isolated from urine of patients with pyelonephritis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.308-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks H. J., O'Grady F., McSherry M. A., Cattell W. R. Uropathogenic properties of Escherichia coli in recurrent urinary-tract infection. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):57–68. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. L., Falkiner F. R., Hardy K. G. Colicin V production by clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.574-579.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A. Adhesion of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):767–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.767-774.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hansson H. A. Escherichia coli pili as possible mediators of attachment to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.229-237.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Höhne C., Noble M. A., Haldane E. V., Lior H., Young L. S. Hemolysin and K antigens in relation to serotype and hemagglutination type of Escherichia coli isolated from extraintestinal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.171-178.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. E., Jr, Stamey T. A. Studies of introital colonization in women with recurrent urinary infections. VII. The role of bacterial adherence. J Urol. 1977 Apr;117(4):472–476. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)58501-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Engberg I., Freter R., Lam J., Olling S., Svanborg Edén C. Ascending, unobstructed urinary tract infection in mice caused by pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.273-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALLMAN R. F., SILINI G. RECUPERATION FROM LETHAL INJURY BY WHOLE-BODY IRRADIATION. I. KINETIC ASPECTS AND THE RELATIONSHIP WITH CONDITIONING DOSE IN C57BL MICE. Radiat Res. 1964 Aug;22:622–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Ahlstedt S. Protective capacity of antibodies against Escherichia coli and K antigens. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):286–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.286-289.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Larsson P. Experimental acute pyelonephritis caused by enterobacteria in animals. A review. J Urol. 1982 Apr;127(4):786–790. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)54049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Larsson P., Nimmich W., Söderström T. Antibodies to Escherichia coli K and O antigens in protection against acute pyelonephritis. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:275–288. doi: 10.1159/000318336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Orskov I., Orskov F. F7 and type 1-like fimbriae from three Escherichia coli strains isolated from urinary tract infections: protein chemical and immunological aspects. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):462–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.462-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux R. U., Baker D. A., Bundle D. R. A methodology for the production of carbohydrate-specific antibody. Can J Biochem. 1977 May;55(5):507–512. doi: 10.1139/o77-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux R. U., Bundle D. R., Baker D. A. The properties of a "synthetic" antigen related to the human blood-group Lewis a. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jul 9;97(14):4076–4083. doi: 10.1021/ja00847a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomberg H., Hanson L. A., Jacobsson B., Jodal U., Leffler H., Edén C. S. Correlation of P blood group, vesicoureteral reflux, and bacterial attachment in patients with recurrent pyelonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 19;308(20):1189–1192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305193082003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael J. C., Ou J. T. Structure of common pili from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):969–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.969-975.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Jorgensen J., Counts G. W., Falkow S. Association of hemolysin production, hemagglutination of human erythrocytes, and virulence for chicken embryos of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.50-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Lark D., Hull R., Norgren M., Båga M., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Genetics of digalactoside-binding adhesin from a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):942–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.942-949.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanley P., Lark D., Normark S., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. K. Mannose-sensitive and Gal-Gal binding Escherichia coli pili from recombinant strains. Chemical, functional, and serological properties. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1713–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORSKOV I., ORSKOV F., JANN B., JANN K. ACIDIC POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGENS OF A NEW TYPE FROM E. COLI CAPSULES. Nature. 1963 Oct 12;200:144–146. doi: 10.1038/200144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olling S. Sensitivity of gram-negative bacilli to the serum bactericidal activity: a marker of the host-parasite relationship in acute and persisting infections. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1977;(10):1–40. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.suppl-10.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Ferencz A., Orskov F. Tamm-Horsfall protein or uromucoid is the normal urinary slime that traps type 1 fimbriated Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1980 Apr 19;1(8173):887–887. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin G. J., Braude A. I. Immobilizing antibodies in urine. II. Prevention of ascending spread of Proteus mirabilis. Invest Urol. 1974 Sep;12(2):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. A., Hardaway K., Kaack B., Fussell E. N., Baskin G. Prevention of pyelonephritis by immunization with P-fimbriae. J Urol. 1984 Mar;131(3):602–607. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)50513-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Hemagglutination by purified type I Escherichia coli pili. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1169–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Cohen L. S. Antipili antibody affords protection against experimental ascending pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):333–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI109458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg-Edén C., Jodal U. Attachment of Escherichia coli to urinary sediment epithelial cells from urinary tract infection-prone and healthy children. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):837–840. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.837-840.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Mayer L. W., Tam M. R. Antigenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane protein(s) III detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot transfer with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):668–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.668-672.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURCK M., PETERSDORF R. G. The epidemiology of nonenteric Escherichia coli infections: prevalence of serological groups. J Clin Invest. 1962 Sep;41:1760–1765. doi: 10.1172/JCI104635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOSTI K. L., GOLDBERG L. M., MONTO A. S., RANTZ L. A. HOST-PARASITE INTERACTION IN PATIENTS WITH INFECTIONS DUE TO ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. THE SEROGROUPING OF E. COLI FROM INTESTINAL AND EXTRAINTESTINAL SOURCES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2377–2385. doi: 10.1172/JCI105112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väisänen V., Elo J., Tallgren L. G., Siitonen A., Mäkelä P. H., Svanborg-Edén C., Källenius G., Svenson S. B., Hultberg H., Korhonen T. Mannose-resistant haemagglutination and P antigen recognition are characteristic of Escherichia coli causing primary pyelonephritis. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1366–1369. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92796-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bosch J. F., Verboom-Sohmer U., Postma P., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant adherence to human uroepithelial cells and urinary virulence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.226-233.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]