Abstract
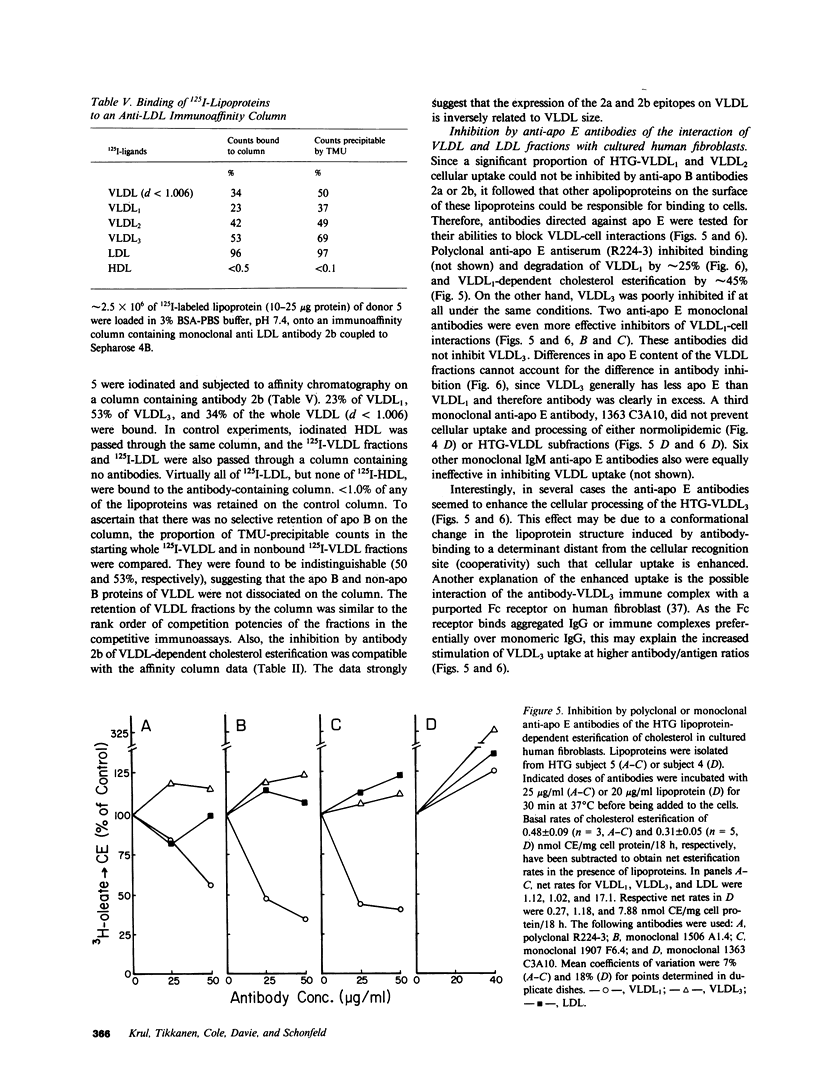
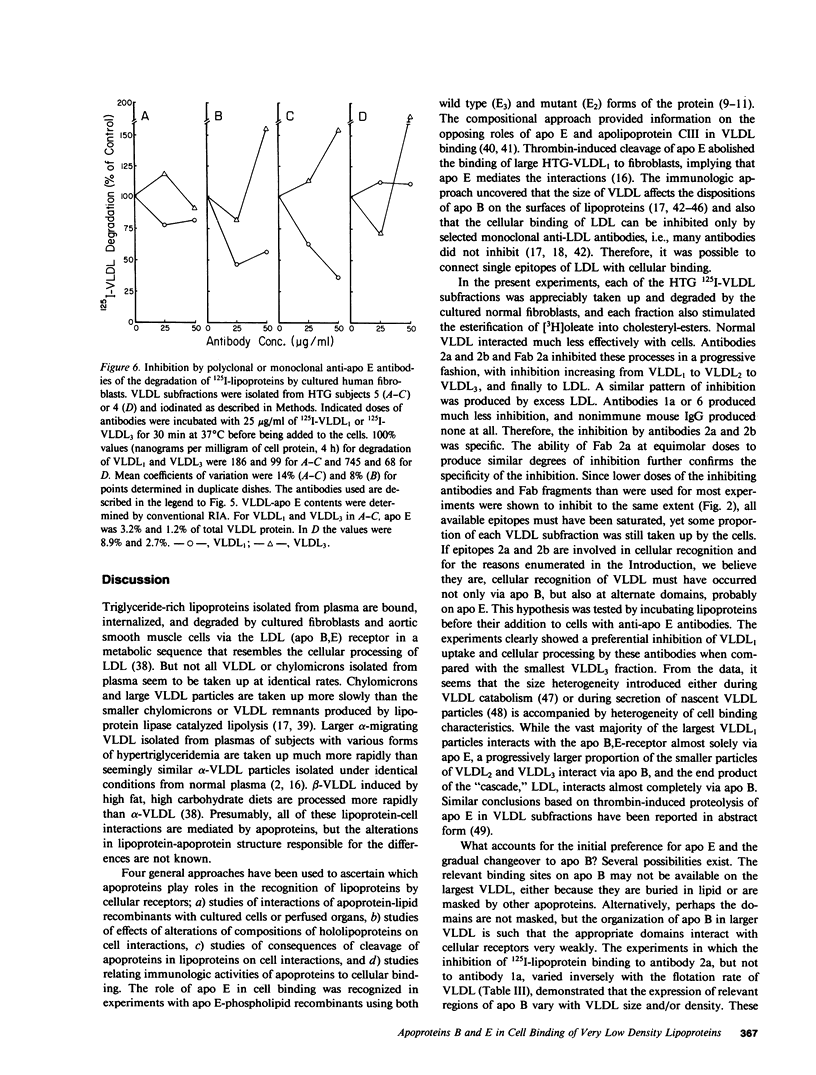
Apoproteins B and E both interact with cellular low density lipoprotein (LDL) apolipoprotein B and E (apo B,E)-receptors, and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) contain both apo B and apo E. Our aim was to study the relative importance of apo B and apo E in the binding of VLDL subfractions to cells. Two monoclonal anti-LDL-apo B antibodies (464B1B3 and 464B1B6, 2a and 2b, respectively) and two anti-apo E antibodies (1506 A1.4 and 1907 F6.4) were used to inhibit lipoprotein-cell interactions. In confirmation of previous findings, the binding and degradation of 125I-LDL by human fibroblasts were inhibited approximately 90% by antibodies 2a or 2b or the antigen-binding fragments of 2a, whereas the cellular processing of 125I-VLDL3 (Sf20-60), 125I-VLDL2 (Sf60-120), and 125I-VLDL1 (Sf greater than 120) were inhibited by only approximately 50%, approximately 25%, and less than 10%, respectively. The VLDL1-3 and LDL-dependent intracellular esterification of cholesterol with [3H]oleate were inhibited to a similar extent. Other monoclonal anti-human apo B antibodies inhibited lipoprotein-cell interactions much less effectively and nonimmune IgG isolated from mouse serum did not inhibit at all. 20-fold excesses of LDL produced about the same patterns of inhibition of degradation of 125I-VLDL1-3 and LDL by cells as did antibodies 2a and 2b, whereas homologous unlabeled VLDL1-3 in like amounts inhibited the matched 125I-VLDL subfraction more effectively. Two anti-apo E monoclonal antibodies and a polyclonal anti-apo E antibody inhibited cell-mediated degradation of and lipoprotein-dependent cholesterol esterification by VLDL1 but not VLDL3 or LDL. The results suggest that receptor recognition sites on apo E in preference to sites on apo B mediate the cellular binding of hypertriglyceridemic VLDL1. However, the proportion of particles bound via apo B seems to increase as VLDL decreases in size toward LDL, and virtually all of LDL binding is mediated by apo B.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Aron L., Sciacca R. Radioimmunoassay studies of human apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1172/JCI109975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. G., Patsch W., Kuisk I., Gonen B., Schonfeld G. Increases in dietary cholesterol and fat raise levels of apoprotein E-containing lipoproteins in the plasma of man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jun;56(6):1108–1115. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-6-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of human plasma apolipoprotein B. I. Apolipoprotein B binding of mouse hybridoma antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15213–15221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falko J. M., Schonfeld G., Witztum J. L., Kolar J. B., Weidman S. W., Steelman R. Effects of diet on apoprotein E levels and on the apoprotein E subspecies in human plasma lipoproteins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Mar;50(3):521–528. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-3-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Albers J. J., Kudchodkar B. J., Bierman E. L. Receptor-dependent uptake of human chylomicron remnants by cultured skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):425–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Einsfelder B. Induction of surface IgG receptors in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):213–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Brown F. B., Gotto A. M., Jr, Bradley W. A. Receptor-mediated uptake of hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins by normal human fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):984–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Gotto A. M., Jr, Hwang S. L., Karlin J. B., Lin A. H., Prasad S. C., Bradley W. A. Apolipoprotein E mediates uptake of Sf 100-400 hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins by the low density lipoprotein receptor pathway in normal human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4526–4533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Gotto A. M., Jr, Jackson R. L., Patsch J. R., Sybers H. D., Taunton O. D., Yeshurun D. L., Smith L. C. Control of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity in cultured human fibroblasts by very low density lipoproteins of subjects with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):320–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI108942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Packard C. J., Shepherd J., Smith L. C., Catapano A. L., Sybers H. D., Gotto A. M., Jr Abnormal suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity in cultured human fibroblasts by hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoprotein subclasses. Lipids. 1980 Jun;15(6):456–463. doi: 10.1007/BF02534072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. C., Rubinstein A., Bukberg P. R., Brown W. V. Apolipoprotein E-enriched lipoprotein subclasses in normolipidemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jul;24(7):886–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Dana S. E., Brown M. S. Esterification of low density lipoprotein cholesterol in human fibroblasts and its absence in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4288–4292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahm K. S., Tikkanen M. J., Dargar R., Cole T. G., Davie J. M., Schonfeld G. Limited proteolysis selectively destroys epitopes on apolipoprotein B in low density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jul;24(7):877–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P. Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia: predominance of a specific apoprotein species in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2015–2019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Heterogeneity of lipoprotein particles in hepatic Golgi fractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):833–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Enhanced binding by cultured human fibroblasts of apo-E-containing lipoproteins as compared with low density lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1440–1447. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Hardman D. A., Paulus H. E. Heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B: isolation of a new species from human chylomicrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Sata T., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Apoprotein composition of very low density lipoproteins of human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1622–1634. doi: 10.1172/JCI108245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. Labelling of plasma proteins with radioactive iodine. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):135–143. doi: 10.1042/bj0620135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao S. J., Kazmar R. E., Silverfield J. C., Alley M. C., Kluge K., Fathman C. G. Immunochemical properties of human low density lipoproteins as explored by monoclonal antibodies. Binding characteristics distinct from those of conventional serum antibodies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne R. W., Theolis R., Jr, Verdery R. B., Marcel Y. L. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):23–30. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. A., Tasch M. A., Tikkanen M., Dargar R., Schonfeld G. Evolution of low density lipoprotein structure probed with monoclonal antibodies. J Lipid Res. 1984 Aug;25(8):821–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund R. E., Jr, Pfleger B., Schonfeld G. Role of microtubules in low density lipoprotein processing by cultured cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):75–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI109281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Patsch J. R., Kostner G. M., Sailer S., Braunsteiner H. Isolation of subfractions of human very low density lipoproteins by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4911–4915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Patsch J. R., Kostner G. M., Sailer S., Braunsteiner H. Isolation of subfractions of human very low density lipoproteins by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4911–4915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Arnold K. S., Mahley R. W. Rate and equilibrium constants for binding of apo-E HDLc (a cholesterol-induced lipoprotein) and low density lipoproteins to human fibroblasts: evidence for multiple receptor binding of apo-E HDLc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Cell surface receptor binding of phospholipid . protein complexes containing different ratios of receptor-active and -inactive E apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5454–5460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Michalopoulos G., Schirmer B. The effect of human C apolipoproteins on the in vitro hepatic metabolism of triglyceride emulsions in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14642–14647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Lees R. S., George P. K., Pfleger B. Assay of total plasma apolipoprotein B concentration in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI107694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Patsch W., Pfleger B., Witztum J. L., Weidman S. W. Lipolysis produces changes in the immunoreactivity and cell reactivity of very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1288–1297. doi: 10.1172/JCI109584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shireman R. B., Fisher W. R. Apolipoprotein B: its role in the control of fibroblast cholesterol biosynthesis and in the regulation of its own binding to cellular receptors. J Lipid Res. 1979 Jul;20(5):594–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B., Hart R. G. Changes in apolipoproteins and properties of rabbit very low density lipoproteins on induction of cholesteremia. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. C., Jr, Reynolds J. A. Characterization of the apolipoprotein B polypeptide of human plasma low density lipoprotein in detergent and denaturation solutions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1633–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Kuehl K. S. Separation of apolipoproteins by an acrylamide-gradient sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 28;446(2):561–565. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen M. J., Cole T. G., Hahm K. S., Krul E. S., Schonfeld G. Expression of apolipoprotein B epitopes in very low density lipoprotein subfractions. Studies with monoclonal antibodies. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):138–146. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen M. J., Cole T. G., Schonfeld G. Differential reactivity of human low density lipoproteins with monoclonal antibodies. J Lipid Res. 1983 Nov;24(11):1494–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen N. J., Dargar R., Pfleger B., Gonen B., Davie J. M., Schonfeld G. Antigenic mapping of human low density lipoprotein with monoclonal antibodies. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):1032–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of human plasma apolipoprotein B. II. Expression of apolipoprotein B epitopes on native lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15222–15228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zile J., Kilpatrick M., Laimins M., Sagel J., Colwell J., Virella G. Platelet aggregation and release of ATP after incubation with soluble immune complexes purified from the serum of diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1981 Jul;30(7):575–579. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.7.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]