Abstract
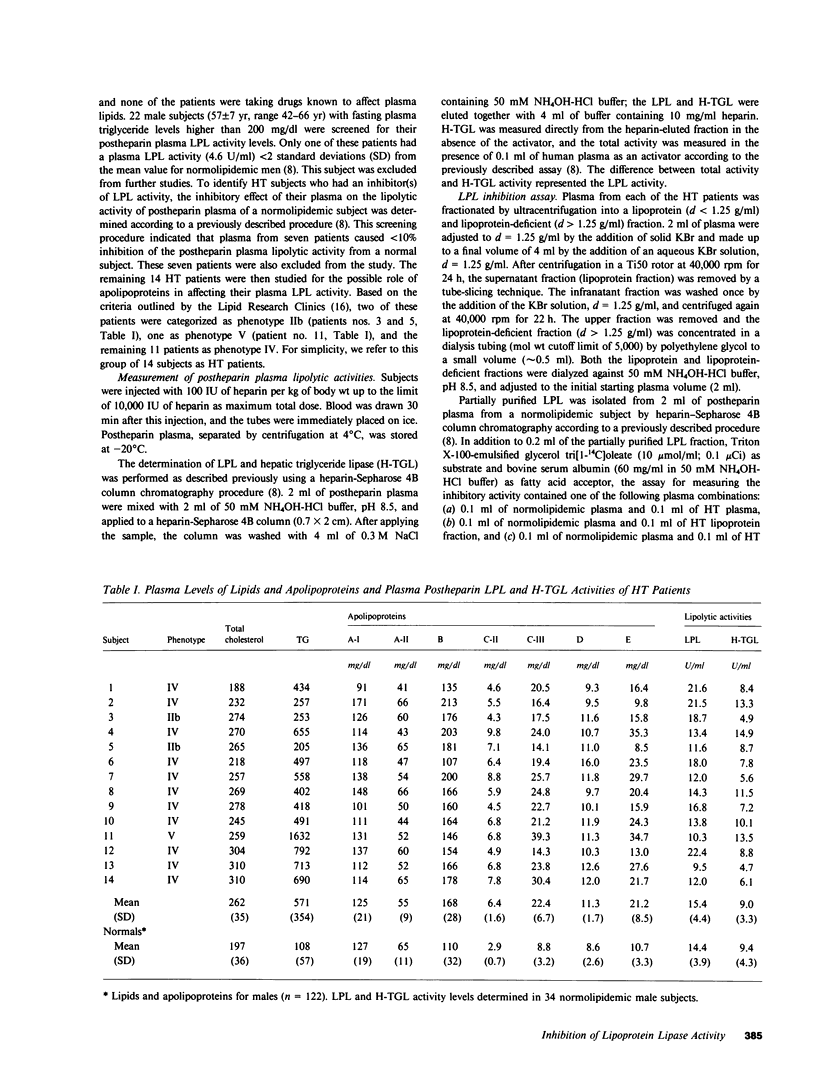
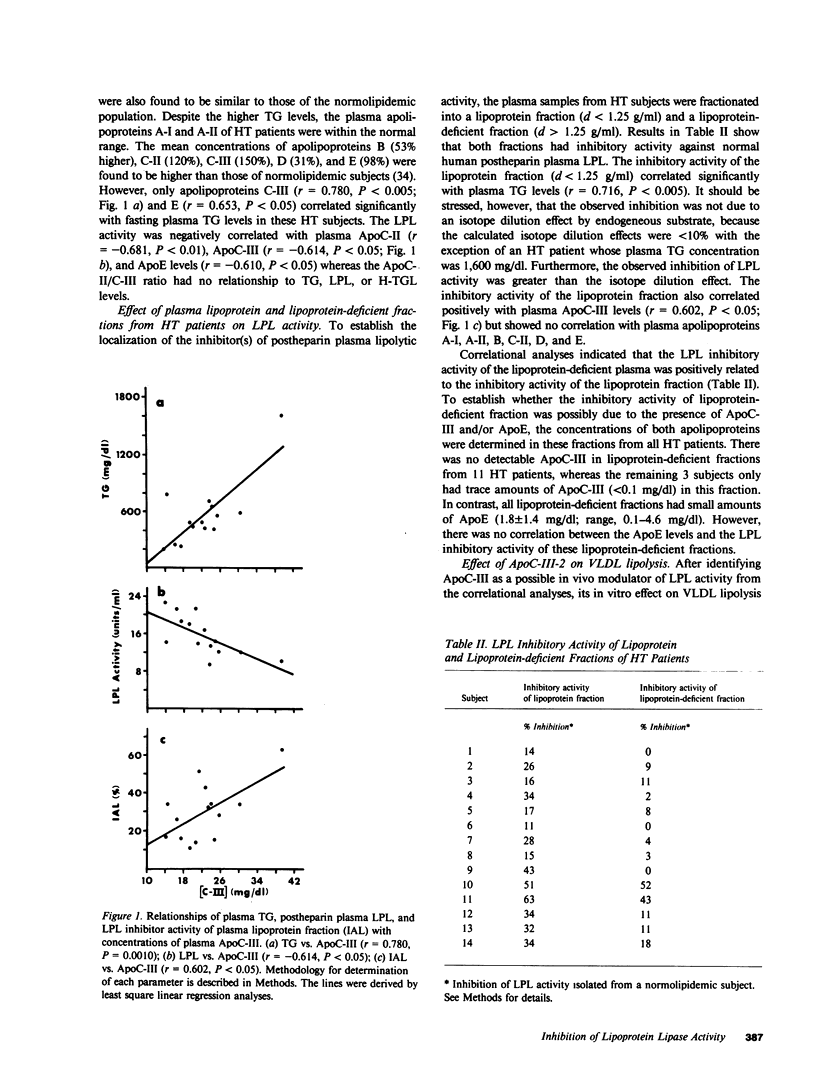
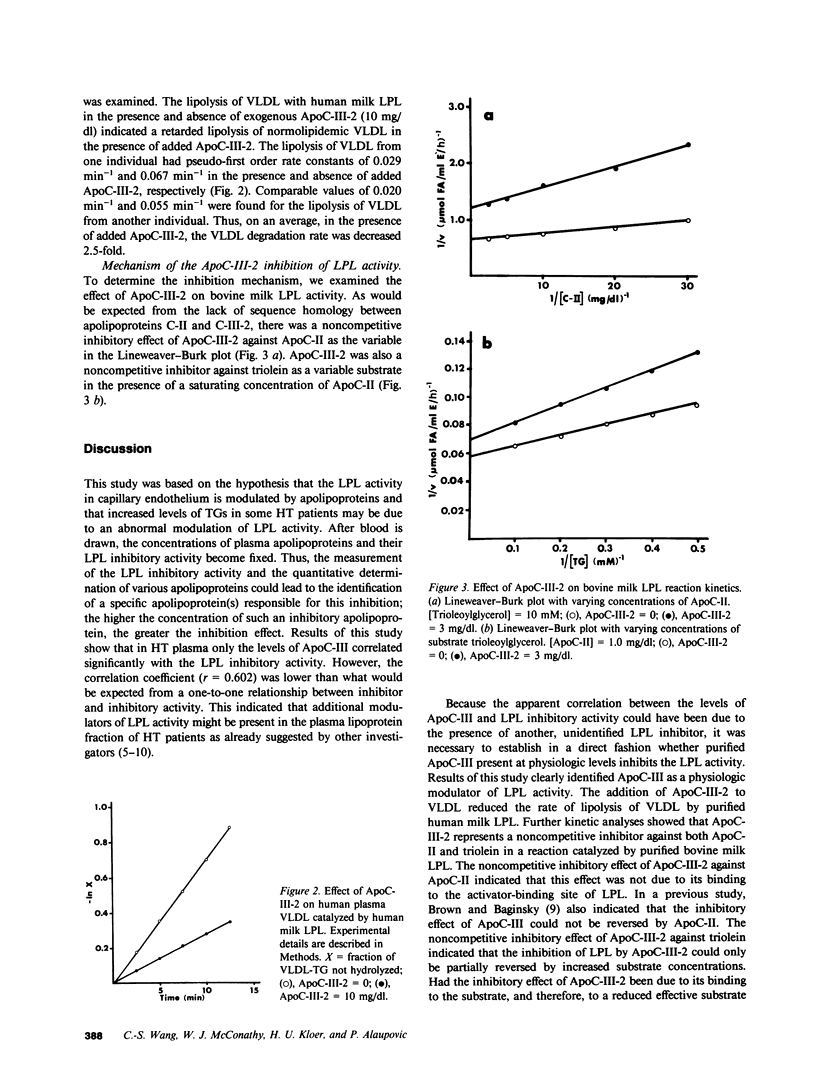
From a total of 22 hypertriglyceridemic subjects tested, 14 subjects were selected on the basis of normal postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase (LPL) levels and the presence of LPL inhibitory activity in their fasting plasma. The inhibitory activity was detected in both the lipoprotein fraction (d less than 1.25 g/ml) and the lipoprotein-deficient fraction (d greater than 1.25 g/ml). Correlational analyses of LPL inhibitory activity and apolipoprotein levels present in the lipoprotein fraction (d less than 1.25 g/ml) indicated that only apolipoprotein C-III (ApoC-III) was significantly correlated (r = 0.602, P less than 0.05) with the inhibition activity of the lipoprotein fraction. Furthermore, it was found that LPL-inhibitory activities of the plasma lipoprotein fraction and lipoprotein-deficient fraction were also correlated (r = 0.745, P less than 0.005), though the activity in the lipoprotein-deficient plasma was not related to the ApoC-III or apolipoprotein E levels. Additional correlational analyses indicated that the LPL levels in the postheparin plasma of these subjects were inversely related to the levels of plasma apolipoproteins C-II, C-III, and E. To explain some of these observations, we directly examined the in vitro effect of ApoC-III on LPL activity. The addition of ApoC-III-2 resulted in a decreased rate of lipolysis of human very low density lipoproteins by LPL. Kinetic analyses indicated that ApoC-III-2 was a noncompetitive inhibitor of LPL suggesting a direct interaction of the inhibitor with LPL. Results of these studies suggest that ApoC-III may represent a physiologic modulator of LPL activity levels and that the incidence of LPL inhibitory activity in the plasma of hypertriglyceridemic subjects is more common than previously recognized.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Ehnholm C., Steinberg D., Brown W. V. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from pig adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2220–2227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Shulman R., Herbert P., Ronan R., Wehrly K. The complete amino acid sequence of alanine apolipoprotein (apoC-3), and apolipoprotein from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4975–4984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Baginsky M. L. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Miller N. E., Alaupovic P., St Hilaire R. J., Wang C. S., Sarson D. L., Bloom S. R., Lewis B. Familial chylomicronemia due to a circulating inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase activity. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):12–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Ballantyne D. Changing relative proportions of apolipoproteins CII and CIII of very low density lipoproteins in hypertriglyceridaemia. Atherosclerosis. 1976 May-Jun;23(3):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Albers J. J., Brunzell J. D. Very low density lipoprotein overproduction in genetic forms of hypertriglyceridaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;10(1):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., Gustafson A., Alaupovic P., McConathy W. J. Electroimmunoassay, radioimmunoassay, and radial immunodiffusion assay evaluated for quantification of human apolipoprotein B. Clin Chem. 1978 Feb;24(2):280–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P., Ledford J. H., Popović M. Determination of human apolipoprotein E by electroimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 9;439(2):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P. Quantitative determination of human apolipoprotein D by electroimmunoassay and radial immunodiffusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):232–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., McConathy W. J., Fesmire J. D., Alaupovic P. Quantitative determination of apolipoproteins C-I and C-II in human plasma by separate electroimmunoassays. Clin Chem. 1981 Apr;27(4):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., McConathy W. J., Fesmire J. D., Alaupovic P. Quantitative determination of human apolipoprotein C-III by electroimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 21;617(3):503–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erkelens D. W., Mocking J. A. The CII/CIII ratio of transferable apolipoprotein in primary and secondary hypertriglyceridemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 May 6;121(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1977 May;101(5):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Mok H. Y., Zech L., Steinberg D., Berman M. Transport of very low density lipoprotein triglycerides in varying degrees of obesity and hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1274–1283. doi: 10.1172/JCI109422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Pattus F., de Haas G. Mechanism of action of milk lipoprotein lipase at substrate interfaces: effects of apolipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 22;19(2):373–378. doi: 10.1021/bi00543a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., McPherson J., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Linkage of human apolipoproteins A-I and C-III genes. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):371–373. doi: 10.1038/304371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Alfarsi S., Adams P. W. Integrated regulation of very low density lipoprotein triglyceride and apolipoprotein-B kinetics in man: normolipemic subjects, familial hypertriglyceridemia and familial combined hyperlipidemia. Metabolism. 1981 Sep;30(9):856–868. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kompiang I. P., Bensadoun A., Yang M. W. Effect of an anti-lipoprotein lipase serum on plasma triglyceride removal. J Lipid Res. 1976 Sep;17(5):498–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Selective measurement of two lipase activities in postheparin plasma from normal subjects and patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1107–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI107855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., Bergseth M., Nestruck A. C. Preparative isoelectric focussing of apolipoproteins C and E from human very low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 27;573(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConathy W. J., Quiroga C., Alaupovic P. Studies of the composition and structure of plasma lipoproteins. C- and N-terminal amino acids of C-I polypeptide ("R-Val") of human plasma apolipoprotein C. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 1;19(4):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz H. G., Matsuoka N., Jackson R. L. Phospholipase activity of bovine milk lipoprotein lipase on phospholipid vesicles: influence of apolipoproteins C-II and C-III. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S. O., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P. Isolation and partial characterization of a new acidic apolipoprotein (apolipoprotein F) from high density lipoproteins of human plasma. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1032–1036. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner I., Wang C. S., McConathy W. J. Kinetics of bovine milk lipoprotein lipase and the mechanism of enzyme activation by apolipoprotein C-II. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4041–4047. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner I., Wang C. S., McConathy W. J. The comparative kinetics of soluble and heparin-Sepharose-immobilized bovine lipoprotein lipase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):306–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Shoulders C. C., Stocks J., Galton D. J., Baralle F. E. DNA polymorphism adjacent to human apoprotein A-1 gene: relation to hypertriglyceridaemia. Lancet. 1983 Feb 26;1(8322):444–446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz M. C., Garfinkel A. S., Huebotter R. J., Stewart J. E. A rapid assay for lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jan;11(1):68–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Rat heart lipoprotein lipase. Atherosclerosis. 1975 Nov-Dec;22(3):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(75)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. S., Bass H. B., Downs D., Whitmer R. K. Modified heparin-Sepharose procedure for determination of plasma lipolytic activities of normolipidemic and hyperlipidemic subjects after injection of heparin. Clin Chem. 1981 May;27(5):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. S. Human milk bile salt-activated lipase. Further characterization and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10198–10202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. S., Weiser D., Alaupovic P., McConathy W. J. Studies on the degradation of human very low density lipoproteins by human milk lipoprotein lipase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Smith R. L. Lowry determination of protein in the presence of Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



