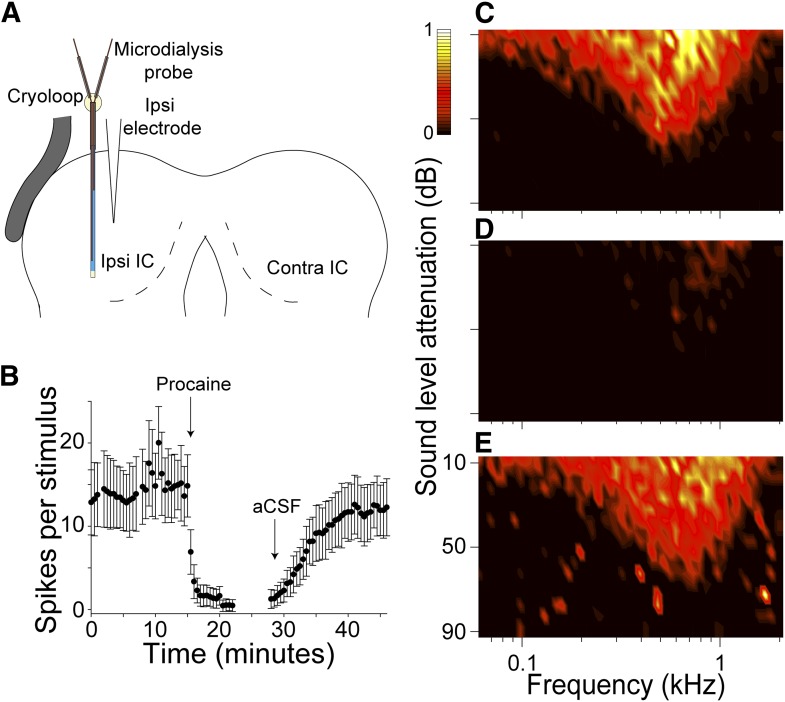
Figure 1. Microdialysis of procaine into the IC produced a rapid, reversible deactivation of spiking.
(A) Schematic coronal image of the setup for recording the effects of procaine on neuronal activity in the left IC. (B) Mean (±SD) firing rate of multi-units recorded by an electrode adjacent to the probe, each point represents the average spikes per stimulus value in response to 100 repetitions of a CF tone at 20 dB above threshold. Procaine caused an immediate and persistent deactivation throughout infusion. After switching back to aCSF, firing recovered to near control levels after 20 min. (C) Multi-unit FRA recorded from an electrode adjacent to the microdialysis probe. (D) Procaine infusion abolished firing at virtually all frequencies and levels. (E) Response area shape and firing rate recovered similar to control.