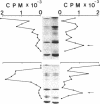
Abstract
When blood coagulation takes place in the presence of calcium ions, alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor (alpha 2PI) is cross-linked to fibrin by activated coagulation Factor XIII (XIIIa) and thereby contributes to the resistance of fibrin to fibrinolysis. It was previously shown that the cross-linking reaction is a reversible one, since the alpha 2PI-fibrinogen cross-linked complex could be dissociated. In the present study we have shown that the alpha 2PI-fibrin cross-linking reaction is also a reversible reaction and alpha 2PI which had been cross-linked to fibrin can be released from fibrin by disrupting the equilibrium, resulting in a decrease of its resistance to fibrinolysis. When the fibrin clot formed from normal plasma in the presence of calcium ions was suspended in alpha 2PI-deficient plasma of buffered saline, alpha 2PI was gradually released from fibrin on incubation. When alpha 2PI was present in the suspending milieu, the release was decreased inversely to the concentrations of alpha 2PI in the suspending milieu. The release was accelerated by supplementing XIIIa or the presence of a high concentration of the NH2-terminal 12-residue peptide of alpha 2PI (N-peptide) which is cross-linked to fibrin in exchange for the release of alpha 2PI. When the release of alpha 2PI from fibrin was accelerated by XIIIa or N-peptide, the fibrin became less resistant to the fibrinolytic process, resulting in an acceleration of fibrinolysis which was proportional to the degree of the release of alpha 2PI. These results suggest the possibility that alpha 2PI could be released from fibrin in vivo by disrupting the equilibrium of the alpha 2PI-fibrin cross-linking reaction, and that the release would result in accelerated thrombolysis.
Full text
PDF

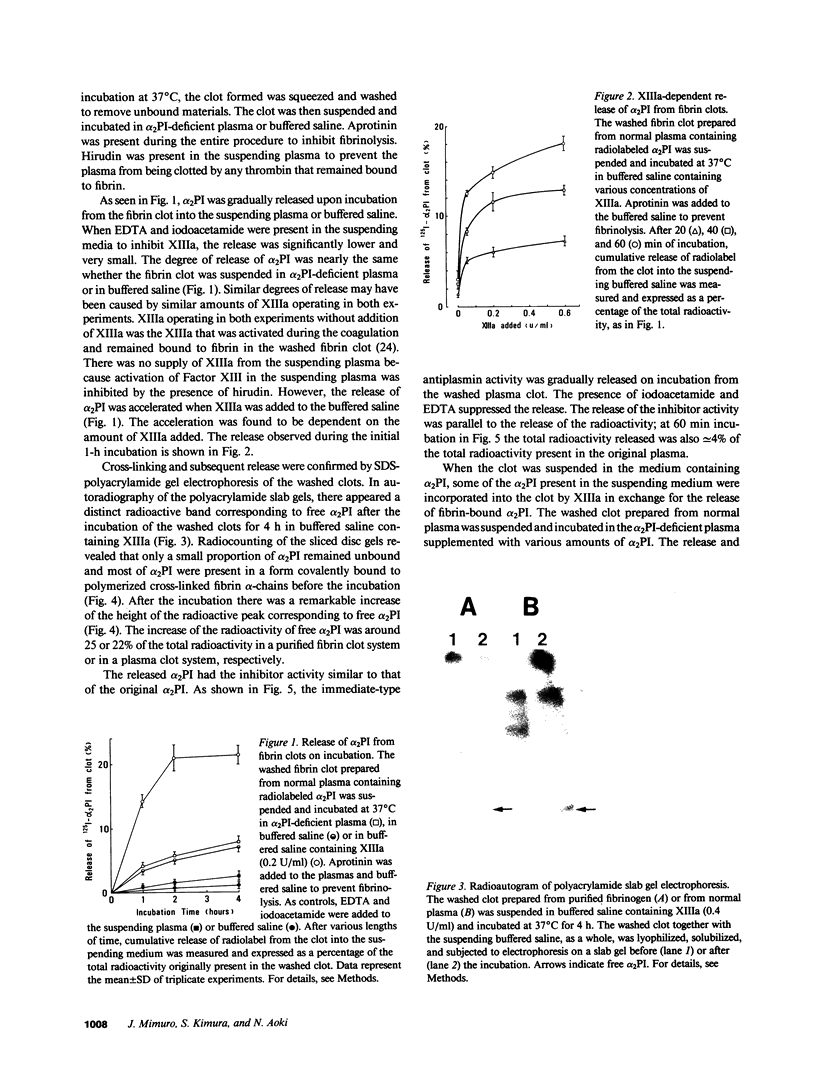
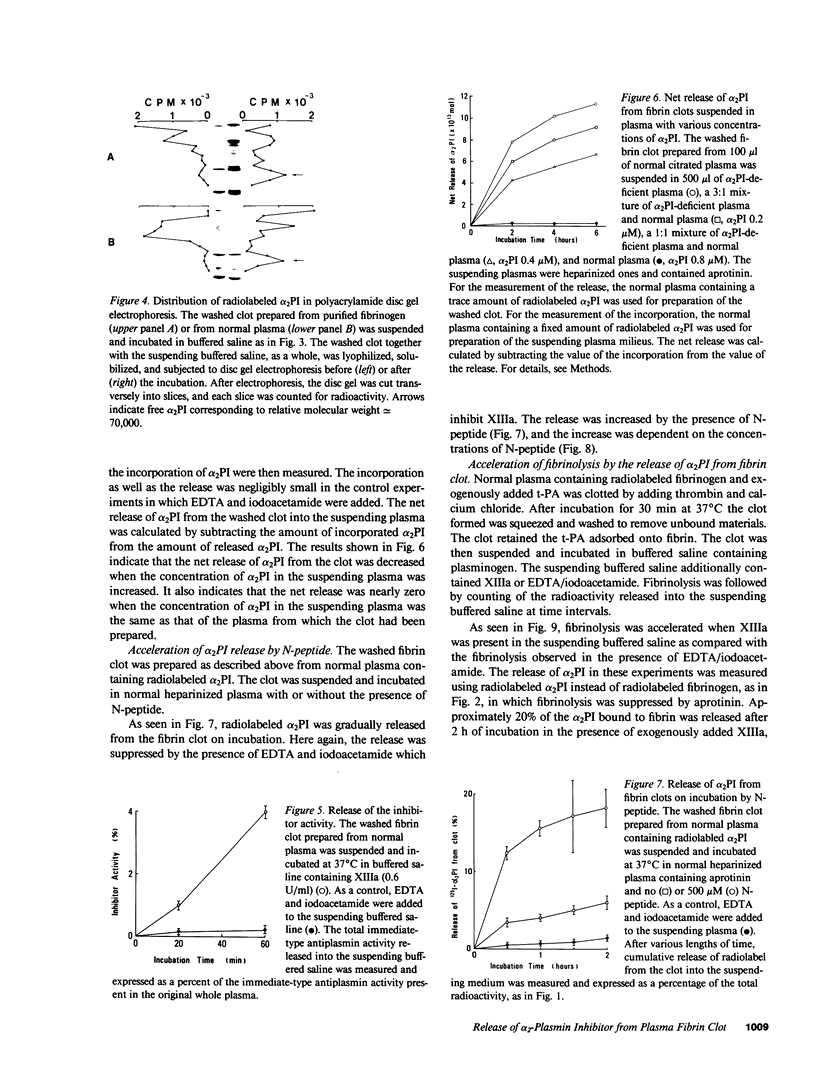
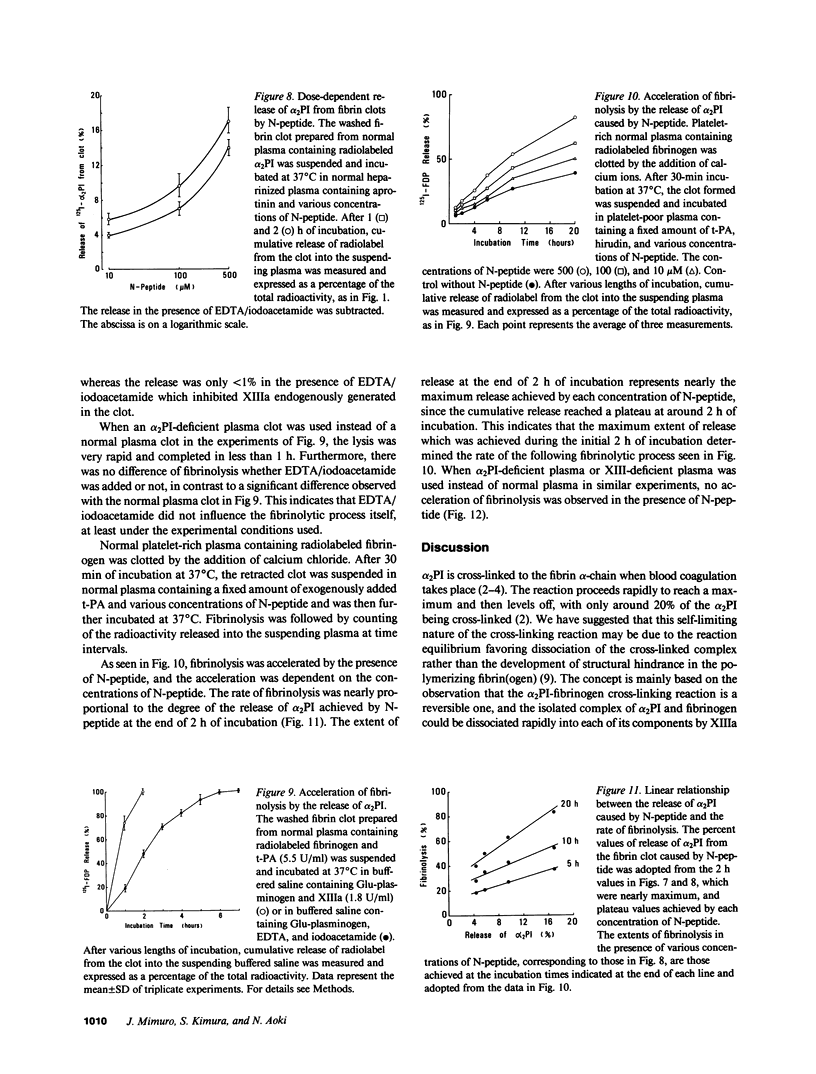



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Harpel P. C. Inhibitors of the fibrinolytic enzyme system. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):24–41. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Matsuda M., Tachiya K. The behavior of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in fibrinolytic states. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI108784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Saito H., Kamiya T., Koie K., Sakata Y., Kobakura M. Congenital deficiency of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor associated with severe hemorrhagic tendency. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):877–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI109387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Sakata Y., Ichinose A. Fibrin-associated plasminogen activation in alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor deficiency. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):1118–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Folk J. E. Kinetic studies with transglutaminases. The human blood enzymes (activated coagulation factor 13 and the guinea pig hair follicle enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2798–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Lewis M. S., Folk J. E. Relationships of the catalytic properties of human plasma and platelet transglutaminases (activated blood coagulation factor XIII) to their subunit structures. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):940–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Verstraete M. alpha 2-Antiplasmin consumption and fibrinogen breakdown during thrombolytic therapy. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):631–639. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Lorand L. Fibrin-stabilizing factor (factor XIII). Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:177–191. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Stenberg P., Chou C. H., Gray A., Brown K. L., Lorand L. Titration and subunit localization of active center cysteine in fibrinoligase (thrombin-activated fibrin stabilizing fector). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90952-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E. Mechanism of action of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. VI. Order of substrate addition. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3707–3713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Yamada K. Role of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor in the appearance of fibrinolytic activity during urokinase administration, and an evaluation of the optimal urokinase dosage. Thromb Res. 1979;16(3-4):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Aoki N. Reversible cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrinogen by fibrin-stabilizing factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 7;706(2):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Tamaki T., Aoki N. Factor XIII-mediated cross-linking of NH2-terminal peptide of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):369–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80645-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Tamaki T., Aoki N. Acceleration of fibrinolysis by the N-terminal peptide of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumada T., Abiko Y. Physiological role of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor in rats. Thromb Res. 1984 Oct 15;36(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Conrad S. M. Transglutaminases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;58(1-2):9–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00240602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Lockridge O. M., Campbell L. K., Myhrman R., Bruner-Lorand J. Transamidating enzymes. II. A continuous fluorescent method suited for automating measurements of factor XIII in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L. A rapid method for the purification of bovine thrombin and the inhibition of the purified enzyme wtih phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2501–2506. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattler L. E., Bang N. U. Serine protease specificity for peptide chromogenic substrates. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Dec 15;38(4):776–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Aoki N. Assay of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor activity by means of a plasmin specific tripeptide substrate. Thromb Res. 1978 Jun;12(6):1147–1156. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):290–297. doi: 10.1172/JCI109671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Significance of cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin in inhibition of fibrinolysis and in hemostasis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI110479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor and fibronectin to fibrin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 13;661(2):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin catalyzed by activated fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14767–14772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento M., Vaheri A. Dissociation of fibronectin from gelatin-agarose by amino compounds. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):333–336. doi: 10.1042/bj1750333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Wiman B. Characterization of human plasminogen. II. Separation and partial characterization of different molecular forms of human plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):122–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]