Abstract
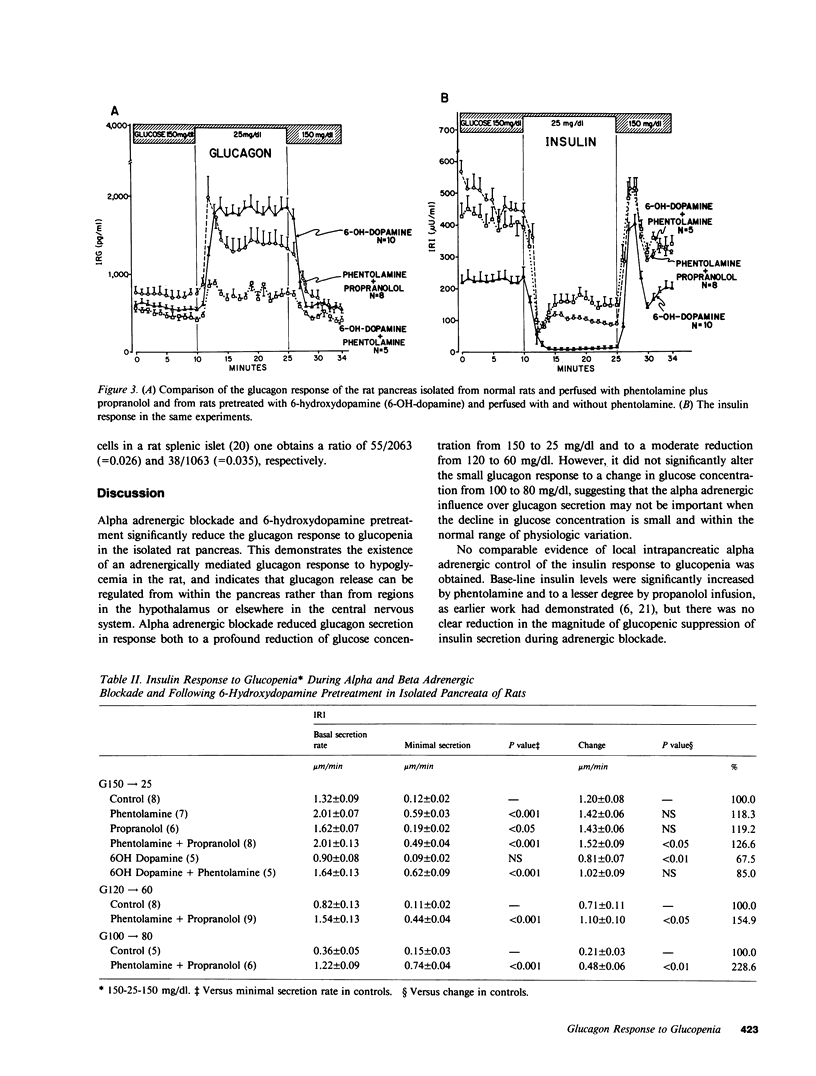
Alpha adrenergic blockade with phentolamine (10 microM) reduces the glucagon response to severe glucopenia (from 150 to 25 mg/dl) to 22% of the control values in the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Propranolol (10 microM) had no significant effect. Neither alpha nor beta adrenergic blockade reduced the magnitude of glucopenic suppression of insulin secretion, but phentolamine increased insulin levels before and during glucopenia. The pattern of somatostatin secretion in these experiments resembled that of insulin. Depletion of norepinephrine from sympathetic nerve endings by pretreatment with 6-hydroxydopamine lowered the pancreatic norepinephrine content to less than 20% of control values and reduced the glucagon response to glucopenia to 69% of the controls. Combined alpha and beta adrenergic blockade during less severe glucopenia (from 120 to 60 mg/dl) reduced the glucagon response to 21% of controls. However, slight glucopenia (from 100 to 80 mg/dl), which elicited only 11% increase in glucagon in the control experiments, was not altered significantly by combined alpha and beta adrenergic blockade. Morphologic studies of adrenergic nerve terminals labeled with [3H]norepinephrine revealed associations with alpha cells. It is concluded that in the isolated rat pancreas adrenergic mediation accounts for most of the glucagon but not insulin response to glucopenia. It is controlled within the pancreas itself, possibly through a direct enhancement by glucopenia of norepinephrine release from nerve endings.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baetens D., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Endocrine pancreas: three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.390711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum D., Porte D., Jr, Ensinck J. Hyperglucagonemia and alpha-adrenergic receptor in acute hypoxia. Am J Physiol. 1979 Nov;237(5):E404–E408. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.5.E404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. The release of pancreatic glucagon and inhibition of insulin in response to stimulation of the sympathetic innervation. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):157–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the autonomic innervation in the control of glucagon release during hypoglycaemia in the calf. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):611–623. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Reichard G. A., Jr, Hoeldtke R. D., Rezvani I., Owen O. E. Severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia associated with deficiencies in the release of counterregulatory hormones. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 12;305(20):1200–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111123052007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Gerich J. E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Interaction of anti-insulin antibodies and impaired glucagon and epinephrine secretion. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):134–141. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cegrell L. The occurrence of biogenic monoamines in the mammalian endocrine pancreas. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1968;314:1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Iversen J. Release of large amounts of noradrenaline from the isolated perfused canine pancreas during glucose deprivation. Diabetologia. 1973 Oct;9(5):396–399. doi: 10.1007/BF01239435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Glucose counterregulation in man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):261–264. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Bernardis L. L. Effect of hypothalamic stimulation on plasma glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1596–1603. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. T., Bailey P. T. The effect of adrenergic and ganglionic blockers upon the L-dopa-stimulated release of glucagon in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jan;157(1):1–4. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-39978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Stimulation of glucagon secretion by epinephrine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Sep;37(3):479–481. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science. 1973 Oct 12;182(4108):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4108.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H. Studies on the mechanism of epinephrine-induced hyperglycemia in man. Evidence for participation of pancreatic glucagon secretion. Diabetes. 1976 Jan;25(1):65–71. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardier L., Seydoux J., Campfield L. A. Control of A and B cells in vivo by sympathetic nervous input and selective hyper or hypoglycemia in dog pancreas. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):801–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Fanska R. E. The in vitro perfused pancreas. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:364–372. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey W. D., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effect of adrenergic blockade on exercise-induced hyperglucagonemia. Endocrinology. 1974 May;94(5):1254–1258. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-5-1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J. Adrenergic receptors and the secretion of glucagon and insulin from the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2102–2116. doi: 10.1172/JCI107395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Ensinck J. W. Stimulation of glucagon secretion by scorpion toxin in the perfused rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1976 Aug;25(8):645–649. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.8.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kajinuma H., Kosaka K. Effect of alpha adrenoreceptor stimulants infused intrapancreatically on glucagon and insulin secretion. Horm Metab Res. 1977 Jul;9(4):267–271. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kajinuma H., Kosaka K. Effect of splanchnic nerve stimulation on glucagon and insulin output in the dog. Endocrinology. 1975 Jan;96(1):143–150. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik K. U., McGiff J. C. Relationship of glucose metabolism to adrenergic transmission in rat mesenteric arteries. Effects of glucose deprivation, glucose metabolites, and changes in ionic composition on adrenergic mechanisms. Circ Res. 1974 Oct;35(4):553–574. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Henry D. P., Benson J. W., Johnson D. G., Ensinck J. W. Glucagon response to hypoglycemia in sympathectomized man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):522–525. doi: 10.1172/JCI108305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refshauge C., Kissinger P. T., Dreiling R., Blank L., Freeman R., Adams R. N. New high performance liquid chromatographic analysis of brain catecholamines. Life Sci. 1974 Jan 16;14(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Weir G. C. Adrenergic modulation of pancreatic A, B, and D cells alpha-Adrenergic suppression and beta-adrenergic stimulation of somatostatin secretion, alpha-adrenergic stimulation of glucagon secretion in the perfused dog pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):230–238. doi: 10.1172/JCI109294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez B., Harris V., Unger R. H. Extraction of somatostatin from human plasma on octadecylsilyl silica. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Oct;55(4):807–809. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-4-807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R. M., Dudl R. J., Palmer J. P., Ensinck J. W. The effect of adrenergic blockade on the glucagon responses to starvation and hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1214–1220. doi: 10.1172/JCI107864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Knowlton S. D., Martin D. B. Glucagon secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. Studies with glucose and catecholamines. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1403–1412. doi: 10.1172/JCI107887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




