Abstract
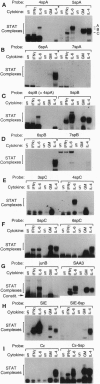
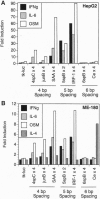
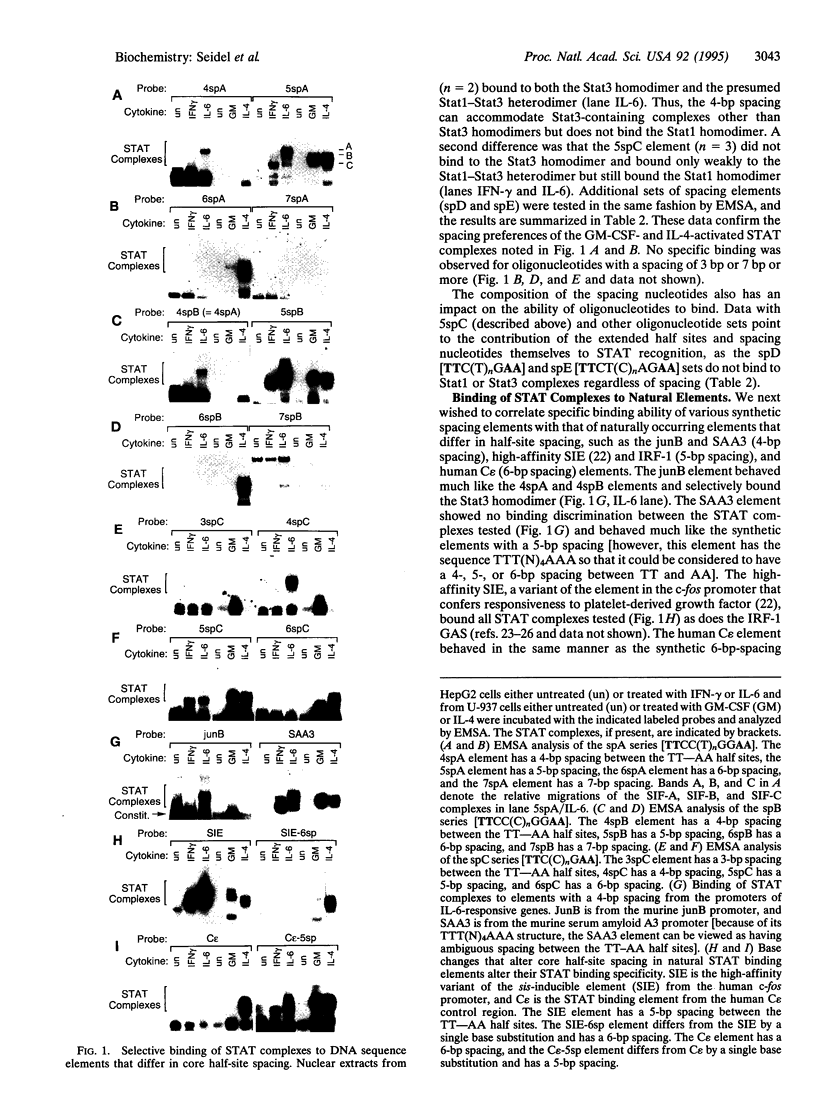
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT proteins) bind to palindromic sequence elements related to interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) activation sites, which were first identified in the promoters of IFN-gamma-inducible genes. Although the sequences of the natural palindromic STAT-binding elements vary considerably, they conform to the general structure TT(N)5AA. We have systematically examined the effects of the spacing between the TT and AA core half sites on the binding of the STAT complexes activated by IFN-gamma, interleukin (IL) 6, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and IL-4. We show that (i) as suggested earlier, a core palindromic TT--AA motif with a 5-bp spacing displays general STAT binding, (ii) a palindromic motif with a spacing of 4 bp selectively binds to complexes containing Stat3, and (iii) a motif with a 6-bp spacing selectively binds the STAT complexes activated by IL-4. We have examined natural elements in the promoters of cytokine-responsive genes that differ in half-site spacing and found that they display binding properties predicted from the synthetic binding sites. Furthermore, the observed differential selective binding characteristics for the most part correlate with the ability to mediate transcriptional activation of transfected test genes in response to the cytokines tested. Our results thus demonstrate that the specificity of STAT-directed transcription in response to particular cytokines or cytokine families depends in part on the spacing of half sites within the conserved response element sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg C. RXR-independent action of the receptors for thyroid hormone, retinoid acid and vitamin D on inverted palindromes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 30;195(3):1345–1353. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Abraham L. J., Northemann W., Fey G. H. Acute-phase reaction induces a specific complex between hepatic nuclear proteins and the interleukin 6 response element of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2364–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Ho T. C., Brasseur M., McKnight S. L. An interleukin-4-induced transcription factor: IL-4 Stat. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1701–1706. doi: 10.1126/science.8085155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Yamamoto K., Thierfelder W. E., Kreider B., Silvennoinen O. Signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily: JAKs and STATs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Kozak C. A., Schindler C., Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ozato K. The genomic structure of the murine ICSBP gene reveals the presence of the gamma interferon-responsive element, to which an ISGF3 alpha subunit (or similar) molecule binds. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3951–3963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Taga T., Akira S. Cytokine signal transduction. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Harada N., Yokota T., Arai K. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:295–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Kusafuka T., Takeda T., Fujitani Y., Nakae K., Hirano T. Identification of a novel interleukin-6 response element containing an Ets-binding site and a CRE-like site in the junB promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3027–3041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz R., Durbin J. E., Levy D. E. Acute phase response factor and additional members of the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 family integrate diverse signals from cytokines, interferons, and growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24391–24395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman P., Chen Y. Y., Lutzker S., Li S. C., Stewart V., Coffman R., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of germ line immunoglobulin heavy-chain epsilon transcripts: interleukin-4 plus lipopolysaccharide-directed switching to C epsilon. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1672–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Kashleva H., Pernis A., Pine R., Rothman P. STF-IL-4: a novel IL-4-induced signal transducing factor. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1350–1356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Mizuta T. R., Kanamori H., Suzuki N., Okamoto M., Kuze K., Ohno H., Doi S., Fukuhara S., Hassan M. S. Production of sterile transcripts of C gamma genes in an IgM-producing human neoplastic B cell line that switches to IgG-producing cells. Int Immunol. 1989;1(6):631–642. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. H., Cha Y., Romine M. F., Gao P. Q., Gottlieb K., Deisseroth A. B. A novel interferon-inducible domain: structural and functional analysis of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):690–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. The alphas, betas, and kinases of cytokine receptor complexes. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90506-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter U., Texido G., Hofstetter H. Expression of human lymphocyte IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RII/CD23). Identification of the Fc epsilon RIIa promoter and its functional analysis in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):3087–3092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Z., Stavnezer J. Regulation of transcription of immunoglobulin germ-line gamma 1 RNA: analysis of the promoter/enhancer. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):145–155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05037.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Decker T., Schindler C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The signalling pathways of interleukin-6 and gamma interferon converge by the activation of different transcription factors which bind to common responsive DNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1657–1668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]