Abstract
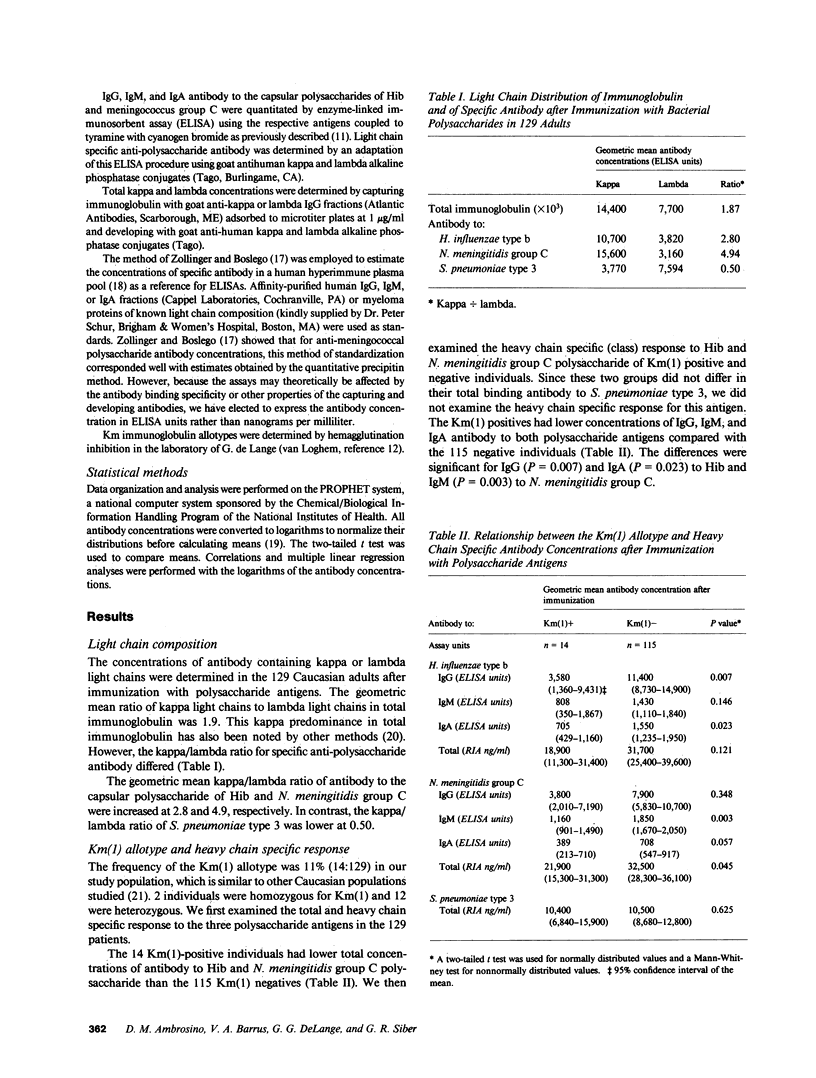
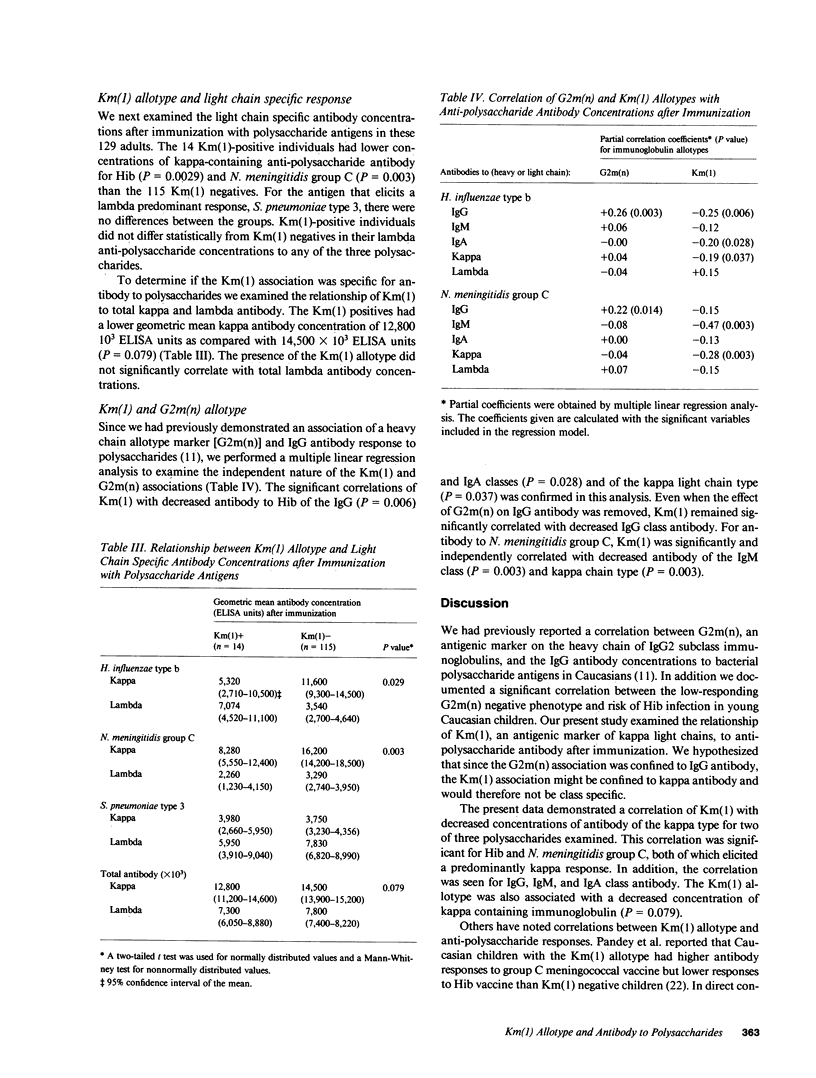
Km allotype antigens are serologic markers expressed on kappa light chains of human immunoglobulins. To determine whether th Km phenotype of an individual is related to his ability to make antibodies to polysaccharide antigens, we correlated the Km allotypes of 129 healthy caucasian adults with the concentrations of specific antibodies to three bacterial polysaccharide antigens after immunization. The 14 individuals expressing the Km(1) allotype had lower concentrations of IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and total antibody by radioimmunoassay to Haemophilus influenzae type b and Neisseria meningitidis group C capsular polysaccharides when compared with the 115 Km(1) negative individuals. The Km-associated differences in H. influenzae type b and N. meningitidis group C antibody concentrations were confined to kappa light chain-containing antibody (P = 0.029 and 0.003, respectively). Similarly, the Km(1) positives had slightly lower kappa chain-containing Ig than the Km(1) negatives (P = 0.079). We conclude that genes in or near the kappa light chain locus play a role in the regulation of kappa-containing antibody production to some bacterial polysaccharides and perhaps to other antigens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrosino D. M., Schiffman G., Gotschlich E. C., Schur P. H., Rosenberg G. A., DeLange G. G., van Loghem E., Siber G. R. Correlation between G2m(n) immunoglobulin allotype and human antibody response and susceptibility to polysaccharide encapsulated bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1935–1942. doi: 10.1172/JCI111909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosino D., Schreiber J. R., Daum R. S., Siber G. R. Efficacy of human hyperimmune globulin in prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in infant rats. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):709–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.709-714.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Gold R., Zimmerly J. G., Wyle F. A., Schneider H., Harkins C. Prevention of meningococcal disease by group C polysaccharide vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 19;282(8):417–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002192820803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R. Some observations on the pneumococcus and on the current status of pneumococcal disease and its prevention. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3 (Suppl):S1–17. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.supplement_1.s1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulehan J. L., Michaels R. H., Williams K. E., Lemley D. K., North C. Q., Jr, Welty T. K., Rogers K. D. Bacterial meningitis in Navojo Indians. Public Health Rep. 1976 Sep-Oct;91(5):464–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G. R., Volkers W. S., Bernini L. F., van Loghem E., Meera Khan P., Nijenhuis L. E. Gene frequencies in a Dutch population. Hum Hered. 1974;24(5-6):435–448. doi: 10.1159/000152680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Rey M., Triau R., Sparks K. J. Quantitative determination of the human immune response to immunization with meningococcal vaccines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):89–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI106801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Pandey J. P., Boies E., Squires J., Munson R. S., Jr, Suarez B. Response to immunization with Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-pertussis vaccine and risk of Haemophilus meningitis in children with the Km(1) immunoglobulin allotype. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1708–1714. doi: 10.1172/JCI111588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Squires J. E., Munson R. S., Jr, Suarez B. Siblings of patients with Haemophilus meningitis have impaired anticapsular antibody responses to Haemophilus vaccine. J Pediatr. 1983 Aug;103(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Okumura K., Cantor H., Sato V. L., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Herzenberg L. A. T-cell regulation of antibody responses: demonstration of allotype-specific helper T cells and their specific removal by suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):330–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzelberger D., Eichmann K. Recognition of idiotypes in lymphocyte interactions. I. Idiotypic selectivity in the cooperation between T and B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Dec;8(12):846–852. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Michaels R. H., Melish M. Effect of previous infection on antibody response of children to vaccination with capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae Type b. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt N., Haber J., Wortis H. H. Influence of Igh-linked gene products on the generation of T helper cells in the response to sheep erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1225–1235. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Anderson P., Ingram D. L., Peter G., Smith D. H. Circulating polyribophosphate in Hemophilus influenzae, type b meningitis. Correlation with clinical course and antibody response. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1012–1022. doi: 10.1172/JCI108148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Fudenberg H. H., Virella G., Kyong C. U., Loadholt C. B., Galbraith R. M., Gotschlich E. C., Parke J. C., Jr Association between immunoglobulin allotypes and immune responses to Haemophilus influenzae and Meningococcus polysaccharides. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):190–192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Käyhty H., Sivonen A., Mäkelä H. Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide vaccine in children: a double-blind field study of 100,000 vaccinees 3 months to 5 years of age in Finland. Pediatrics. 1977 Nov;60(5):730–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman G., Douglas R. M., Bonner M. J., Robbins M., Austrian R. A radioimmunoassay for immunologic phenomena in pneumococcal disease and for the antibody response to pneumococcal vaccines. I. Method for the radioimmunoassay of anticapsular antibodies and comparison with other techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(2):133–144. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(80)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Rodrigues L. P., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Immunity to disease caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b. II. Specificity and some biologic characteristics of "natural," infection-acquired, and immunization-induced antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1081–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Ransil B. J. Methods for the analysis of antibody responses to vaccines or other immune stimuli. Methods Enzymol. 1983;93:60–78. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)93034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Schur P. H., Aisenberg A. C., Weitzman S. A., Schiffman G. Correlation between serum IgG-2 concentrations and the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F., Barandun S., Kuffer F., Probst M. Veränderungen des kappa/lambda-Verhältnisses der menschlichen Serumimmunglobuline im Verlaufe der Entwicklung. Blut. 1976 Oct;33(4):281–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00995225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. I., Margolis H. S., Lum M. K., Fraser D. W., Bender T. R., Anderson P. Haemophilus influenzae disease in Alaskan Eskimos: characteristics of a population with an unusual incidence of invasive disease. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1281–1285. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whisnant J. K., Rogentine G. N., Gralnick M. A., Schlesselman J. J., Robbins J. B. Host factors and antibody response Haemophilus influenza type b meningitis and epiglottitis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Apr;133(4):448–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland R., Cantor H. Idiotype-specific T helper cells are required to induce idiotype-positive B memory cells to secrete antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):600–606. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Boslego J. W. A general approach to standardization of the solid-phase radioimmunoassay for quantitation of class-specific antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


