Abstract
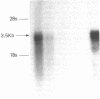
Atrophoderma is a rare dermal disorder characterized by a patchy distribution of areas apparently devoid of elastic fibers. Skin fibroblast cultures were established from the normal and affected dermis of a patient with this disorder. Human tropoelastin was identified in culture medium by use of electroblotting and anti-elastin antisera. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to establish that significantly less elastin accumulated in the media of cultured cells from lesional fibroblasts over a 3-d period. Since elastin biosynthesis in most tissues is under pretranslational control, molecular hybridization to a nick-translated genomic elastin probe was performed; however, elastin messenger RNA levels were equivalent in both cell strains. Both strains produced less elastin than did normal skin fibroblasts. Extracellular proteolysis of elastin was evaluated as a possible mechanism. Elastase activity was increased and porcine tropoelastin was degraded four times faster, on a per-cell basis, in lesional fibroblast cultures than in cells derived from an unaffected site. The two cell strains exhibited no significant differences in collagen production or collagenase activity. These results are the first demonstration of elastin production by cultured human skin fibroblasts, and they suggest that the primary defect in atrophoderma may be a result of enhanced degradation of newly synthesized elastin precursors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer E. A., Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Collagenase production by human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):232–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieth J., Spiess B., Wermuth C. G. The synthesis and analytical use of a highly sensitive and convenient substrate of elastase. Biochem Med. 1974 Dec;11(4):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Polak K. L., Uitto J. Collagen biosynthesis by human skin fibroblasts. I. Optimization of the culture conditions for synthesis of type I and type III procollagens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 28;607(1):145–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Crystal R. G. The molecular aspects of elastin gene expression. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79 (Suppl 1):133s–137s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12546011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Shibahara S., Boyd C., Mason M. L., Tolstoshev P., Crystal R. G. Elastin mRNA levels during foetal development of sheep nuchal ligament and lung. Hybridization to complementary and cloned DNA. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):653–663. doi: 10.1042/bj2200653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Shibahara S., Schafer M. P., Harrison M., Leach C., Tolstoshev P., Crystal R. G. Sheep elastin genes. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a 9.9-kilobase genomic clone. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):643–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2200643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A. Elastin structure and biosynthesis: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):559–570. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Rich C. B., Karr S. R. Elastin gene expression. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:65–95. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau C., Faris B. Biosynthesis of insoluble elastin in cell and organ cultures. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):615–637. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. The cell biology of aging. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Jul;73(1):8–14. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12532752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Davidson J. M., Rennard S., Szapiel S., Gadek J. E., Crystal R. G. Elastin fragments attract macrophage precursors to diseased sites in pulmonary emphysema. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):925–927. doi: 10.1126/science.7233186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Anderson C. W. Block to multiplication of adenovirus serotype 2 in monkey cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1650–1668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1650-1668.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom J. Biosynthesis of soluble elastin in organ and cell culture. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):716–731. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryhänen L., Rantala-Ryhänen S., Tan E. M., Uitto J. Assay of collagenase activity by a rapid, sensitive, and specific method. Coll Relat Res. 1982 Mar;2(2):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(82)80028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg L. B., Soskel N. T., Leslie J. G. Elastin structure, biosynthesis, and relation to disease states. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 5;304(10):566–579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103053041004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Mecham R. P. Chemotactic activity of elastin-derived peptides. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):859–862. doi: 10.1172/JCI109926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Paul J. L., Brockley K., Pearce R. H., Clark J. G. Elastic fibers in human skin: quantitation of elastic fibers by computerized digital image analyses and determination of elastin by radioimmunoassay of desmosine. Lab Invest. 1983 Oct;49(4):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Ryhänen L., Abraham P. A., Perejda A. J. Elastin in diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79 (Suppl 1):160s–168s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12546063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
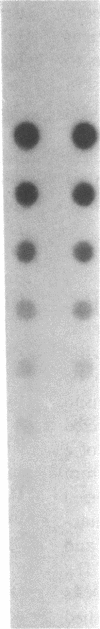
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]