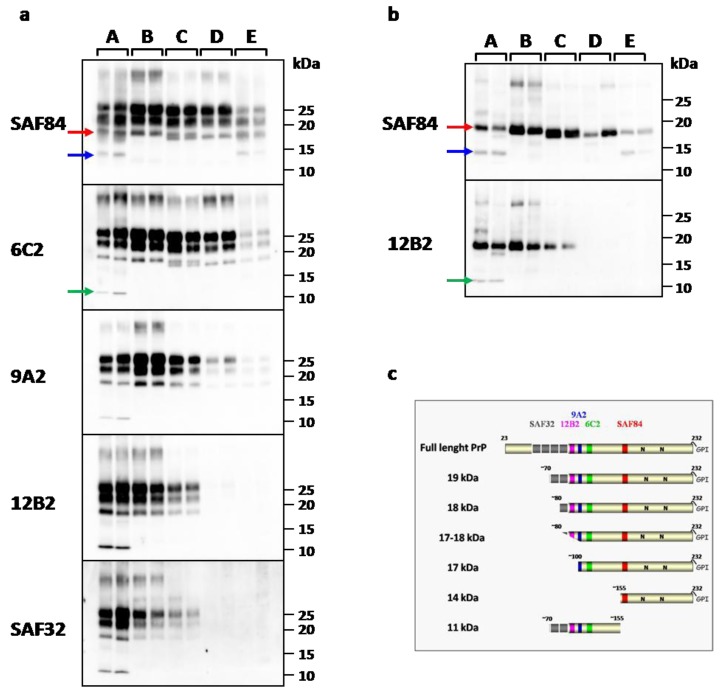
Figure 1.
(a) Western Blot analysis of PK resistant PrPSc in representative vole-adapted prion strains. Replica blots were probed with different monoclonal antibodies indicated on the left of each blot. Representative samples for each PrPres type were loaded from the highest (type A) to the lowest (types D and E) MW, as reflected by the progressive loss of N-terminal epitopes. PrPres types are indicated on the top of the blots. Type A (lanes 1-2): CJD type 1; type B (lanes 3-4): sheep scrapie It93 and UK85; type C (lanes 5-6): sCJD MV2; type D (lanes 7-8): BSE; type E (lanes 9-10): sCJD MM2; (b) Samples shown in (a) after deglycosylation. (a,b) Red Arrow: 19 kDa fragment; blue arrow: 14 kDa fragment; green arrow: 11 kDa fragment. (c) Schematic representation of full length PrP and PrPres fragments identified by epitope mapping and deglycosylation. The cleavage sites were determinate by the presence or absence of epitopes examinated (a). The presence of glycosylation sites were confirmed by deglycosylation treatment (b). The location of SAF32, 12B2, 9A2, 6C2, SAF84 mAbs used for the PrPres-epitope mapping are shown.