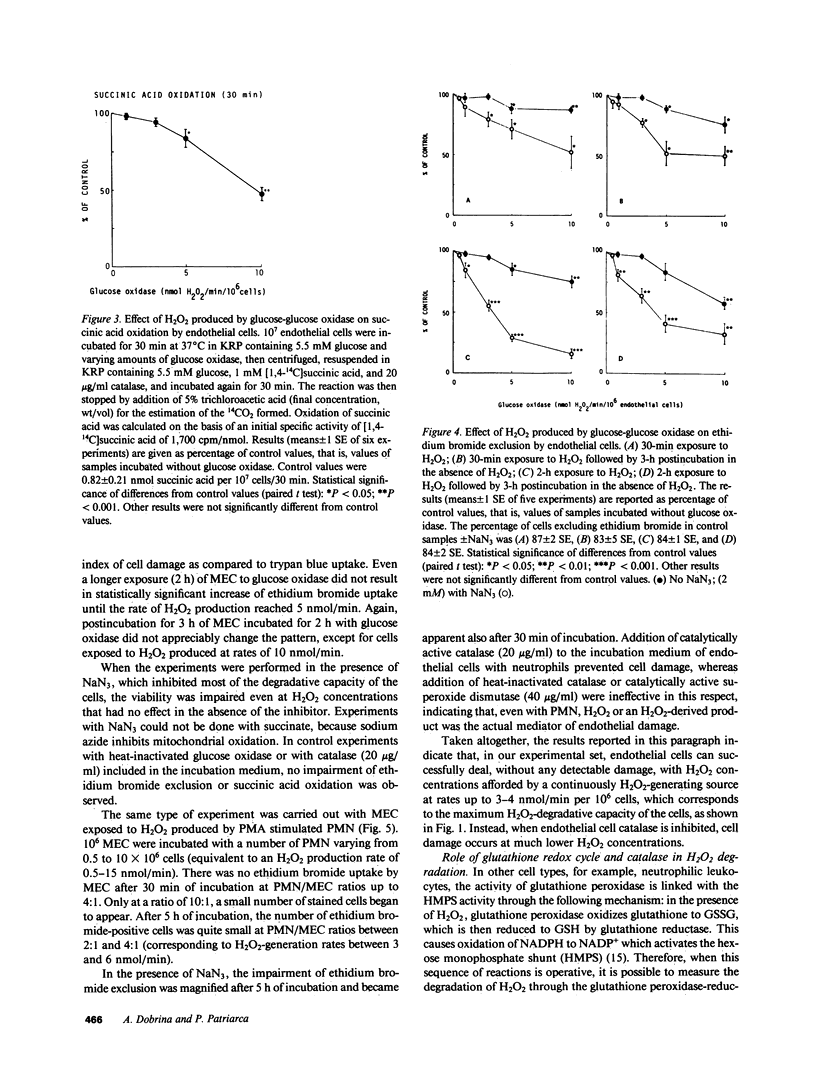
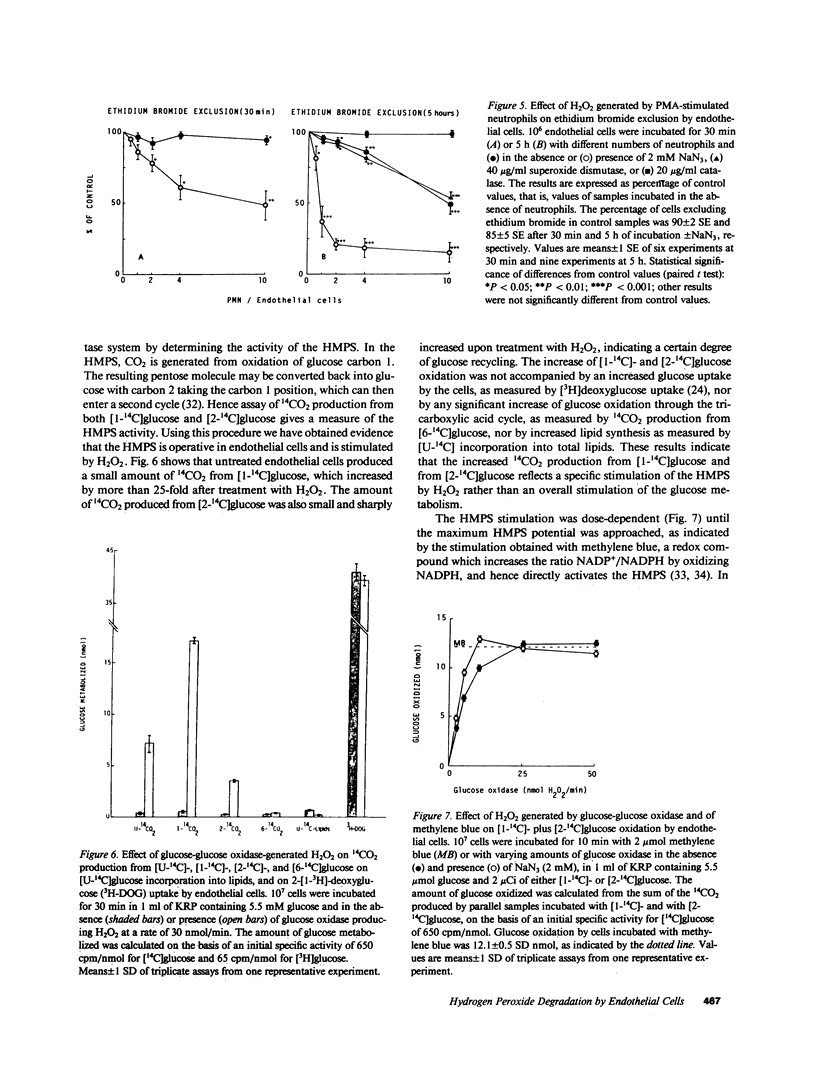
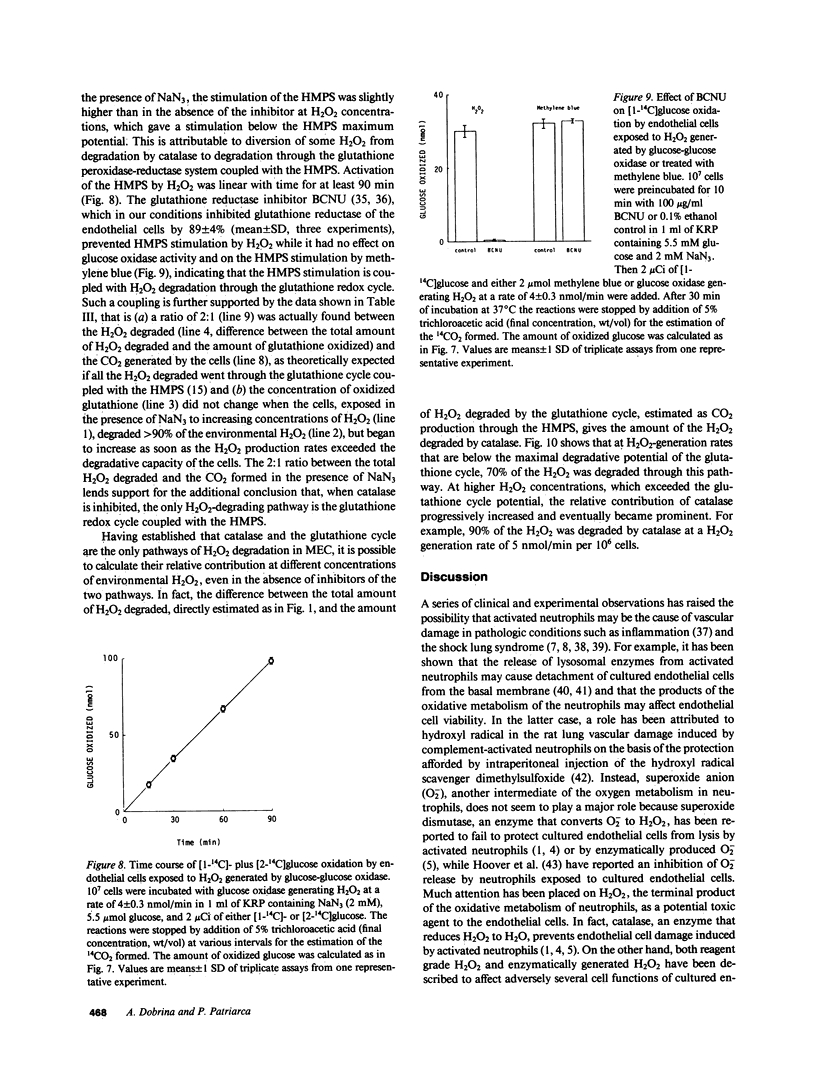
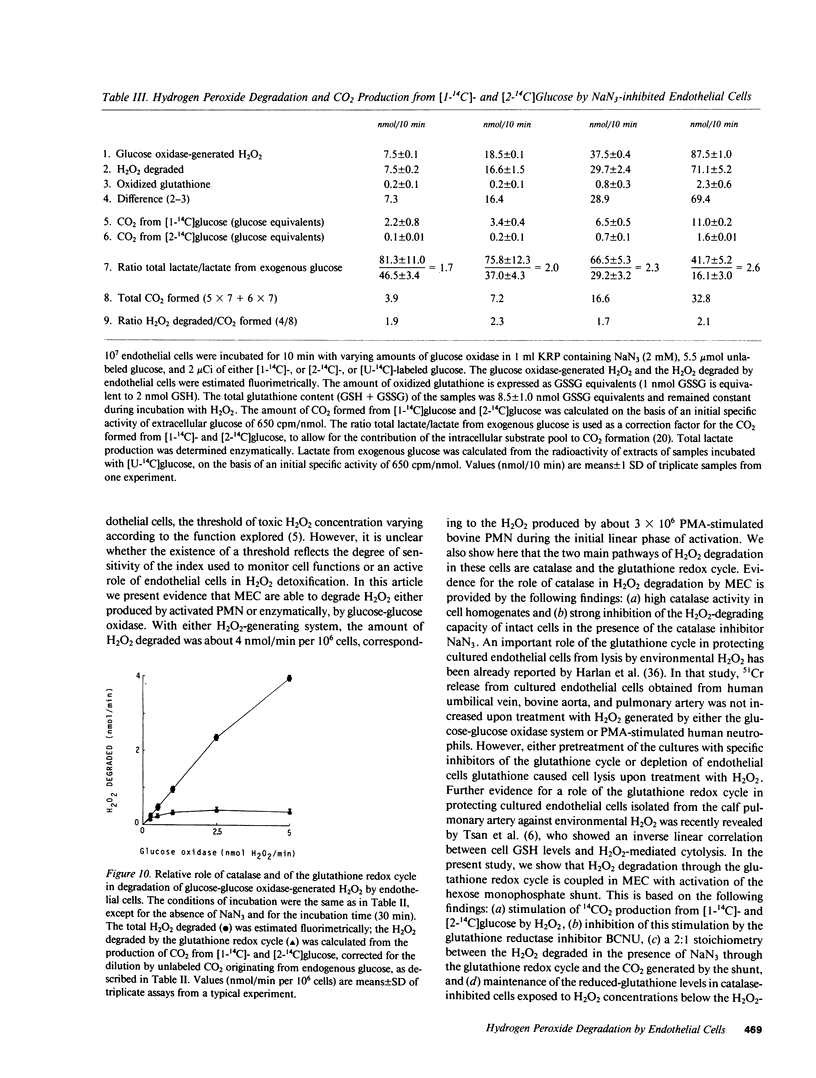
Abstract
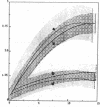
Bovine microvascular endothelial cells (MEC) were able to degrade the H2O2 generated by phorbol myristate acetate-activated bovine neutrophils or by glucose oxidase with a maximal capacity of 4.0 +/- 1.2 (SD) nmol/10(6) cells/min, corresponding to the H2O2 released by about 3 X 10(6) neutrophils. H2O2 degradation occurred via the glutathione redox cycle and catalase. Degradation via the glutathione redox cycle was coupled with a marked stimulation of the hexose monophosphate shunt activity. The effect of H2O2 on ethidium bromide exclusion and on succinate oxidation was studied. Neither parameter was altered when MEC were exposed to H2O2 produced at rates within their degradative capacity. As soon as this was exceeded, impairment of both functions occurred. It is concluded that endothelial cells can protect themselves from H2O2-induced injury in a well-defined range of environmental H2O2 concentrations by actively degrading the peroxide.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ager A., Gordon J. L. Differential effects of hydrogen peroxide on indices of endothelial cell function. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):592–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIN M., YONEMOTO R. H. Stimulation of the glucose oxidative pathway in human erythrocytes by methylene blue. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):307–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babson J. R., Reed D. J. Inactivation of glutathione reductase by 2-chloroethyl nitrosourea-derived isocyanates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jul 28;83(2):754–762. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellavite P., Dri P., Bisiacchi B., Patriarca P. Catalase deficiency in myeloperoxidase deficient polymorphonuclear leucocytes from chicken. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 1;81(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80931-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson G. P., Kaneko J. J. Isolation of leukocytes from bovine peripheral blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):853–856. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogen R. B., Taubman S. B., Tuddenham E. G. Detachment of endothelial cells by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro: potentiation by antibody coating and prevention by inflammatory exudate. J Periodontol. 1981 Nov;52(11):668–672. doi: 10.1902/jop.1981.52.11.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrina A., Rossi F. Metabolic properties of freshly isolated bovine endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 5;762(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrina A., Soranzo M. R., Rossi F. Isolation of metabolically active endothelial cells in high yield from bovine cavernous bodies. A model for functional studies on freshly isolated microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;232(3):579–591. doi: 10.1007/BF00216430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dri P., Bisiacchi B., Cramer R., Bellavite P., de Nicola G., Patriarca P. Oxidative metabolism of chicken polymorphonuclear leucocytes during phagocytosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Dec 22;22(2-3):159–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00496242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dri P., Cramer R., Soranzo M. R., Comin A., Miotti V., Patriarca P. New approaches to the detection of myeloperoxidase deficiency. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):323–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):412–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro R., Schneider C., de Nicola G., Cian F., Romeo D. Biochemical properties of bovine granulocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Mar;157(3):342–347. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Callahan K. S. Role of hydrogen peroxide in the neutrophil-mediated release of prostacyclin from cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI111440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Killen P. D., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Wright D. G. Neutrophil-mediated endothelial injury in vitro mechanisms of cell detachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Levine J. D., Callahan K. S., Schwartz B. R., Harker L. A. Glutathione redox cycle protects cultured endothelial cells against lysis by extracellularly generated hydrogen peroxide. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):706–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI111263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs E. A., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Inflammatory effects of prostacyclin (PGI2) and 6-oxo-PGF1alpha in the rat paw. Prostaglandins. 1978 Aug;16(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall C. E., Bass D. A., Cousart S., DeChatelet L. R. Enhancement of hexose uptake in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by activated complement component C5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5896–5900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Harkin M. M., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Suppression by superoxide dismutase of immune-complex--induced pulmonary alveolitis and dermal inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jan;102(1):55–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Showell H. J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Transport of sodium, potassium, and calcium across rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Effect of chemotactic factor. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):428–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. P., Kiesow L. A. Enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase at 25 degrees C (with molar extinction coefficients of H 2 O 2 solutions in the UV). Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):474–478. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWENS C. W., BELCHER R. V. A COLORIMETRIC MICRO-METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF GLUTATHIONE. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:705–711. doi: 10.1042/bj0940705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W. Glutathione and the hexose monophosphate shunt in phagocytizing and hydrogen peroxide-treated rat leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2459–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory-distress syndrome: changing concepts of lung injury and repair. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):900–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Zabucchi G., Marzi T., Rossi F. Kinetic and enzymatic features of metabolic stimulation of alveolar and peritoneal macrophages challenged with bacteria. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Apr;78(2):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth E. F., Jr, Nagel R. L., Neuman G., Vanderhoff G., Kaplan B. H., Jaffé E. R. Metabolic effects of antisickling amounts of nitrogen and nor-nitrogen mustard on rabbit and human erythrocytes. Blood. 1975 Jun;45(6):779–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnells G., Voigt W. H., Redl H., Schlag G., Glatzl A. Electron-microscopic investigation of lung biopsies in patients with post-traumatic respiratory insufficiency. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1980;499:9–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Simon L. M. Lung cell oxidant injury. Enhancement of polymorphonuclear leukocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in lung cells exposed to sustained in vitro hyperoxia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):342–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI110623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., Danis E. H., Del Vecchio P. J., Rosano C. L. Enhancement of intracellular glutathione protects endothelial cells against oxidant damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):270–276. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voetman A. A., Loos J. A., Roos D. Changes in the levels of glutathione in phagocytosing human neutrophils. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):741–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voetman A. A., Roos D. Endogenous catalase protects human blood phagocytes against oxidative damage by extracellularly generated hydrogen peroxide. Blood. 1980 Nov;56(5):846–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. G., KATZ J. The distribution of C14 in the hexose phosphates and the effect of recycling in the pentose cycle. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1279–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Till G. O., Kunkel R., Beauchamp C. Evidence for role of hydroxyl radical in complement and neutrophil-dependent tissue injury. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):789–801. doi: 10.1172/JCI111050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Morley J. Prostaglandins as potentiators of increased vascular permeability in inflammation. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):215–217. doi: 10.1038/246215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Peck M. J. Role of prostaglandin-mediated vasodilatation in inflammation. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):530–532. doi: 10.1038/270530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada O., Moldow C. F., Sacks T., Craddock P. R., Boogaerts M. A., Jacob H. S. Deleterious effects of endotoxin on cultured endothelial cells: an in vitro model of vascular injury. Inflammation. 1981 Jun;5(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00914201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]