Abstract
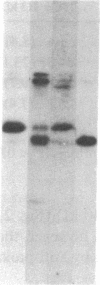
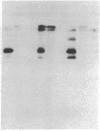
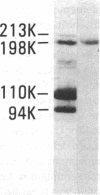
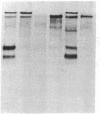
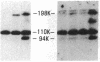
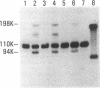
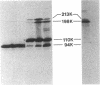
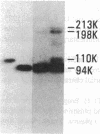
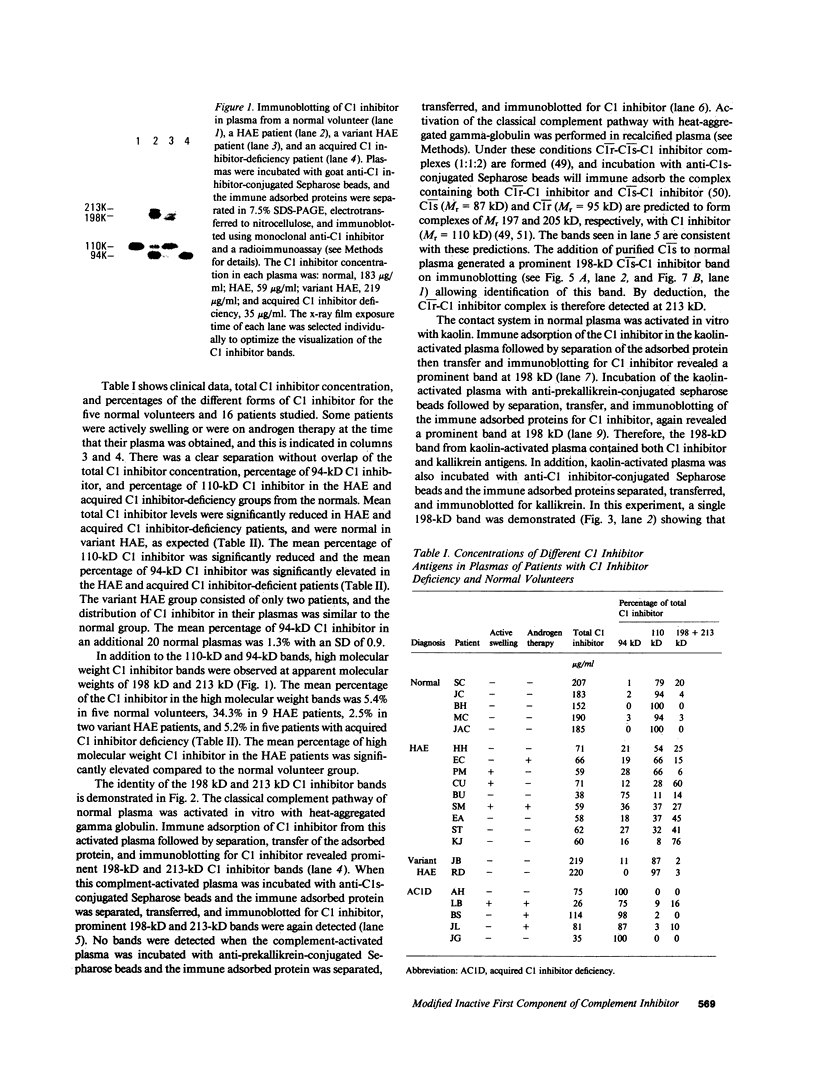
The first component of complement (C1) inhibitor plays a critical role in the regulation of the classical complement pathway and the contact system, and the deficiency of C1 inhibitor protein or function is associated with recurrent angioedema. In this study we evaluated the size of the C1 inhibitor antigens present in the plasmas of C1 inhibitor-deficient patients. We found that the C1 inhibitor in the plasmas existed in three forms: high molecular weight forms in complex with proteases, native 110-kD C1 inhibitor, and a modified inactive 94-kD form. The proportion of the total C1 inhibitor in the 94-kD form was 28% in nine hereditary angioedema patients, 92% in five acquired C1 inhibitor-deficiency patients, and 1.2% in five normal controls. In vitro activation of normal plasma with kaolin, but not heat-aggregated gamma-globulin generated 94-kD C1 inhibitor from 110-kD C1 inhibitor. Neither kaolin activation nor heat-aggregated gamma-globulin activation generated 94-kD C1 inhibitor in Hageman factor-deficient plasma. These results suggest that 94-kD C1 inhibitor is generated in vitro by activation of the contact system. The in vivo mechanism of 94-kD C1 inhibitor generation in C1 inhibitor-deficient patients is not known.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubry M., Bieth J. Kinetics of the inactivation of human and bovine trypsins and chymotrypsins by alpha1-proteinase inhibitor and of their reactivation by alpha2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Aug 1;78(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Jackson C. M., Jörnvall H., Lavine K. K., Nordling K., Salsgiver W. J. The active site of antithrombin. Release of the same proteolytically cleaved form of the inhibitor from complexes with factor IXa, factor Xa, and thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2406–2411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Harpel P. C. Proteolytic cleavage and inactivation of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor and C1 inactivator by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9849–9854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesne S., Villiers C. L., Arlaud G. J., Lacroix M. B., Colomb M. G. Fluid-phase interaction of C1 inhibitor (C1 Inh) and the subcomponents C1r and C1s of the first component of complement, C1. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):61–70. doi: 10.1042/bj2010061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D. Dissemination of contact activation in plasma by plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):608–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Activation of plasminogen by human plasma kallikrein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J. G., Prograis L. J., Jr, Cochrane C. G. Detection of active kallikrein in induced blister fluids of hereditary angioedema patients. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):742–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Harrison R. A. Complexes between C1-inhibitor, kallikrein, high molecular weight kininogen, plasma thromboplastin antecedent, and plasmin in normal human plasma and hereditary angioneurotic edema plasmas containing dysmorphic C1-inhibitors: role of cold activation. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):121–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Harrison R. A., Rosen F. S., Bing D. H., Kindness G., Canar J., Wagner C. J., Awad S. Variability in purified dysfunctional C1(-)-inhibitor proteins from patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. Functional and analytical gel studies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):124–132. doi: 10.1172/JCI111664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Ratnoff O. D., Dias Da Silva W., Rosen F. S. Permeability-increasing activity in hereditary angioneurotic edema plasma. II. Mechanism of formation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):642–653. doi: 10.1172/JCI106022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Rosen F. S., Bing D. H. Role of the second component of complement (C2) and plasmin in kinin release in hereditary angioneurotic edema (H.A.N.E.) plasma. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1977;90:174–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields T., Ghebrehiwet B., Kaplan A. P. Kinin formation in hereditary angioedema plasma: evidence against kinin derivation from C2 and in support of "spontaneous" formation of bradykinin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Jul;72(1):54–60. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Boss G. R., Conley C. L., Reinhart R., Frank M. M. Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency and angioedema: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Jul;58(4):321–328. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197907000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Mason J. W., Colman R. W., Austen K. F. Interaction of plasma kallikrein with the C1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The stoichiometric measurement of the serum inhibition of the first component of complement by the inhibition of immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1154–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith G. H., Jr, Saito H., Ratnoff O. S. The activation of plasminogen by Hageman factor (Factor XII) and Hageman factor fragments. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):54–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI109113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hannema A. J., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Out T. A., Aalberse R. C. A C1-inhibitor-complex assay (INCA): a method to detect C1 activation in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1450–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Lewin M. F., Kaplan A. P. Distribution of plasma kallikrein between C-1 inactivator and alpha 2-macroglobulin in plasma utilizing a new assay for alpha 2-macroglobulin-kallikrein complexes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4257–4263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A. Human C1 inhibitor: improved isolation and preliminary structural characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):5001–5007. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Travis J. Human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor mechanism of action: evidence for activation by limited proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90956-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Fish W. W., Björk I. The thrombin cleavage site in bovine antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80532-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Immunochemical studies of human high molecular weight kininogen and of its complexes with plasma prekallikrein or kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3952–3958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDERMAN N. S., WEBSTER M. E., BECKER E. L., RATCLIFFE H. E. Hereditary angioneurotic edema. II. Deficiency of inhibitor for serum globulin permeability factor and/or plasma kallikrein. J Allergy. 1962 Jul-Aug;33:330–341. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(62)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine A., Davril M., Hayem A., Loucheux-Lefevbre A. H. Comparison of the interactions of human alpha1-antichymotrypsin with human leukocyte cathepsin G and bovine chymotrypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91709-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Johnson U., Mårtensson U., Sjöholm A. G. Formation of complexes composed of C1r, C1s, and C1 inactivator in human serum on activation of C1. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Dec;86C(6):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Comparative studies of the fibrinolytic activity of cultured vascular cells. Thromb Res. 1979;15(5-6):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. On the interaction of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor and proteases. Evidence for the formation of a covalent crosslinkage and non-covalent weak bondings between the inhibitor and proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 10;482(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T. On the interaction between human plasma kallikrein and C1-esterase inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Jun 28;49(3):193–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Sjöholm I., Wiman B. Structural and circular-dichroism studies on the interaction between human C1-esterase inhibitor and C1s. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):617–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2130617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Wiman B. Purification and characterization of human C1-esterase inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 26;705(2):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsche J. F., Tucker E. S., 3rd, Sugimoto S., Vaughan J. H., Curd J. G. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis of C4 and C4d. A simple sensitive method for detecting complement activation in plasma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Nov;76(5):679–684. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/76.5.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENSKY J., LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Partial purification of a serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1674–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensky J., Schwick H. G. Human serum inhibitor of C'1 esterase: identity with alpha-2-neuraminoglycoprotein. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):698–699. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts J. S., Donaldson V. H., Forristal J., Wyatt R. J. Remissions induced in hereditary angioneurotic edema with an attenuated androgen (danazol): correlation between concentrations of C1-inhibitor and the forth and second components of complement. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Oct;92(4):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pixley R. A., Schapira M., Colman R. W. The regulation of human factor XIIa by plasma proteinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1723–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN F. S., PENSKY J., DONALDSON V., CHARACHE P. HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: TWO GENETIC VARIANTS. Science. 1965 May 14;148(3672):957–958. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3672.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G. The relationship of structure and function in human Hageman factor. The association of enzymatic and binding activities with separate regions of the molecule. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI108361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Catanese J. J., Kress L. F., Travis J. Primary structure of the reactive site of human C1-inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2432–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Schmaier A. H., Prograis L. J., Jr, Curd J. G., Colman R. W. Prekallikrein activation and high-molecular-weight kininogen consumption in hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 5;308(18):1050–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305053081802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffer A. L., Austen K. F., Rosen F. S., Fearon D. T. Acquired deficiency of the inhibitor of the first component of complement: report of five additional cases with commentary on the syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Jun;75(6):640–646. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Arlaud G. J., Colomb M. G. Kinetics of reaction of human C1-inhibitor with the human complement system proteases C1r and C1s. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 11;612(2):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A. Preparation and properties of human C1 inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):43–54. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B. The human complement system serine proteases C1r and C1s and their proenzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):26–42. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead N., Kaplan A. P., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of activated factor XII by antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6481–6488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss V., Engel J. Heparin-stimulated modification of C1-inhibitor by subcomponent C1s of human complement. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Mar;364(3):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J. A new role for C-1-inhibitor in homeostasis: control of activation of the first component of human complement. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2505–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Agostini A., Schapira M., Wachtfogel Y. T., Colman R. W., Carrel S. Human plasma kallikrein and C1 inhibitor form a complex possessing an epitope that is not detectable on the parent molecules: demonstration using a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5190–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Bouma B. N. Inactivation of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Griffin J. H., Bouma B. N. Interaction of human plasma kallikrein and its light chain with C1 inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4860–4866. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]