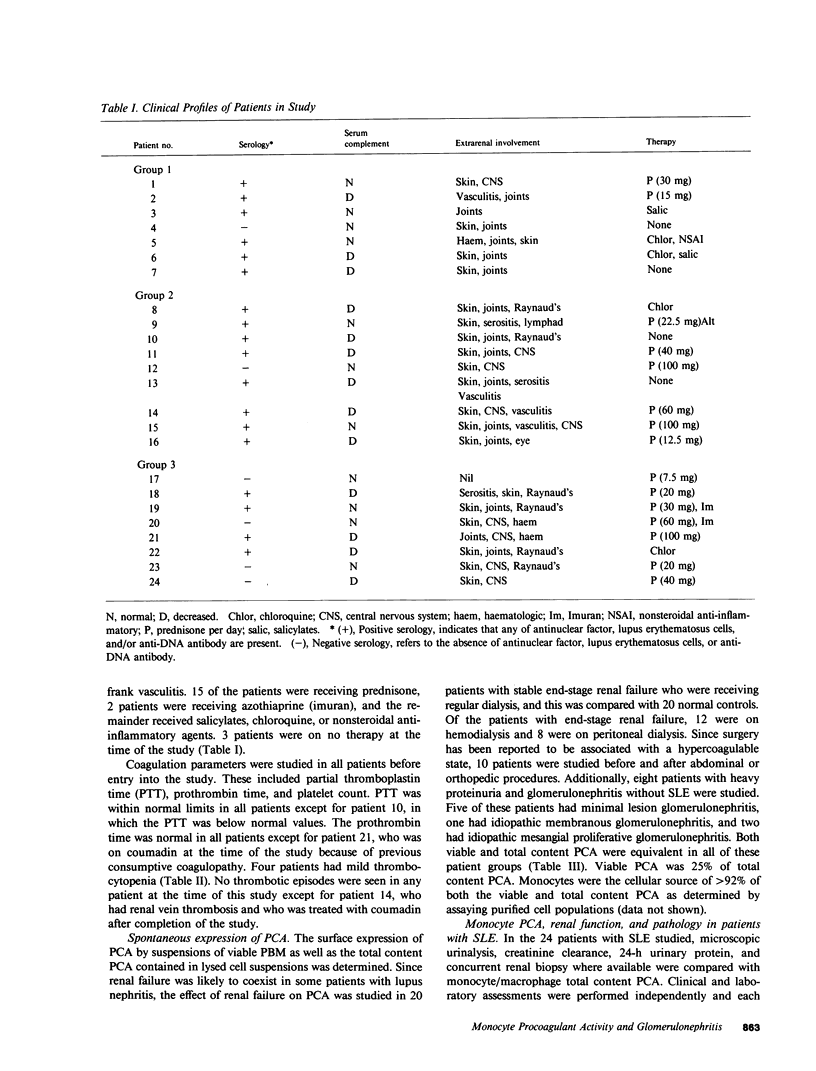
Abstract
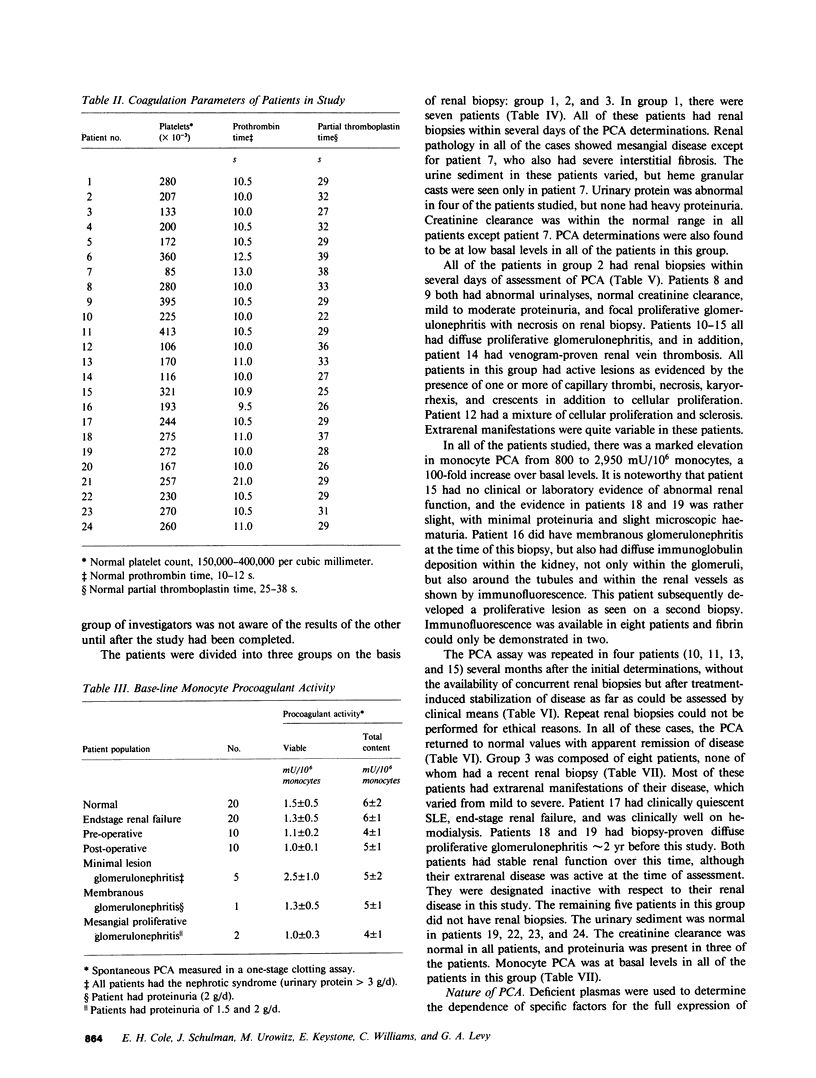
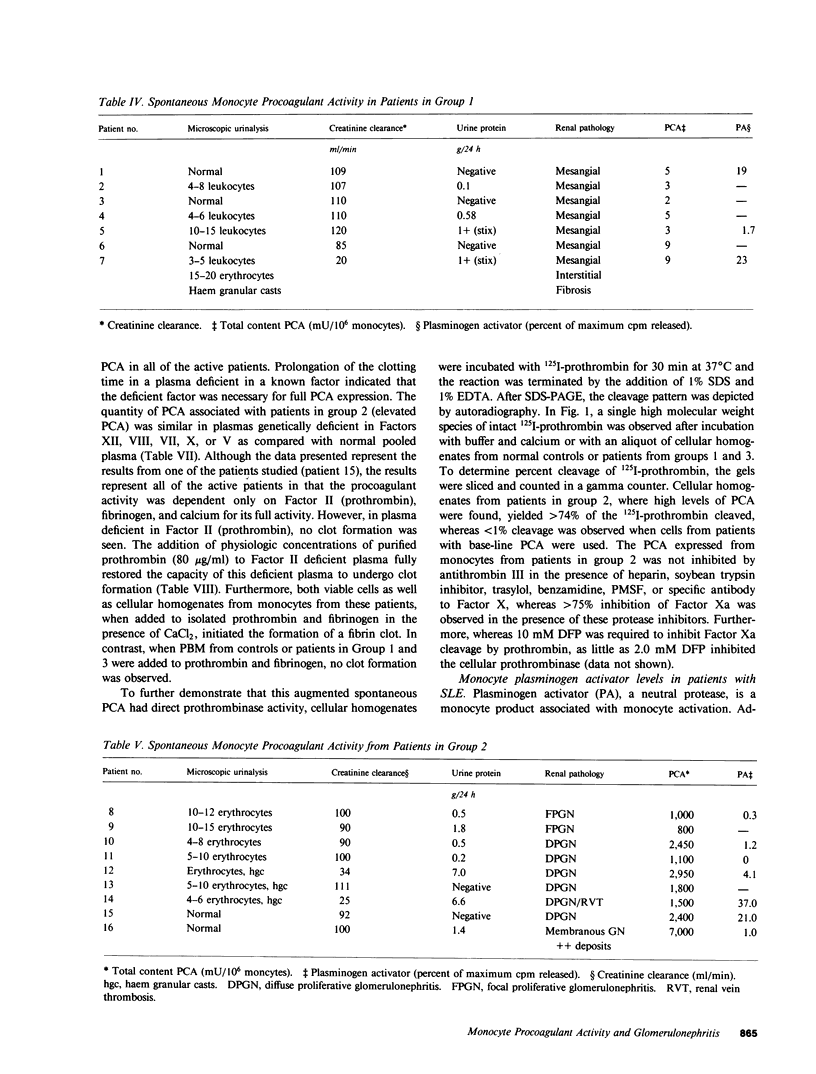
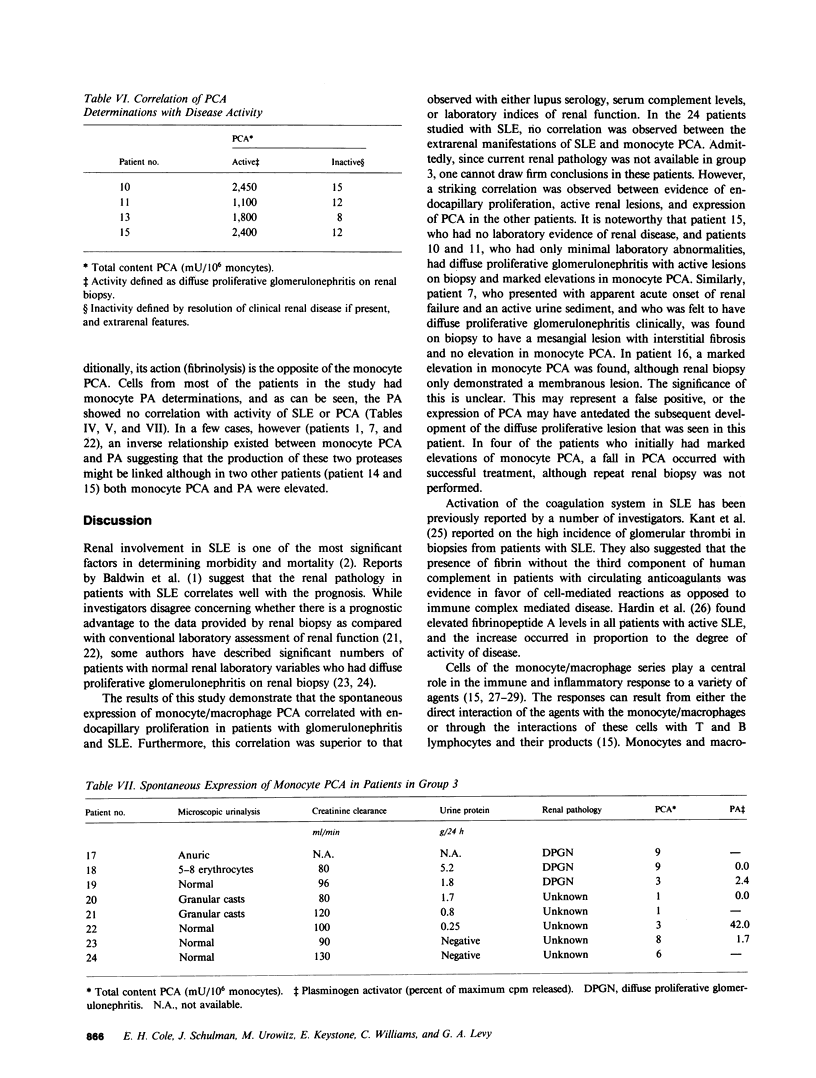
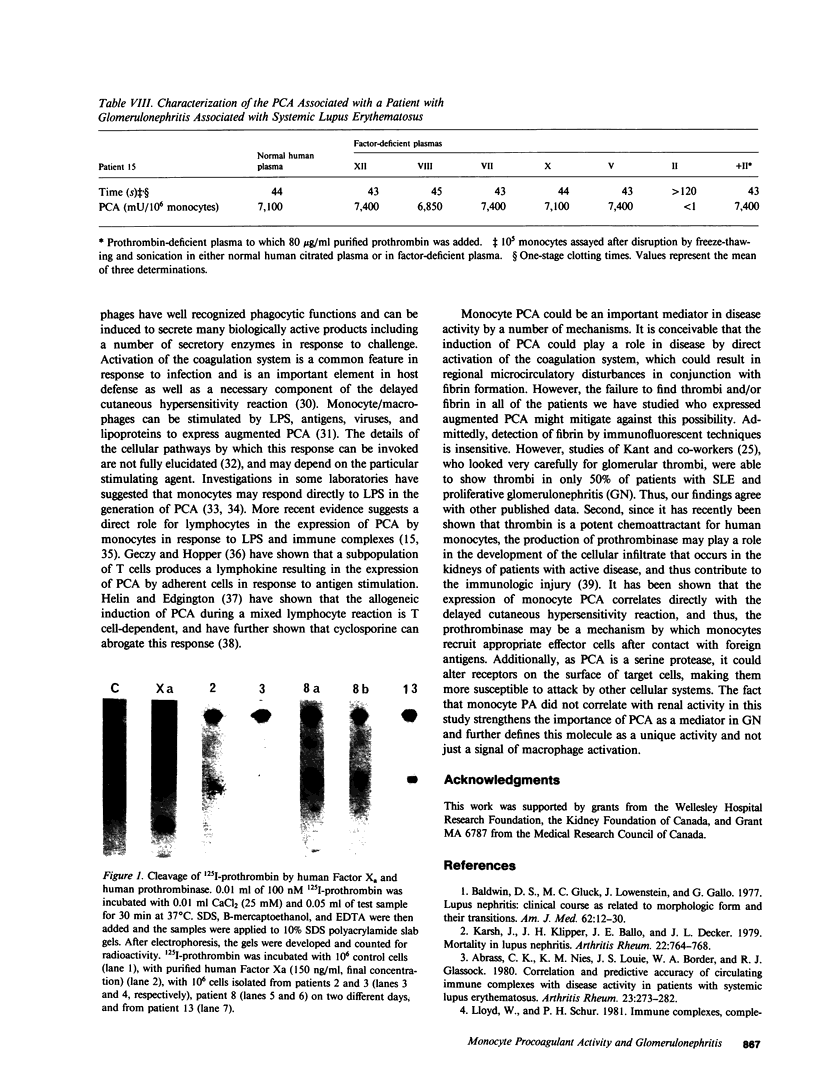
Monocyte infiltration and activation of the coagulation system have been implicated in the pathophysiology of glomerulonephritis. In this study, spontaneous procoagulant activity (PCA) was measured in circulating mononuclear cells to determine whether elevated PCA correlated with the presence of proliferative glomerulonephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). No increase in PCA was found in 20 patients with end-stage renal failure, 8 patients with glomerulonephritis without SLE, and 10 patients undergoing abdominal surgical or orthopedic procedures as compared with 20 normal controls. In eight patients with SLE but with no apparent active renal disease, PCA was not elevated above normal basal levels. Seven additional patients with SLE who had only mesangial proliferation on biopsy also had no increase in PCA. In contrast, eight patients with focal or diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis, and one patient with membranous nephritis who ultimately developed a proliferative lesion, had a marked increase in PCA with greater than 100 times the base-line levels. The activity was shown to originate in the monocyte fraction of the mononuclear cells and was shown to be capable of cleaving prothrombin directly. The prothrombinase activity was not Factor Xa, because it was not neutralized by anti-Factor X serum and was not inhibited by an established panel of Factor Xa inhibitors. Monocyte plasminogen activator determinations did not correlate with renal disease activity. We conclude that monocyte procoagulant activity, a direct prothrombinase, seems to correlate with endocapillary proliferation in lupus nephritis and could be a mediator of tissue injury.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrass C. K., Nies K. M., Louie J. S., Border W. A., Glassock R. J. Correlation and predictive accuracy of circulating immune complexes with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):273–282. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWIE E. J., THOMPSON J. H., Jr, PASCUZZI C. A., OWEN C. A., Jr THROMBOSIS IN SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS DESPITE CIRCULATING ANTICOAGULANTS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Sep;62:416–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. S., Gluck M. C., Lowenstein J., Gallo G. R. Lupus nephritis. Clinical course as related to morphologic forms and their transitions. Am J Med. 1977 Jan;62(1):12–30. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Wilner G. D., Fenton J. W., 2nd Monocyte chemotaxis: stimulation by specific exosite region in thrombin. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6836310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin R. B., Mosesson M. W., Dvorak H. F. Delayed-type hypersensitivity skin reactions in congenital afibrinogenemia lack fibrin deposition and induration. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1302–1306. doi: 10.1172/JCI109425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. L., Rickles F. R. The role of human T cells (and T cell products) for monocyte tissue factor generation. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):606–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Porta J., Liang M. H. Marginal benefit of renal biopsy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Sep;138(9):1386–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg S. K., Niemetz J. Tissue factor activity of normal and leukemic cells. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy C. L., Hopper K. E. A mechanism of migration inhibition in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. II. Lymphokines promote procoagulant activity of macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A., Cronlund M., Haber E., Bloch K. J. Activation of blood clotting in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to disease activity. Am J Med. 1978 Sep;65(3):430–436. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90769-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H. J., Edgington T. S. Cyclosporin A regulates monocyte/macrophage effector functions by affecting instructor T cells: inhibition of monocyte procoagulant response to allogeneic stimulation. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1074–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H., Edgington T. S. Allogeneic induction of the human T cell-instructed monocyte procoagulant response is rapid and is elicited by HLA-DR. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):962–975. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B. Abrogation of macrophage-dependent injury in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rabbit. Use of an antimacrophage serum. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):686–698. doi: 10.1172/JCI110304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Thomson N. M., Glasgow E. F., Atkins R. C. The effect of defibrination on macrophage participation in rabbit nephrotoxic nephritis: studies using glomerular culture and electronmicroscopy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):38–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollcraft R. M., Dubois E. L., Lundberg G. D., Chandor S. B., Gilbert S. B., Quismorio F. P., Barbour B. H., Friou G. J. Renal damage in systemic lupus erythematosus with normal renal function. J Rheumatol. 1976 Sep;3(3):251–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Shearer T. P., Plattner S. B., Weisenburger D. The role of monocytes in serum sickness nephritis. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):413–425. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett M. P., Sablay L. B., Walter L., Barland P., Grayzel A. I. The effect of continuous normalization of serum hemolytic complement on the course of lupus nephritis: a five year prospective study. Am J Med. 1981 May;70(5):1067–1072. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90870-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kant K. S., Pollak V. E., Weiss M. A., Glueck H. I., Miller A. N., Hess E. V. Glomerular thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and significance. Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 Mar;60(2):71–86. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsh J., Klippel J. H., Balow J. E., Decker J. L. Mortality in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jul;22(7):764–769. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. The treatment of chronic mesangiocapillary (membranoproliferative) glomerulonephritis with impaired renal function. Med J Aust. 1972 Sep 9;2(11):587–592. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb47498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. A., Edgington T. S. Lymphocyte cooperation is required for amplification of macrophage procoagulant activity. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1232–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. A., Schwartz B. S., Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Plasma lipoprotein induction and suppression of the generation of cellular procoagulant activity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1614–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI110196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan S. K., Ordóez N. G., Feitelson P. J., Lim V. S., Spargo B. H., Katz A. I. Lupus nephropathy without clinical renal involvement. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Nov;56(6):493–501. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197711000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak V. E., Glueck H. I., Weiss M. A., Lebron-Berges A., Miller M. A. Defibrination with ancrod in glomerulonephritis: effects on clinical and histologic findings and on blood coagulation. Am J Nephrol. 1982;2(4):195–207. doi: 10.1159/000166646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Hardin J. A., Pitlick F. A., Hoyer L. W., Conrad M. E. Tissue factor activity in lymphocyte cultures from normal individuals and patients with hemophilia A. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1427–1434. doi: 10.1172/JCI107316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Zimmerman T. S., Spiegelberg H. L., Vaughan J. H. Leukocyte procoagulant activity: enhancement of production in vitro by IgG and antigen-antibody complexes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):549–557. doi: 10.1172/JCI108670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Edgington T. S. Immune complex-induced human monocyte procoagulant activity. I. a rapid unidirectional lymphocyte-instructed pathway. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):892–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Levy G. A., Fair D. S., Edgington T. S. Murine lymphoid procoagulant activity induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide and immune complexes is a monocyte prothrombinase. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1464–1479. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Mannik M., Tung M. Y. Role of marrow-derived monocytes and mesangial cells in removal of immune complexes from renal glomeruli. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):127–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundsmo J. S., Fair D. S. Relationships among the complement, kinin, coagulation, and fibrinolytic systems. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(2-3):231–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00205875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. M., Simpson I. J., Peters D. K. A quantitative evaluation of anticoagulants in experimental nephrotoxic nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Feb;19(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting-O'Keefe Q., Riccardi P. J., Henke J. E., Shearn M. A., Hopper J., Jr, Epstein W. V. Recognition of information in renal biopsies of patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 1):723–727. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]