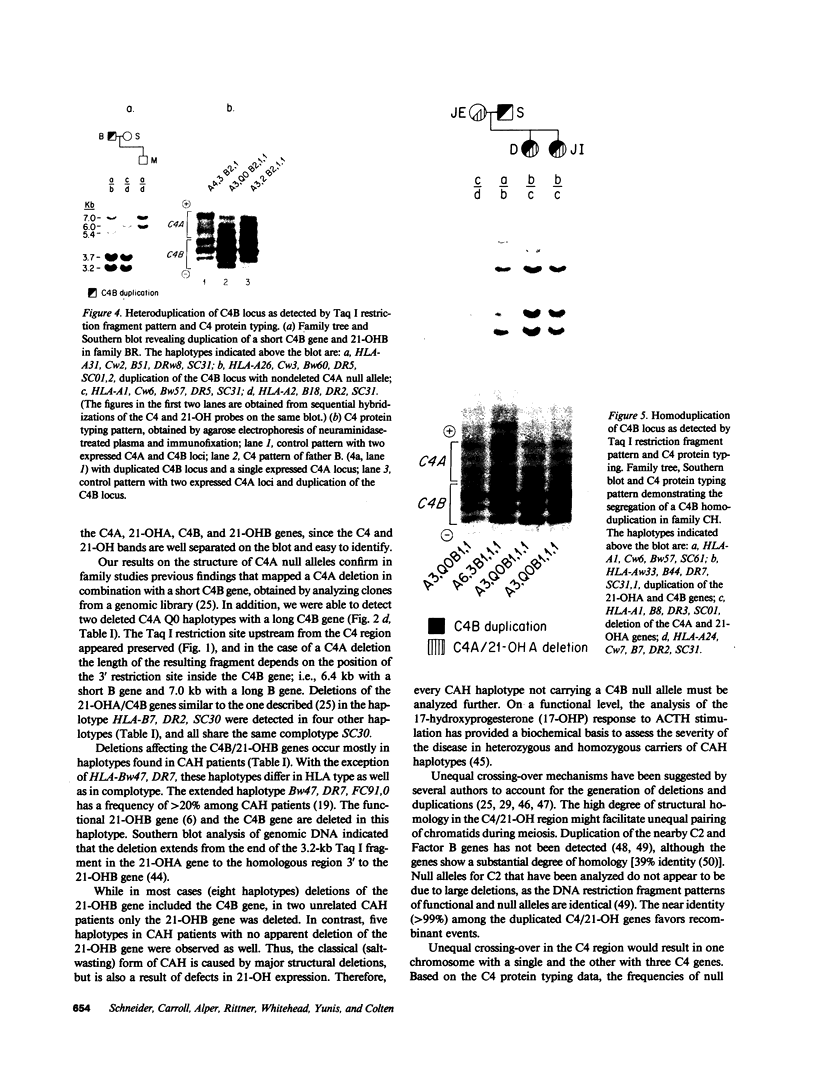
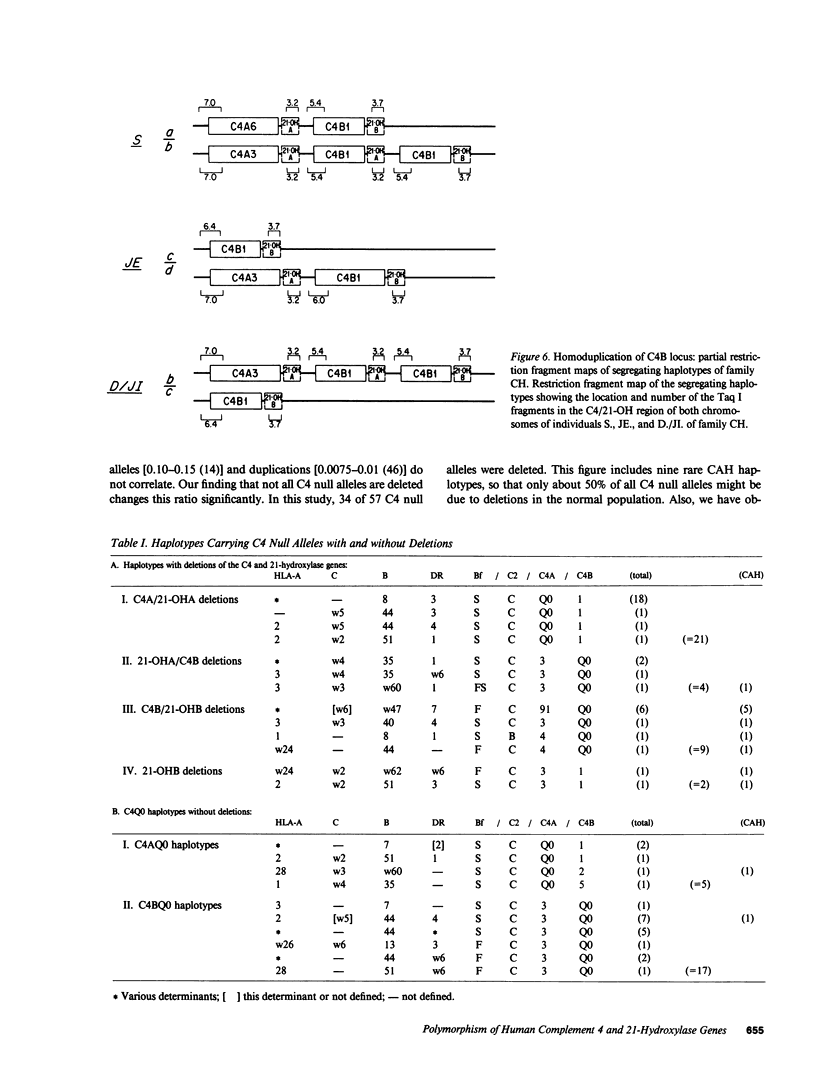
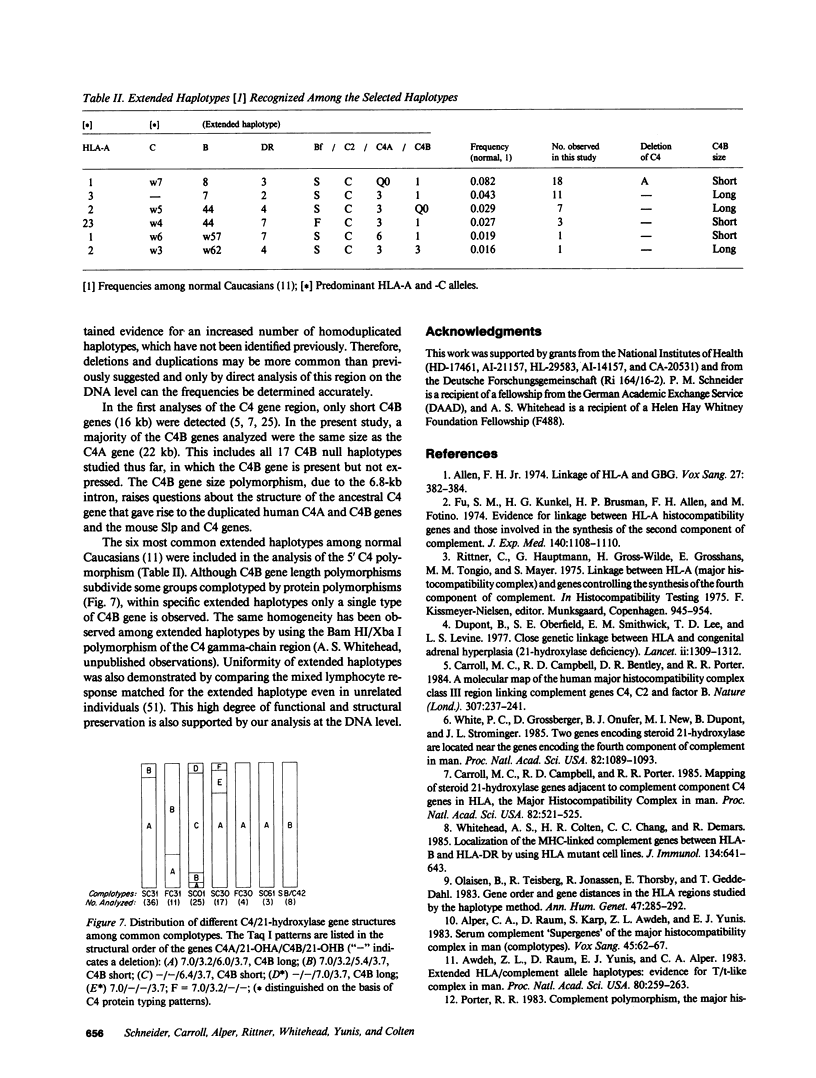
Abstract
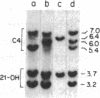
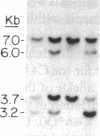
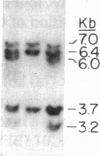
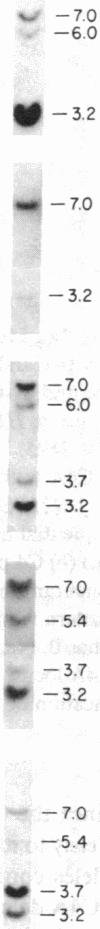
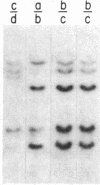
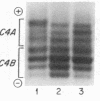
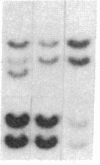
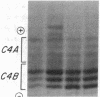
Several autoimmune disorders as well as congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) are either associated or closely linked with genetic variants of the fourth component of complement (C4A and C4B) and the enzyme steroid 21-hydroxylase (21-OH). These proteins are encoded by genes that are located downstream from the genes for complement proteins, C2 and factor B (BF) between HLA-B and -DR in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Previous studies of variants and null alleles were based on electrophoretic mobility of C4 protein and linkage with disease phenotypes. These data did not permit analysis of the basis for the observed null alleles and duplicated variants. We studied this region of the MHC in 126 haplotypes for a structural analysis of the four adjacent loci, C4A, 21-OHA, C4B, and 21-OHB. About half of the C4 genes typed as C4 null are deleted and several unrecognized homoduplicated C4 alleles were detected. Hence the frequencies of different C4 structural variants must be recalculated based on a direct analysis of the genes. Analysis of the C4/21-OH genes of patients with the classical (salt-wasting) form of CAH showed that some involve a deletion of the C4B and 21-OHB genes; whereas for two only the 21-OHB gene is deleted, i.e., the C4B gene is present. Together, these data provide a better understanding of the mechanisms generating and importance of deleted C4 and 21-OH null alleles in human disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen F. H., Jr Linkage of HL-A and GBG. Vox Sang. 1974;27(4):382–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1974.tb02433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Boenisch T., Watson L. Genetic polymorphism in human glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Raum D., Karp S., Awdeh Z. L., Yunis E. J. Serum complement 'supergenes' of the major histocompatibility complex in man (complotypes). Vox Sang. 1983;45(1):62–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb04124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A., Eynon E., Alosco S. M., Stein R., Yunis E. J. Unrelated individuals matched for MHC extended haplotypes and HLA-identical siblings show comparable responses in mixed lymphocyte culture. Lancet. 1985 Oct 19;2(8460):853–856. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Alper C. A. Genetic polymorphism of human complement C4 and detection of heterozygotes. Nature. 1979 Nov 8;282(5735):205–207. doi: 10.1038/282205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):259–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Yu C. Y., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Polymorphism of human complement component C4. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00364869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Belt K. T., Palsdottir A., Yu Y. Molecular genetics of the fourth component of human complement and steroid 21-hydroxylase. Immunol Rev. 1985 Oct;87:39–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Palsdottir A., Belt K. T., Porter R. R. Deletion of complement C4 and steroid 21-hydroxylase genes in the HLA class III region. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2547–2552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Cloning of a human complement component C4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):264–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Whitehead A. S., Auerbach H. S., Lint T., Zeitz H. J., Kilbridge P., Colten H. R. The molecular basis for genetic deficiency of the second component of human complement. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 4;313(1):11–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507043130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Law S. K., Porter R. R. The origin of the very variable haemolytic activities of the common human complement component C4 allotypes including C4-A6. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2239–2244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Oberfield S. E., Smithwick E. M., Lee T. D., Levine L. S. Close genetic linkage between HLA and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielder A. H., Walport M. J., Batchelor J. R., Rynes R. I., Black C. M., Dodi I. A., Hughes G. R. Family study of the major histocompatibility complex in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: importance of null alleles of C4A and C4B in determining disease susceptibility. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 5;286(6363):425–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischnick E., Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Granados J., Alosco S. M., Crigler J. F., Jr, Gerald P. S., Giles C. M., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended MHC haplotypes in 21-hydroxylase-deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia: shared genotypes in unrelated patients. Lancet. 1983 Jan 22;1(8317):152–156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G., Brusman H. P., Allen F. H., Jr, Fotino M. Evidence for linkage between HL-A histocompatibility genes and those involved in the synthesis of the second component of complement. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1108–1111. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D., Raum D., Gibson D., Stillman J. S., Schur P. H. Inherited deficiency of the second component of complement. Rheumatic disease associations. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):853–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Young J. R. The molecular basis for the difference in immune hemolysis activity of the Chido and Rodgers isotypes of human complement component C4. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3019–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Dodds A. W., Porter R. R. A comparison of the properties of two classes, C4A and C4B, of the human complement component C4. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1819–1823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I. Clinical and endocrinological aspects of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;458:1–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb14585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaisen B., Teisberg P., Jonassen R., Thorsby E., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr Gene order and gene distances in the HLA region studied by the haplotype method. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Oct;47(Pt 4):285–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb00998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palsdottir A., Cross S. J., Edwards J. H., Carroll M. C. Correlation between a DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism and C4A6 protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):615–616. doi: 10.1038/306615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. Complement polymorphism, the major histocompatibility complex and associated diseases: a speculation. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. L., Schneider P. M., Strominger J. L. C4B gene polymorphism detected in a human cosmid clone. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):274–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00373024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Anderson J., Strong L., Granados J., Teran L., Giblett E., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Human C4 haplotypes with duplicated C4A or C4B. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):72–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittner C., Bertrams J. On the significance of C2, C4, and factor B polymorphisms in disease. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):235–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00274674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittner C., Meier E. M., Stradmann B., Giles C. M., Köchling R., Mollenhauer E., Kreth H. W. Partial C4 deficiency in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(4):407–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00345615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Mollenhauer E., Démant P., Rittner C. A molecular basis for the two locus model of human complement component C4. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):854–856. doi: 10.1038/298854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Thalassemia revisited. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Colten H. R., Chang C. C., Demars R. Localization of the human MHC-linked complement genes between HLA-B and HLA-DR by using HLA mutant cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):641–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Woods D. E., Fleischnick E., Chin J. E., Yunis E. J., Katz A. J., Gerald P. S., Alper C. A., Colten H. R. DNA polymorphism of the C4 genes. A new marker for analysis of the major histocompatibility complex. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 12;310(2):88–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401123100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]