Abstract
In an effort to evaluate the synthesis and function of eicosanoids in myocardial infarction, we have developed a technique of in vivo myocardial infarction in rabbits followed by ex vivo cardiac perfusion. Isolated Langendorff perfused infarcted hearts (removed 1 or 4 d after infarction) responded to the inflammatory cell agonist N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) with (a) the release of leukotrienes B4, C4, and D4; (b) the release of large amounts of thromboxane (235 +/- 66 ng/5 min), prostacyclin (714 +/- 285 ng/5 min), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (330 +/- 108 ng/5 min); and (c) a coronary vasoconstriction (21.1 +/- 2.5% increase in coronary perfusion pressure) that was specifically inhibited by the peptidoleukotriene receptor antagonist FPL-55712. While noninfarcted hearts challenged with fMLP also released leukotrienes B4, C4, and D4, they released only small amounts of the cyclooxygenase products (thromboxane, 30 +/- 9 ng/5 min; prostacyclin, 120 +/- 54 ng/5 min; PGE2, 27 +/- 10 ng/5 min) and showed minimal vasoconstriction (5.6 +/- 2.1% increase in perfusion pressure). Similarly, hearts challenged with fMLP 30 d following infarction released only small amounts of the cyclooxygenase products (thromboxane, 42 +/- 8 ng/5 min; prostacyclin, 386 +/- 31 ng/5 min; PGE2, 79 +/- 25 ng/5 min). When bradykinin was administered, no leukotrienes were produced, but acutely infarcted hearts released 10 times more thromboxane, prostacyclin, and PGE2 than normal hearts and significantly larger amounts of these products than 30-d infarcted hearts. Histologic analysis showed no inflammatory cells in normal hearts, a prominent polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration in 1-d infarcted tissue, fibroblast proliferation with mononuclear cell invasion in 4-d infarcted tissue, and a fibrotic scar with scanty mononuclear cell infiltrate in 30-d infarcted tissue. Inflammatory cell invasion was temporarily associated with augmented cyclooxygenase metabolism, suggesting that infiltrating leukocytes may be responsible for production of thromboxane, prostacyclin, and PGE2 in acutely infarcted hearts. The finding that endogenously produced peptidoleukotrienes are potent coronary vasoconstrictors in infarcted rabbit hearts suggests that these products may contribute to tissue injury in myocardial infarction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aehringhaus U., Peskar B. A., Wittenberg H. R., Wölbling R. H. Effect of inhibition of synthesis and receptor antagonism of SRS-A in cardiac anaphylaxis. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;80(1):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Reed P. W. Stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in the polymorphonuclear leukocyte by an N-formylated peptide. Comparison with ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10223–10226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli R., Goldstein R. E., Davenport N., Epstein S. E. Influence of sulfinpyrazone and naproxen on infarct size in the dog. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Apr;47(4):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonow R. O., Lipson L. C., Sheehan F. H., Capurro N. L., Isner J. M., Roberts W. C., Goldstein R. E., Epstein S. E. Lack of effect of aspirin on myocardial infarct size in the dog. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Feb;47(2):258–264. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Metabolism of arachidonic acid in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Structural analysis of novel hydroxylated compounds. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7865–7869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Formation of a novel dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2643–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. A., Levi R., Guo Z. G., Corey E. J. Leukotrienes C4, D4 and E4: effects on human and guinea-pig cardiac preparations in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Apr;221(1):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):264–265. doi: 10.1038/286264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. E., Cheli C. D. Arachidonic acid and prostaglandin endoperoxide metabolism in isolated rabbit and coronary microvessels and isolated and cultivated coronary microvessel endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1658–1671. doi: 10.1172/JCI111125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore N., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins released by the spleen. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1135–1140. doi: 10.1038/2181135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly S. R., Lucchesi B. R. Effect of BW755C in an occlusion-reperfusion model of ischemic myocardial injury. Am Heart J. 1983 Jul;106(1 Pt 1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90431-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P. E., Leahy K. M., DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K., Needleman P. Cellular interactions and exaggerated arachidonic acid metabolism in rabbit renal injury. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Jan;35(1):55–64. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jugdutt B. I., Hutchins G. M., Bulkley B. H., Pitt B., Becker L. C. Effect of indomethacin on collateral blood flow and infarct size in the conscious dog. Circulation. 1979 Apr;59(4):734–743. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.59.4.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letts L. G., Piper P. J. The actions of leukotrienes C4 and D4 on guinea-pig isolated hearts. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 May;76(1):169–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. The biologically active leukotrienes. Biosynthesis, metabolism, receptors, functions, and pharmacology. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):889–897. doi: 10.1172/JCI111312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey E. R., Corr P. B., Lee B. I., Saffitz J. E., Needleman P. The arachidonic acid metabolic capacity of canine myocardium is increased during healing of acute myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 1982 Dec;51(6):743–750. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.6.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelassi F., Landa L., Hill R. D., Lowenstein E., Watkins W. D., Petkau A. J., Zapol W. M. Leukotriene D4: a potent coronary artery vasoconstrictor associated with impaired ventricular contraction. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):841–843. doi: 10.1126/science.6808665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullane K. M., Moncada S. The salvage of ischaemic myocardium by BW755C in anaesthetised dogs. Prostaglandins. 1982 Aug;24(2):255–266. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullane K. M., Read N., Salmon J. A., Moncada S. Role of leukocytes in acute myocardial infarction in anesthetized dogs: relationship to myocardial salvage by anti-inflammatory drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):510–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Key S. L., Denny S. E., Isakson P. C., Marshall G. R. Mechanism and modification of bradykinin-induced coronary vasodilation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2060–2063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okegawa T., Jonas P. E., DeSchryver K., Kawasaki A., Needleman P. Metabolic and cellular alterations underlying the exaggerated renal prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis in ureter obstruction in rabbits. Inflammatory response involving fibroblasts and mononuclear cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):81–90. doi: 10.1172/JCI110754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLAK O. J. Mast cells in the circulatory system of man. Circulation. 1957 Dec;16(6):1084–1089. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.16.6.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Stepney R. J., Higgs G. A., Eakins K. E. Chemokinetic activity of arachidonic and lipoxygenase products on leuocyctes of different species. Prostaglandins. 1980 Aug;20(2):411–418. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(80)80058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Rapid extraction of arachidonic acid metabolites from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica. Methods Enzymol. 1982;86:467–477. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)86218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold D. F., Watters K., Holmberg S., Needleman P. Differential biosynthesis of prostaglandins by hydronephrotic rabbit and cat kidneys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romson J. L., Hook B. G., Kunkel S. L., Abrams G. D., Schork M. A., Lucchesi B. R. Reduction of the extent of ischemic myocardial injury by neutrophil depletion in the dog. Circulation. 1983 May;67(5):1016–1023. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.5.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
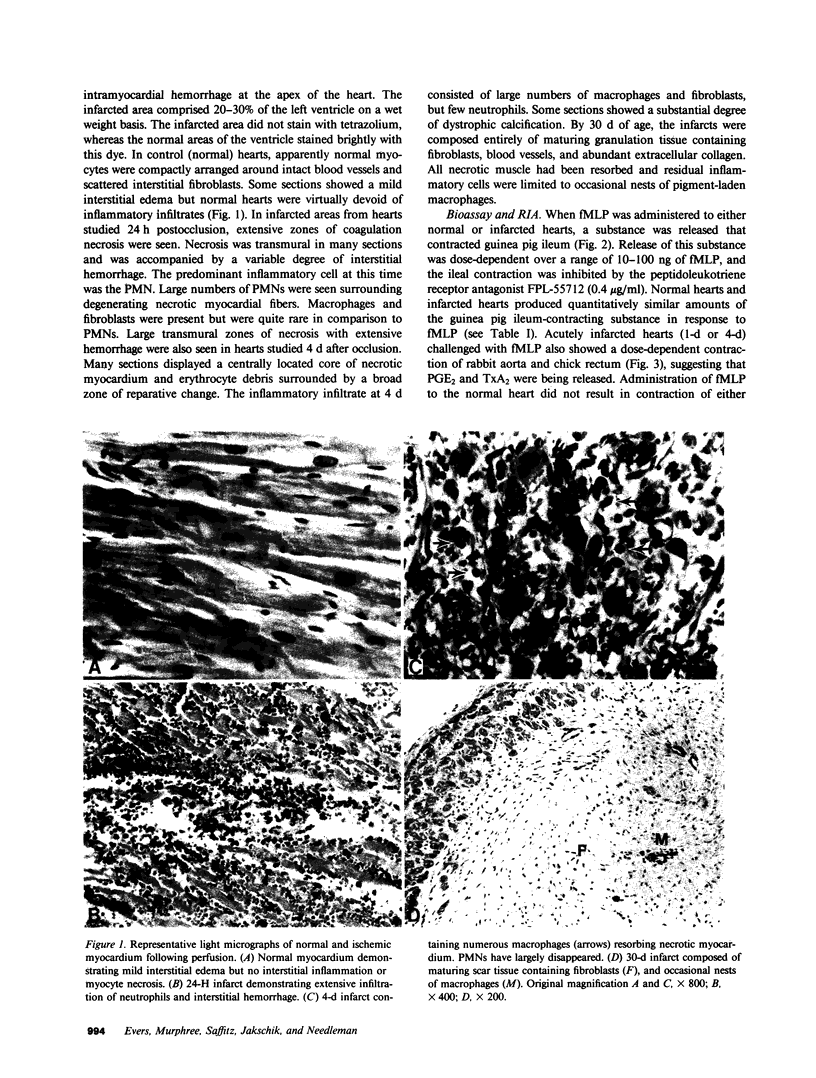
- SOMMERS H. M., JENNINGS R. B. EXPERIMENTAL ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; HISTOLOGIC AND HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF EARLY MYOCARDIAL INFARCTS INDUCED BY TEMPORARY OR PERMANENT OCCLUSION OF A CORONARY ARTERY. Lab Invest. 1964 Dec;13:1491–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Goldyne M., Granström E., Hamberg M., Hammarström S., Malmsten C. Prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:997–1029. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Pawlowski N. A., Andreach M., Cohn Z. A. Resting macrophages produce distinct metabolites from exogenous arachidonic acid. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):535–547. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Fudman E. J. Demonstration of a chemotactic factor receptor on macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2754–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Goetzl E. J. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of leukocyte chemotaxis. Science. 1981 Aug 21;213(4510):830–837. doi: 10.1126/science.6266014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
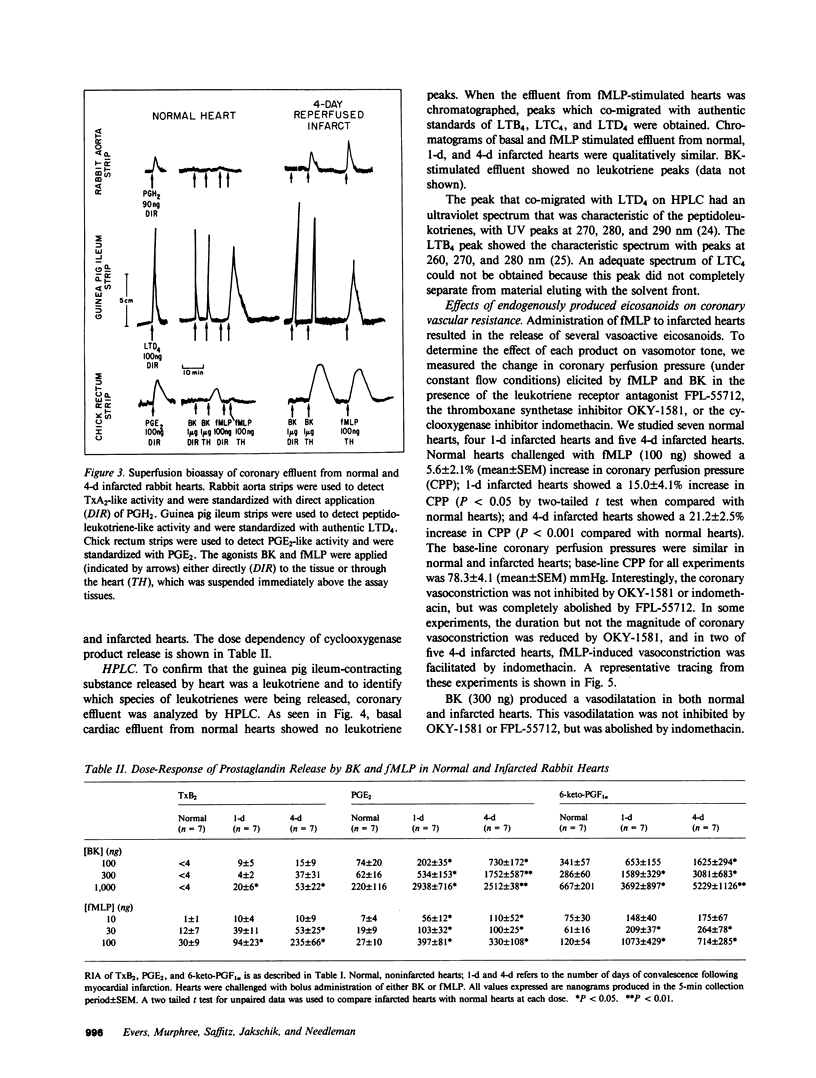
- Trachte G. J., Lefer A. M., Aharony D., Smith J. B. Potent constriction of cat coronary arteries by hydroperoxides of arachidonic acid and its blockade by anti-inflammatory agents. Prostaglandins. 1979 Dec;18(6):909–914. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Smolen J. E., Korchak H. M. Release of inflammatory mediators from stimulated neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):27–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]