Abstract
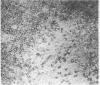
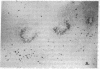
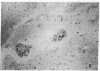
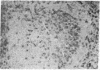
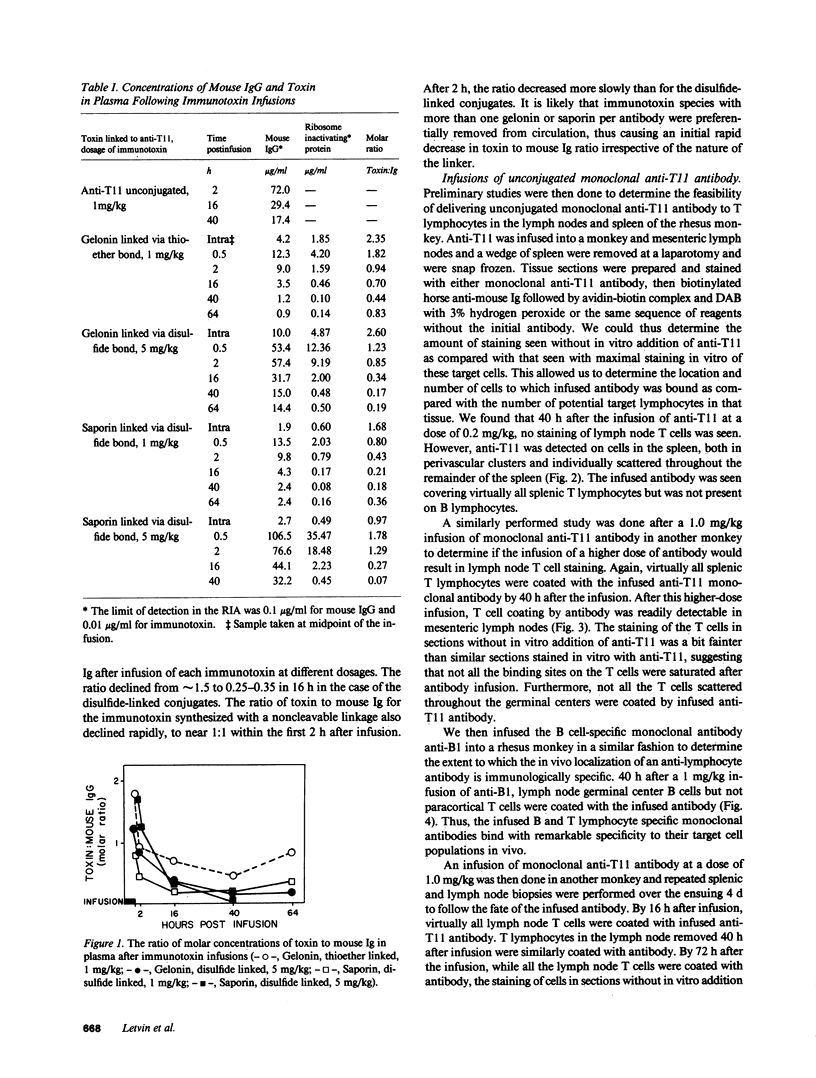
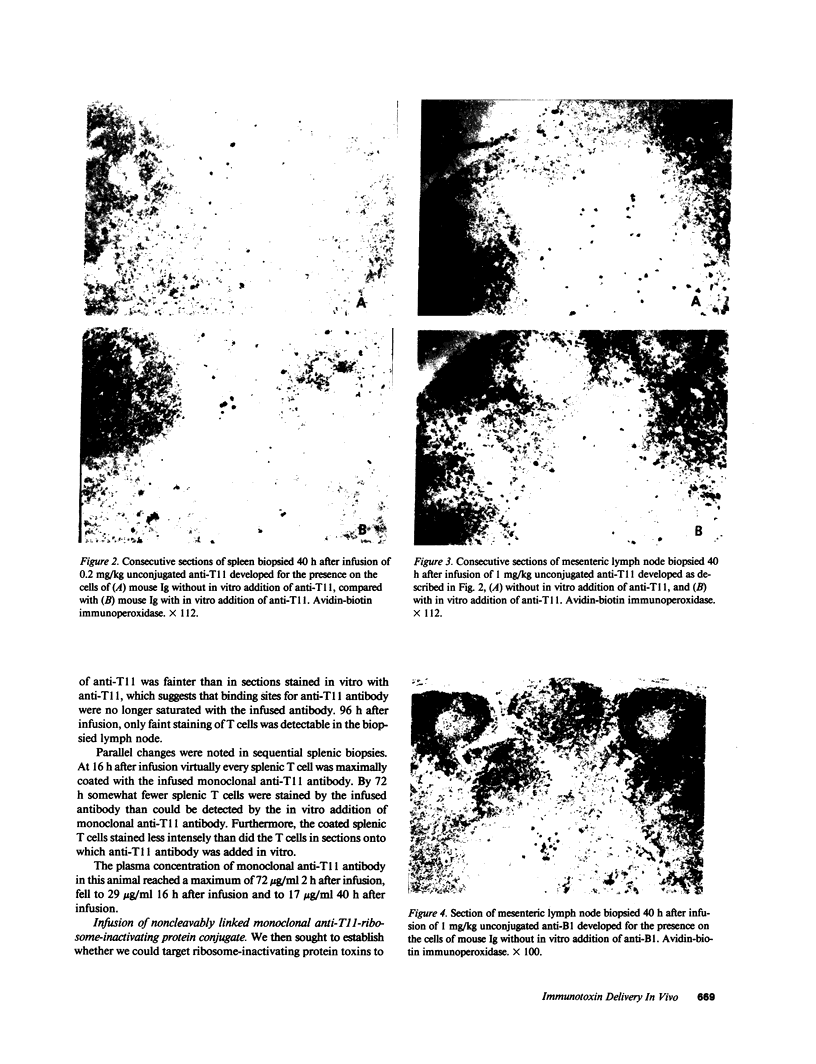
The selective delivery in vivo of a T lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibody and immunotoxin conjugates to T cells in lymph node and spleen was assessed in rhesus monkeys. A transient coating of all T lymphocytes in the lymph nodes and spleens of healthy rhesus monkeys could be achieved after infusion of unconjugated anti-T11. Because derivatized antibody is cleared more rapidly than unconjugated antibody, it was necessary to infuse a higher dose of immunotoxin than antibody alone to achieve saturation of the lymphocyte binding sites with anti-T11. When sufficient antibody-toxin conjugate was infused, toxin was readily demonstrable on lymph node and spleen T cells by 16 h after infusion. This demonstration that toxins can be successfully delivered with specificity to target T cell populations in the monkey suggests that killing of restricted cell populations in vivo should be feasible.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson J., Drevin H., Axén R. Protein thiolation and reversible protein-protein conjugation. N-Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate, a new heterobifunctional reagent. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):723–737. doi: 10.1042/bj1730723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifoux L. V., Schlossman S. F., Letvin N. L. Delineation of lymphocyte subsets in lymph nodes of nonhuman primates. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Apr;31(1):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Dowell D. L., Hensley L. L., Gore I., Metzgar R. S. Human T cell antigen expression by primate T cells. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.6171885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. M., Senter P. D., Yau-Young A., Blättler W. A., Goldmacher V. S. Purified immunotoxins that are reactive with human lymphoid cells. Monoclonal antibodies conjugated to the ribosome-inactivating proteins gelonin and the pokeweed antiviral proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12035–12041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Aldrich W. R., Thorley-Lawson D. A., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Surface antigen changes during B-lymphocyte activation in primates. Cell Immunol. 1984 Mar;84(1):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Goldmacher V. S., Ritz J., Yetz J. M., Schlossman S. F., Lambert J. M. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates. In vivo stability of disulfide-linked immunotoxin conjugates. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):977–984. doi: 10.1172/JCI112399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., King N. W., Reinherz E. L., Hunt R. D., Lane H., Schlossman S. F. T lymphocyte surface antigens in primates. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Apr;13(4):345–347. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Ritz J., Guida L. J., Yetz J. M., Lambert J. M., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates: I. Effects of anti-T11 antibodies on the circulating T cell pool. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):961–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Todd R. F., 3rd, Palley L. S., Schlossman S. F., Griffin J. D. Conservation of myeloid surface antigens on primate granulocytes. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):408–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palley L. S., Schlossman S. F., Letvin N. L. Common tree shrews and primates share leukocyte membrane antigens. J Med Primatol. 1984;13(2):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan S., Houston L. L. Immunological and biological stability of immunotoxins in vivo as studied by the clearance of disulfide-linked pokeweed antiviral protein-antibody conjugates from blood. Cancer Res. 1985 May;45(5):2031–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Falasca A., Abbondanza A., Stevens W. A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from the seeds of Saponaria officinalis L. (soapwort), of Agrostemma githago L. (corn cockle) and of Asparagus officinalis L. (asparagus), and from the latex of Hura crepitans L. (sandbox tree). Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):617–625. doi: 10.1042/bj2160617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Gelonin, a new inhibitor of protein synthesis, nontoxic to intact cells. Isolation, characterization, and preparation of cytotoxic complexes with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6947–6953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: harnessing nature's poisons. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):i–x. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: redirecting nature's poisons. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):653–654. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]