Abstract
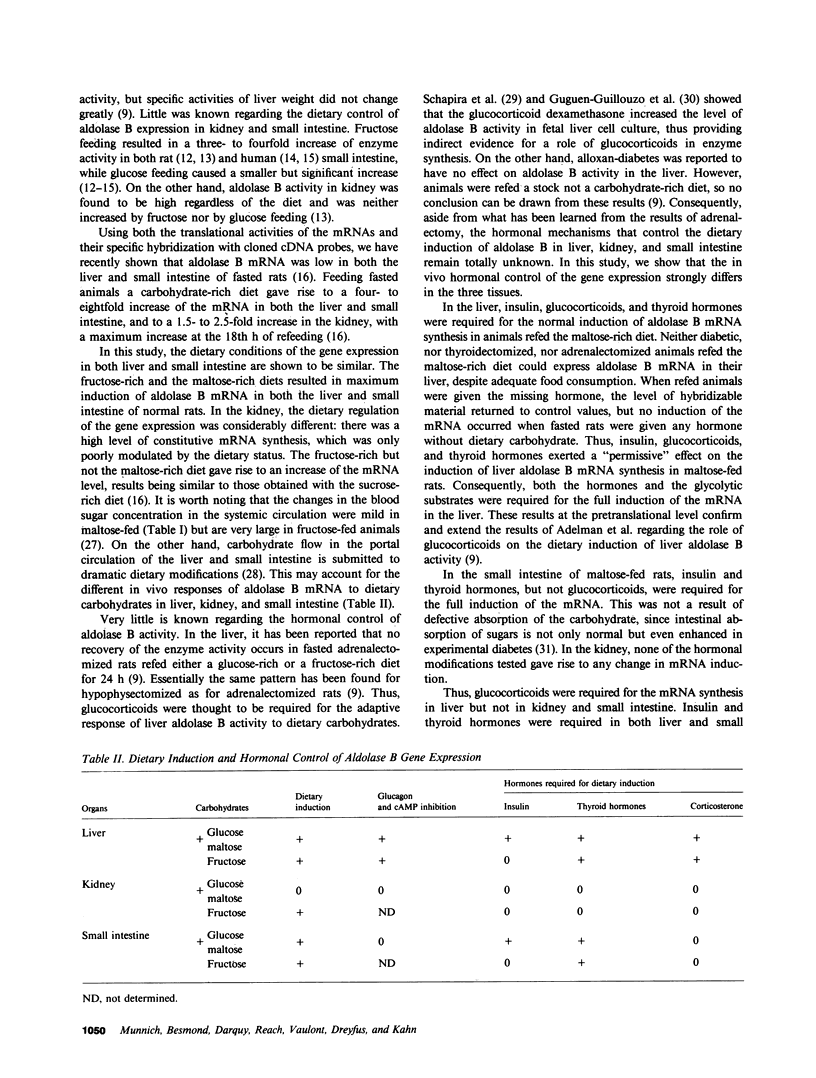
Aldolase B is an enzyme of the glycolytic pathway whose activity and mRNA levels in the liver fluctuate according to dietary status. Both the enzyme activity and the mRNA concentration decline during fasting and increase four- to eightfold upon refeeding of a carbohydrate-rich diet. The mechanism, however, of the mRNA induction remains unknown. To elucidate the mechanisms that regulate this induction responsive to dietary stimuli, we have studied the roles of hormones and glycolytic substrates on aldolase B gene expression in three tissues that synthesize the enzyme. Using a cDNA probe complementary to rat aldolase B mRNA, we determined the amount of cytoplasmic RNAs in the liver, kidney, and small intestine of normal, adrenalectomized, thyroidectomized, diabetic, and glucagon- or cAMP-treated animals refed either a fructose-rich or a maltose-rich diet. The in vivo hormonal control of gene expression was found to be very different in the three organs tested. In the liver, cortisone and thyroid hormones were required for the induction of the specific mRNA by carbohydrates, while in the kidney none of the hormonal modifications tested altered the level of mRNA induction. In the liver, but not in the kidney, diabetes and glucagon administration abolished the induction of aldolase B mRNAs in animals refed the maltose-rich diets. In the small intestine, only diabetes and thyroidectomy affected the gene expression. Finally, no induction occurred when normal fasted rats were given any of the hormones. Thus, the in vivo hormonal control of liver aldolase B gene expression differs significantly from that of kidney and small intestine. In the liver, the mRNA induction requires the presence of dietary carbohydrates, of permissive hormones, and the cessation of glucagon release, while in the kidney, the induction of the mRNAs by fructose occurs regardless of the hormonal status of the animals. The hormonal control of aldolase B mRNA levels in the small intestine is intermediate.
Full text
PDF

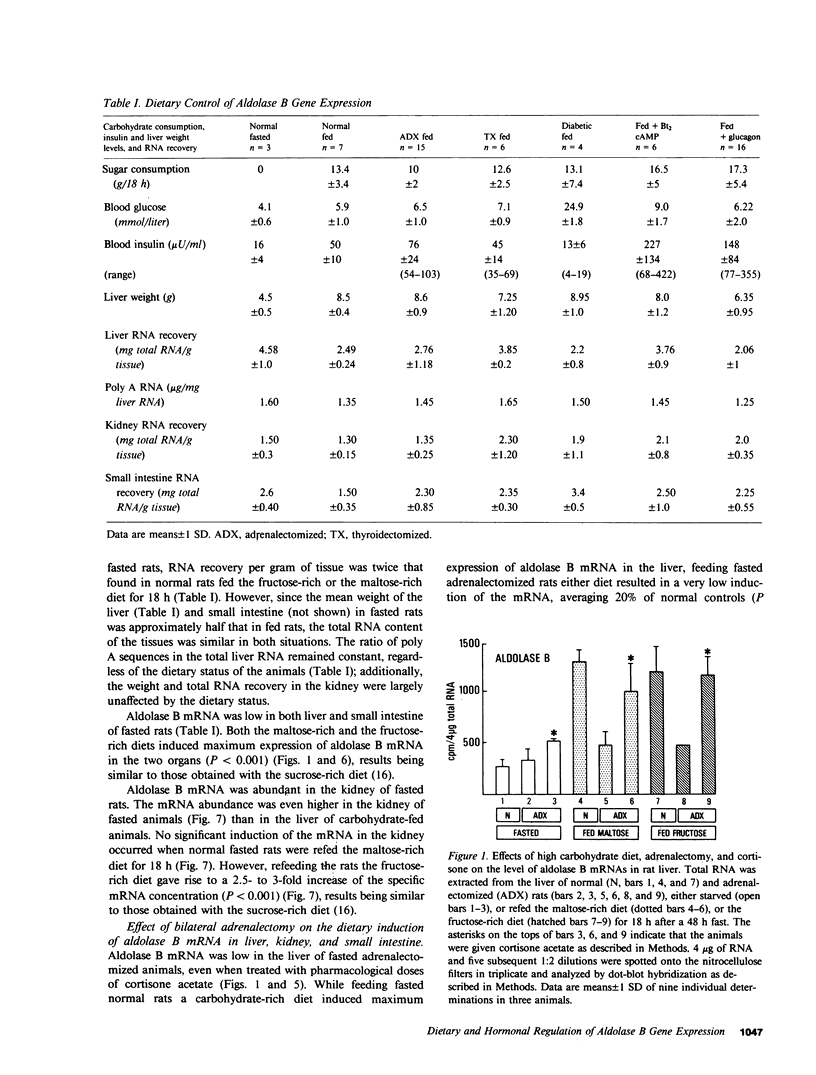


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman R. C., Spolter P. D., Weinhouse S. Dietary and hormonal regulation of enzymes of fructose metabolism in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5467–5472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOSTEIN R., RUTTER W. J. COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF LIVER AND MUSCLE ALDOLASE. II. IMMUNOCHEMICAL AND CHROMATOGRAPHIC DIFFERENTIATION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3280–3285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
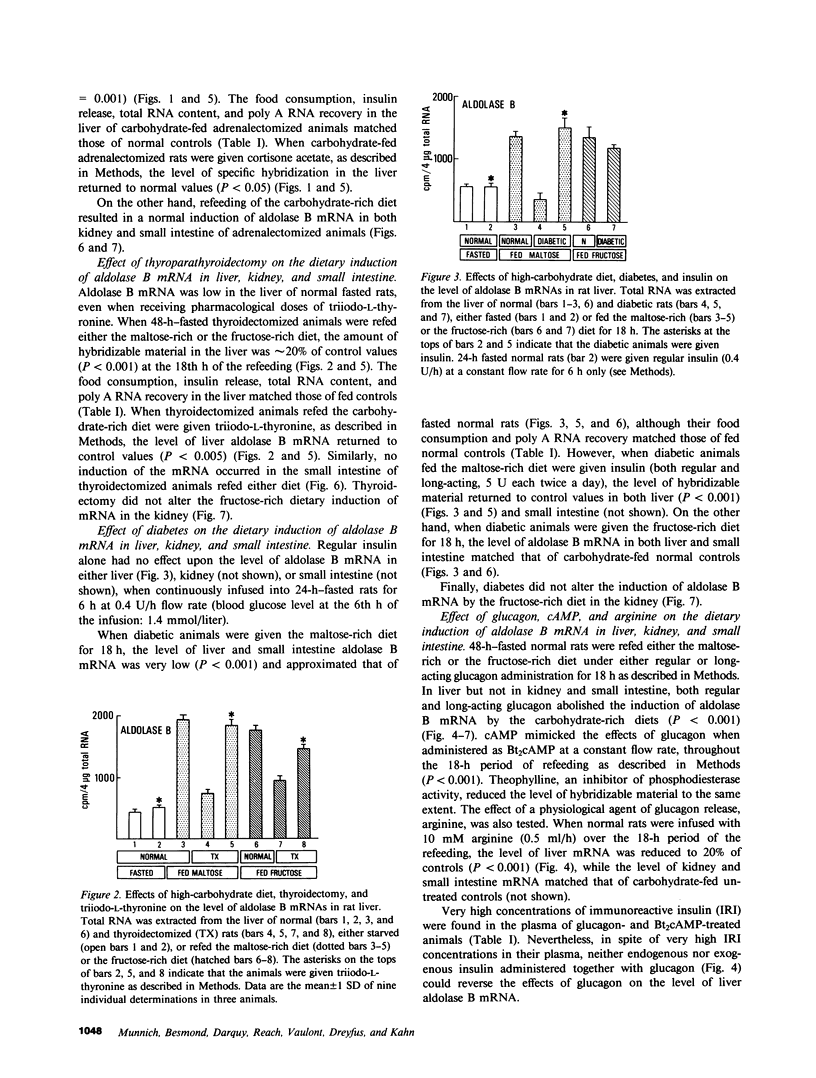
- Besmond C., Dreyfus J. C., Gregori C., Frain M., Zakin M. M., Sala Trepat J., Kahn A. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human aldolase B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Rosbash M. Polynucleotide sequences in eukaryotic DNA and RNA that form ribonuclease-resistant complexes with polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley J. N., Macdonald I. The influence in male baboons, of a high sucrose diet on the portal and arterial levels of glucose and fructose following a sucrose meal. Nutr Metab. 1970;12(3):171–178. doi: 10.1159/000175290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Feldman D., Edelman I. S. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat kidney: the binding of tritiated-dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):1005–1013. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Charles M. A., Grodsky G. M. Characterization of the effects of arginine and glucose on glucagon and insulin release from the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):833–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI107823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Charles M. A., Grodsky G. M. Regulation of pancreatic insulin and glucagon secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:353–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Schneider V., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Prevention of human diabetic ketoacidosis by somatostatin. Evidence for an essential role of glucagon. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 8;292(19):985–989. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505082921901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G., KUSAKA T. Le metabolisme du fructose-1-phosphate dans le foie. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jul;11(3):427–437. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
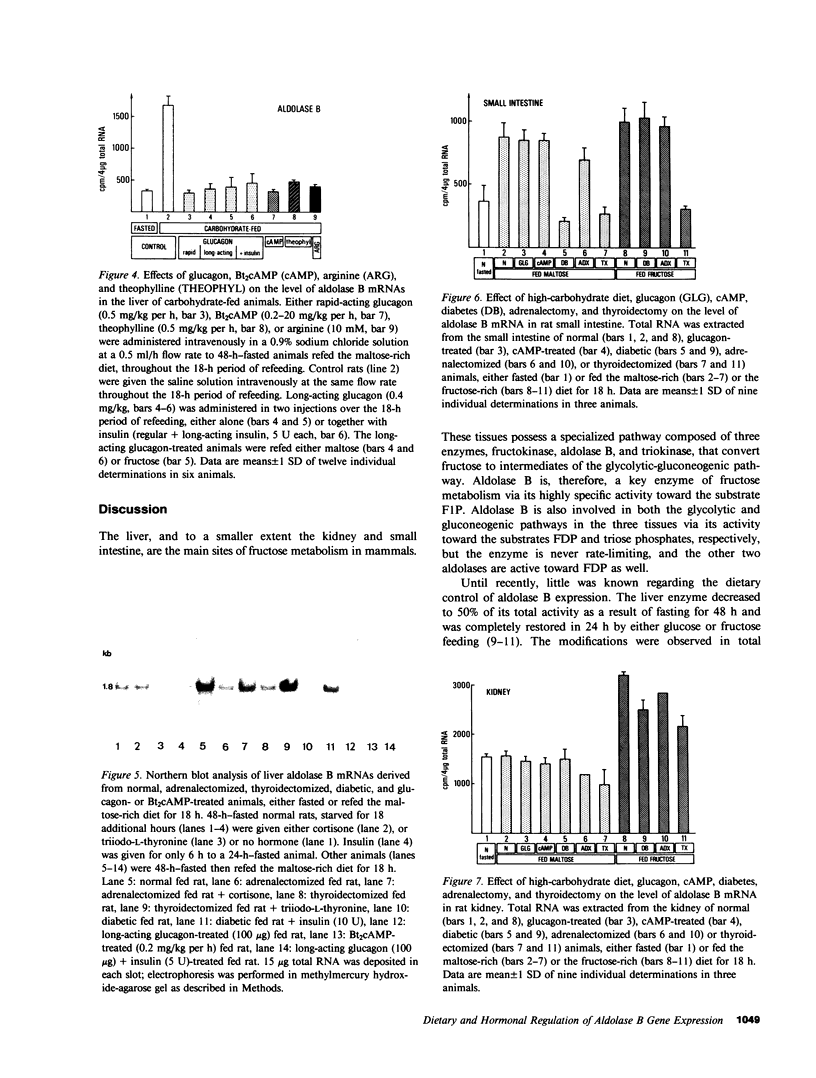
- Heinz F. Enzyme des Fructosestoffwechsels. Anderungen von Enzymaktivitäten in Leber und Niere der Ratte bei fructose- und glucosereicher Ernährung. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Apr;349(4):399–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning S. J., Ballard P. L., Kretchmer N. A study of the cytoplasmic receptors for glucocorticoids in intestine of pre- and postweanling rats. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2073–2079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U. Diabetes mellitus: changes in the transport properties of isolated intestinal microvillous membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Cottreau D., Daegelen D., Dreyfus J. C. Cell-free translation of messenger RNAs from adult and fetal human muscle. Characterization of neosynthesized glycogen phosphorylase, phosphofructokinase and glucose phosphate isomerase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER M., DRUCKER W. R., OWENS J. E., CRAIG J. W., WOODWARD H., Jr Metabolism of intravenous fructose and glucose in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1952 Jan;31(1):115–125. doi: 10.1172/JCI102569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood H. A., Wood P. J., Marks V. The effect of induced hyperglucagonaemia on the Zucker fatty rat. Diabetologia. 1978 Jun;14(6):405–412. doi: 10.1007/BF01228135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrias D. A., Mayer R. J. Metabolism of fructose in the small intestine. 1. The effect of fructose feeding on fructose transport and metabolism in rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 26;291(2):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90504-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnich A., Marie J., Reach G., Vaulont S., Simon M. P., Kahn A. In vivo hormonal control of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression. Effects of glucagon, cyclic AMP, insulin, cortisone, and thyroid hormones on the dietary induction of mRNAs in the liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10228–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Koerner D., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Specific nuclear triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver and kidney. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):330–333. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEANASKY R. J., LARDY H. A. Bovine liver aldolase. II. Physical and chemical measurements on the crystalline enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):371–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENOLD A. E., HASTINGS A. B., NESBETT F. B. Studies on carbohydrate metabolism in rat liver slices. III. Utilization of glucose and fructose by liver from normal and diabetic animals. J Biol Chem. 1954 Aug;209(2):687–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskin P., Unger R. H. Hyperglucagonemia and its suppression. Importance in the metabolic control of diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 31;299(9):433–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808312990901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosensweig N. S., Stifel F. B., Herman R. H., Zakim D. The dietary regulation the glycoytic enzymes. II. Adaptive changes in human jejunum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):228–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosensweig N. S., Stifel F. B., Zakim D., Herman R. H. Time response of human jejunal glycolytic enzymes to a high sucrose diet. Gastroenterology. 1969 Aug;57(2):143–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA F. [Fructose-1-phosphoaldolase activity of mammalian tissues. I. Distribution of fructose-1-phosphoaldolase activity in mammalian tissues]. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1961;43:1357–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira F., Delain D., Lacroix Y. Multiple molecular forms of aldolase in fetal liver cell cultures: action of dexamethasone. Enzyme. 1971;12(5):545–552. doi: 10.1159/000459584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira F., Nordmann Y. Présence de trois types d'aldolase dans le foie humain. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Nov;26(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira F. Resurgence of fetal isozymes in cancer: study of aldolase, pyruvate kinase, lactic dehydrogenase, and beta-hexosaminidase. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1981;5:27–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillero A., Sillero M. A., Sols A. Regulation of the level of key enzymes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):351–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillero M. A., Sillero A., Sols A. Enzymes involved in fructose metabolism in lir and the glyceraldehyde metabolic crossroads. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. P., Besmond C., Cottreau D., Weber A., Chaumet-Riffaud P., Dreyfus J. C., Trépat J. S., Marie J., Kahn A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat L-type pyruvate kinase and aldolase B. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14576–14584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stifel F. B., Rosenweig N. S., Zakim D., Herman R. H. Dietary regulation of glycolytic enzymes. I. Adaptive changes in rat jejunum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata Y., Chang T. M. Intermittent vascular access for extracorporeal circulation in conscious rats: a new technique. Artif Organs. 1982 May;6(2):213–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.1982.tb04087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping D. L., Mayes P. A. The concentration of fructose, glucose and lactate in the splanchnic blood vessels of rats absorbing fructose. Nutr Metab. 1971;13(6):331–338. doi: 10.1159/000175352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Mukai T., Hidaka S., Miyahara H., Tsutsumi R., Tanaka T., Hori K., Ishikawa K. Rat aldolase isozyme gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6537–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. The essential role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
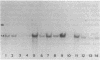
- Weber A., Marie J., Cottreau D., Simon M. P., Besmond C., Dreyfus J. C., Kahn A. Dietary control of aldolase B and L-type pyruvate kinase mRNAs in rat. Study of translational activity and hybridization with cloned cDNA probes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1798–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L. K., Morris S. M., Jr, Fisch J. E., Glynias M. J., Jenik R. A., Goodridge A. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA sequences for avian malic enzyme. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of malic enzyme mRNA levels in avian liver cells in vivo and in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1337–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]