Abstract
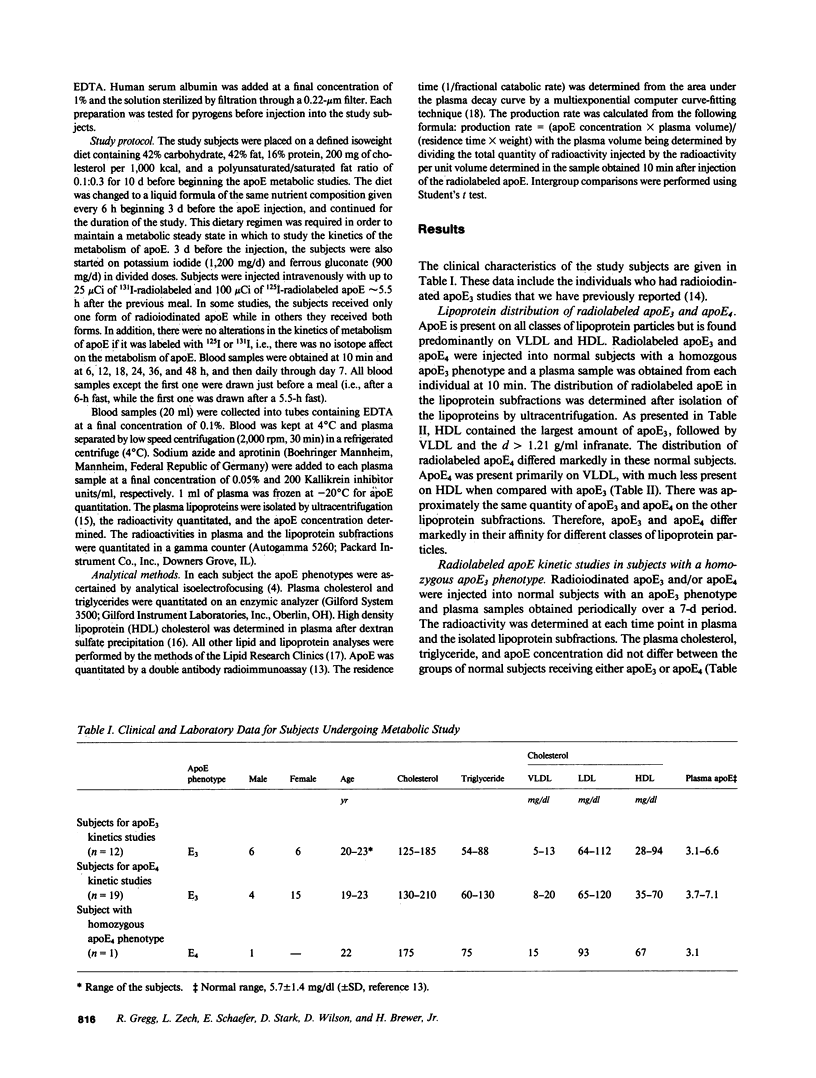
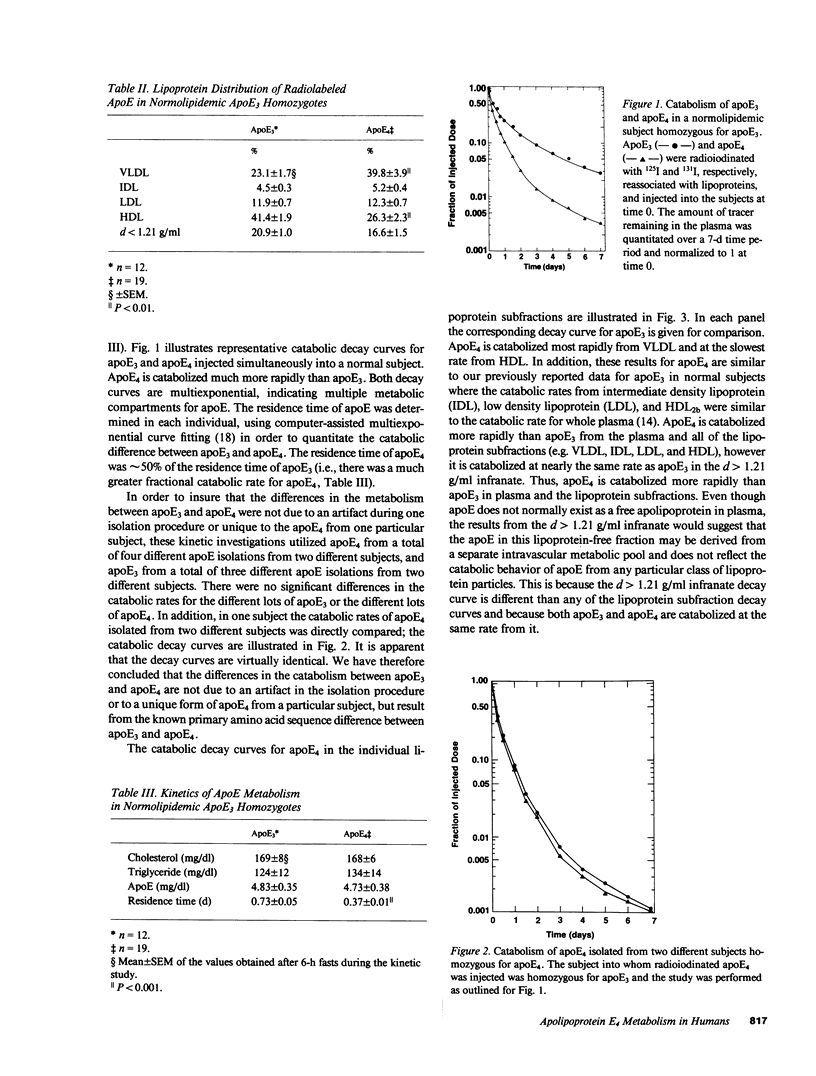
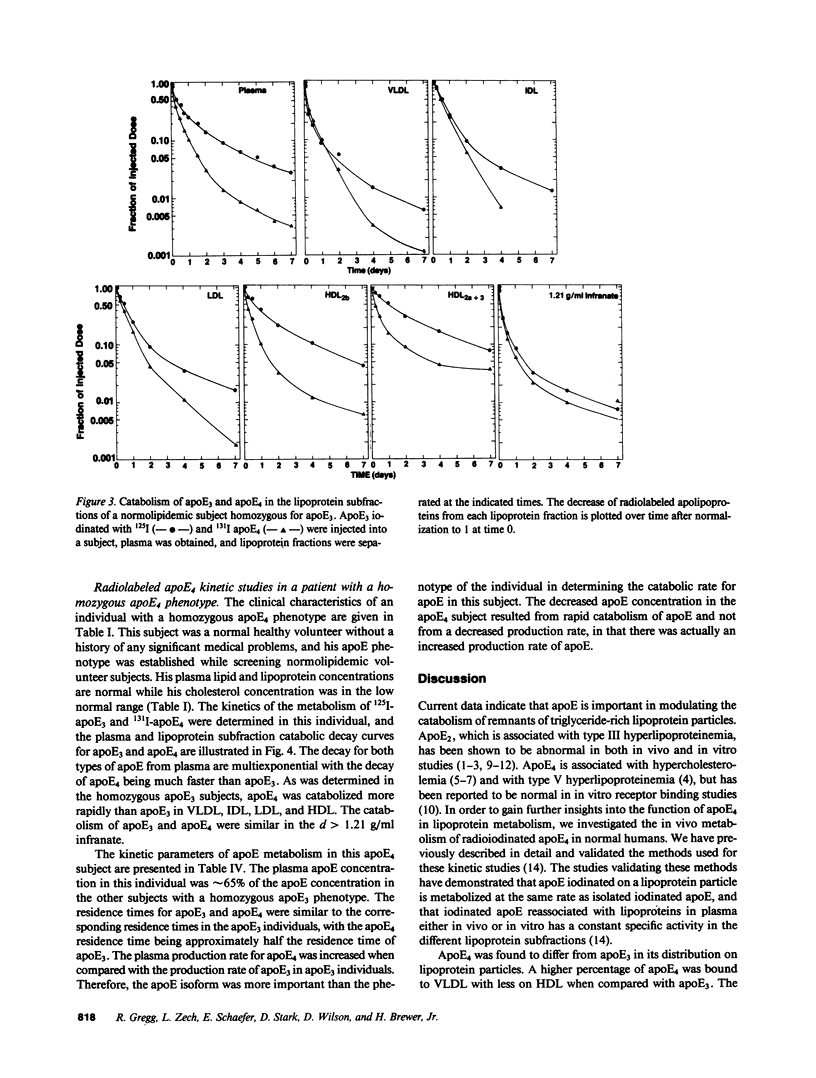
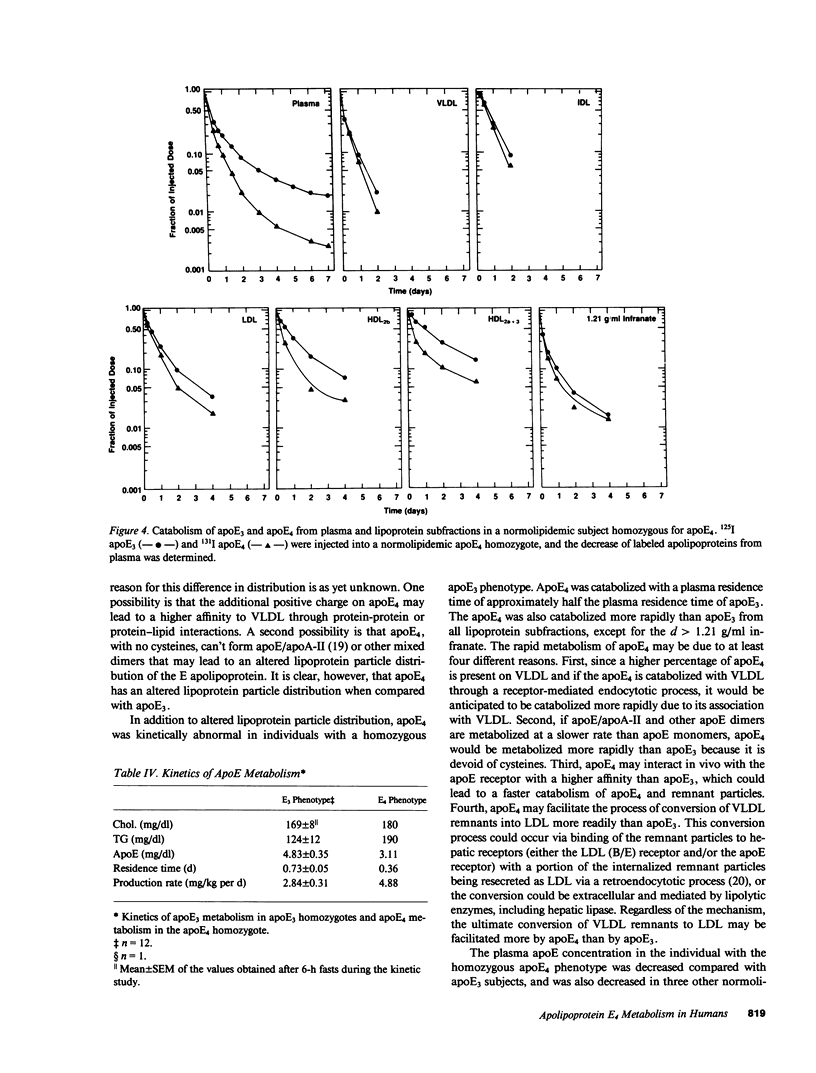
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is important in modulating the catabolism of remnants of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particles. It is a polymorphic protein with the three common alleles coding for apoE2, apoE3, and apoE4. ApoE3 is considered the normal isoform, while apoE4 is associated both with hypercholesterolemia and type V hyperlipoproteinemia. We quantitated the kinetics of metabolism of apoE4 in 19 normolipidemic apoE3 homozygotes and 1 normolipidemic apoE4 homozygote, and compared this with the metabolism of apoE3 in 12 normolipidemic apoE3 homozygotes. In the apoE3 homozygous subjects, apoE4 was catabolized twice as fast as apoE3, with a mean plasma residence time of 0.37 +/- 0.01 d (+/- SEM) and 0.73 +/- 0.05 (P less than 0.001), respectively. When plasma was fractionated into the lipoprotein subclasses, the greatest amount of labeled apoE4 was present on very low density lipoproteins, while the largest fraction of labeled apoE3 was associated with high density lipoproteins. The plasma apoE concentration was decreased in an apoE4 homozygote compared with the apoE3 homozygotes (3.11 mg/dl vs. 4.83 +/- 0.35 mg/dl). The reduced apoE4 concentration was entirely due to a decreased apoE4 residence time in the apoE4 homozygote (0.36 d vs. 0.73 +/- 0.05 d for apoE3 in apoE3 homozygotes). These results indicate that apoE4 is kinetically different than apoE3, and suggest that the presence of apoE4 in hypercholesterolemic and type V hyperlipoproteinemic individuals may play an important pathophysiological role in the development of these dyslipoproteinemias.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assmann G., Schmitz G., Menzel H. J., Schulte H. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and hyperlipidemia. Clin Chem. 1984 May;30(5):641–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulinskas T. H., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Bierman E. L., Gevers W., Coetzee G. A. Retro-endocytosis of low density lipoprotein by cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 22;664(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M., Hall M., 3rd, Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Phair R. D., Goebel R. H. Metabolsim of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetic studies in normal and hyperlipoproteininemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):38–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthillier D., Sing C. F., Davignon J. Apolipoprotein E phenotyping with a single gel method: application to the study of informative matings. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1060–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Zech L. A., Gregg R. E., Schwartz D., Schaefer E. J. NIH conference. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: diagnosis, molecular defects, pathology, and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1983 May;98(5 Pt 1):623–640. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-5-623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. H., Segrest J. P. Resistance of a very low density lipoprotein subpopulation from familial dysbetalipoproteinemia to in vitro lipolytic conversion to the low density lipoprotein density fraction. J Lipid Res. 1983 Sep;24(9):1148–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Mahley R. W., Chappell D. A., Weisgraber K. H., Ludwig E., Witztum J. L. Role of apolipoprotein E in the lipolytic conversion of beta-very low density lipoproteins to low density lipoproteins in type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5566–5570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo S. S., Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr, Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. The localization of the gene for apolipoprotein C-II to chromosome 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):687–693. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Assignment of the human gene for the low density lipoprotein receptor to chromosome 19: synteny of a receptor, a ligand, and a genetic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2826–2830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Schaefer E. J., Zech L. A., Gregg R. E., Brewer H. B., Jr Increased prevalence of apolipoprotein E4 in type V hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):474–477. doi: 10.1172/JCI110638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein E metabolism in normolipoproteinemic human subjects. J Lipid Res. 1984 Nov;25(11):1167–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: defective metabolism of an abnormal apolipoprotein E. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.7455696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Eddy R. L., Robertson M. E., Priestley L. M., Scott J., Shows T. B. Chromosomal localization of the human apoprotein CI gene and of a polymorphic apoprotein AII gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):299–306. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaisen B., Teisberg P., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr The locus for apolipoprotein E (apoE) is linked to the complement component C3 (C3) locus on chromosome 19 in man. Hum Genet. 1982;62(3):233–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00333526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard C. J., Munro A., Lorimer A. R., Gotto A. M., Shepherd J. Metabolism of apolipoprotein B in large triglyceride-rich very low density lipoproteins of normal and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2178–2192. doi: 10.1172/JCI111644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P. R., Cortese C., Wootton R., Marenah C., Miller N. E., Lewis B. Plasma apolipoprotein B metabolism in familial type III dysbetalipoproteinaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;15(2):100–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1985.tb00152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Jaeschke M., Menzel J. Familial hyperlipoproteinemia type III: deficiency of a specific apolipoprotein (apo E-III) in the very-low-density lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Kindermann I., Kaffarnik H., Steinmetz A. Apolipoprotein E phenotypes and hyperlipidemia. Hum Genet. 1984;65(3):232–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00286508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Vogelberg K. H., Steinmetz A., Schoenborn W., Pruin N., Jaeschke M., Hees M., Canzler H. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. II. Genetics of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):37–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnick G. R., Benderson J., Albers J. J. Dextran sulfate-Mg2+ precipitation procedure for quantitation of high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1982 Jun;28(6):1379–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Apoprotein (E--A-II) complex of human plasma lipoproteins. I. Characterization of this mixed disulfide and its identification in a high density lipoprotein subfraction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6281–6288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



