Abstract
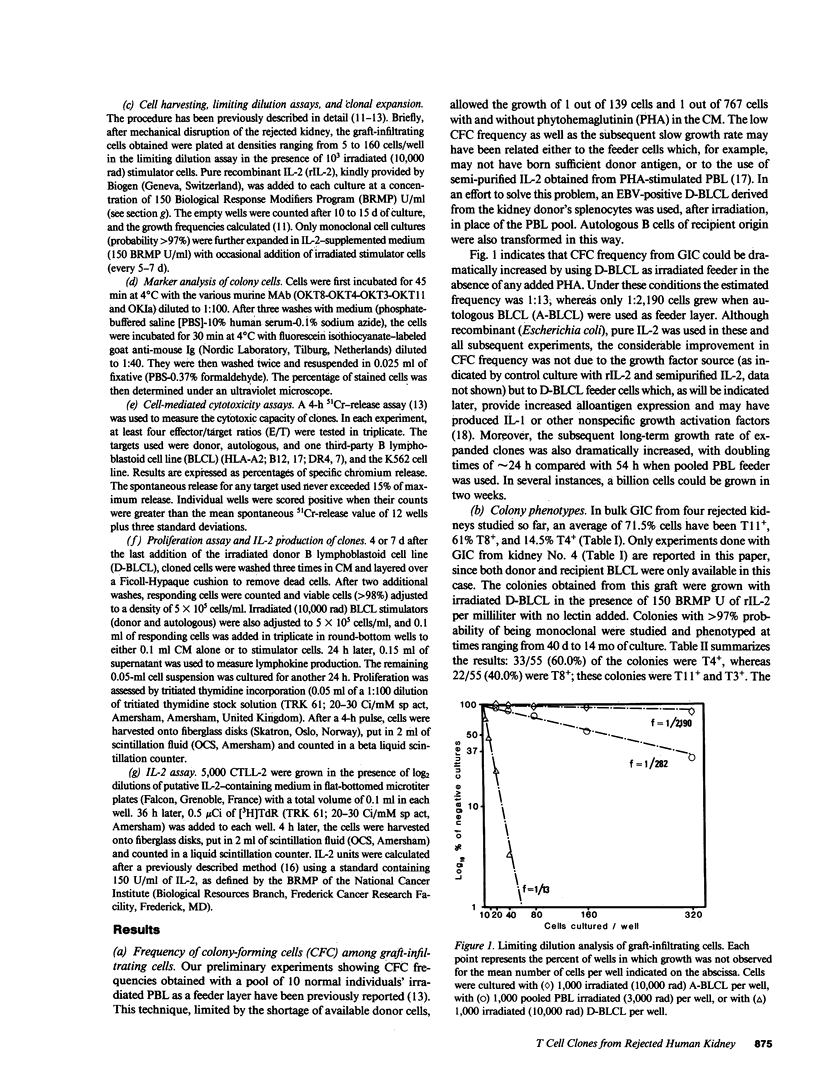
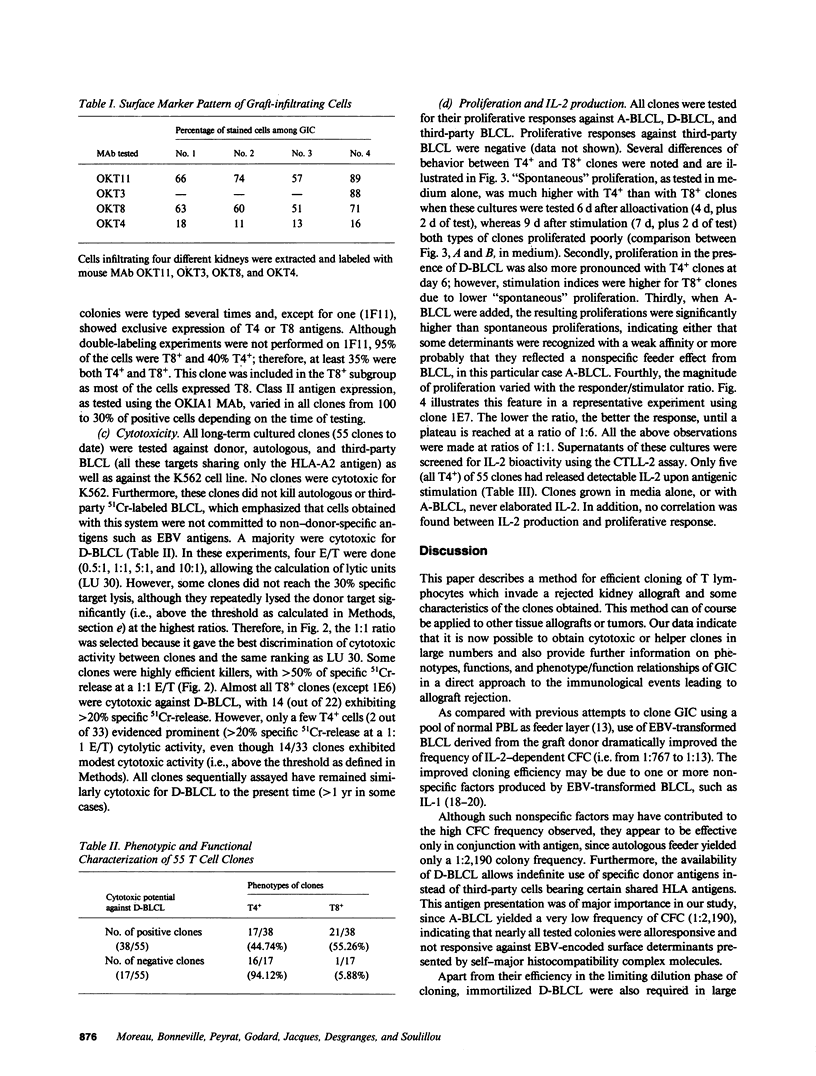
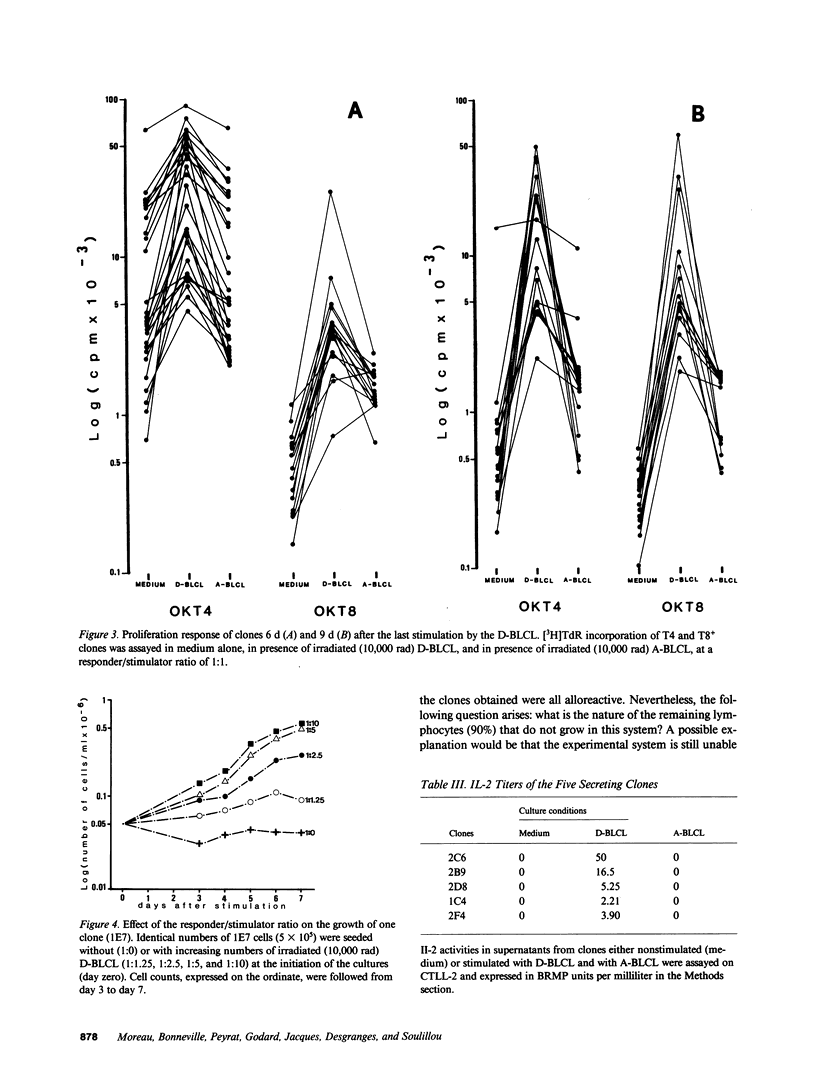
Mechanically harvested lymphocytes invading an irreversibly rejected human kidney allograft were seeded at limiting dilution to calculate the frequency of growing precursors. Optimal growth frequency (1/13) was obtained when Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed donor B lymphocytes were used as stimulators (D-BLCL) in the presence of interleukin 2 (IL-2). The 55 clones analyzed were all T11+ and T3+, and all expressed DR antigens (45% were T8+ and 55% T4+). Only one clone had a double-labeled (T4+ T8+) surface. All cells proliferated significantly against D-BLCL, although T4+ clones had a significantly shorter average doubling time than T8+ clones. Nearly all T8+ clones were specifically cytotoxic for D-BLCL, while both T4 and T8 did not react against K562, autologous EBV-BLCL, and third-party EBV-BLCL. Detectable IL-2 was found in the culture supernatants of only a minority of clones (all T4+).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold A., Lipkowitz S., Suthanthiran M., Novogrodsky A., Stenzel K. H. Human B lymphoblastoid cell lines provide an interleukin 1-like signal for mitogen-treated T lymphocytes via direct cell contact. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3876–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher N. L., Chen S., Hoffman R. A., Simmons R. L. Maturation of cytotoxic T cells within sponge matrix allografts. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):617–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher N. L., Hoffman R., Hanto D. W., Simmons R. L. Cellular events within the rejecting allograft. Transplantation. 1983 Mar;35(3):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First French workshop on standardization of human IL-2: joint report. Lymphokine Res. 1982;1(4):121–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godard A., Naulet J., Peyrat M. A., Vie H., Moreau J. F., Bignon J. D., Soulillou J. P. Preparative two-step purification of human IL-2 by HPLC and hydrophobic affinity chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1984 May 25;70(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Thomson N. M., Atkins R. C. Composition of interstitial cellular infiltrate identified by monoclonal antibodies in renal biopsies of rejecting human renal allografts. Transplantation. 1983 May;35(5):458–463. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198305000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., von Willebrand E. Transplant aspiration cytology. Transplantation. 1984 Jul;38(1):7–12. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198407000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immunosuppression. Cyclosporine. Transplant Proc. 1985 Feb;17(1 Pt 2):1158–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveland B. E., Hogarth P. M., Ceredig R., McKenzie I. F. Cells mediating graft rejection in the mouse. I. Lyt-1 cells mediate skin graft rejection. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1044–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca F., Barocci S., Kunkl A., Gurreri G., Costantini M., Celada F. Recognition of donor fibroblast antigens by lymphocytes homing in the human grafted kidney. Transplantation. 1983 Dec;36(6):670–674. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198336060-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer T. G., Fuller A. A., Fuller T. C., Lazarovits A. I., Boyle L. A., Kurnick J. T. Characterization of in vivo-activated allospecific T lymphocytes propagated from human renal allograft biopsies undergoing rejection. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):258–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Cooper D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed at autologous virus-transformed targets: further evidence for linkage of genetic restriction to T4 and T8 surface glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):186–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Lisco H., Stitt D., Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau J. F., Miller R. G. Growth at limiting dilution of human T cell colonies from T cell-depleted peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1139–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau J. F., Peyrat M. A., Vie H., Bonneville M., Soulillou J. P. T cell colony-forming frequency of mononucleated cells extracted from rejected human kidney transplants. Functional and phenotypic studies of the colonies. Transplantation. 1985 Jun;39(6):649–656. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198506000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., LeBien T. W., Michael A. F. Interstitial mononuclear cell populations in renal graft rejection. Identification by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):17–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D., Fuller L., Esquenazi V., Kyriakides G. K., Pardo V., Miller J. The biologic significance of the mixed lymphocyte kidney culture in humans. Transplantation. 1985 Oct;40(4):376–383. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198510000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmuller D. Which T cells mediate allograft rejection? Transplantation. 1985 Sep;40(3):229–233. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom T. B., Tilney N. L., Carpenter C. B., Busch G. J. Identity and cytotoxic capacity of cells infiltrating renal allografts. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jun 12;292(24):1257–1263. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197506122922402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom T. B., Tilney N. L., Paradysz J. M., Bancewicz J., Carpenter C. B. Cellular components of allograft rejection: identity, specificity, and cytotoxic function of cells infiltrating acutely rejecting allografts. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2020–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufveson G., Forsum U., Claesson K., Klareskog L., Larsson E., Karlsson-Parra A., Frödin L. T-lymphocyte subsets and HLA-DR-expressing cells in rejected human kidney grafts. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jul;18(1):37–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Griend R. J., Van Krimpen B. A., Bol S. J., Thompson A., Bolhuis R. L. Rapid expansion of human cytotoxic T cell clones: growth promotion by a heat-labile serum component and by various types of feeder cells. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 10;66(2):285–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Lehman D. H., McCoy R. C., Gunnells J. C., Jr, Stickel D. L. Antitubular basement membrane antibodies after renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1974 Nov;18(5):447–452. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197411000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Griend R. J., Bolhuis R. L. Rapid expansion of allospecific cytotoxic T cell clones using nonspecific feeder cell lines without further addition of exogenous IL2. Transplantation. 1984 Oct;38(4):401–406. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198410000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Willebrand E. OKT4/8 ratio in the blood and in the graft during episodes of human renal allograft rejection. Cell Immunol. 1983 Apr 1;77(1):196–201. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



