Abstract
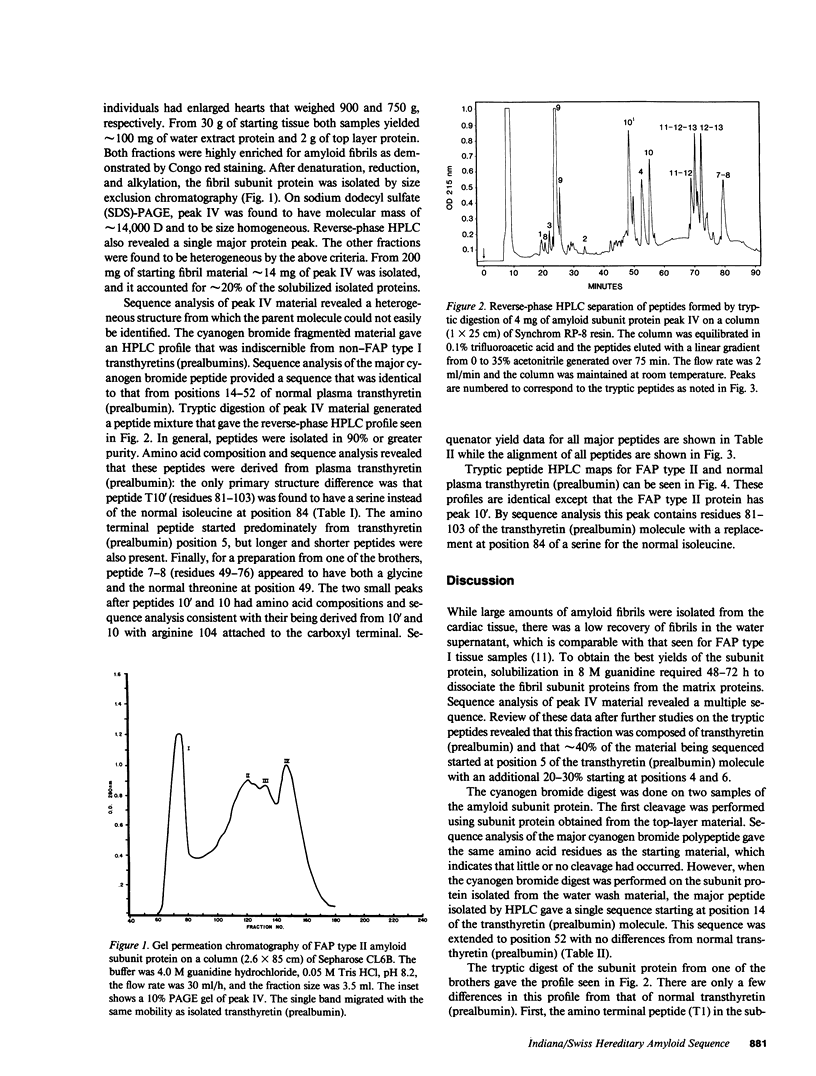
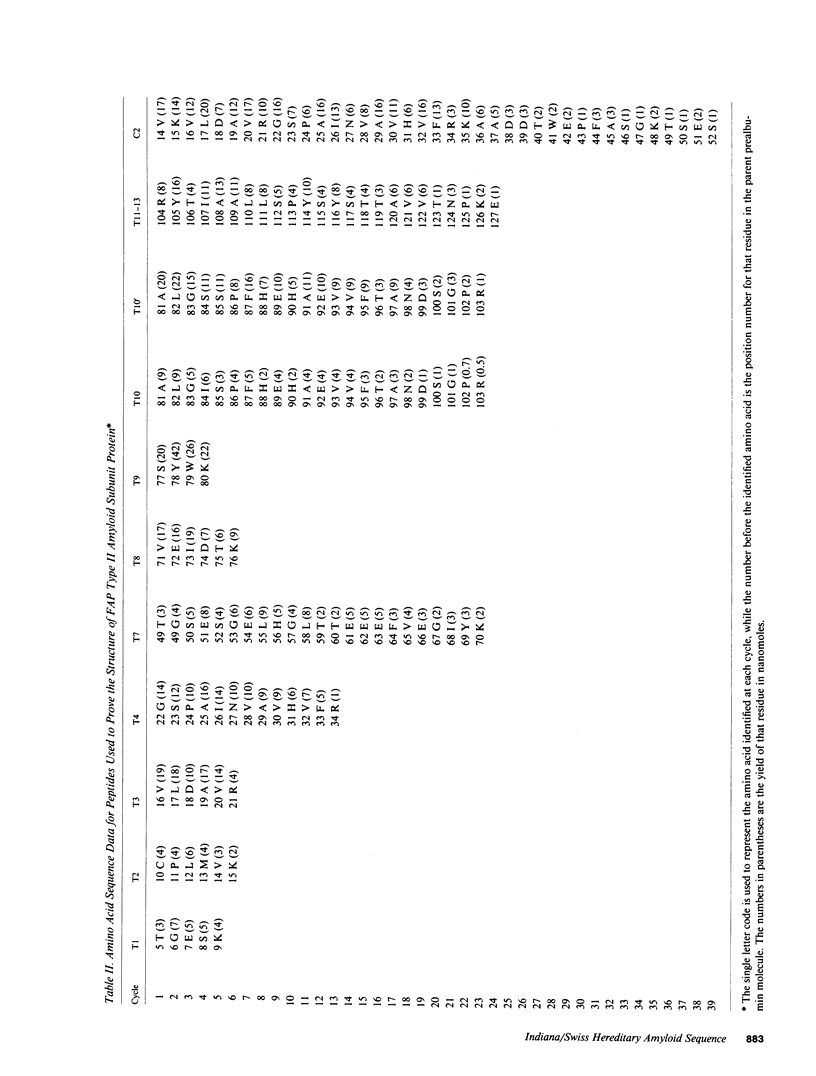
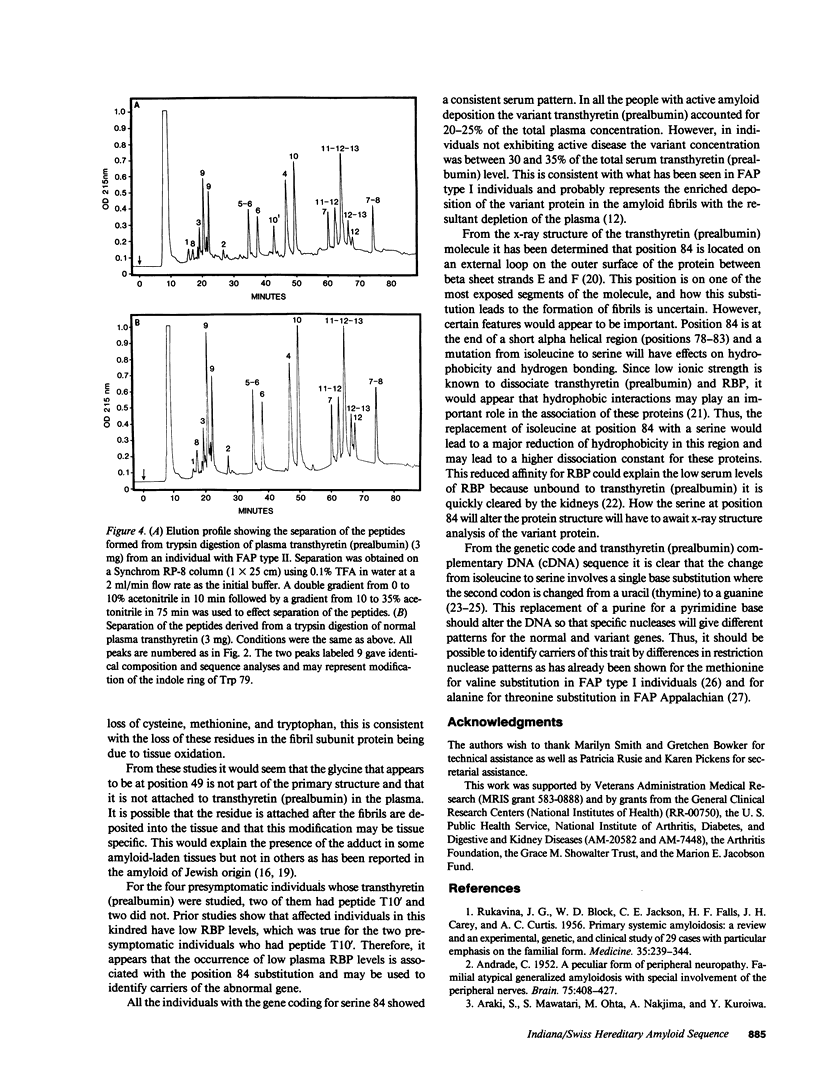
Amyloid fibrils were isolated from cardiac tissue of two brothers who died from familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) type II. Sequence analysis on peptides derived from proteolytic cleavage with trypsin and fragmentation with cyanogen bromide reveal that the fibril subunit protein is derived from plasma transthyretin (prealbumin). About two-thirds of the fibril subunit protein was found to contain an amino acid substitution at position 84 where the normal isoleucine residue has been replaced by serine. Sequence analysis of the plasma transthyretin (prealbumin) from the two brothers as well as two clinically diagnosed FAP type II family members and two of four children of affected individuals showed the presence of serine at position 84. The presence of this substitution also correlates with low serum levels of retinol-binding protein and thus transthyretin (prealbumin) position 84 may be involved with the interaction of these two proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952 Sep;75(3):408–427. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCK W. D., CAREY J. G., CURTIS A. C., FALLS H. F., JACKSON C. E., RUKAVINA J. G. Primary systemic amyloidosis: a review and an experimental, genetic, and clinical study of 29 cases with particular emphasis on the familial form. Medicine (Baltimore) 1956 Sep;35(3):239–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Dwulet F. E. Prealbumin and retinol binding protein serum concentrations in the Indiana type hereditary amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1493–1498. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D. Partial amino acid sequence homology between an heredofamilial amyloid protein and human plasma prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1035–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Geisow M. J., Oatley S. J., Rérat B., Rérat C. Structure of prealbumin: secondary, tertiary and quaternary interactions determined by Fourier refinement at 1.8 A. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. P., Figueira A. S., Bravo F. R. Amyloid fibril protein related to prealbumin in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Polymorphism of human plasma thyroxine binding prealbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90831-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Primary structure of an amyloid prealbumin and its plasma precursor in a heredofamilial polyneuropathy of Swedish origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERIKSEN T., GOTZSCHE H., HARBOE N., KIAER W., MELLEMGAARD K. Familial primary amyloidosis with severe amyloid heart disease. Am J Med. 1962 Sep;33:328–348. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein, prealbumin, and vitamin A transport. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1976;5:313–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J., Vital C., Vallat J. M., Lagueny A., Ferrer X. Neuropathies amyloides familiales dans trois familles d'origine française. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1983;139(4):259–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kametani F., Tonoike H., Hoshi A., Shinoda T., Kito S. A variant prealbumin-related low molecular weight amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy of Japanese origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):622–628. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahloudji M., Teasdall R. D., Adamkiewicz J. J., Hartmann W. H., Lambird P. A., McKusick V. A. The genetic amyloidoses with particular reference to hereditary neuropathic amyloidosis, type II (Indiana or Rukavina type). Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jan;48(1):1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Maeda S., Shimada K., Araki S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human prealbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):558–564. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Tawara S., Matsuo H., Araki S. Revised analysis of amino acid replacement in a prealbumin variant (SKO-III) associated with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):921–928. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Franklin E. C., Prelli F., Frangione B. A variant of prealbumin from amyloid fibrils in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):989–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Cheng S. Y., Gershengorn M. C., Glinoer D., Cahnmann H. J., Edelnoch H. Thyroxine transport proteins of plasma. Molecular properties and biosynthesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1978;34:477–519. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571134-0.50017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva M. J., Birken S., Costa P. P., Goodman D. S. Amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, Portuguese type. Definition of molecular abnormality in transthyretin (prealbumin). J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):104–119. doi: 10.1172/JCI111390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Sakaki Y., Matsuo H., Goto I., Kuroiwa Y., Sahashi I., Takahashi A., Shinoda T., Isobe T., Takagi Y. Diagnosis of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy by recombinant DNA techniques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):636–642. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawara S., Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Araki S. Identification of amyloid prealbumin variant in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):880–888. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Allen M. W., Frohlich J. A., Davis J. R. Inherited predisposition to generalized amyloidosis. Clinical and pathological study of a family with neuropathy, nephropathy, and peptic ulcer. Neurology. 1969 Jan;19(1):10–25. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Dwulet F. E., Conneally P. M., Benson M. D. Biochemical and molecular genetic characterization of a new variant prealbumin associated with hereditary amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):6–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI112573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Naylor S. L., Kluve-Beckerman B., Long G. L., McDonald L., Shows T. B., Benson M. D. Localization of the human prealbumin gene to chromosome 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):753–758. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91956-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




