Abstract
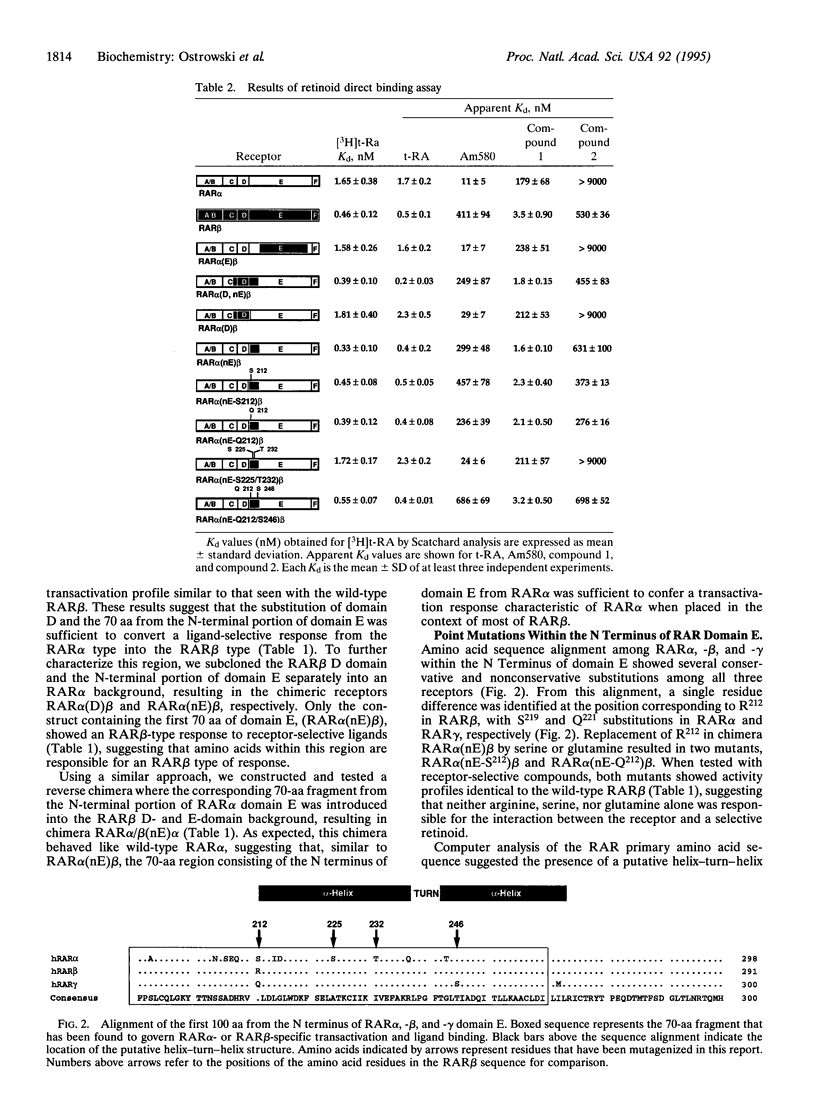
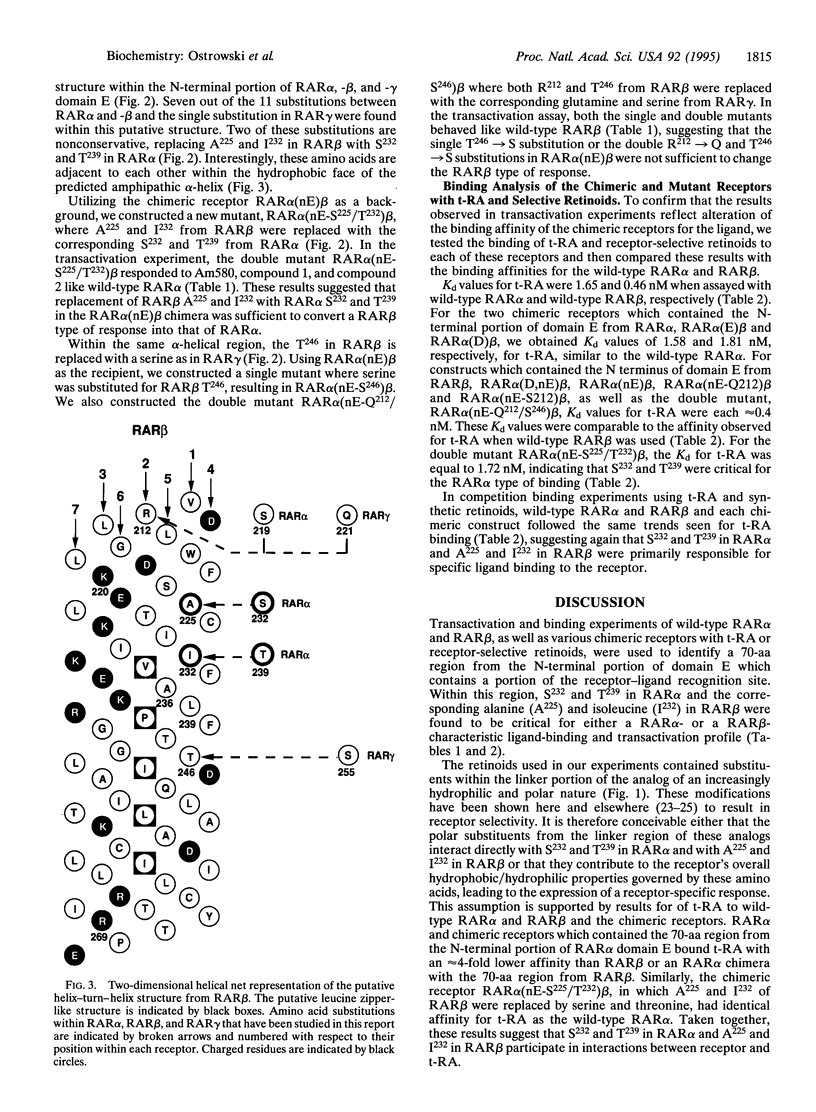
Utilizing a strategy involving domain exchange between retinoic acid receptors alpha and beta (RAR alpha and RAR beta) and monitoring the transcriptional activity of the resulting chimeric receptors with receptor-selective retinoids, we identified a 70-aa region within the N-terminal portion of the RAR alpha and -beta domain E which is important for an RAR alpha- or RAR beta-specific response. Two amino acid residues within this region, serine-232 (S232) and threonine-239 (T239) in RAR alpha and the corresponding alanine-225 (A225) and isoleucine-232 (I232) in RAR beta, were found to be essential for this effect. In addition, binding studies using the chimeric receptors expressed in Escherichia coli showed that the N-terminal portion of domain E was also important for the characteristic binding profile of t-RA and various retinoids with RAR alpha or RAR beta. Structural predictions of the primary amino acid sequence in this region indicate the presence of an amphipathic helix-turn-helix structure with five hydrophobic amino acids that resemble a leucine zipper motif. The amino acid residues identified by domain swapping, S232 and T239 in RAR alpha and A225 and I232 in RAR beta, were found within the hydrophobic face of an alpha-helix in close proximity to this zipper motif, suggesting that the ligand may interact with the receptor in the region adjacent to a surface involved in protein-protein interactions. This finding may link ligand binding to other processes important for transcriptional activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. Y., Ransom S. C., McPhie P., Bhat M. K., Mixson A. J., Wintraub B. D. Analysis of the binding of 3,3',5-triiodo-L-thyronine and its analogues to mutant human beta 1 thyroid hormone receptors: a model of the hormone binding site. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 12;33(14):4319–4326. doi: 10.1021/bi00180a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Ostrowski J., Kjelsberg M. A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Discrete amino acid sequences of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor determine the selectivity of coupling to phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1633–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Heyman R. A., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Functional inhibition of retinoic acid response by dominant negative retinoic acid receptor mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2989–2993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delescluse C., Cavey M. T., Martin B., Bernard B. A., Reichert U., Maignan J., Darmon M., Shroot B. Selective high affinity retinoic acid receptor alpha or beta-gamma ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;40(4):556–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Dimerization among nuclear hormone receptors. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1293–1301. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Yang C. R., Au M., Casanova J., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. A domain containing leucine-zipper-like motifs mediate novel in vivo interactions between the thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1610–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graupner G., Malle G., Maignan J., Lang G., Pruniéras M., Pfahl M. 6'-substituted naphthalene-2-carboxylic acid analogs, a new class of retinoic acid receptor subtype-specific ligands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1554–1561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91750-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Petkovich M., Gaub M. P., Kagechika H., Shudo K., Chambon P. The retinoic acid receptors alpha and beta are expressed in the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;3(7):1046–1052. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-7-1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Hänni C., Coll J., Catzeflis F., Stéhelin D. Evolution of the nuclear receptor gene superfamily. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maksymowych A. B., Hsu T. C., Litwack G. A novel, highly conserved structural motif is present in all members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Receptor. 1992 Winter;2(4):225–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J. Vitamin A receptors. Nutr Rev. 1994 Feb;52(2 Pt 2):S32–S44. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1994.tb01385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhie P., Parkison C., Lee B. K., Cheng S. Y. Structure of the hormone binding domain of human beta 1 thyroid hormone nuclear receptor: is it an alpha/beta barrel? Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 27;32(29):7460–7465. doi: 10.1021/bi00080a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier C. A., Dickstein B. M., Ashizawa K., McClaskey J. H., Muchmore P., Ransom S. C., Menke J. B., Hao E. H., Usala S. J., Bercu B. B. Variable transcriptional activity and ligand binding of mutant beta 1 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptors from four families with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):248–258. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell A. L., Koenig R. J. Mutational analysis identifies a new functional domain of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):715–720. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. D., Beninghof E. G., Koenig R. J. Dimerization interfaces of thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, vitamin D, and retinoid X receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11534–11541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe A., Brickell P. M. The nuclear retinoid receptors. Int J Exp Pathol. 1993 Apr;74(2):117–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G. Mechanisms of transactivation by retinoic acid receptors. Bioessays. 1993 May;15(5):309–315. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tairis N., Gabriel J. L., Gyda M., 3rd, Soprano K. J., Soprano D. R. Arg269 and Lys220 of retinoic acid receptor-beta are important for the binding of retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19516–19522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate B. F., Allenby G., Janocha R., Kazmer S., Speck J., Sturzenbecker L. J., Abarzúa P., Levin A. A., Grippo J. F. Distinct binding determinants for 9-cis retinoic acid are located within AF-2 of retinoic acid receptor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2323–2330. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S., Bartelmez S., Heyman R., Damm K., Evans R., Collins S. J. A mutated retinoic acid receptor-alpha exhibiting dominant-negative activity alters the lineage development of a multipotent hematopoietic cell line. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2258–2269. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Cook R. G., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. COUP transcription factor is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):163–166. doi: 10.1038/340163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



