Abstract
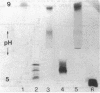
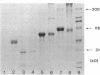
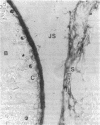
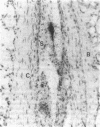
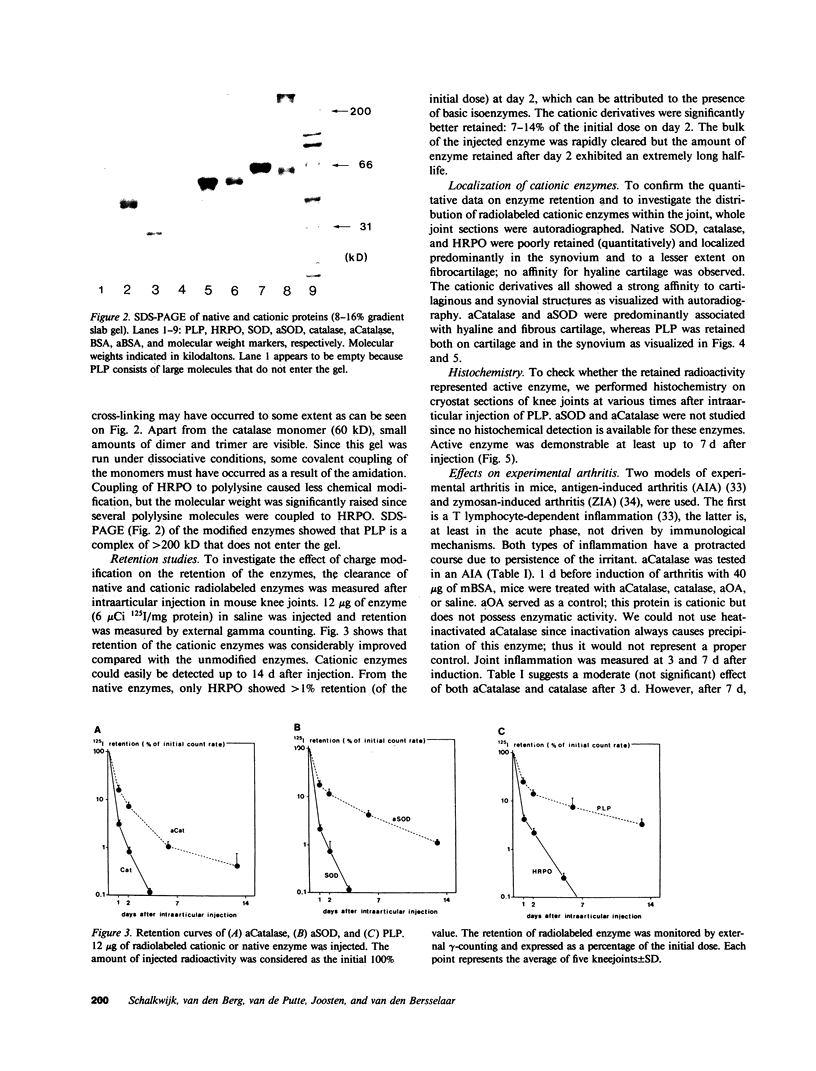
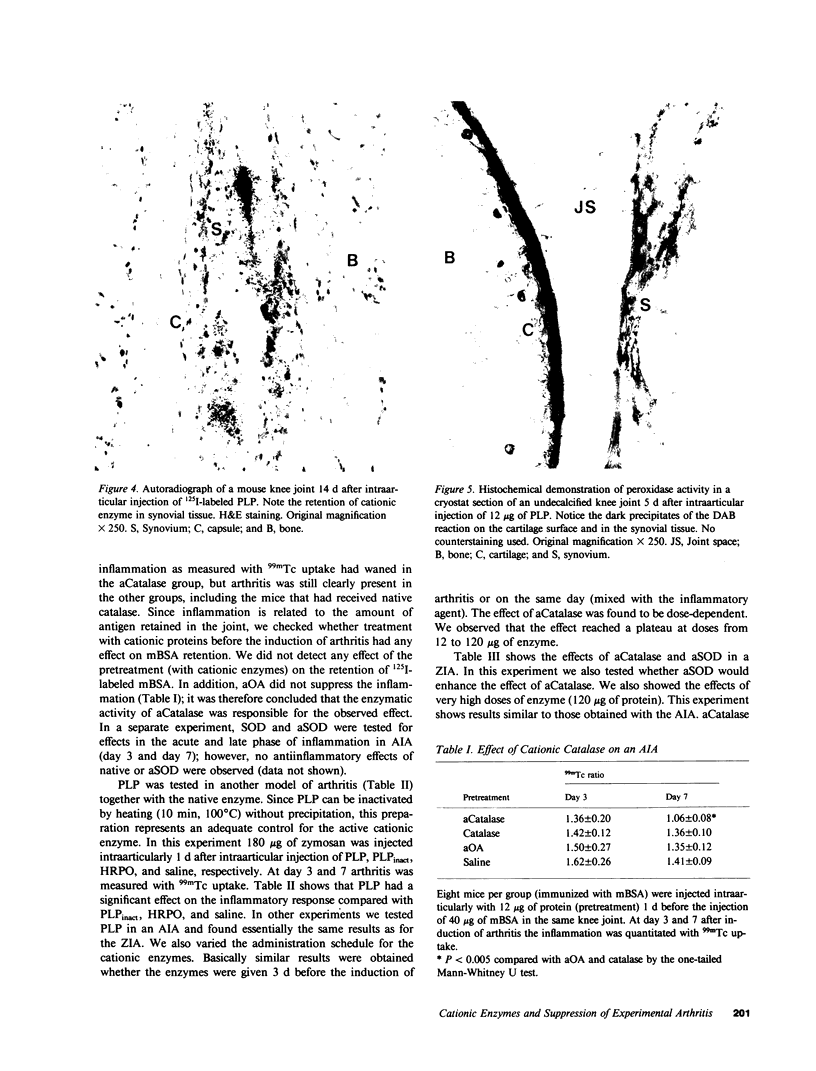
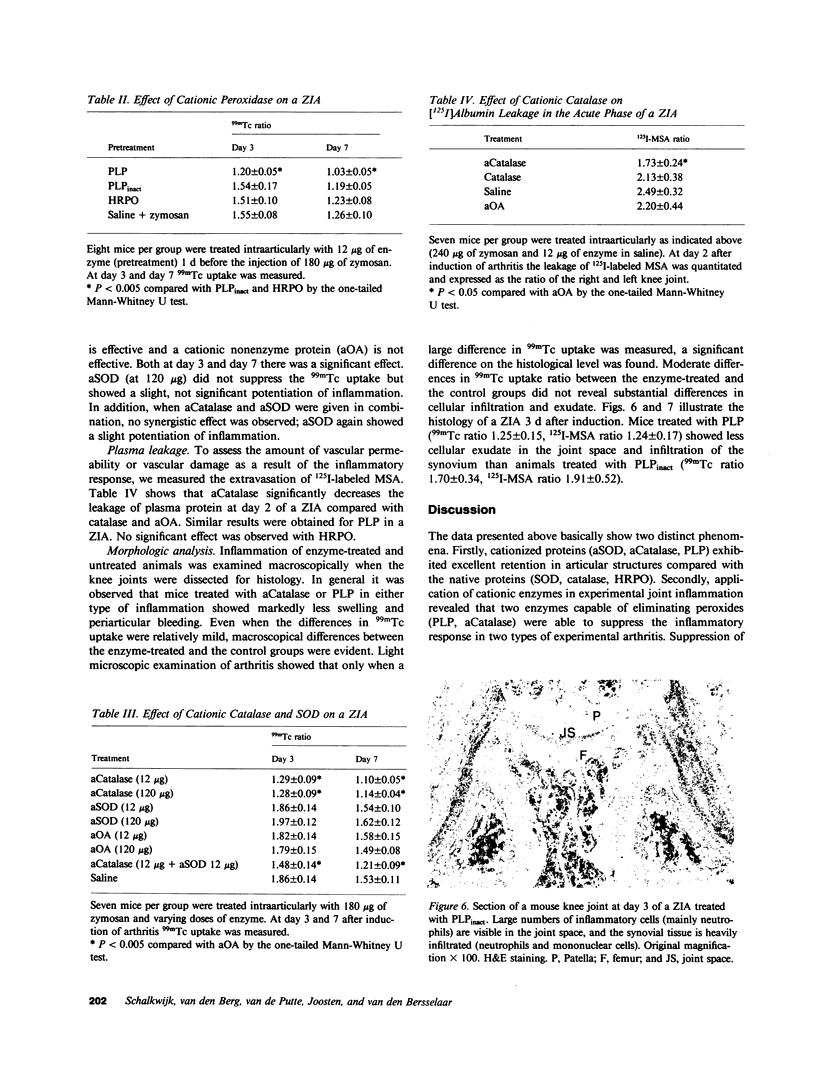
Several enzymes and other proteins were made cationic either by coupling to polylysine or by shielding of anionic sites. These cationic proteins, all having an isoelectric point greater than 8.5 exhibited excellent retention in articular structures when injected in mouse knee joints. Autoradiography and histochemistry showed that cationic forms of catalase, superoxide dismutase, and horseradish peroxidase were firmly retained by synovial and cartilaginous tissues. The half-life of these enzymes in the joint is thus significantly extended compared with native enzymes. The native enzymes and their cationic derivatives were tested for antiinflammatory properties in mice, using antigen-induced arthritis and zymosan-induced arthritis. It was found that injection of cationic catalase or peroxidase induced a marked suppression of some parameters of the inflammatory response in both types of arthritis, as measured by 99m technetium pertechnetate uptake and leakage of 125I-labeled albumin. Native catalase and peroxidase were less, or not at all effective. Cationic superoxide dismutase or cationic nonenzyme proteins did not suppress inflammation. The observed suppression of two different types of inflammation (an immune and a nonimmune arthritis) by catalase and peroxidase suggests that elimination of peroxides contributes to the suppression of an inflammatory response. We would hypothesize that cationic enzymes offer the possibility for investigating the mechanisms of inflammation and, in addition, might be interesting from a therapeutical point of view.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ager A., Gordon J. L. Differential effects of hydrogen peroxide on indices of endothelial cell function. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):592–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batsford S. R., Takamiya M., Vogt A. A model of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat employing cationized ferritin. Clin Nephrol. 1980 Nov;14(5):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake D. R., Hall N. D., Bacon P. A., Dieppe P. A., Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Effect of a specific iron chelating agent on animal models of inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Feb;42(1):89–93. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerbooms A. M., Buys W. C. Rapid assessment of 99mTc-pertechnetate uptake in the knee joint as a parameter of inflammatory activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Apr;21(3):348–352. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Ward H. J., Kamil E. S., Cohen A. H. Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):451–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI110469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Mackay I. R. Antigen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Induction of arthritis in various strains of mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragt P. C., Bansberg J. I., Bonta I. L. Antiinflammatory effects of free radical scavengers and antioxidants: further support for proinflammatory roles of endogenous hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxides. Inflammation. 1980 Sep;4(3):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00915030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Sies H., Boveris A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):527–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon D., Goldstein L., Marikovsky Y., Skutelsky E. Use of cationized ferritin as a label of negative charges on cell surfaces. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Mar;38(5):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Cook H. W., Lands W. E. Prostaglandin biosynthesis can be triggered by lipid peroxides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 1;193(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschelmann R., Bekemeier H. Effects of catalase, peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and 10 scavengers of oxygen radicals in carrageenin edema and in adjuvant arthritis of rats. Experientia. 1981 Dec 15;37(12):1313–1314. doi: 10.1007/BF01948381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Schorlemmer H. U., Pope C., Allison A. C. Zymosan-induced arthritis: a model of chronic proliferative arthritis following activation of the alternative pathway of complement. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Sep-Oct;20(7):1396–1401. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijsen M. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., van den Broek W. J. Detection and quantification of experimental joint inflammation in mice by measurement of 99mTc-pertechnetate uptake. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):640–642. doi: 10.1007/BF01978775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Quantitation of arthritis by 99mTc-uptake measurements in the mouse knee-joint: correlation with histological joint inflammation scores. Agents Actions. 1984 Jun;14(5-6):723–728. doi: 10.1007/BF01978915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. A superoxide-activated chemotactic factor and its role in the inflammatory process. Agents Actions. 1980 Dec;10(6):522–527. doi: 10.1007/BF02024157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation: protection of synovial fluid by superoxide dismutase. Science. 1974 Aug 9;185(4150):529–531. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4150.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Harkin M. M., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Suppression by superoxide dismutase of immune-complex--induced pulmonary alveolitis and dermal inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jan;102(1):55–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyanagui Y. Participation of superoxide anions at the prostaglandin phase of carrageenan foot-oedema. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jul 1;25(13):1465–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehan A., Johnson K. J., Wiggins R. C., Kunkel R. G., Ward P. A. Evidence for the role of oxygen radicals in acute nephrotoxic nephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Oct;51(4):396–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijntjes N. V., Van de Putte L. B., Van der Pol M., Guelen P. J. Cryosectioning of undecalcified tissues for immunofluorescence. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner I. A., Goldberg V. M., Getzy L., Moskowitz R. W. A trial of intraarticular orgotein, a superoxide dismutase, in experimentally-induced osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1980 Jan-Feb;7(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R., Farber J. L. Mechanisms of the killing of cultured hepatocytes by hydrogen peroxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., Scoggin C. H., Patterson D. Hydrogen peroxide causes the fatal injury to human fibroblasts exposed to oxygen radicals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7181–7186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Till G. O., Kunkel R., Beauchamp C. Evidence for role of hydroxyl radical in complement and neutrophil-dependent tissue injury. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):789–801. doi: 10.1172/JCI111050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens D. G., Graff T. L., Lunec J., Dormandy T. L. Free-radical mediated aggregation of human gamma-globulin. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):650–651. doi: 10.1007/BF01978780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsu K., Ohkura Y. New fluorogenic substrates for horseradish peroxidase: rapid and sensitive assays for hydrogen peroxide and the peroxidase. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Kruijsen M. W., van de Putte L. B., van Beusekom H. J., van der Sluis-van der Pol M., Zwarts W. A. Antigen-induced and zymosan-induced arthritis in mice: studies on in vivo cartilage proteoglycan synthesis and chondrocyte death. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Jun;62(3):308–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van Beusekom H. J., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., van der Sluis M. Antigen handling in antigen-induced arthritis in mice: an autoradiographic and immunofluorescence study using whole joint sections. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jul;108(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., Joosten L. A. Electrical charge of the antigen determines intraarticular antigen handling and chronicity of arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1850–1859. doi: 10.1172/JCI111604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]