Abstract
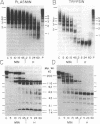
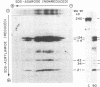
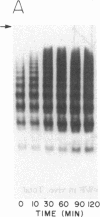
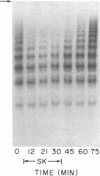
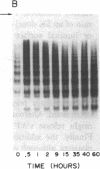
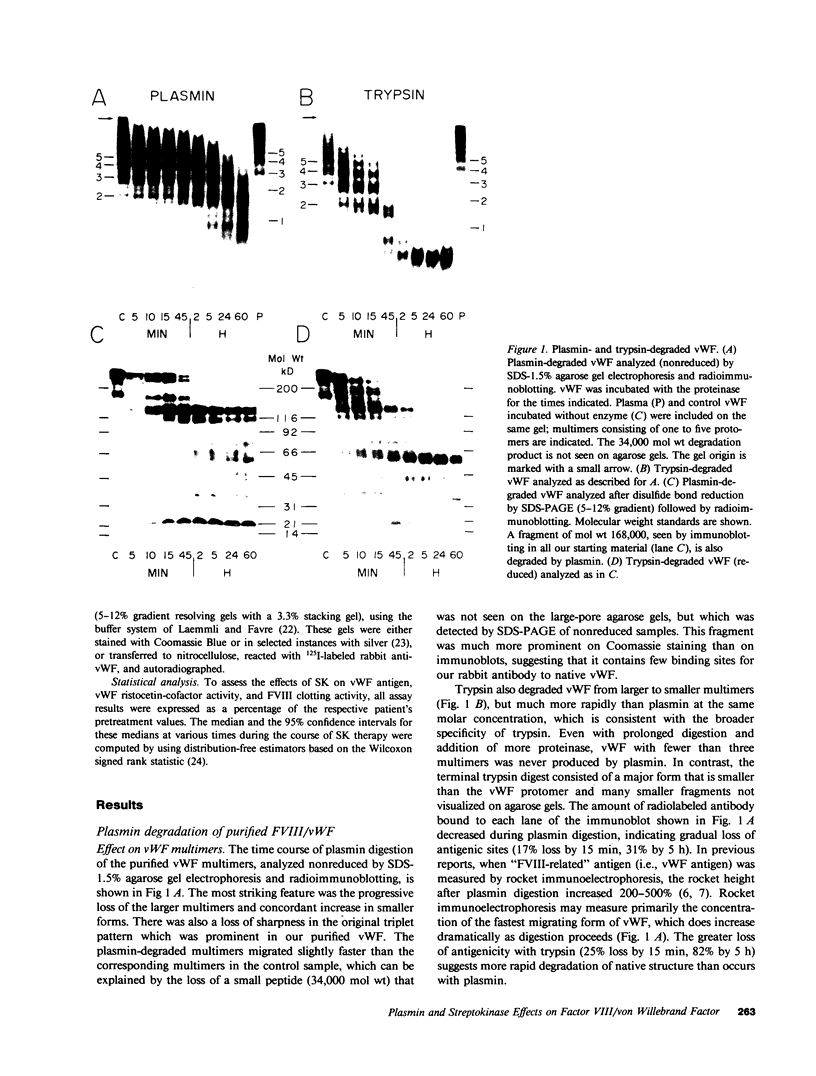
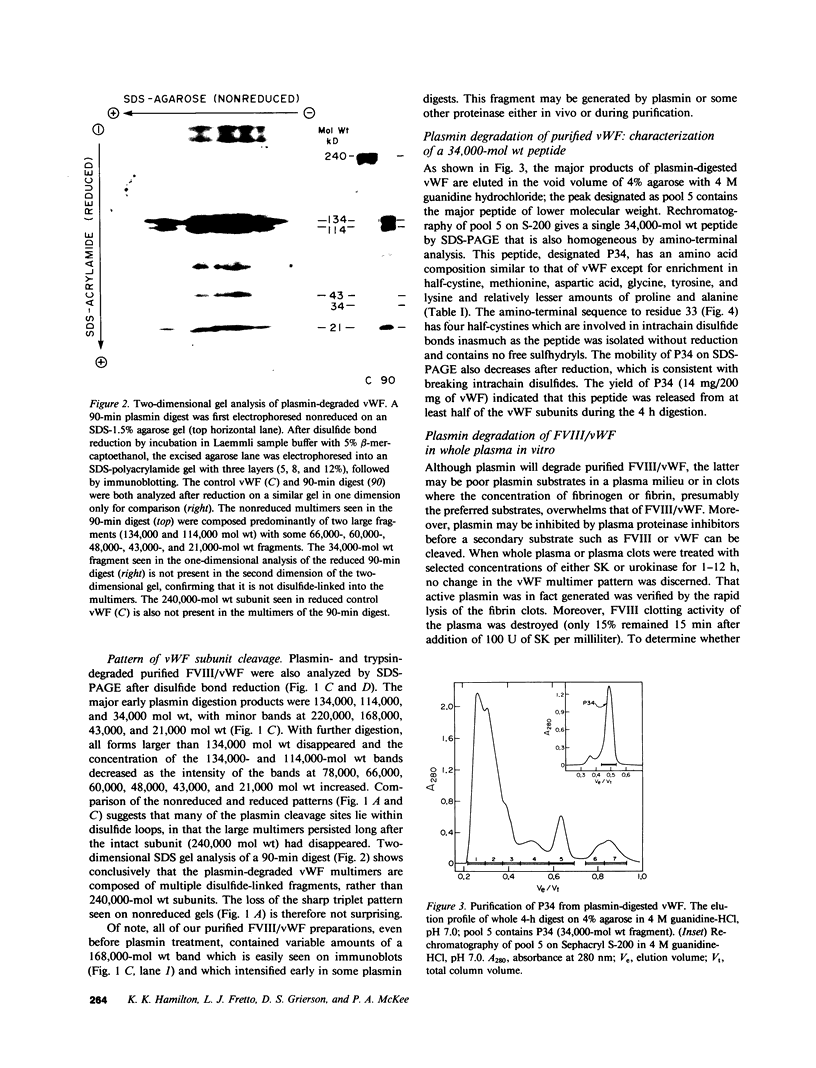
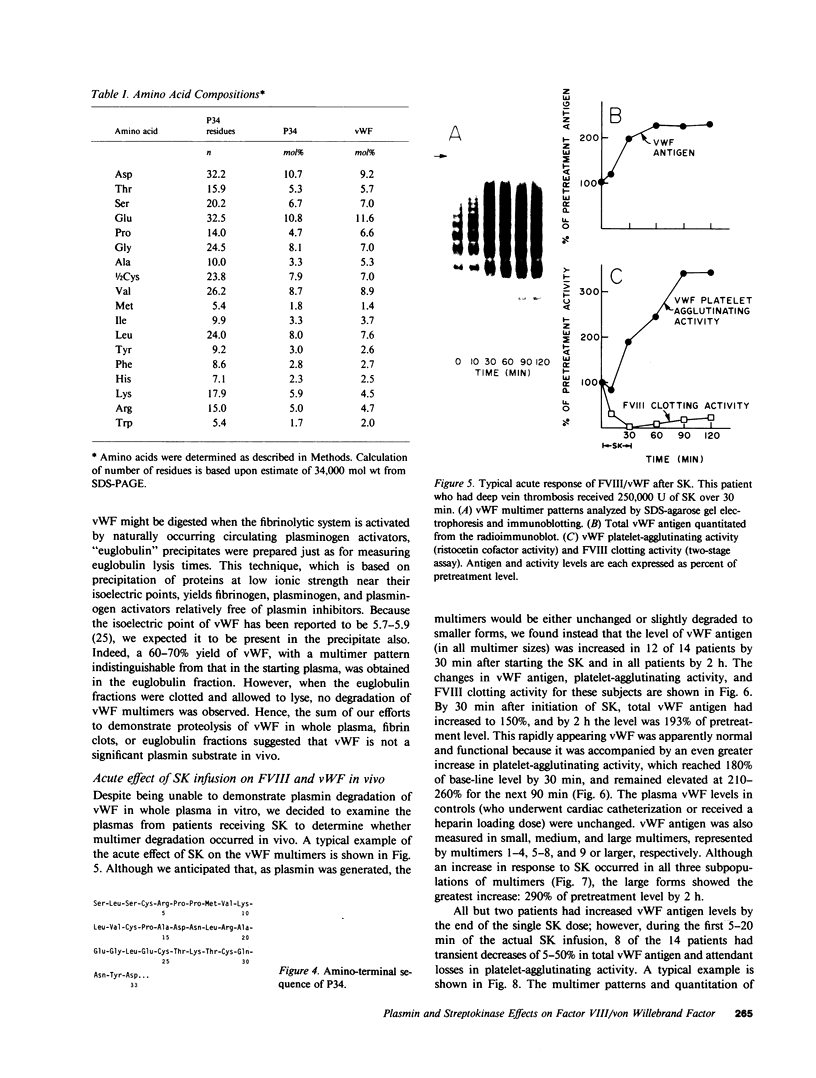
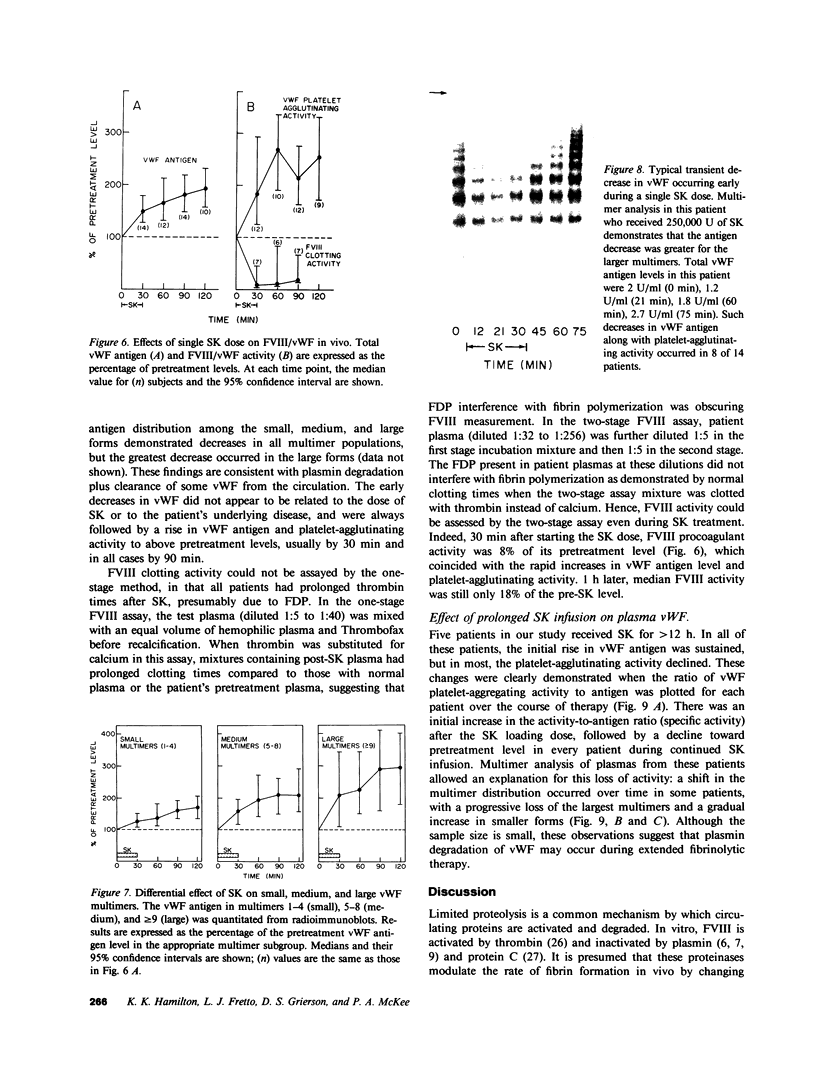
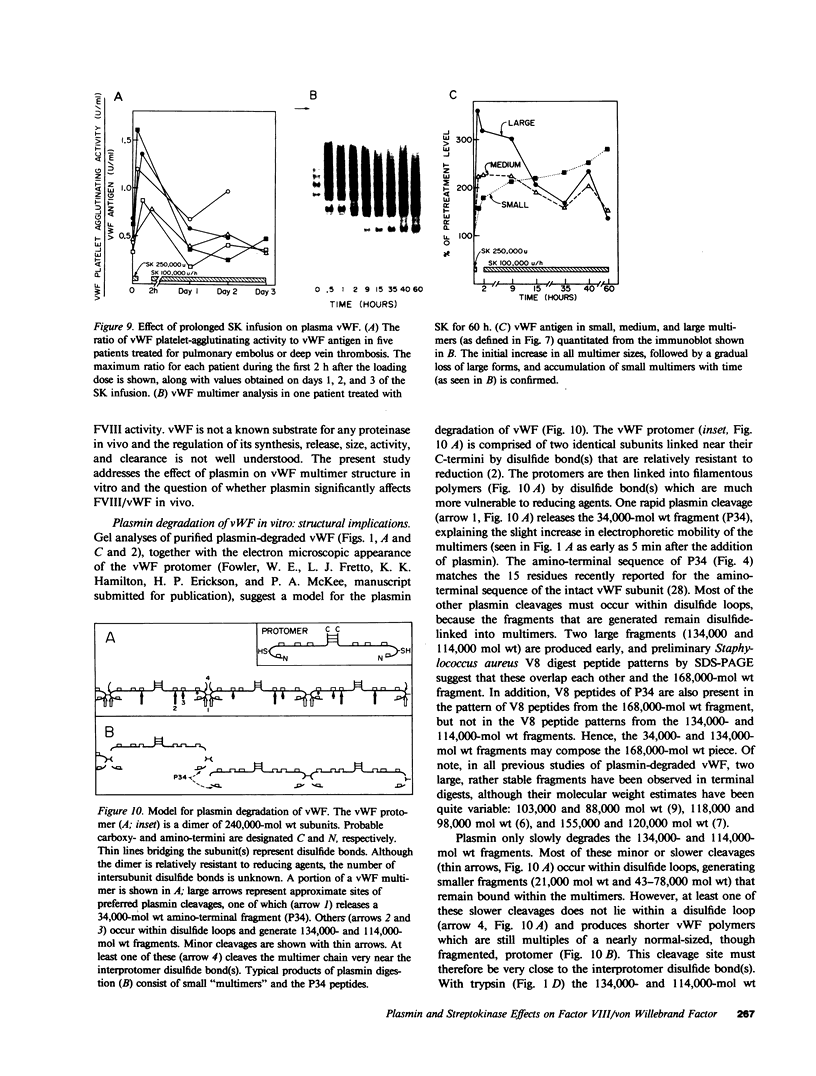
von Willebrand factor (vWF), a multimeric protein that mediates platelet adhesion, circulates in association with the procoagulant Factor VIII (FVIII). In previous reports, plasmin was shown in vitro to inactivate FVIII and cleave the vWF subunit extensively, but to cause only a modest decrease in vWF platelet-agglutinating activity. In the present study, the digestion of vWF multimers by plasmin was analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-agarose gel electrophoresis and radioimmunoblotting. In vitro, plasmin degraded the large vWF multimers to smaller forms that could be distinguished from the small multimers present before digestion only by a slightly increased electrophoretic mobility. These plasmin-cleaved "multimers" were composed of disulfide-linked fragments with no intact vWF subunits. Thus, many plasmin cleavages occur within disulfide loops. The slight increase in mobility of plasmin-digested vWF is in part explained by the early cleavage from the multimers of a 34,000-mol wt peptide, which was purified and partially sequenced. The amino-terminal sequence (33 residues) agrees with the previously reported sequence (15 residues) for the amino terminus of the intact vWF subunit. Analysis of plasmin-digested vWF allowed deduction of a model for the native vWF structure, including the approximate location of the interprotomer disulfide bond(s). To determine whether plasmin would digest vWF in vivo, plasmas from 12 patients and 2 normal volunteers who received intravenous streptokinase (SK) were analyzed. Rather than vWF digestion, a two- to threefold rise in vWF antigen and platelet-agglutinating activity occurred within 2 h after a single SK dose, and the increase was greatest among the largest multimers. In contrast, FVIII clotting activity dropped to 10-20% of pre-SK levels. Thus, although plasmin destroys FVIII, a pharmacologically induced fibrinolytic state is associated with significant release of vWF from endothelial cells, platelets, or some other storage pool.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. C., Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Support of ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation by procoagulant-inactive and plasmin-cleaved forms of human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atichartakarn V., Marder V. J., Kirby E. P., Budzynski A. Z. Effects of enzymatic degradation on the subunit composition and biologic properties of human factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):281–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awbrey B. J., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of human thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4092–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho A. C., Bellman S. M., Saullo V. J., Quinn D., Zapol W. M. Altered factor VIII in acute respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1113–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts R. B., Paskell S. L., Elgee S. K. Disulfide bonds and the quaternary structure of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):702–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI109178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretto L. J., Ferguson E. W., Steinman H. M., McKee P. A. Localization of the alpha-chain cross-link acceptor sites of human fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2184–2195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Gardiner J. E., Griffin J. H., Zimmerman T. S. Proteolytic inactivation of human factor VIII procoagulant protein by activated human protein C and its analogy with factor V. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):486–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Isoelectric focusing of human von Willebrand factor in urea-agarose gels. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guisasola J. A., Cockburn C. G., Hardisty R. M. Plasmin digestion of factor VIII: characterization of the breakdown products with respect to antigenicity and von Willebrand activity. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Oct 31;40(2):302–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head D. R., Bowman R. P., Marmer D. J., Brossoit A. D. An improvemed assay for von Willebrand factor. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;72(6):991–995. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.6.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessel B., Jörnvall H., Thorell L., Söderman S., Larsson U., Egberg N., Blombäck B., Holmgren A. Structure-function relationships of human factor VIII complex studied by thioredoxin dependent disulfide reduction. Thromb Res. 1984 Sep 15;35(6):637–651. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Shainoff J. R. Factor VIII-related protein circulates in normal human plasma as high molecular weight multimers. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1056–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanneau C., Sultan Y. Localization of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor antigen by immunoelectron microscopy in human endothelial cells using Fab fragments coupled to peroxidase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Nov;30(11):1091–1096. doi: 10.1177/30.11.6815260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopitsky R. G., Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Thrombin potentiation of factor VIII procoagulant activity: assessment by the two-stage assay. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffel G. L., Braunwald E. Thrombolytic therapy. A new strategy for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction (1). N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 13;311(11):710–717. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409133111105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Joseph M. L., Counts R. B. Thrombin-mediated release of factor VIII antigen from human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):531–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian E. C., Nunez R. L., Harkness D. R. In vivo and in vitro effects of thrombin and plasmin on human factor VIII (AHF). Am J Hematol. 1976;1(4):481–491. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830010413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi R., Mannucci P. M., Seghatchian M. J., Garcia V. V., Coppola R. Alterations of factor VIII von Willebrand factor in clinical conditions associated with an increase in its plasma concentration. Br J Haematol. 1981 Sep;49(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb07197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNICOL G. P., GALE S. B., DOUGLAS A. S. In-vitro and in-vivo studies of a preparation of urokinase. Br Med J. 1963 Apr 6;1(5335):909–915. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5335.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Aberg M., Nilsson I. M., Robertson B. Mechanism of plasminogen activator and factor VIII increase after vasoactive drugs. Br J Haematol. 1975 May;30(1):81–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Johnson A. J., Karpatkin M. H., Puszkin S. Methods for the production of clinically effective intermediate- and high-purity factor-VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jul;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Vilhardt H., Holmberg L., Astedt B. Association between factor VIII related antigen and plasminogen activator. Acta Med Scand. 1982;211(1-2):105–112. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb01909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori K., Fretto L. J., Harrison R. L., Switzer M. E., Erickson H. P., McKee P. A. Electron microscopy of human factor VIII/Von Willebrand glycoprotein: effect of reducing reagents on structure and function. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):632–640. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B. A., Furlan M., Beck E. A. Studies on factor VIII-related protein. II. Estimation of molecular size differences between factor VIII oligomers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 23;578(1):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand J. H., Sussman I. I., Gordon R. E., Chu S. V., Solomon V. Localization of factor-VIII-related antigen in human vascular subendothelium. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Mannucci P. M., Lombardi R., Federici A. B., Zimmerman T. S. Multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor following administration of DDAVP: implications for pathophysiology and therapy of von Willebrand's disease subtypes. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffel G., Zimmermann R., Harenberg J., Mörl H. Blood coagulation changes during effective thrombolysis using urokinase and heparin. Thromb Res. 1982 Jan 1;25(1-2):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodetz J. M., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Relationship of sialic acid to function and in vivo survival of human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5538–5546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Immunologic studies of native and modified human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):310–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Reactions of thrombin with human factor VIII/von Willebrande factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10606–10611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Studies on human antihemophilic factor. Evidence for a covalently linked subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):925–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI108369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turitto V. T., Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R. Platelet interaction with rabbit subendothelium in von Willebrand's disease: altered thrombus formation distinct from defective platelet adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1730–1741. doi: 10.1172/JCI111591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot P. G., Gonsalves M. D., Loesberg C., van Buul-Wortelboer M. F., van Aken W. G., van Mourik J. A. Thrombin-induced release of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells is mediated by phospholipid methylation. Prostacyclin synthesis is independent of phospholipid methylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13329–13333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]