Abstract
Wnt/β-catenin pathway alterations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are associated with poor prognosis and resistance. In 598 stage III-IV NSCLC patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy at MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC), we correlated survival with 441 host SNPs in 50 Wnt pathway genes. We then assessed the most significant SNPs in 240 Mayo Clinic patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC, 127 MDACC patients receiving platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy and 340 early stage MDACC patients undergoing surgery alone (cohorts 2–4). In multivariate analysis, survival correlates with SNPs for AXIN2 (rs11868547 and rs4541111, of which rs11868547 was assessed in cohorts 2–4), Wnt-5B (rs12819505), CXXC4 (rs4413407) and WIF-1 (rs10878232). Median survival was 19.7, 15.6, and 10.7 months for patients with 1, 2, and 3–5 unfavorable genotypes, respectively (p= 3.8×10−9). Survival tree analysis classified patients into two groups (MST 11.3 vs 17.3 months, p=4.7×10−8). None of the SNPs achieved significance in cohorts 2–4; however, there was a trend in the same direction as cohort 1 for 3 of the SNPs. Using online databases, we found rs10878232 displayed expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) correlation with the expression of LEMD3, a neighboring gene previously associated with NSCLC survival. In conclusion, results from cohort 1 provide further evidence for an important role for Wnt in NSCLC. Investigation of Wnt inhibitors in advanced NSCLC would be reasonable. Lack of a SNP association with outcome in cohorts 2–4 could be due to low statistical power, impact of patient heterogeneity, or false positive observations in cohort 1.
Keywords: Wnt, pharmacogenetics, NSCLC
Introduction
Lung cancer is the world’s leading cause of cancer death,1 and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80–85% of lung cancer cases. Cisplatin- or carboplatin-based combinations are generally used in metastatic NSCLC,2 and yield median survival times (MSTs) of 8–10 months.3 Platinum-based regimens are combined with radiotherapy for inoperable stage IIIA and IIIB NSCLC,4 with MSTs of 15–18 months,5 and adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy increases 5-year survival rates by approximately 5% in patients with resected NSCLC, with the major benefit being seen in stages II and III.6
The Wingless-type protein (Wnt) signaling pathway helps maintain cancer stem cells,7 and signals through the major (“canonical”) Wnt pathway via β-catenin and through various secondary (“non-canonical”) pathways.7,8 If Wnt is not present, β-catenin is phosphorylated by a complex consisting of Axis inhibition protein (AXIN), adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), and this phosphorylation results in its proteolytic degradation.8 If Wnt is present, it complexes with members of the Frizzled (FZD) family of receptors, lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP), Disheveled (Dvl) and AXIN,7,8 thereby inhibiting GSK-3β and preventing β-catenin destruction.7,8 β-catenin then migrates to the nucleus and complexes with members of T-cell factor (TCF)/Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (LEF) family of transcription factors,8 and interacts with various transcriptional coactivators, such as cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP) or its homolog p300.8 This ultimately leads to expression of cyclin D1,7,9 c-Myc,7 and other target genes.
There are also several Wnt inhibitors, including some members of the Wnt family itself (Wnt-5a and -5b),10 secreted frizzled-related proteins (sFRPs) 7, Wnt inhibitory factor-1 (WIF-1),7 Cerberus,7 Disabled-2 (Dab2),8 members of the Dickkopf (Dkk) family,7 and the Dvl antagonists Idax (coded by the CXXC4 gene11) and human homolog of Dapper (HDPR1).12
In NSCLC cell lines and/or xenografts, Wnt pathway activation, overexpression of various Wnt pathway components or aberrant methylation or down-regulation of expression of Wnt pathway inhibitors is associated with increased cell proliferation or xenograft growth and with increased cellular motility and invasion.13 Similarly, in resected NSCLC tumor samples, Wnt pathway activation, overexpression of various Wnt pathway components or aberrant methylation or down-regulation of expression of Wnt pathway inhibitors is associated with poor prognosis.13 Wnt signaling may also be associated with resistance to cisplatin, docetaxel and radiation.13
Cancers “inherit” genes from the host, and host genotype single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can thereby affect tumor behavior. Across a range of malignancies, various Wnt pathway component SNPs or SNP interactions have correlated with risk of cancer development,14–16 or with tumor grade,17 stage,17 metastases,14 or prognosis.14,18,19 Exploration of the impact of Wnt pathway SNPs in NSCLC has to date been very limited.20 Because the Wnt pathway appears to be very important in NSCLC, and because Wnt signaling is associated with resistance to platinums in cell lines, we hypothesized that Wnt signaling pathway SNPs would correlate with survival of platinum-treated patients with stage III–IV NSCLC.
Methods
Patients for this study were from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) and from the Mayo Clinic, recruited according to protocols approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the two institutions. All patients gave written informed consent. From each patient, blood was drawn into heparinized tubes, and clinical, demographic, therapy and follow-up data were recorded.
Cohort 1
We initially assessed 598 MDACC patients with inoperable stage III–IV NSCLC and no prior chemotherapy that were receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Of these, 331 also received radiotherapy.
Cohorts 2–4
In secondary analyses to assess whether our initial observations could be extrapolated to other NSCLC populations, we assessed 240 consenting Mayo Clinic patients receiving first line platinum-based chemotherapy alone (100 patients) or combined with radiotherapy (140 patients) for inoperable stage III (106 patients) or IV (134 patients) NSCLC (cohort 2). We also assessed 127 MDACC patients with resected NSCLC who received adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy (cohort 3) and 340 MDACC patients undergoing surgical resection alone for NSCLC (cohort 4). The Mayo Clinic cohort was most similar to our initial cohort (metastatic NSCLC treated with platinum-based therapy). The adjuvant chemotherapy group was assessed based on the hypothesis that the impact of a specific SNP on chemotherapy efficacy or on prognosis might hold independent of tumor stage. The surgery alone group was assessed based on the hypothesis that if a SNP were a prognostic factor (linked to tumor aggressivenss) rather than a predictive factor (linked to chemotherapy sensitivity) then if might correlate with outcome even in patients who had not received any chemotherapy.
Polymorphism selection and genotyping
For cohort 1, we utilized Gene Oncology (http://www.geneontology.org) and performed a literature search of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) PubMed (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) database to identify a list of Wnt pathway-related genes. A priority score was assigned to each gene based on its importance and relevance to cancer and to the Wnt signaling pathway. For each gene, we selected haplotype tagging SNPs (htSNPs) located within 10 kb upstream of the transcriptional start site and 10 kb downstream of the transcriptional stop site based on data from the International HapMap Project (http://www.hapmap.org). Using the LD select program (http://droog.gs.washing.edu/ldSelect.html) and the UCSC Golden Path Gene Sorter program (http://genome.ucsc.edu), we further divided identified SNPs into bins based on an r2 threshold of 0.8 and minor allele frequency (MAF) greater than 0.05 in Caucasians to select tagging SNPs. We also included potentially functional SNPs in the coding (synonymous SNPs, nonsynonymous SNPs) and regulatory regions (promoter, splicing site, 5-UTR, and 3-UTR). Selected SNPs were submitted to Illumina technical support for Infinium chemistry designability, beadtype analyses, and iSelect Infinium Beadchip synthesis. Due to limitation on the total number of SNPs that can be incorporated into the initial chip design, some genes of the Wnt pathway could not be included in this analysis (e.g. GSK3β, genes of noncanonical pathways, and downstream targets).
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes and stored at −80° C. Using the standard 3-day protocol for Illumina’s Infinium iSelect HD Custom Genotyping BeadChip (Illumina, San Diego, CA) genotyping was successful in all 441 SNPs selected. BeadStudio software was used to autocall genotypes.
In cohorts 2–4, SNPs emerging as being most important in cohort 1 were then assessed using Taqman genotyping assay for Mayo Clinic patients and Illumina iSelect Infinium Beadchip for the MDACC adjuvant chemotherapy group and surgery alone group.
Statistical analysis
STATA software (version 10; STATA Corporation, College Station, TX) was used for statistical analyses. In cohort 1, Chi square test was used to assess differences between alive and dead patient groups for categorical variables in the host population. Cox’s proportional hazards model was used to estimate Hazard Ratios (HRs) for the multivariate survival analyses, with adjustment for age, sex, ethnicity, smoking status, clinical stage, and performance status (PS). Kaplan-Meier curves were used to assess genotype effect on overall survival and log rank tests were used to assess survival differences across genotypes. The most common genotype served as the reference group. All statistical analyses were two sided. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. To correct for the effect of multiple comparisons, q values (false discovery rate adjusted P-values) were calculated by published methods21 implemented in the R package. SNPs with q<0.10 were then used to assess the combined effects of unfavorable genotypes. Survival tree analysis was performed to assess higher-order gene-gene interactions using the STREE program (http://masal.med.yale.edu/stree/), which utilizes recursive-partitioning to identify subgroups of individuals with similar risk.
In cohorts 2–4, we assessed SNPs that were found to be important in cohort 1 and used multivariate Cox proportional hazards model to determine their association with outcome in each of cohorts 2–4 singly. Meta-analysis was conducted using HR and 95% CI derived from the Cox regression analysis in each of cohorts 2–4 to estimate the HR and 95% CI in cohorts 2–4 combined, and in the Mayo Clinic cohort (cohort 2) combined with the MDACC cohort that received adjuvant chemotherapy (cohort 3).
eQTL ANALYSIS
We checked for potential functional effects of identified SNPs on gene expression through the analysis of gene-SNP associations in expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) studies compiled by the Genevar (GENe Expression VARiation) database (http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/genevar/)22 using the HapMap3 dataset, the seeQTL database (http://www.bios.unc.edu/research/genomic_software/seeQTL/),23 and the University of Chicago eQTL (http://eqtl.uchicago.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/eqtl/). All analyses were performed in the CEU population with MAF≥0.05.
Results
Characteristics of patients in cohort 1 are outlined in Table 1. Of the 441 SNPs assessed (Table 2), 57 were significantly associated with survival in multivariate analysis after adjusting for patients’ age, ethnicity, pack-year smoking history, clinical stage, and performance status (p<0.05, Table 3), including SNPs in AXIN2 (9 SNPs), LRP 5 (7 SNPs), Wnt-5A (4 SNPs), AXIN1, LRP6, WIF1, Wnt-2, Wnt-4, Wnt-3 and Wnt-5B (3 SNPs each), CXXC4, Wnt-3A, Wnt-7A, Wnt-9A and TLE2 (2 SNPs each), and DVL3, FRZB, FZD4, Wnt-6, Wnt-9B and Wnt-11 (1 SNP each). None of the 5 SNPs assessed from the gene for β-catenin (CTNNB1) correlated with patient survival.
Table 1.
Characteristics of 598 patients assessed in cohort 1
| Variable | No. Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Median survival, months | 12.9 |
| Median age (range), years | 61 (28–81) |
| Pack year, mean (SD) | 45 (27.8) |
| Survival status at last follow-up | |
| Alive | 142 (23.7) |
| Dead | 456 (76.3) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 323 (54.0) |
| Female | 275 (46.0) |
| Clinical stage | |
| Stage IIIA | 82 (13.7) |
| Stage IIIB | |
| No malignant effusion | 142 (23.7) |
| Malignant effusion* | 39 (6.5) |
| Stage IV | 335 (56.0) |
| Smoking status | |
| Never | 112 (18.7) |
| Former | 243 (40.6) |
| Current & Recently Quit (<1 year) | 243 (40.6) |
| ECOG Performance status | |
| 0 | 143 (23.9) |
| 1 | 334 (55.9) |
| 2–4 | 74 (12.4) |
| Unspecified | 47 (7.9) |
| Differentiation | |
| Well | 27 (4.5) |
| Moderate | 61 (10.2) |
| Poor and undifferentiated | 299 (50.0) |
| Unspecified | 211 (35.3) |
| Weight loss | |
| Weight gain or stable | 295 (49.3) |
| 0–5% | 80 (13.4) |
| 5–10% | 88 (14.7) |
| >10% | 63 (10.5) |
| Unknown | 72 (12.0) |
| Race | |
| White | 470 (78.6) |
| Black | 95 (15.9) |
| Others | 33 (5.5) |
| First line chemo agents (331 also received radiotherapy) | |
| Platinum (cisplatin or carboplatin) only | 11 (1.8) |
| Platinum + pemetrexed | 21 (3.5) |
| Platinum + etoposide +/− targretin | 88 (14.7) |
| Platinum + gemcitabine +/− other agent | 25 (4.2) |
| Platinum + taxane | 283 (47.3) |
| Platinum + taxane + other agents | 138 (23.1) |
| Platinum + other agents | 32 (5.4) |
Now considered stage IV per recent revisions to staging systems49
SD- standard deviation
Table 2.
Wnt pathway SNPs that were assessed in cohort 1
| SNP | P value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Gene | Chromo-some | Position | Q value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1882619 | 2.69E-01 | 0.85( 0.64–1.13) | APC | 5 | 112106681 | 0.307820239 |
| rs2439595 | 2.21E-01 | 1.23( 0.88–1.72) | APC | 5 | 112146237 | 0.290363518 |
| rs2431507 | 2.32E-01 | 0.86( 0.67–1.10) | APC | 5 | 112174080 | 0.296677764 |
| rs2707761 | 6.88E-01 | 0.96( 0.77–1.19) | APC | 5 | 112177826 | 0.424838822 |
| rs13167522 | 8.11E-01 | 1.03( 0.78–1.36) | APC | 5 | 112195207 | 0.447606546 |
| rs42427 | 2.35E-01 | 1.18( 0.90–1.55) | APC | 5 | 112204224 | 0.298902339 |
| rs459552 | 7.19E-02 | 1.49( 0.96–2.31) | APC | 5 | 112204655 | 0.222980247 |
| rs2229995 | 8.78E-01 | 0.95( 0.52–1.75) | APC | 5 | 112206694 | 0.468410227 |
| rs41116 | 8.13E-01 | 0.97( 0.78–1.21) | APC | 5 | 112208820 | 0.447606546 |
| rs382427 | 7.86E-01 | 1.03( 0.82–1.30) | APC | 5 | 112215335 | 0.443413702 |
| rs4807928 | 9.96E-02 | 1.18( 0.97–1.43) | APC2 | 19 | 1399180 | 0.247221759 |
| rs12005 | 3.11E-01 | 0.87( 0.67–1.14) | APC2 | 19 | 1408875 | 0.315893774 |
| rs11668593 | 6.94E-01 | 1.04( 0.84–1.29) | APC2 | 19 | 1411473 | 0.424838822 |
| rs265274 | 2.13E-01 | 1.20( 0.90–1.61) | APC2 | 19 | 1423007 | 0.284945038 |
| rs2456163 | 9.50E-02 | 1.29( 0.96–1.75) | APC2 | 19 | 1427432 | 0.246983910 |
| rs2238371 | 1.09E-01 | 0.66( 0.40–1.10) | AXIN1 | 16 | 268917 | 0.247221759 |
| rs373271 | 7.52E-01 | 0.95( 0.72–1.27) | AXIN1 | 16 | 269672 | 0.437337077 |
| rs421195 | 5.30E-01 | 0.92( 0.71–1.19) | AXIN1 | 16 | 273147 | 0.379736909 |
| rs419949 | 2.74E-01 | 1.12( 0.91–1.37) | AXIN1 | 16 | 274891 | 0.308381238 |
| rs2685127 | 4.14E-01 | 1.10( 0.88–1.37) | AXIN1 | 16 | 275374 | 0.354708008 |
| rs400037 | 2.15E-01 | 0.78( 0.52–1.16) | AXIN1 | 16 | 276397 | 0.284945038 |
| rs1048786 | 5.99E-02 | 1.25( 0.99–1.59) | AXIN1 | 16 | 276917 | 0.205417788 |
| rs394128 | 2.99E-01 | 0.82( 0.56–1.19) | AXIN1 | 16 | 277872 | 0.315893774 |
| rs214247 | 2.12E-01 | 1.14( 0.93–1.42) | AXIN1 | 16 | 289222 | 0.284945038 |
| rs214246 | 4.03E-02 | 0.77( 0.61–0.99) | AXIN1 | 16 | 289294 | 0.186192568 |
| rs1204042 | 1.48E-01 | 0.73( 0.47–1.12) | AXIN1 | 16 | 292737 | 0.270394908 |
| rs1981492 | 1.06E-01 | 1.19( 0.96–1.47) | AXIN1 | 16 | 296690 | 0.247221759 |
| rs11644916 | 6.02E-01 | 1.05( 0.87–1.28) | AXIN1 | 16 | 299568 | 0.401557037 |
| rs2301522 | 1.32E-01 | 0.77( 0.55–1.08) | AXIN1 | 16 | 299954 | 0.263342145 |
| rs17136060 | 8.74E-02 | 1.22( 0.97–1.52) | AXIN1 | 16 | 302460 | 0.244482539 |
| rs7359414 | 3.73E-02 | 0.78( 0.61–0.99) | AXIN1 | 16 | 302639 | 0.186192568 |
| rs3916990 | 2.89E-01 | 1.11( 0.91–1.36) | AXIN1 | 16 | 312598 | 0.314961177 |
| rs9921222 | 9.50E-01 | 1.00( 0.87–1.14) | AXIN1 | 16 | 315783 | 0.481138076 |
| rs12719801 | 7.19E-01 | 1.04( 0.85–1.27) | AXIN1 | 16 | 321142 | 0.426451944 |
| rs370681 | 7.03E-01 | 1.04( 0.84–1.30) | AXIN1 | 16 | 332462 | 0.426046532 |
| rs395901 | 5.33E-02 | 0.77( 0.59–1.00) | AXIN1 | 16 | 333343 | 0.196213611 |
| rs2885415 | 3.12E-01 | 1.11( 0.91–1.35) | AXIN1 | 16 | 335397 | 0.315893774 |
| rs758033 | 2.00E-01 | 1.14( 0.93–1.39) | AXIN1 | 16 | 337045 | 0.284431004 |
| rs12599449 | 6.14E-02 | 1.26( 0.99–1.60) | AXIN1 | 16 | 337270 | 0.205417788 |
| rs11645554 | 7.90E-02 | 0.71( 0.49–1.04) | AXIN1 | 16 | 340246 | 0.235767882 |
| rs17136255 | 1.99E-01 | 1.15( 0.93–1.43) | AXIN1 | 16 | 340476 | 0.284431004 |
| rs11860497 | 7.27E-02 | 1.21( 0.98–1.49) | AXIN1 | 16 | 345417 | 0.222980247 |
| rs9888749 | 3.11E-02 | 0.76( 0.60–0.98) | AXIN1 | 16 | 348373 | 0.185653186 |
| rs4340364 | 5.00E-01 | 1.08( 0.86–1.37) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60946245 | 0.377760052 |
| rs8068404 | 8.90E-02 | 0.61( 0.34–1.08) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60946802 | 0.245844226 |
| rs12452196 | 8.52E-01 | 0.98( 0.78–1.23) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60951241 | 0.458967631 |
| rs11868547 | 6.10E-04 | 0.77( 0.66–0.89) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60954065 | 0.095030240 |
| rs7591 | 6.14E-03 | 1.23( 1.06–1.44) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60955544 | 0.135500153 |
| rs4074947 | 4.68E-02 | 1.23( 1.00–1.51) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60957682 | 0.186667333 |
| rs7224837 | 3.44E-02 | 1.28( 1.02–1.62) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60958585 | 0.186192568 |
| rs11655966 | 1.48E-02 | 1.21( 1.04–1.41) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60960112 | 0.144627899 |
| rs4541111 | 1.53E-03 | 0.79( 0.68–0.91) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60965000 | 0.095030240 |
| rs11079571 | 1.62E-02 | 1.29( 1.05–1.59) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60979143 | 0.144627899 |
| rs3923087 | 5.29E-02 | 1.24( 1.00–1.53) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60979723 | 0.196213611 |
| rs3923086 | 1.06E-01 | 1.13( 0.97–1.32) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60979950 | 0.247221759 |
| rs757558 | 3.67E-01 | 1.11( 0.88–1.40) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60992054 | 0.331747799 |
| rs740026 | 4.46E-01 | 0.94( 0.81–1.10) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60992143 | 0.359705483 |
| rs12943295 | 4.39E-01 | 1.09( 0.88–1.36) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60994967 | 0.359395383 |
| rs1548581 | 3.65E-02 | 1.29( 1.02–1.64) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60995973 | 0.186192568 |
| rs1544427 | 3.39E-01 | 1.11( 0.89–1.39) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60996130 | 0.328827360 |
| rs2158520 | 9.29E-01 | 1.02( 0.68–1.52) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60996372 | 0.478174891 |
| rs12942924 | 1.57E-02 | 1.18( 1.03–1.36) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60996861 | 0.144627899 |
| rs9675157 | 6.67E-01 | 0.94( 0.69–1.26) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60997479 | 0.422148501 |
| rs2007085 | 8.21E-01 | 1.03( 0.80–1.33) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60997824 | 0.449815441 |
| rs17207681 | 4.58E-01 | 0.90( 0.69–1.18) | CTN1 | 5 | 138196426 | 0.359705483 |
| rs11744283 | 5.42E-01 | 1.13( 0.76–1.70) | CTN1 | 5 | 138237303 | 0.379736909 |
| rs288030 | 3.79E-01 | 1.09( 0.90–1.33) | CTN1 | 5 | 138244182 | 0.336074710 |
| rs288029 | 6.80E-01 | 1.04( 0.86–1.27) | CTN1 | 5 | 138245204 | 0.424838822 |
| rs10515503 | 7.80E-01 | 0.96( 0.73–1.27) | CTN1 | 5 | 138246077 | 0.443413702 |
| rs288027 | 6.15E-01 | 1.06( 0.85–1.33) | CTN1 | 5 | 138250229 | 0.407840284 |
| rs17031 | 6.17E-01 | 1.09( 0.77–1.55) | CTN1 | 5 | 138298441 | 0.407981867 |
| rs9872276 | 2.10E-01 | 0.86( 0.68–1.09) | CTNNB1 | 3 | 41206972 | 0.284945038 |
| rs1722846 | 1.39E-01 | 0.90( 0.79–1.03) | CTNNB1 | 3 | 41208893 | 0.265029247 |
| rs11564445 | 7.73E-01 | 1.06( 0.73–1.52) | CTNNB1 | 3 | 41242756 | 0.443413702 |
| rs11564447 | 1.04E-01 | 1.33( 0.94–1.89) | CTNNB1 | 3 | 41243358 | 0.247221759 |
| rs4135385 | 9.28E-01 | 1.01( 0.82–1.24) | CTNNB1 | 3 | 41254444 | 0.478174891 |
| rs4413407 | 1.72E-03 | 1.28( 1.10–1.50) | CXXC4 | 4 | 105612810 | 0.095030240 |
| rs4698921 | 4.04E-02 | 1.16( 1.01–1.34) | CXXC4 | 4 | 105633671 | 0.186192568 |
| rs10891310 | 2.49E-01 | 1.13( 0.92–1.38) | DIXDC1 | 11 | 111397269 | 0.301906315 |
| rs7100461 | 9.92E-02 | 0.77( 0.56–1.05) | DKK1 | 10 | 53735827 | 0.247221759 |
| rs1896368 | 3.19E-01 | 1.08( 0.93–1.25) | DKK1 | 10 | 53738910 | 0.317400735 |
| rs1528877 | 4.64E-01 | 1.09( 0.87–1.37) | DKK1 | 10 | 53741348 | 0.359830407 |
| rs3763511 | 5.40E-01 | 0.92( 0.69–1.21) | DKK4 | 8 | 42355015 | 0.379736909 |
| rs222850 | 2.78E-01 | 1.18( 0.88–1.58) | DVL2 | 17 | 7078674 | 0.310012797 |
| rs11919795 | 1.75E-02 | 0.67( 0.48–0.93) | DVL3 | 3 | 185373562 | 0.144627899 |
| rs4666865 | 5.64E-01 | 1.09( 0.81–1.46) | FRZB | 2 | 183406336 | 0.388647584 |
| rs7775 | 8.96E-01 | 1.02( 0.79–1.31) | FRZB | 2 | 183407829 | 0.474806202 |
| rs288326 | 8.17E-01 | 1.03( 0.81–1.31) | FRZB | 2 | 183411581 | 0.448878241 |
| rs12469777 | 1.44E-02 | 0.85( 0.74–0.97) | FRZB | 2 | 183440609 | 0.144627899 |
| rs506197 | 4.59E-01 | 0.95( 0.83–1.09) | FSHB | 11 | 30212399 | 0.359705483 |
| rs506306 | 4.59E-01 | 0.95( 0.83–1.09) | FSHB | 11 | 30212443 | 0.359705483 |
| rs676349 | 4.59E-01 | 0.95( 0.83–1.09) | FSHB | 11 | 30212558 | 0.359705483 |
| rs560078 | 5.44E-01 | 0.96( 0.83–1.10) | FSHB | 11 | 30213698 | 0.379736909 |
| rs12577729 | 2.10E-01 | 1.14( 0.93–1.41) | FSHB | 11 | 30213953 | 0.284945038 |
| rs626869 | 4.59E-01 | 0.95( 0.83–1.09) | FSHB | 11 | 30215346 | 0.359705483 |
| rs12537425 | 7.40E-01 | 1.03( 0.88–1.20) | FZD1 | 7 | 90726006 | 0.433519176 |
| rs6977978 | 9.40E-01 | 1.01( 0.81–1.25) | FZD1 | 7 | 90726349 | 0.478174891 |
| rs3750145 | 6.09E-01 | 0.94( 0.75–1.18) | FZD1 | 7 | 90734767 | 0.405077519 |
| rs10252817 | 4.56E-01 | 0.92( 0.74–1.14) | FZD1 | 7 | 90742874 | 0.359705483 |
| rs17163759 | 1.56E-01 | 0.81( 0.61–1.08) | FZD1 | 7 | 90744979 | 0.270394908 |
| rs4792948 | 1.61E-01 | 0.84( 0.66–1.07) | FZD2 | 17 | 39993014 | 0.271874053 |
| rs4793121 | 7.20E-01 | 0.96( 0.75–1.22) | FZD2 | 17 | 39993435 | 0.426451944 |
| rs7501777 | 2.43E-01 | 0.88( 0.72–1.09) | FZD2 | 17 | 39994203 | 0.301906315 |
| rs1946583 | 5.10E-01 | 1.08( 0.87–1.34) | FZD3 | 8 | 28406672 | 0.377760052 |
| rs352222 | 5.12E-01 | 1.07( 0.87–1.32) | FZD3 | 8 | 28477700 | 0.377760052 |
| rs4732863 | 4.32E-01 | 0.91( 0.72–1.15) | FZD3 | 8 | 28478407 | 0.359395383 |
| rs713065 | 1.99E-02 | 0.79( 0.64–0.96) | FZD4 | 11 | 86335168 | 0.146727575 |
| rs10898563 | 1.96E-01 | 1.22( 0.90–1.67) | FZD4 | 11 | 86336861 | 0.284431004 |
| rs13020497 | 3.57E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.21) | FZD7 | 2 | 202605764 | 0.328827360 |
| rs12994568 | 3.57E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.21) | FZD7 | 2 | 202605821 | 0.328827360 |
| rs13034206 | 3.57E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.21) | FZD7 | 2 | 202609480 | 0.328827360 |
| rs13034579 | 3.57E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.21) | FZD7 | 2 | 202609524 | 0.328827360 |
| rs4673222 | 3.39E-01 | 0.88( 0.68–1.14) | FZD7 | 2 | 202610155 | 0.328827360 |
| rs12474408 | 3.57E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.21) | FZD7 | 2 | 202612051 | 0.328827360 |
| rs12478708 | 3.57E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.21) | FZD7 | 2 | 202612343 | 0.328827360 |
| rs7583130 | 2.26E-01 | 0.85( 0.66–1.10) | FZD7 | 2 | 202613333 | 0.295085709 |
| rs1178947 | 2.83E-01 | 0.90( 0.73–1.10) | FZD9 | 7 | 72488114 | 0.312911216 |
| rs1046890 | 9.10E-01 | 0.99( 0.81–1.21) | FZD10 | 12 | 129215723 | 0.475872051 |
| rs3741568 | 7.88E-01 | 1.03( 0.84–1.26) | FZD10 | 12 | 129215915 | 0.443413702 |
| rs1046895 | 8.96E-01 | 0.99( 0.80–1.22) | FZD10 | 12 | 129215994 | 0.474806202 |
| rs11060753 | 7.88E-01 | 1.03( 0.84–1.26) | FZD10 | 12 | 129216375 | 0.443413702 |
| rs1463865 | 3.43E-01 | 0.83( 0.57–1.22) | FZD10 | 12 | 129217207 | 0.328827360 |
| rs11725638 | 3.18E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.18) | LEF1 | 4 | 109185967 | 0.317400735 |
| rs4245927 | 3.71E-01 | 1.22( 0.79–1.86) | LEF1 | 4 | 109189039 | 0.333220288 |
| rs17439845 | 9.12E-01 | 1.01( 0.78–1.32) | LEF1 | 4 | 109213028 | 0.475872051 |
| rs1291490 | 7.12E-01 | 0.96( 0.76–1.21) | LEF1 | 4 | 109213461 | 0.426046532 |
| rs4956157 | 7.09E-02 | 1.40( 0.97–2.02) | LEF1 | 4 | 109218815 | 0.222980247 |
| rs6533348 | 5.71E-02 | 1.34( 0.99–1.81) | LEF1 | 4 | 109236385 | 0.203076161 |
| rs749414 | 4.98E-01 | 0.94( 0.80–1.12) | LEF1 | 4 | 109247362 | 0.377760052 |
| rs7698367 | 1.35E-01 | 0.85( 0.70–1.05) | LEF1 | 4 | 109249931 | 0.263342145 |
| rs10022956 | 1.25E-01 | 0.86( 0.70–1.04) | LEF1 | 4 | 109253428 | 0.258797750 |
| rs10516550 | 5.68E-01 | 0.92( 0.69–1.22) | LEF1 | 4 | 109255277 | 0.388647584 |
| rs17038617 | 2.49E-01 | 0.88( 0.70–1.10) | LEF1 | 4 | 109266333 | 0.301906315 |
| rs12503104 | 4.62E-01 | 1.08( 0.88–1.34) | LEF1 | 4 | 109281959 | 0.359830407 |
| rs922163 | 6.86E-01 | 0.94( 0.71–1.25) | LEF1 | 4 | 109285815 | 0.424838822 |
| rs64388 | 3.31E-02 | 1.25( 1.02–1.52) | LRP5 | 11 | 67830957 | 0.186192568 |
| rs312009 | 1.12E-01 | 1.18( 0.96–1.45) | LRP5 | 11 | 67833814 | 0.247221759 |
| rs682429 | 1.13E-01 | 1.18( 0.96–1.44) | LRP5 | 11 | 67835895 | 0.247221759 |
| rs11228202 | 9.82E-01 | 1.00( 0.79–1.28) | LRP5 | 11 | 67840804 | 0.494069355 |
| rs4988331 | 2.40E-01 | 0.84( 0.63–1.12) | LRP5 | 11 | 67841909 | 0.301281403 |
| rs4988300 | 9.77E-03 | 0.74( 0.58–0.93) | LRP5 | 11 | 67845407 | 0.135500153 |
| rs2508836 | 1.03E-02 | 0.81( 0.68–0.95) | LRP5 | 11 | 67847841 | 0.135500153 |
| rs3781600 | 9.41E-01 | 0.99( 0.76–1.28) | LRP5 | 11 | 67849913 | 0.478174891 |
| rs606989 | 5.71E-01 | 1.08( 0.82–1.42) | LRP5 | 11 | 67858576 | 0.389104323 |
| rs312778 | 6.07E-02 | 0.78( 0.59–1.01) | LRP5 | 11 | 67864908 | 0.205417788 |
| rs314756 | 1.97E-02 | 0.69( 0.51–0.94) | LRP5 | 11 | 67868248 | 0.146727575 |
| rs729635 | 3.14E-01 | 0.87( 0.67–1.14) | LRP5 | 11 | 67868336 | 0.316902816 |
| rs312786 | 3.81E-02 | 0.66( 0.45–0.98) | LRP5 | 11 | 67876553 | 0.186192568 |
| rs624947 | 7.84E-01 | 1.02( 0.88–1.19) | LRP5 | 11 | 67897358 | 0.443413702 |
| rs638051 | 3.03E-01 | 1.14( 0.89–1.46) | LRP5 | 11 | 67897990 | 0.315893774 |
| rs11826287 | 4.64E-01 | 1.08( 0.88–1.33) | LRP5 | 11 | 67903237 | 0.359830407 |
| rs671191 | 3.61E-01 | 1.14( 0.86–1.51) | LRP5 | 11 | 67906557 | 0.328827360 |
| rs4930573 | 3.19E-01 | 0.84( 0.59–1.19) | LRP5 | 11 | 67920032 | 0.317400735 |
| rs545382 | 2.06E-01 | 0.85( 0.67–1.09) | LRP5 | 11 | 67927589 | 0.284431004 |
| rs2277268 | 4.67E-01 | 0.90( 0.68–1.20) | LRP5 | 11 | 67930698 | 0.360602406 |
| rs640569 | 4.14E-01 | 0.86( 0.61–1.23) | LRP5 | 11 | 67941396 | 0.354708008 |
| rs608343 | 9.14E-01 | 1.01( 0.83–1.24) | LRP5 | 11 | 67953406 | 0.475872051 |
| rs3781586 | 4.47E-02 | 1.26( 1.01–1.57) | LRP5 | 11 | 67955969 | 0.186200636 |
| rs12417014 | 5.18E-01 | 0.92( 0.70–1.20) | LRP5 | 11 | 67957583 | 0.379094638 |
| rs2242340 | 5.10E-01 | 0.92( 0.71–1.19) | LRP5 | 11 | 67970695 | 0.377760052 |
| rs676318 | 4.18E-02 | 0.75( 0.57–0.99) | LRP5 | 11 | 67973996 | 0.186192568 |
| rs2302684 | 1.14E-01 | 0.84( 0.68–1.04) | LRP6 | 12 | 12169735 | 0.247221759 |
| rs1012672 | 1.09E-02 | 1.47( 1.09–1.97) | LRP6 | 12 | 12176182 | 0.135500153 |
| rs11054704 | 9.12E-01 | 0.99( 0.78–1.25) | LRP6 | 12 | 12191036 | 0.475872051 |
| rs2302685 | 5.05E-01 | 0.93( 0.75–1.15) | LRP6 | 12 | 12193165 | 0.377760052 |
| rs11054709 | 2.00E-01 | 0.84( 0.65–1.10) | LRP6 | 12 | 12193689 | 0.284431004 |
| rs7301012 | 3.00E-01 | 1.12( 0.90–1.39) | LRP6 | 12 | 12198911 | 0.315893774 |
| rs12310020 | 1.58E-01 | 0.83( 0.64–1.08) | LRP6 | 12 | 12212448 | 0.270394908 |
| rs12833575 | 7.44E-01 | 0.95( 0.68–1.32) | LRP6 | 12 | 12216108 | 0.434472104 |
| rs11054721 | 1.37E-01 | 1.19( 0.95–1.49) | LRP6 | 12 | 12222594 | 0.263578639 |
| rs10845493 | 4.39E-01 | 1.09( 0.87–1.37) | LRP6 | 12 | 12223463 | 0.359395383 |
| rs10492120 | 6.94E-01 | 1.04( 0.85–1.28) | LRP6 | 12 | 12224619 | 0.424838822 |
| rs10845498 | 7.58E-01 | 0.97( 0.78–1.20) | LRP6 | 12 | 12285841 | 0.437484457 |
| rs12823867 | 7.93E-01 | 1.03( 0.83–1.27) | LRP6 | 12 | 12287397 | 0.443989861 |
| rs10743980 | 5.74E-02 | 1.15( 1.00–1.32) | LRP6 | 12 | 12304062 | 0.203076161 |
| rs12309338 | 6.00E-01 | 0.93( 0.71–1.22) | LRP6 | 12 | 12312326 | 0.401557037 |
| rs7136900 | 5.61E-01 | 1.04( 0.90–1.21) | LRP6 | 12 | 12314360 | 0.388164447 |
| rs12816278 | 9.69E-01 | 1.00( 0.80–1.25) | LRP6 | 12 | 12317344 | 0.488452597 |
| rs7296283 | 2.57E-01 | 1.10( 0.93–1.31) | LRP6 | 12 | 12319275 | 0.302073322 |
| rs11054760 | 1.67E-02 | 1.53( 1.08–2.17) | LRP6 | 12 | 12320749 | 0.144627899 |
| rs10431302 | 4.21E-02 | 0.80( 0.65–0.99) | LRP6 | 12 | 12320918 | 0.186192568 |
| rs10491321 | 9.39E-01 | 1.01( 0.82–1.24) | PPP2CA | 5 | 133555489 | 0.478174891 |
| rs4246019 | 6.39E-01 | 0.94( 0.74–1.20) | PPP2CA | 5 | 133593991 | 0.414986215 |
| rs254057 | 5.79E-02 | 1.26( 0.99–1.60) | PPP2CA | 5 | 133599755 | 0.203076161 |
| rs6993129 | 6.45E-01 | 0.95( 0.77–1.18) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30753679 | 0.415574805 |
| rs7017734 | 6.45E-01 | 0.95( 0.77–1.18) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30754985 | 0.415574805 |
| rs11780378 | 6.93E-01 | 1.06( 0.80–1.39) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30760201 | 0.424838822 |
| rs4733509 | 8.33E-01 | 1.04( 0.74–1.46) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30761490 | 0.452520518 |
| rs13268487 | 9.84E-01 | 1.00( 0.73–1.38) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30766081 | 0.494172410 |
| rs1116003 | 9.46E-02 | 1.39( 0.94–2.04) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30774905 | 0.246983910 |
| rs4733200 | 5.92E-01 | 1.08( 0.81–1.45) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30784198 | 0.397139194 |
| rs4733518 | 5.92E-01 | 1.08( 0.81–1.45) | PPP2CB | 8 | 30793453 | 0.397139194 |
| rs2248033 | 5.18E-02 | 0.82( 0.67–1.00) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53619722 | 0.196213611 |
| rs1624779 | 6.98E-02 | 0.83( 0.68–1.01) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53620813 | 0.222980247 |
| rs16976371 | 9.05E-01 | 1.02( 0.79–1.30) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53624141 | 0.475872051 |
| rs11071189 | 1.98E-01 | 1.16( 0.93–1.45) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53624380 | 0.284431004 |
| rs11858624 | 6.54E-01 | 0.93( 0.67–1.28) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53625877 | 0.418665386 |
| rs7183943 | 7.79E-02 | 0.84( 0.69–1.02) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53662358 | 0.235608553 |
| rs7181481 | 4.50E-01 | 1.10( 0.86–1.41) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53674236 | 0.359705483 |
| rs7181496 | 7.52E-01 | 0.97( 0.79–1.18) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53674260 | 0.437337077 |
| rs12898968 | 5.39E-01 | 0.93( 0.73–1.18) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53674548 | 0.379736909 |
| rs2917844 | 7.31E-01 | 0.96( 0.75–1.22) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53675019 | 0.431489740 |
| rs552292 | 6.84E-01 | 0.97( 0.84–1.12) | PYGO1 | 15 | 53676324 | 0.424838822 |
| rs6474328 | 2.94E-01 | 1.11( 0.91–1.36) | SFRP1 | 8 | 41236656 | 0.315417003 |
| rs3242 | 3.12E-01 | 1.08( 0.93–1.26) | SFRP1 | 8 | 41238711 | 0.315893774 |
| rs12914 | 3.10E-01 | 1.11( 0.91–1.36) | SFRP1 | 8 | 41239309 | 0.315893774 |
| rs1127379 | 2.93E-01 | 1.14( 0.89–1.46) | SFRP1 | 8 | 41240437 | 0.315417003 |
| rs12639885 | 6.31E-01 | 1.05( 0.86–1.29) | SFRP2 | 4 | 154919824 | 0.413471411 |
| rs10014299 | 6.37E-01 | 1.05( 0.85–1.29) | SFRP2 | 4 | 154920308 | 0.414986215 |
| rs2039826 | 7.59E-01 | 0.95( 0.70–1.30) | SFRP5 | 10 | 99516658 | 0.437484457 |
| rs7478323 | 7.57E-01 | 0.95( 0.70–1.30) | SFRP5 | 10 | 99516933 | 0.437484457 |
| rs4919139 | 5.02E-01 | 1.07( 0.87–1.32) | SFRP5 | 10 | 99522850 | 0.377760052 |
| rs168649 | 5.66E-01 | 1.07( 0.86–1.32) | TCF7 | 5 | 133472819 | 0.388647584 |
| rs244952 | 4.18E-01 | 0.89( 0.66–1.19) | TCF7 | 5 | 133474171 | 0.354708008 |
| rs2436323 | 4.18E-01 | 0.89( 0.66–1.19) | TCF7 | 5 | 133474960 | 0.354708008 |
| rs151822 | 6.55E-01 | 1.05( 0.85–1.29) | TCF7 | 5 | 133483860 | 0.418665386 |
| rs152402 | 1.92E-01 | 1.15( 0.93–1.43) | TCF7 | 5 | 133506240 | 0.284431004 |
| rs30489 | 8.72E-01 | 0.98( 0.75–1.28) | TCF7 | 5 | 133509366 | 0.466081299 |
| rs4958216 | 1.13E-01 | 1.19( 0.96–1.48) | TCF7 | 5 | 133514162 | 0.247221759 |
| rs390258 | 4.64E-03 | 1.64( 1.16–2.30) | TLE2 | 19 | 2947339 | 0.128006452 |
| rs423232 | 2.21E-02 | 0.74( 0.57–0.96) | TLE2 | 19 | 2947483 | 0.152312051 |
| rs4806893 | 1.04E-01 | 0.81( 0.63–1.04) | TLE2 | 19 | 2947889 | 0.247221759 |
| rs14089 | 7.35E-01 | 0.96( 0.75–1.22) | TLE2 | 19 | 2948790 | 0.432545906 |
| rs1688128 | 7.36E-01 | 1.04( 0.83–1.30) | TLE2 | 19 | 2981168 | 0.432545906 |
| rs3743309 | 1.72E-01 | 1.19( 0.93–1.51) | TLE3 | 15 | 68127565 | 0.277576313 |
| rs2807304 | 4.23E-01 | 0.94( 0.79–1.10) | TLE4 | 9 | 81375174 | 0.357966724 |
| rs4355856 | 9.34E-01 | 1.01( 0.82–1.24) | TLE4 | 9 | 81532323 | 0.478174891 |
| rs4285553 | 9.34E-01 | 1.01( 0.82–1.24) | TLE4 | 9 | 81532471 | 0.478174891 |
| rs11667371 | 4.00E-01 | 0.83( 0.54–1.28) | TLE6 | 19 | 2927724 | 0.349296428 |
| rs17681742 | 4.11E-01 | 1.10( 0.88–1.37) | TLE6 | 19 | 2928599 | 0.354708008 |
| rs1446527 | 2.87E-01 | 0.87( 0.68–1.12) | WIF1 | 12 | 63733304 | 0.313365199 |
| rs3782497 | 6.73E-01 | 0.93( 0.68–1.28) | WIF1 | 12 | 63746341 | 0.423223626 |
| rs3782499 | 3.07E-01 | 1.16( 0.87–1.55) | WIF1 | 12 | 63752919 | 0.315893774 |
| rs6581606 | 1.24E-01 | 1.12( 0.97–1.30) | WIF1 | 12 | 63753893 | 0.258519177 |
| rs12818732 | 3.02E-01 | 1.21( 0.84–1.73) | WIF1 | 12 | 63755986 | 0.315893774 |
| rs7397906 | 1.48E-01 | 0.90( 0.78–1.04) | WIF1 | 12 | 63769889 | 0.270394908 |
| rs7309476 | 1.43E-01 | 1.11( 0.96–1.29) | WIF1 | 12 | 63773962 | 0.270394908 |
| rs1466828 | 1.59E-01 | 0.79( 0.56–1.10) | WIF1 | 12 | 63790221 | 0.270394908 |
| rs17101044 | 5.78E-01 | 1.08( 0.82–1.42) | WIF1 | 12 | 63791366 | 0.392545122 |
| rs7301320 | 2.72E-03 | 1.35( 1.11–1.65) | WIF1 | 12 | 63800533 | 0.100176561 |
| rs17101051 | 4.36E-01 | 0.91( 0.72–1.15) | WIF1 | 12 | 63803872 | 0.359395383 |
| rs2336434 | 5.44E-01 | 0.87( 0.55–1.37) | WIF1 | 12 | 63805533 | 0.379736909 |
| rs17101056 | 5.14E-01 | 0.92( 0.72–1.18) | WIF1 | 12 | 63806743 | 0.377760052 |
| rs7304867 | 6.68E-02 | 0.61( 0.36–1.03) | WIF1 | 12 | 63806806 | 0.217115370 |
| rs10878232 | 2.16E-03 | 1.36( 1.12–1.66) | WIF1 | 12 | 63808914 | 0.095602299 |
| rs1155722 | 6.21E-03 | 1.32( 1.08–1.61) | WIF1 | 12 | 63809424 | 0.135500153 |
| rs12318130 | 3.98E-01 | 1.12( 0.86–1.47) | WIF1 | 12 | 63810846 | 0.349296428 |
| rs6946781 | 2.87E-02 | 0.63( 0.42–0.95) | WNT2 | 7 | 116694979 | 0.176207503 |
| rs887574 | 3.59E-01 | 1.08( 0.92–1.27) | WNT2 | 7 | 116703248 | 0.328827360 |
| rs887575 | 1.59E-01 | 0.91( 0.79–1.04) | WNT2 | 7 | 116703464 | 0.270394908 |
| rs4730775 | 8.60E-02 | 1.23( 0.97–1.56) | WNT2 | 7 | 116704354 | 0.244482539 |
| rs2228946 | 6.25E-01 | 0.95( 0.78–1.16) | WNT2 | 7 | 116705321 | 0.410945313 |
| rs733153 | 8.63E-01 | 1.02( 0.80–1.31) | WNT2 | 7 | 116706028 | 0.463958815 |
| rs2896218 | 2.29E-01 | 0.88( 0.72–1.08) | WNT2 | 7 | 116707214 | 0.296677764 |
| rs3779548 | 5.15E-01 | 1.05( 0.91–1.20) | WNT2 | 7 | 116718131 | 0.377760052 |
| rs17139625 | 6.60E-01 | 0.94( 0.73–1.22) | WNT2 | 7 | 116722714 | 0.420006663 |
| rs39306 | 2.32E-01 | 0.89( 0.73–1.08) | WNT2 | 7 | 116728472 | 0.296677764 |
| rs6947329 | 4.41E-02 | 1.29( 1.01–1.65) | WNT2 | 7 | 116730371 | 0.186200636 |
| rs1989836 | 1.87E-01 | 0.87( 0.72–1.07) | WNT2 | 7 | 116734432 | 0.284431004 |
| rs2285545 | 3.44E-02 | 0.87( 0.76–0.99) | WNT2 | 7 | 116735407 | 0.186192568 |
| rs2239956 | 9.43E-02 | 1.26( 0.96–1.64) | WNT2 | 7 | 116736522 | 0.246983910 |
| rs739517 | 1.85E-01 | 0.83( 0.63–1.09) | WNT2 | 7 | 116742935 | 0.284431004 |
| rs39315 | 1.71E-01 | 0.90( 0.78–1.04) | WNT2 | 7 | 116750798 | 0.277576313 |
| rs254536 | 1.65E-01 | 0.87( 0.71–1.06) | WNT2 | 7 | 116757818 | 0.274758970 |
| rs6961545 | 8.37E-01 | 0.97( 0.74–1.28) | WNT2 | 7 | 116759067 | 0.452937961 |
| rs254538 | 2.56E-01 | 0.89( 0.74–1.08) | WNT2 | 7 | 116760524 | 0.302008524 |
| rs3795821 | 1.84E-01 | 0.87( 0.71–1.07) | WNT2B | 1 | 112802088 | 0.284431004 |
| rs2488787 | 2.02E-01 | 0.91( 0.78–1.05) | WNT2B | 1 | 112807331 | 0.284431004 |
| rs1175649 | 8.69E-01 | 0.98( 0.75–1.27) | WNT2B | 1 | 112820800 | 0.465726073 |
| rs1175650 | 1.10E-01 | 0.83( 0.67–1.04) | WNT2B | 1 | 112821097 | 0.247221759 |
| rs10776751 | 7.01E-01 | 1.06( 0.80–1.39) | WNT2B | 1 | 112821821 | 0.426046532 |
| rs1620668 | 8.45E-01 | 1.02( 0.83–1.26) | WNT2B | 1 | 112825503 | 0.456546450 |
| rs974442 | 4.02E-01 | 0.90( 0.72–1.14) | WNT2B | 1 | 112829794 | 0.349296428 |
| rs351359 | 6.62E-01 | 1.05( 0.85–1.29) | WNT2B | 1 | 112841800 | 0.420006663 |
| rs351360 | 1.58E-01 | 0.83( 0.64–1.08) | WNT2B | 1 | 112841944 | 0.270394908 |
| rs11807828 | 4.69E-01 | 1.11( 0.84–1.47) | WNT2B | 1 | 112844072 | 0.360602406 |
| rs351361 | 9.30E-01 | 0.99( 0.81–1.22) | WNT2B | 1 | 112844081 | 0.478174891 |
| rs351364 | 5.23E-01 | 1.12( 0.79–1.59) | WNT2B | 1 | 112846584 | 0.379736909 |
| rs3790604 | 1.59E-01 | 0.81( 0.60–1.09) | WNT2B | 1 | 112848402 | 0.270394908 |
| rs3790606 | 3.47E-01 | 0.91( 0.74–1.11) | WNT2B | 1 | 112853709 | 0.328827360 |
| rs351370 | 5.38E-01 | 1.08( 0.84–1.38) | WNT2B | 1 | 112856182 | 0.379736909 |
| rs3790609 | 3.51E-01 | 1.11( 0.89–1.37) | WNT2B | 1 | 112858513 | 0.328827360 |
| rs2273368 | 2.62E-01 | 1.13( 0.91–1.39) | WNT2B | 1 | 112865294 | 0.306380050 |
| rs3790611 | 1.58E-01 | 0.89( 0.75–1.05) | WNT2B | 1 | 112869315 | 0.270394908 |
| rs3809857 | 3.48E-02 | 0.80( 0.65–0.98) | WNT3 | 17 | 42203482 | 0.186192568 |
| rs199506 | 9.52E-01 | 0.99( 0.81–1.23) | WNT3 | 17 | 42214192 | 0.481138076 |
| rs199500 | 6.37E-01 | 0.95( 0.77–1.17) | WNT3 | 17 | 42218572 | 0.414986215 |
| rs2074404 | 2.46E-01 | 1.28( 0.84–1.94) | WNT3 | 17 | 42220599 | 0.301906315 |
| rs2074405 | 2.55E-01 | 1.10( 0.93–1.31) | WNT3 | 17 | 42221161 | 0.302008524 |
| rs199497 | 7.89E-01 | 1.03( 0.82–1.29) | WNT3 | 17 | 42221762 | 0.443413702 |
| rs199496 | 3.51E-01 | 1.12( 0.89–1.41) | WNT3 | 17 | 42221887 | 0.328827360 |
| rs11658976 | 1.22E-02 | 1.45( 1.08–1.94) | WNT3 | 17 | 42221965 | 0.142078914 |
| rs12452064 | 1.98E-01 | 1.17( 0.92–1.50) | WNT3 | 17 | 42223353 | 0.284431004 |
| rs199494 | 2.77E-01 | 1.15( 0.89–1.47) | WNT3 | 17 | 42224229 | 0.310012797 |
| rs7218567 | 4.29E-03 | 1.68( 1.18–2.40) | WNT3 | 17 | 42225421 | 0.128006452 |
| rs8080199 | 1.92E-01 | 1.17( 0.93–1.47) | WNT3 | 17 | 42228781 | 0.284431004 |
| rs11650531 | 1.21E-01 | 0.87( 0.74–1.04) | WNT3 | 17 | 42229159 | 0.254403903 |
| rs1563304 | 8.83E-01 | 1.02( 0.81–1.28) | WNT3 | 17 | 42229617 | 0.469718466 |
| rs7207916 | 2.06E-01 | 0.83( 0.62–1.11) | WNT3 | 17 | 42234514 | 0.284431004 |
| rs3933652 | 5.34E-01 | 1.07( 0.86–1.34) | WNT3 | 17 | 42243714 | 0.379736909 |
| rs3933653 | 3.68E-01 | 0.82( 0.54–1.26) | WNT3 | 17 | 42243741 | 0.331747799 |
| rs3916033 | 7.70E-01 | 1.03( 0.84–1.27) | WNT3 | 17 | 42244702 | 0.442803211 |
| rs11079738 | 3.37E-01 | 0.90( 0.73–1.11) | WNT3 | 17 | 42259048 | 0.328827360 |
| rs708108 | 1.05E-01 | 1.18( 0.97–1.45) | WNT3A | 1 | 226256478 | 0.247221759 |
| rs708110 | 2.73E-02 | 1.26( 1.03–1.55) | WNT3A | 1 | 226257428 | 0.175417920 |
| rs708122 | 4.29E-01 | 0.92( 0.75–1.13) | WNT3A | 1 | 226283620 | 0.359395383 |
| rs10916258 | 1.74E-01 | 0.87( 0.71–1.06) | WNT3A | 1 | 226286505 | 0.278295542 |
| rs3121309 | 7.14E-01 | 1.08( 0.72–1.61) | WNT3A | 1 | 226289659 | 0.426046532 |
| rs3121310 | 1.47E-02 | 1.39( 1.07–1.82) | WNT3A | 1 | 226291447 | 0.144627899 |
| rs7412010 | 3.83E-01 | 1.11( 0.88–1.40) | WNT4 | 1 | 22309033 | 0.338387524 |
| rs4654783 | 1.77E-02 | 1.58( 1.08–2.31) | WNT4 | 1 | 22312107 | 0.144627899 |
| rs3765351 | 1.82E-01 | 1.19( 0.92–1.52) | WNT4 | 1 | 22318578 | 0.284431004 |
| rs12131703 | 7.04E-01 | 0.96( 0.77–1.20) | WNT4 | 1 | 22320804 | 0.426046532 |
| rs7526484 | 4.59E-01 | 0.93( 0.76–1.14) | WNT4 | 1 | 22324432 | 0.359705483 |
| rs10917155 | 7.32E-03 | 1.54( 1.12–2.11) | WNT4 | 1 | 22324553 | 0.135500153 |
| rs2235525 | 5.44E-01 | 0.93( 0.75–1.16) | WNT4 | 1 | 22326912 | 0.379736909 |
| rs10917158 | 5.44E-01 | 0.93( 0.75–1.16) | WNT4 | 1 | 22326960 | 0.379736909 |
| rs2865174 | 9.04E-01 | 0.98( 0.71–1.35) | WNT4 | 1 | 22337747 | 0.475872051 |
| rs7515106 | 2.09E-02 | 1.61( 1.07–2.42) | WNT4 | 1 | 22345997 | 0.149155672 |
| rs7521775 | 9.31E-02 | 1.24( 0.96–1.60) | WNT4 | 1 | 22348236 | 0.246983910 |
| rs7542242 | 2.66E-01 | 1.12( 0.92–1.37) | WNT4 | 1 | 22350080 | 0.307524913 |
| rs7548239 | 8.34E-01 | 1.05( 0.68–1.60) | WNT4 | 1 | 22351780 | 0.452520518 |
| rs1499890 | 9.62E-02 | 0.89( 0.78–1.02) | WNT5A | 3 | 55464838 | 0.247172881 |
| rs629537 | 1.95E-02 | 1.29( 1.04–1.60) | WNT5A | 3 | 55466053 | 0.146727575 |
| rs503022 | 3.62E-02 | 1.26( 1.01–1.56) | WNT5A | 3 | 55466476 | 0.186192568 |
| rs508407 | 1.08E-01 | 1.22( 0.96–1.57) | WNT5A | 3 | 55467460 | 0.247221759 |
| rs476986 | 8.01E-01 | 0.94( 0.60–1.49) | WNT5A | 3 | 55468554 | 0.445017693 |
| rs11706227 | 7.94E-01 | 1.03( 0.82–1.31) | WNT5A | 3 | 55471300 | 0.443989861 |
| rs597437 | 2.72E-02 | 1.43( 1.04–1.95) | WNT5A | 3 | 55471449 | 0.175417920 |
| rs11710229 | 6.22E-01 | 1.06( 0.84–1.34) | WNT5A | 3 | 55472993 | 0.410413148 |
| rs590386 | 9.43E-02 | 1.22( 0.97–1.54) | WNT5A | 3 | 55474447 | 0.246983910 |
| rs1047898 | 8.53E-02 | 0.89( 0.78–1.02) | WNT5A | 3 | 55474821 | 0.244482539 |
| rs1829556 | 1.33E-01 | 0.90( 0.79–1.03) | WNT5A | 3 | 55476215 | 0.263342145 |
| rs7622120 | 6.52E-02 | 0.79( 0.61–1.02) | WNT5A | 3 | 55479770 | 0.214878269 |
| rs11918967 | 4.30E-01 | 1.10( 0.87–1.40) | WNT5A | 3 | 55480430 | 0.359395383 |
| rs648872 | 1.93E-01 | 1.15( 0.93–1.42) | WNT5A | 3 | 55494897 | 0.284431004 |
| rs566926 | 2.11E-01 | 0.90( 0.77–1.06) | WNT5A | 3 | 55495818 | 0.284945038 |
| rs557077 | 4.73E-02 | 1.40( 1.00–1.96) | WNT5A | 3 | 55506307 | 0.186667333 |
| rs4765829 | 1.55E-01 | 0.87( 0.71–1.06) | WNT5B | 12 | 1591055 | 0.270394908 |
| rs10773974 | 2.69E-01 | 0.90( 0.74–1.09) | WNT5B | 12 | 1619633 | 0.307820239 |
| rs2270038 | 1.69E-01 | 0.90( 0.78–1.05) | WNT5B | 12 | 1620166 | 0.277576313 |
| rs2240509 | 2.84E-01 | 0.88( 0.70–1.11) | WNT5B | 12 | 1620858 | 0.312911216 |
| rs2240510 | 2.85E-01 | 0.83( 0.59–1.17) | WNT5B | 12 | 1623486 | 0.312911216 |
| rs2240511 | 1.77E-01 | 0.86( 0.69–1.07) | WNT5B | 12 | 1623551 | 0.279313968 |
| rs7132752 | 8.10E-01 | 0.96( 0.69–1.34) | WNT5B | 12 | 1623995 | 0.447606546 |
| rs3803164 | 1.76E-01 | 0.87( 0.72–1.06) | WNT5B | 12 | 1625915 | 0.279313968 |
| rs3803163 | 2.72E-01 | 0.83( 0.60–1.15) | WNT5B | 12 | 1626221 | 0.308376026 |
| rs12819505 | 1.37E-03 | 1.58( 1.19–2.09) | WNT5B | 12 | 1626926 | 0.095030240 |
| rs1003939 | 9.87E-03 | 0.56( 0.36–0.87) | WNT5B | 12 | 1626939 | 0.135500153 |
| rs6489314 | 8.65E-02 | 0.82( 0.66–1.03) | WNT5B | 12 | 1627431 | 0.244482539 |
| rs4766403 | 1.03E-02 | 1.21( 1.05–1.39) | WNT5B | 12 | 1630739 | 0.135500153 |
| rs4766408 | 3.50E-01 | 0.91( 0.74–1.11) | WNT5B | 12 | 1634790 | 0.328827360 |
| rs7296858 | 1.71E-01 | 1.21( 0.92–1.59) | WNT5B | 12 | 1636194 | 0.277576313 |
| rs7596898 | 4.86E-02 | 0.80( 0.64–1.00) | WNT6 | 2 | 219427976 | 0.188401227 |
| rs940469 | 2.50E-01 | 1.13( 0.92–1.39) | WNT6 | 2 | 219428221 | 0.301906315 |
| rs751135 | 6.56E-01 | 1.04( 0.88–1.22) | WNT6 | 2 | 219428593 | 0.418665386 |
| rs690877 | 3.43E-01 | 1.10( 0.90–1.35) | WNT6 | 2 | 219430908 | 0.328827360 |
| rs2053101 | 6.88E-01 | 0.92( 0.62–1.38) | WNT7A | 3 | 13825667 | 0.424838822 |
| rs9864832 | 9.03E-03 | 1.52( 1.11–2.08) | WNT7A | 3 | 13827744 | 0.135500153 |
| rs11712819 | 3.55E-01 | 0.91( 0.75–1.11) | WNT7A | 3 | 13830800 | 0.328827360 |
| rs2163910 | 7.99E-01 | 1.03( 0.81–1.31) | WNT7A | 3 | 13832893 | 0.445017693 |
| rs1124480 | 5.25E-01 | 0.93( 0.73–1.17) | WNT7A | 3 | 13832970 | 0.379736909 |
| rs1946620 | 1.10E-02 | 1.32( 1.07–1.63) | WNT7A | 3 | 13833800 | 0.135500153 |
| rs3796316 | 5.08E-01 | 1.09( 0.85–1.39) | WNT7A | 3 | 13834174 | 0.377760052 |
| rs3796314 | 3.09E-01 | 1.12( 0.90–1.38) | WNT7A | 3 | 13834333 | 0.315893774 |
| rs9840696 | 3.33E-01 | 0.90( 0.73–1.11) | WNT7A | 3 | 13840076 | 0.328827360 |
| rs12492620 | 4.02E-01 | 0.92( 0.75–1.13) | WNT7A | 3 | 13842256 | 0.349296428 |
| rs867606 | 5.24E-01 | 1.07( 0.86–1.33) | WNT7A | 3 | 13844302 | 0.379736909 |
| rs934453 | 6.91E-01 | 0.95( 0.75–1.21) | WNT7A | 3 | 13845053 | 0.424838822 |
| rs12634816 | 1.37E-01 | 1.29( 0.92–1.81) | WNT7A | 3 | 13847271 | 0.263578639 |
| rs11711182 | 1.21E-01 | 1.19( 0.95–1.49) | WNT7A | 3 | 13851910 | 0.254403903 |
| rs12634112 | 4.59E-01 | 0.92( 0.73–1.15) | WNT7A | 3 | 13853890 | 0.359705483 |
| rs11922919 | 5.87E-01 | 1.06( 0.86–1.30) | WNT7A | 3 | 13854617 | 0.396598092 |
| rs9863149 | 2.71E-01 | 1.18( 0.88–1.58) | WNT7A | 3 | 13858361 | 0.308376026 |
| rs4257529 | 5.13E-01 | 1.07( 0.87–1.32) | WNT7A | 3 | 13869117 | 0.377760052 |
| rs3762721 | 5.52E-01 | 0.93( 0.73–1.18) | WNT7A | 3 | 13870807 | 0.383590947 |
| rs12639607 | 3.62E-01 | 1.11( 0.89–1.38) | WNT7A | 3 | 13871285 | 0.328827360 |
| rs9819887 | 4.33E-01 | 1.06( 0.91–1.24) | WNT7A | 3 | 13873619 | 0.359395383 |
| rs13069140 | 1.98E-01 | 0.84( 0.64–1.10) | WNT7A | 3 | 13878304 | 0.284431004 |
| rs6442416 | 1.34E-01 | 0.90( 0.78–1.03) | WNT7A | 3 | 13882101 | 0.263342145 |
| rs9864031 | 2.02E-01 | 0.87( 0.71–1.08) | WNT7A | 3 | 13883072 | 0.284431004 |
| rs12632968 | 2.51E-01 | 0.92( 0.80–1.06) | WNT7A | 3 | 13887198 | 0.301906315 |
| rs4685048 | 4.71E-01 | 0.95( 0.82–1.09) | WNT7A | 3 | 13897736 | 0.360699651 |
| rs1077524 | 6.70E-01 | 0.96( 0.79–1.17) | WNT7A | 3 | 13905134 | 0.422621937 |
| rs6768050 | 8.13E-02 | 1.29( 0.97–1.72) | WNT7A | 3 | 13905491 | 0.239365623 |
| rs217259 | 4.45E-01 | 1.14( 0.82–1.58) | WNT8A | 5 | 137440862 | 0.359705483 |
| rs10440755 | 2.94E-01 | 0.88( 0.70–1.11) | WNT8A | 5 | 137442365 | 0.315417003 |
| rs4835761 | 6.94E-01 | 1.05( 0.82–1.34) | WNT8A | 5 | 137445768 | 0.424838822 |
| rs10036244 | 5.82E-01 | 0.94( 0.77–1.16) | WNT8A | 5 | 137447624 | 0.394635311 |
| rs2040862 | 3.75E-01 | 1.10( 0.89–1.35) | WNT8A | 5 | 137447888 | 0.333860360 |
| rs4919464 | 1.49E-01 | 0.89( 0.75–1.04) | WNT8B | 10 | 102211185 | 0.270394908 |
| rs3793771 | 1.15E-01 | 0.88( 0.74–1.03) | WNT8B | 10 | 102212947 | 0.247366510 |
| rs12762598 | 8.24E-01 | 1.02( 0.87–1.20) | WNT8B | 10 | 102217746 | 0.450428119 |
| rs7552818 | 9.03E-01 | 1.01( 0.82–1.25) | WNT9A | 1 | 226167514 | 0.475872051 |
| rs10916243 | 2.01E-01 | 1.10( 0.95–1.28) | WNT9A | 1 | 226167742 | 0.284431004 |
| rs1009658 | 1.10E-01 | 0.84( 0.68–1.04) | WNT9A | 1 | 226170404 | 0.247221759 |
| rs12748472 | 2.78E-02 | 1.18( 1.02–1.38) | WNT9A | 1 | 226170998 | 0.175417920 |
| rs8192633 | 9.90E-01 | 1.00( 0.62–1.59) | WNT9A | 1 | 226176094 | 0.495714725 |
| rs10127943 | 1.27E-01 | 1.17( 0.96–1.43) | WNT9A | 1 | 226176687 | 0.259279357 |
| rs12046421 | 7.15E-01 | 0.96( 0.79–1.18) | WNT9A | 1 | 226177357 | 0.426046532 |
| rs680997 | 1.48E-01 | 0.79( 0.57–1.09) | WNT9A | 1 | 226193850 | 0.270394908 |
| rs680148 | 4.05E-02 | 1.25( 1.01–1.54) | WNT9A | 1 | 226194014 | 0.186192568 |
| rs681239 | 5.30E-01 | 0.89( 0.61–1.29) | WNT9A | 1 | 226206295 | 0.379736909 |
| rs6665129 | 2.53E-01 | 0.87( 0.69–1.10) | WNT9A | 1 | 226207083 | 0.301906315 |
| rs2083798 | 9.16E-01 | 0.99( 0.81–1.21) | WNT9B | 17 | 42276896 | 0.475872051 |
| rs2083797 | 4.03E-01 | 1.14( 0.84–1.54) | WNT9B | 17 | 42276928 | 0.349470404 |
| rs4968275 | 9.42E-01 | 1.01( 0.81–1.25) | WNT9B | 17 | 42279659 | 0.478174891 |
| rs7212246 | 9.42E-01 | 1.01( 0.81–1.25) | WNT9B | 17 | 42280490 | 0.478174891 |
| rs12150651 | 7.07E-01 | 0.96( 0.77–1.19) | WNT9B | 17 | 42288568 | 0.426046532 |
| rs2165846 | 2.48E-01 | 1.15( 0.91–1.47) | WNT9B | 17 | 42296365 | 0.301906315 |
| rs12952746 | 4.35E-01 | 1.10( 0.87–1.39) | WNT9B | 17 | 42298412 | 0.359395383 |
| rs6504591 | 3.06E-01 | 0.93( 0.81–1.07) | WNT9B | 17 | 42299827 | 0.315893774 |
| rs4968281 | 4.42E-01 | 1.16( 0.79–1.71) | WNT9B | 17 | 42305121 | 0.359705483 |
| rs1530364 | 4.45E-02 | 0.67( 0.45–0.99) | WNT9B | 17 | 42306776 | 0.186200636 |
| rs754474 | 2.52E-01 | 1.24( 0.86–1.78) | WNT9B | 17 | 42308855 | 0.301906315 |
| rs17603901 | 8.32E-01 | 1.03( 0.79–1.34) | WNT9B | 17 | 42313021 | 0.452520518 |
| rs10177996 | 7.78E-01 | 1.03( 0.83–1.28) | WNT10A | 2 | 219454805 | 0.443413702 |
| rs4574113 | 7.12E-01 | 1.04( 0.84–1.30) | WNT10A | 2 | 219470906 | 0.426046532 |
| rs833839 | 4.98E-01 | 1.08( 0.86–1.35) | WNT10B | 12 | 47653157 | 0.377760052 |
| rs7311091 | 4.72E-01 | 1.11( 0.84–1.46) | WNT10B | 12 | 47669474 | 0.360699651 |
| rs664499 | 3.06E-01 | 0.86( 0.65–1.15) | WNT11 | 11 | 75565334 | 0.315893774 |
| rs626207 | 2.39E-01 | 1.13( 0.92–1.38) | WNT11 | 11 | 75565460 | 0.301281403 |
| rs4944091 | 8.02E-01 | 0.97( 0.78–1.21) | WNT11 | 11 | 75566622 | 0.445017693 |
| rs647159 | 2.64E-01 | 1.18( 0.88–1.57) | WNT11 | 11 | 75570389 | 0.307231178 |
| rs11236644 | 3.62E-01 | 0.94( 0.81–1.08) | WNT11 | 11 | 75572655 | 0.328827360 |
| rs581794 | 6.45E-01 | 0.95( 0.75–1.19) | WNT11 | 11 | 75572939 | 0.415574805 |
| rs12277860 | 4.39E-01 | 0.91( 0.73–1.15) | WNT11 | 11 | 75574295 | 0.359395383 |
| rs17749202 | 4.67E-02 | 1.39( 1.00–1.92) | WNT11 | 11 | 75575022 | 0.186667333 |
| rs7936750 | 2.15E-01 | 0.81( 0.57–1.13) | WNT11 | 11 | 75577055 | 0.284945038 |
| rs10899175 | 1.02E-01 | 1.20( 0.96–1.50) | WNT11 | 11 | 75577129 | 0.247221759 |
| rs882151 | 7.14E-01 | 0.96( 0.78–1.18) | WNT11 | 11 | 75581785 | 0.426046532 |
| rs3781730 | 5.45E-01 | 1.07( 0.86–1.33) | WNT11 | 11 | 75585731 | 0.379736909 |
| rs689095 | 1.63E-01 | 0.87( 0.71–1.06) | WNT11 | 11 | 75591735 | 0.273188390 |
| rs663907 | 2.31E-01 | 0.84( 0.63–1.12) | WNT11 | 11 | 75600717 | 0.296677764 |
| rs689419 | 7.88E-01 | 0.97( 0.79–1.19) | WNT11 | 11 | 75604615 | 0.443413702 |
| rs12416814 | 3.74E-01 | 1.23( 0.78–1.92) | WNT11 | 11 | 75605089 | 0.333860360 |
| rs3757552 | 5.68E-01 | 0.93( 0.72–1.20) | WNT16 | 7 | 120751201 | 0.388647584 |
| rs3801387 | 1.52E-01 | 1.15( 0.95–1.40) | WNT16 | 7 | 120762001 | 0.270394908 |
| rs3801385 | 7.16E-01 | 1.05( 0.80–1.37) | WNT16 | 7 | 120764779 | 0.426046532 |
| rs2707461 | 2.06E-01 | 0.77( 0.51–1.16) | WNT16 | 7 | 120774586 | 0.284431004 |
| rs2536182 | 1.30E-01 | 0.90( 0.78–1.03) | WNT16 | 7 | 120778073 | 0.263051430 |
Table 3.
Wnt pathway SNPs associated with survival in multivariate analysis in cohort 1 (P<0.05)*
| SNP | P value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Gene | Chromo-some | Position | Q value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11868547 | 0.0006 | 0.77 (0.66–0.89) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60954065 | 0.095030240 |
| rs12819505 | 0.0014 | 1.58 (1.19–2.09) | WNT5B | 12 | 1626926 | 0.095030240 |
| rs4541111 | 0.0015 | 0.79 (0.68–0.91) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60965000 | 0.095030240 |
| rs4413407 | 0.0017 | 1.28 (1.10–1.50) | CXXC4 | 4 | 105612810 | 0.095030240 |
| rs10878232 | 0.0022 | 1.36 (1.12–1.66) | WIF1 | 12 | 63808914 | 0.095602299 |
| rs7301320 | 0.0027 | 1.35 (1.11–1.65) | WIF1 | 12 | 63800533 | 0.100176561 |
| rs7218567 | 0.0043 | 1.68 (1.18–2.40) | WNT3 | 17 | 42225421 | 0.128006452 |
| rs390258 | 0.0046 | 1.64 (1.16–2.30) | TLE2 | 19 | 2947339 | 0.128006452 |
| rs7591 | 0.0061 | 1.23 (1.06–1.44) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60955544 | 0.135500153 |
| rs1155722 | 0.0062 | 1.32 (1.08–1.61) | WIF1 | 12 | 63809424 | 0.135500153 |
| rs10917155 | 0.0073 | 1.54 (1.12–2.11) | WNT4 | 1 | 22324553 | 0.135500153 |
| rs9864832 | 0.0090 | 1.52 (1.11–2.08) | WNT7A | 3 | 13827744 | 0.135500153 |
| rs4988300 | 0.0098 | 0.74 (0.58–0.93) | LRP5 | 11 | 67845407 | 0.135500153 |
| rs1003939 | 0.0099 | 0.56 (0.36–0.87) | WNT5B | 12 | 1626939 | 0.135500153 |
| rs4766403 | 0.010 | 1.21 (1.05–1.39) | WNT5B | 12 | 1630739 | 0.135500153 |
| rs2508836 | 0.010 | 0.81 (0.68–0.95) | LRP5 | 11 | 67847841 | 0.135500153 |
| rs1012672 | 0.011 | 1.47 (1.09–1.97) | LRP6 | 12 | 12176182 | 0.135500153 |
| rs1946620 | 0.011 | 1.32 (1.07–1.63) | WNT7A | 3 | 13833800 | 0.135500153 |
| rs11658976 | 0.012 | 1.45 (1.08–1.94) | WNT3 | 17 | 42221965 | 0.142078914 |
| rs12469777 | 0.014 | 0.85 (0.74–0.97) | FRZB | 2 | 183440609 | 0.144627899 |
| rs3121310 | 0.015 | 1.39 (1.07–1.82) | WNT3A | 1 | 226291447 | 0.144627899 |
| rs11655966 | 0.015 | 1.21 (1.04–1.41) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60960112 | 0.144627899 |
| rs12942924 | 0.016 | 1.18 (1.03–1.36) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60996861 | 0.144627899 |
| rs11079571 | 0.016 | 1.29 (1.05–1.59) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60979143 | 0.144627899 |
| rs11054760 | 0.017 | 1.53 (1.08–2.17) | LRP6 | 12 | 12320749 | 0.144627899 |
| rs11919795 | 0.018 | 0.67 (0.48–0.93) | DVL3 | 3 | 185373562 | 0.144627899 |
| rs4654783 | 0.018 | 1.58 (1.08–2.31) | WNT4 | 1 | 22312107 | 0.144627899 |
| rs629537 | 0.020 | 1.29 (1.04–1.60) | WNT5A | 3 | 55466053 | 0.146727575 |
| rs314756 | 0.020 | 0.69 (0.51–0.94) | LRP5 | 11 | 67868248 | 0.146727575 |
| rs713065 | 0.020 | 0.79 (0.64–0.96) | FZD4 | 11 | 86335168 | 0.146727575 |
| rs7515106 | 0.021 | 1.61 (1.07–2.42) | WNT4 | 1 | 22345997 | 0.149155672 |
| rs423232 | 0.022 | 0.74 (0.57–0.96) | TLE2 | 19 | 2947483 | 0.152312051 |
| rs597437 | 0.027 | 1.43 (1.04–1.95) | WNT5A | 3 | 55471449 | 0.17541792 |
| rs708110 | 0.027 | 1.26 (1.03–1.55) | WNT3A | 1 | 226257428 | 0.17541792 |
| rs12748472 | 0.028 | 1.18 (1.02–1.38) | WNT9A | 1 | 226170998 | 0.17541792 |
| rs6946781 | 0.029 | 0.63 (0.42–0.95) | WNT2 | 7 | 116694979 | 0.176207503 |
| rs9888749 | 0.031 | 0.76 (0.60–0.98) | AXIN1 | 16 | 348373 | 0.185653186 |
| rs64388 | 0.033 | 1.25 (1.02–1.52) | LRP5 | 11 | 67830957 | 0.186192568 |
| rs7224837 | 0.034 | 1.28 (1.02–1.62) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60958585 | 0.186192568 |
| rs2285545 | 0.034 | 0.87 (0.76–0.99) | WNT2 | 7 | 116735407 | 0.186192568 |
| rs3809857 | 0.035 | 0.80 (0.65–0.98) | WNT3 | 17 | 42203482 | 0.186192568 |
| rs503022 | 0.036 | 1.26 (1.01–1.56) | WNT5A | 3 | 55466476 | 0.186192568 |
| rs1548581 | 0.037 | 1.29 (1.02–1.64) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60995973 | 0.186192568 |
| rs7359414 | 0.037 | 0.78 (0.61–0.99) | AXIN1 | 16 | 302639 | 0.186192568 |
| rs312786 | 0.038 | 0.66 (0.45–0.98) | LRP5 | 11 | 67876553 | 0.186192568 |
| rs214246 | 0.040 | 0.77 (0.61–0.99) | AXIN1 | 16 | 289294 | 0.186192568 |
| rs4698921 | 0.040 | 1.16 (1.01–1.34) | CXXC4 | 4 | 105633671 | 0.186192568 |
| rs680148 | 0.041 | 1.25 (1.01–1.54) | WNT9A | 1 | 226194014 | 0.186192568 |
| rs676318 | 0.042 | 0.75 (0.57–0.99) | LRP5 | 11 | 67973996 | 0.186192568 |
| rs10431302 | 0.042 | 0.80 (0.65–0.99) | LRP6 | 12 | 12320918 | 0.186192568 |
| rs6947329 | 0.044 | 1.29 (1.01–1.65) | WNT2 | 7 | 116730371 | 0.186200636 |
| rs1530364 | 0.045 | 0.67 (0.45–0.99) | WNT9B | 17 | 42306776 | 0.186200636 |
| rs3781586 | 0.045 | 1.26 (1.01–1.57) | LRP5 | 11 | 67955969 | 0.186200636 |
| rs17749202 | 0.047 | 1.39 (1.00–1.92) | WNT11 | 11 | 75575022 | 0.186667333 |
| rs4074947 | 0.047 | 1.23 (1.00–1.51) | AXIN2 | 17 | 60957682 | 0.186667333 |
| rs557077 | 0.047 | 1.40 (1.00–1.96) | WNT5A | 3 | 55506307 | 0.186667333 |
| rs7596898 | 0.049 | 0.80 (0.64–1.00) | WNT6 | 2 | 219427976 | 0.188401227 |
Adjusted for age, race, sex, pack-year smoking, clinical stage, and performance status
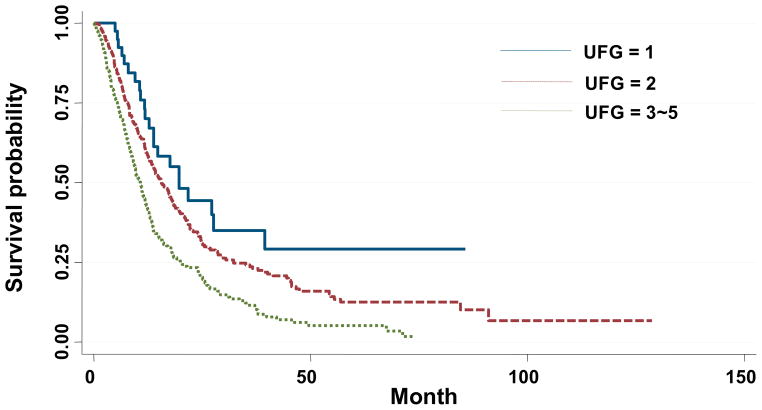
Of the 57 SNPs with p<0.05, 5 had q<0.10 after correction for multiple comparisons (Table 4). Compared to the reference genotypes, variants for rs11868547 and rs4541111 (both in AXIN2) were associated with improved survival, while variants for rs12819505 (WNT5B), rs4413407 (CXXC4) and rs10878232 (WIF1) were associated with worse survival after adjusting for clinical variables, as outlined above. MSTs were 19.7 months for patients with just one of these 5 unfavorable SNPs vs. 15.6 months for patients with 2 unfavorable SNPs and 10.7 months for patients with 3–5 unfavorable SNPs (p for trend 3.8 × 10−9, log rank p=1.86 × 10−7, Table 5, Figure 1). Each of these SNPs remained significantly (p<0.005) associated with survival after adjusting for agents (taxane vs other) given concurrently with cisplatin or carboplatin (data not shown). MAF of these SNPs by race is presented in Table 6.
Table 4.
Wnt pathway SNPs with q<0.10 in cohort 1
| SNP | Gene | Location | Allelic change | Minor Allele Frequency | Model | Hazard Ratio* (95% CI) | P value | q value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11868547 | AXIN2 | 3′ flanking | G>C | 0.421 | Additive | 0.77 (0.66–0.89) | 6.10E-04 | 0.09503 |
| rs12819505 | WNT5B | 3′ flanking | A>G | 0.07 | Dominant | 1.58 (1.19–2.09) | 1.37E-03 | 0.09503 |
| rs4541111 | AXIN2 | Intron | C>A | 0.456 | Additive | 0.79 (0.68–0.91) | 1.53E-03 | 0.09503 |
| rs4413407 | CXXC4 | 3′ UTR | G>A | 0.299 | Additive | 1.28 (1.10–1.50) | 1.72E-03 | 0.09503 |
| rs10878232 | WIF1 | 5′ flanking | A>C | 0.242 | Dominant | 1.36 (1.12–1.66) | 2.16E-03 | 0.09560 |
Adjusted for age, race, sex, pack-year smoking, clinical stage, and performance status
Table 5.
Impact of number of unfavorable genotypes on survival in cohort 1
| No. unfavorable genotypes | No. (%) alive | No. (%) dead | Hazard ratio (95% CI) (1 SNP = reference) | P value | Median Survival Time (mo.) | Log-rank p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 (46.3) | 22 (53.7) | 19.67 | |||
| 2 | 83 (26.9) | 226 (73.1) | 1.53 (0.97–2.41) | 6.8 × 10−2 | 15.56 | |
| 3–5 | 40 (16.1) | 208 (83.9) | 2.61 (1.65–4.12) | 4.3 × 10−5 | 10.72 | 1.9 × 10−7 |
| trend | 3.8 × 10−9 |
Figure 1.
Kaplan Meier survival estimates for patients with 1 (blue line) vs 2 (red line) vs 3–5 (green line) unfavorable genotypes (UFGs) in our initial cohort (median survival times 19.7 vs 15.7 vs 10.7 months, p for trend = 3.8 × 10−9, log rank p = 1.9 × 10−7)
Table 6.
Minor Allele Frequency by race for SNPs significantly associated with patient survival
| SNP | All | White | Black | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11868547 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.56 |
| rs12819505 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| rs4541111 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.20 | 0.54 |
| rs4413407 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.33 |
| rs10878232 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.27 |
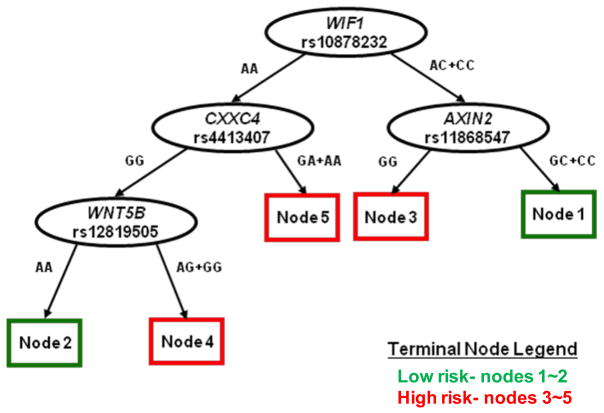
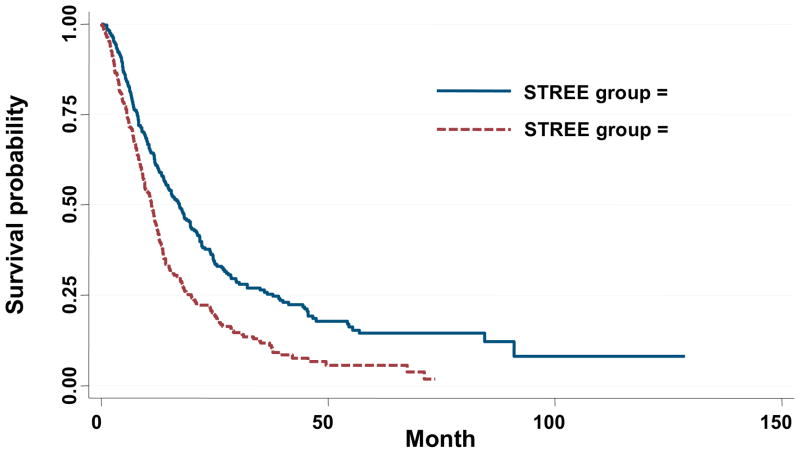
For these 5 most significant SNPs, recursive partitioning STREE analysis (Figure 2) indicated high order gene-gene interaction and divided patients into 5 distinct “nodes” with significant survival differences. These nodes could be further classified into two groups of low and high risk. Nodes 1 and 2 combined had significantly better survival than nodes 3, 4 and 5 combined (17.3 vs 11.3 months, log rank p=4.7 × 10−8, Wilcoxon p=1.0 × 10−8) (Table 7 and Fig 3). The 75th percentile, 50th percentile and 25th percentile survival times were 7.4 months (95% CI 6.5–8.8 months), 16.2 (13.8–18.0) months and 32.2 (26.8–41.3) months, respectively, in the combined Nodes 1 and 2 group, and were 5.9 (4.6–7.1) months, 11.1 (9.6–11.9) months and 22.2 (18.4–26.3) months, respectively, in the combined Nodes 3, 4 and 5 group (log rank p=1.04 × 10−4, Wilcoxon p=5.87 × 10−5).
Figure 2.
Survival tree analysis of significant SNPs associated with NSCLC survival identified from the single SNP analysis (q<0.10) in our initial cohort. Five terminal nodes were identified, which could be classified into two groups of low and high risk.
Table 7.
Hazard ratios and median survival times for different recursive partitioning nodes in cohort 1
| STREE Nodes | Dead N (%) |
Alive N (%) |
Adjusted Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | P value | Median Survival (months) | Log Rank Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34 (69.39) | 15 (30.61) | 1.00 (reference) | 18.82 | ||
| 2 | 192 (69.82) | 83 (30.18) | 1.09 (0.73–1.62) | 0.067 | 17.27 | |
| 3 | 163 (82.32) | 35 (17.68) | 1.93 (1.30–2.89) | 0.001 | 10.07 | |
| 4 | 39 (86.67) | 6 (13.33) | 1.79 (1.08–2.96) | 0.024 | 13.52 | |
| 5 | 28 (90.32) | 3(9.68) | 1.98 (1.17–3.37) | 0.011 | 11.94 | 2.68 × 10−6 |
| STREE Group | ||||||
| Nodes 1~2 | 226 (69.75) | 98 (30.25) | 1.00 (reference) | 17.27 | ||
| Nodes 3~5 | 230 (83.94) | 44 (16.06) | 1.78 (1.46–2.17) | 1 × 10−8 | 11.09 | 4.66 × 10−8 |
Figure 3.
Kaplan Meier survival estimates for the two risk groups identified from the survival tree analysis of our initial cohort. Survival of NSCLC patients in STREE groups 1 (49 patients) and 2 (275 patients) (blue line) was significantly better than for groups 3 (198 patients), 4 (45 patients) and 5 (31 patients) combined (red line) (17.3 vs 11.1 months, Wilcoxon p=1.0 × 10−8, log rank p = 4.66 × 10−8).
Characteristics of patients in Cohorts 2, 3 and 4 are presented in Table 8. Since there was high linkage disequilibrium between the two AXIN2 SNPs s4341111 and rs11868547 (R2>0.80), we only considered the one with the more significant p-value rs11868547 in the secondary analysis involving cohorts 2–4. None of the 4 SNPs assessed correlated significantly with survival in any of cohorts 2–4 assessed individually, nor in meta-analyses combining cohorts 2–4 together, nor in the meta-analysis combining cohort 2 (Mayo Clinic patients) with cohort 3 (MDACC adjuvant chemotherapy patients) (Table 9). However, for rs11868547, the hazard ratios for each of cohorts 2–4 and for the 2 meta-analyses was in the same direction as in cohort 1. For rs12819707, the hazard ratio for cohort 2 (the Mayo Clinic group), cohort 4 (the surgery alone group) and the overall meta-analysis of cohorts 2–4 was in the same direction as in cohort 1, and for rs10878232, the hazard ratio for two of the 3 secondary analysis cohorts and for both meta-analyses secondary analysis groupings was in the same direction as in cohort 1.
Table 8.
Characteristics of patients assessed in cohorts 2, 3 and 4
| Variable | Cohort 2 No. Patients (%) |
Cohort 3 No. Patients (%) |
Cohort 4 No. Patients (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median survival, months | 21.09 | 118.3 | 86.05 |
| Median age (range), years | 64.02* | 63 (29–83) | 67 (34–86) |
| Pack year, median (range)** | 40.48* | 40 (0.1–159) | 45 (0.2–256) |
| Survival status at last follow-up | |||
| Alive | 49 | 88 | 210 |
| Dead | 191 | 39 | 130 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 142 | 68 | 166 |
| Female | 98 | 59 | 174 |
| Clinical stage | |||
| Stage IA | 23 | 181 | |
| Stage IB | 55 | 113 | |
| Stage IIA | 14 | 10 | |
| Stage IIB | 35 | 36 | |
| Stage III | 106 | ||
| Stage IV | 134 | ||
| Smoking status | |||
| Never | 14 | 16 | 48 |
| Former | 150 | 67 | 168 |
| Current & Recently Quit (<1 year) | 76 | 44 | 124 |
| ECOG Performance status | |||
| 0 | 64 | ||
| 1 | 120 | ||
| 2–4 | 13 | ||
| Tumor Type | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 74 | 213 | |
| Squamous | 34 | 87 | |
| NSCLC not otherwise specified | 7 | 11 | |
| Other | 12 | 29 | |
| Race | |||
| White | 109 | 305 | |
| Black | 10 | 25 | |
| Others | 8 | 10 | |
| Treatment | |||
| Chemotherapy (platinum regimen) only | 100 | ||
| Platinum regimen + radiotherapy | 140 | ||
| Surgery + adjuvant platinum regimen | 127 | ||
| Surgery alone | 340 | ||
mean instead of median; range not available
among ever smokers
Table 9.
Assessment of SNPs in secondary analyses (cohorts 2–4)
| SNP | Mayo Clinic (Cohort 2)† | MDACC Adjuvant Chemo (Cohort 3)‡ | MDACC Surgery Alone (Cohort 4)‡ | Mayo + Adjuvant (Cohorts 2 + 3) | Mayo + Adjuvant + Surgery (Cohorts 2 + 3 + 4) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR(95% CI) | P | HR(95% CI) | P | HR(95% CI) | P | HR(95% CI) | P | P-H* | HR(95% CI) | P | P-H* | |
| rs11868547 | 0.94(0.75–1.18) | 0.58 | 0.89(0.55–1.45) | 0.65 | 0.96( 0.74–1.24) | 0.75 | 0.93(0.76–1.14) | 0.48 | 0.85 | 0.94(0.80–1.11) | 0.46 | 0.96 |
| rs12819505 | 1.30(0.85–1.99) | 0.23 | 0.40(0.14–1.18) | 0.10 | 1.12( 0.67–1.86) | 0.68 | 0.80(0.26–2.50) | 0.70 | 0.04 | 1.11(0.81–1.52) | 0.51 | 0.13 |
| rs4413407 | 0.88(0.69–1.13) | 0.32 | 1.10(0.61–2.01) | 0.75 | 0.99( 0.76–1.30) | 0.96 | 0.91(0.72–1.15) | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.94(0.79–1.13) | 0.52 | 0.72 |
| rs10878232 | 1.00(0.77–1.28) | 0.98 | 1.80(0.91–3.56) | 0.09 | 1.05( 0.79–1.41) | 0.73 | 1.07(0.85–1.36) | 0.58 | 0.11 | 1.06(0.88–1.28) | 0.52 | 0.28 |
P-H: P value for heterogeneity
Advanced stage patients
Early stage patients
In assessing correlation of these SNPs with NSCLC stage across all 4 cohorts, we found that none of the SNPs were significantly associated with stage except for rs10878232 in cohort 4 (the surgery alone group) (p<0.05).
To explore whether any of the 4 SNPs have functional relevance, we conducted expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) analysis. We checked 3 databases including Genevar, seeQTL, and University of Chicago eQTL. Among candidate SNPs, a highly significant correlation was consistently shown for rs10878232 and LEMD3. Genevar analysis showed that the C allele was consistently correlated with higher expression of LEMD3 in adipose tissues, lymphoblastoid cell lines and skin tissues obtained from healthy female twins (Figure 4). All p-values are less than 10−6 for Spearman’s correlation and <10−4 for permutation test. Similar results were obtained by exploring the seeQTL and University of Chicago eQTL. rs10878232 is located in the 5′ flanking region between WIF1 and LEMD3. No cis-eQTL correlation was found for the other SNPs.
Figure 4.
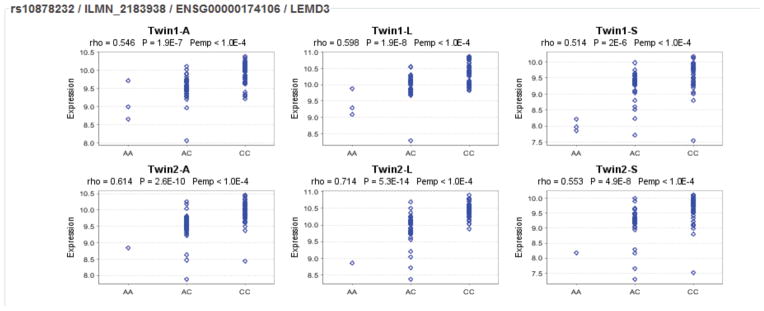
Rs10878232 genotypes and LEMD3 gene expression in cell lines and tissues from healthy female twins based on eQTL analysis in Genevar database of SNP-gene associations. Twin2-A, adipose tissue; Twin2-L, lymphoblastoid cell lines; Twin2-S, skin tissue. Rho, correlation value; Pemp, non-parametric permutation p value for 10,000 reiterations.
Discussion
Results from our initial cohort suggested that selected host genotype Wnt pathway SNPs may affect outcome in platinum-treated patients with stage III–IV NSCLC: 57 SNPs in 21 different Wnt pathway components correlated with survival. Of these, 5 SNPs in 4 pathway genes remained significant in multivariate analysis after correcting for the effect of multiple comparisons and after adjusting for other clinical factors. Survival worsened as the number of unfavorable genotypes increased, revealing the joint effect of these SNPs. Survival tree analysis revealed potential higher order gene-gene interactions.
In our follow-up studies exploring impact of these SNPs in other patient groups, cohort 2 (from the Mayo Clinic) was most similar to our initial cohort (platinum-based chemotherapy +/− radiotherapy for stage III–IV NSCLC), although the Mayo Clinic patient population was smaller (only 240 patients). As with cohort 1, rs11868547 G to C allelic change in Mayo Clinic patients was associated with improved survival and rs12819505 A to G allelic change was associated with worse survival. This suggests that these associations in particular warrant further assessment, although these associations did not achieve statistical significance in the Mayo Clinic patients. The lack of statistical significance in the Mayo Clinic patients (and outcomes for rs4413407 and rs10878232) may have been due to a true lack of biological importance of these SNPs (with the association in cohort 1 being due to chance alone), or could instead have been related to low statistical power (due to relatively small patient numbers in the Mayo Clinic cohort) or impact of unappreciated differences in the patient populations or therapy details. It would also be worthwhile assessing whether these differences might be related to differences in second or third line therapy between the 2 groups. We did not have data available on therapy received following first line platinum-based regimens, and so cannot directly test this here, but it is possible that an association of the SNPs with survival could have been impacted by specific therapies received.
None of the SNPs correlated significantly with outcome in cohort 3 (the MDACC postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy NSCLC group) nor in cohort 4 (the MDACC surgery alone NSCLC group), indicating that we cannot extrapolate from our advanced disease patients to our early stage patients. Again, this may have been due to patient numbers/low statistical power or it could have been due to the differences that existed between the patient groups or to actual lack of biological importance of the SNPs identified in cohort 1.
When we did a meta-analysis adding cohorts 2–4 together, the direction of association (decreased risk for rs11868547 G to C allelic change and increased risk for rs12819505 A to G allelic change and rs10878232 A to C allelic change) was the same in the meta-analysis as in cohort 1, supporting further assessment of these SNPs, although the associations were again not statistically significant.
With respect to the SNPs that emerged as being most important in our initial cohort, each of AXIN2, CXX4 and WIF1 are potentially important in NSCLC as Wnt pathway inhibitors. AXIN2 allelic loss is common in NSCLC,20 hypermethylation of AXIN is often seen in resected NSCLC tumor samples,24 risk of developing lung adenocarcinoma varies with the host genotype for codon 50 of AXIN2,20 and lung cancer cell line transfection with AXIN increased apoptosis, inhibited cell line proliferation, and decreased cell invasiveness.25
While Wnt-5a appears to be important in NSCLC, there is less information available on Wnt-5b, although Wnt-5b expression is upregulated by exposure of bronchial epithelium to cigarette smoke extract.26 Both Wnt-5a and Wnt-5b are non-canonical Wnts and may inhibit canonical Wnt signaling.10
The CXXC4 gene codes for the Disheveled (Dvl) inhibitor Idax.11 While little is known about the role of CXXC4 or Idax in NSCLC, Dvl is probably important. Dvl is frequently expressed in NSCLC tumor samples,27 and expression is associated with poor prognosis.28 In NSCLC cell lines, exogenous Dvl enhanced tumor cell invasiveness,27 and inhibition of Dvl inhibited growth.29
The Wnt pathway inhibitor WIF-1 is frequently hypermethylated and/or down-regulated in NSCLC tumor samples and cell lines,30–32 particularly in squamous cell lung carcinomas31 and in patients with COPD,32 and promoter hypermethylation of WIF-1 was associated with poor prognosis in NSCLC patients.32,33 In lung cancer cell lines, methylation inhibitors34 or transfection with WIF-135 demethylated WIF-1,34 increased WIF-1 expression,34 inhibited the canonical Wnt pathway,34 inhibited cell line proliferation,35 and induced apoptosis.34,35
Little is known regarding the functional impact of the SNPs observed. Further assessment of the functional impact would be useful in better understanding how these SNPs may have contributed to patient outcome and for validation in a larger independent cohort. None of the 5 most significant SNPs were in gene coding or promoter regions. While little is known about how these specific SNPs could affect gene/gene product functions, there are several possibilities. For example, SNPs in flanking regions may be in transcriptional enhancers that affect nearby gene expression,36 SNPs in the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) may affect microRNA binding37 and mRNA stability,38 nuclear transport,39 polyadenylation status39 and subcellular targeting,39 and intronic SNPs may affect alternative splicing40 and gene product function.41
To check for functional relevance for the identified SNPs from cohort 1, we carried out eQTL analysis using Genevar database (a public resource containing four eQTL studies42–45), and found highly significant correlation between rs10878232 and LEMD3 expression. The rs10878232 data are available in the MuTHER pilot study implemented in Genevar. LEMD3 (also known as MAN1) encodes a LEM domain-containing gene that serves to antagonize transforming growth factor beta signaling at the inner nuclear membrane.46 Mutations of this gene have been found in osteopoikilosis, Buscheke-Ollendorff syndrome, and melorheostosis.47 Interestingly, the expression level of LEMD3 correlated with two loci associated with overall survival in never smokers with NSCLC in a previous study from our group.48 Although our current dataset of late-stage NSCLC patient is too small for stratified analysis by smoking status, we found a stronger association of rs10878232 with survival in never smokers while weak or no significant association was found in ever smokers, suggesting a potential interaction of this SNP with smoking status. In light of the known association of negative smoking history with epidermal growth factor (EGFR) mutations, one might question whether there might be an interaction of rs10878232 with EGFR mutation status, but this cannot be addressed in our study since EGFR mutation status was not known for most patients. Further study in a larger population of NSCLC patients is necessary to verify our findings and to assess any potential interaction with EGFR mutation status.
In summary, the pharmacogenetic data from our initial patient cohort suggest that host genotype SNPs may modulate the impact of the Wnt pathway on outcome of patients with advanced NSCLC, although SNP associations with outcome in secondary analyses using cohorts 2–4 were much weaker. Overall, available evidence from cell lines and resected tumors suggests that Wnt pathway signaling is important in NSCLC tumorigenesis, patient prognosis and resistance to therapy.13 Targeting of the Wnt pathway (through Wnt antagonists, demethylating agents, and other steps to restore function of silenced Wnt inhibitors) warrants assessment in the treatment of NSCLC.
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by NIH grants R01 CA111646, P50 CA070907, R01 CA55769, R01-CA80127 and R01-CA84354, and Mayo Foundation fund
Footnotes
Disclosures: None of the authors have disclosures directly related to the topic of this paper
Contributor Information
David J. Stewart, University of Ottawa.
David W. Chang, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Departments of Epidemiology.
Yuanqing Ye, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Departments of Epidemiology.
Margaret Spitz, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Departments of Epidemiology.
Charles Lu, Thoracic/Head and Neck Medical Oncology.
Xiang Shu, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Departments of Epidemiology.
Jason A. Wampfler, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Departments of Health Sciences Research
Randolph S. Marks, Medical Oncology.
Yolanda I Garces, Radiation Oncology.
Ping Yang, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Departments of Health Sciences Research.
Xifeng Wu, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Departments of Epidemiology.
References
- 1.Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2011;61:69–90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Higgins MJ, Ettinger DS. Chemotherapy for lung cancer: the state of the art in 2009. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009;9:1365–78. doi: 10.1586/era.09.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stinchcombe TE, Lee CB, Socinski MA. Current approaches to advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: first-line therapy in patients with a good functional status. Clin Lung Cancer. 2006;7 (Suppl 4):S111–7. doi: 10.3816/clc.2006.s.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kepka L, Sprawka A, Casas F, Abdel-Wahab S, Agarwal JP, Jeremic B. Combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced NSCLC. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009;9:1389–403. doi: 10.1586/era.09.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fietkau R. Stage-III NSClC: multimodality therapy for inoperable tumours. Lung Cancer. 2004;45 (Suppl 2):S113–23. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.07.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV, et al. Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:3552–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.9030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mazieres J, He B, You L, Xu Z, Jablons DM. Wnt signaling in lung cancer. Cancer letters. 2005;222:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.08.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Takahashi-Yanaga F, Kahn M. Targeting Wnt signaling: can we safely eradicate cancer stem cells? Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2010;16:3153–62. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Teng Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Ma D. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cancer stem cells in lung cancer A549 cells. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2010;392:373–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.van Tienen FH, Laeremans H, van der Kallen CJ, Smeets HJ. Wnt5b stimulates adipogenesis by activating PPARgamma, and inhibiting the beta-catenin dependent Wnt signaling pathway together with Wnt5a. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2009;387:207–11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kojima T, Shimazui T, Hinotsu S, et al. Decreased expression of CXXC4 promotes a malignant phenotype in renal cell carcinoma by activating Wnt signaling. Oncogene. 2009;28:297–305. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yang ZQ, Zhao Y, Liu Y, et al. Downregulation of HDPR1 is associated with poor prognosis and affects expression levels of p120-catenin and beta-catenin in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Molecular carcinogenesis. 2010;49:508–19. doi: 10.1002/mc.20622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stewart DJ. The Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt356. In Press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Nakajima K, et al. Wnt antagonist gene polymorphisms and renal cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:4488–503. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tuupanen S, Turunen M, Lehtonen R, et al. The common colorectal cancer predisposition SNP rs6983267 at chromosome 8q24 confers potential to enhanced Wnt signaling. Nature genetics. 2009;41:885–90. doi: 10.1038/ng.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang X, Goode EL, Fredericksen ZS, et al. Association of genetic variation in genes implicated in the beta-catenin destruction complex with risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:2101–8. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Agalliu I, Suuriniemi M, Prokunina-Olsson L, et al. Evaluation of a variant in the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and prostate cancer risk in a population-based study. Prostate. 2008;68:740–7. doi: 10.1002/pros.20732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang SP, Ting WC, Chen LM, et al. Association analysis of Wnt pathway genes on prostate-specific antigen recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:312–22. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0698-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ting WC, Chen LM, Pao JB, et al. Common genetic variants in Wnt signaling pathway genes as potential prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. PloS one. 2013;8:e56196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kanzaki H, Ouchida M, Hanafusa H, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism of the AXIN2 gene is preferentially associated with human lung cancer risk in a Japanese population. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18:279–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Storey JD. A direct approach to false discovery rates. J R Statist Soc B. 2002;64:479–98. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yang TP, Beazley C, Montgomery SB, et al. Genevar: a database and Java application for the analysis and visualization of SNP-gene associations in eQTL studies. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2474–6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xia K, Shabalin AA, Huang S, et al. seeQTL: a searchable database for human eQTLs. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:451–2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang LH, Xu HT, Li QC, et al. Abnormal hypermethylation and clinicopathological significance of Axin gene in lung cancer. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2013;34:749–57. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0604-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu HT, Wei Q, Liu Y, et al. Overexpression of axin downregulates TCF-4 and inhibits the development of lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:3251–9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-007-9555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Heijink IH, de Bruin HG, van den Berge M, et al. Role of aberrant WNT signalling in the airway epithelial response to cigarette smoke in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2013 doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-201667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wei Q, Zhao Y, Yang ZQ, et al. Dishevelled family proteins are expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and function differentially on tumor progression. Lung Cancer. 2008;62:181–92. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhao Y, Yang ZQ, Wang Y, et al. Dishevelled-1 and dishevelled-3 affect cell invasion mainly through canonical and noncanonical Wnt pathway, respectively, and associate with poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Molecular carcinogenesis. 2010;49:760–70. doi: 10.1002/mc.20651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Uematsu K, He B, You L, Xu Z, McCormick F, Jablons DM. Activation of the Wnt pathway in non small cell lung cancer: evidence of dishevelled overexpression. Oncogene. 2003;22:7218–21. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wissmann C, Wild PJ, Kaiser S, et al. WIF1, a component of the Wnt pathway, is down-regulated in prostate, breast, lung, and bladder cancer. The Journal of pathology. 2003;201:204–12. doi: 10.1002/path.1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Korobko EV, Kalinichenko SV, Shepelev MV, et al. Suppression of WIFI transcript and protein in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 2007:13–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Suzuki M, Wada H, Yoshino M, et al. Molecular characterization of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-related non-small cell lung cancer through aberrant methylation and alterations of EGFR signaling. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:878–88. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee SM, Park JY, Kim DS. Wif1 hypermethylation as unfavorable prognosis of non-small cell lung cancers with EGFR mutation. Molecules and cells. 2013 doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-0060-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu YL, Yang HP, Zhou XD, Gong L, Tang CL, Wang HJ. The hypomethylation agent bisdemethoxycurcumin acts on the WIF-1 promoter, inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway and induces apoptosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Current cancer drug targets. 2011;11:1098–110. doi: 10.2174/156800911798073041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim J, You L, Xu Z, et al. Wnt inhibitory factor inhibits lung cancer cell growth. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133:733–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.09.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sotelo J, Esposito D, Duhagon MA, et al. Long-range enhancers on 8q24 regulate c-Myc. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:3001–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906067107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, Wang SP, Tang SM, Zhang GZ. Biological functions of microRNAs: a review. J Physiol Biochem. 2010 doi: 10.1007/s13105-010-0050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vilborg A, Wilhelm MT, Wiman KG. Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 at the RNA level. J Mol Med. 2010;88:645–52. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0609-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Reamon-Buettner SM, Cho SH, Borlak J. Mutations in the 3′-untranslated region of GATA4 as molecular hotspots for congenital heart disease (CHD) BMC Med Genet. 2007;8:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Markovic D, Challiss RA. Alternative splicing of G protein-coupled receptors: physiology and pathophysiology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:3337–52. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0093-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Farrall M. Quantitative genetic variation: a post-modern view. Human molecular genetics. 2004;13(Spec No 1):R1–7. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Stranger BE, Montgomery SB, Dimas AS, et al. Patterns of cis regulatory variation in diverse human populations. PLoS genetics. 2012;8:e1002639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dimas AS, Deutsch S, Stranger BE, et al. Common regulatory variation impacts gene expression in a cell type-dependent manner. Science. 2009;325:1246–50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nica AC, Parts L, Glass D, et al. The architecture of gene regulatory variation across multiple human tissues: the MuTHER study. PLoS genetics. 2011;7:e1002003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Grundberg E, Small KS, Hedman AK, et al. Mapping cis- and trans-regulatory effects across multiple tissues in twins. Nature genetics. 2012;44:1084–9. doi: 10.1038/ng.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lin F, Morrison JM, Wu W, Worman HJ. MAN1, an integral protein of the inner nuclear membrane, binds Smad2 and Smad3 and antagonizes transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Human molecular genetics. 2005;14:437–45. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Couto AR, Bruges-Armas J, Peach CA, et al. A novel LEMD3 mutation common to patients with osteopoikilosis with and without melorheostosis. Calcified tissue international. 2007;81:81–4. doi: 10.1007/s00223-007-9043-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wu X, Wang L, Ye Y, et al. Genome-wide association study of genetic predictors of overall survival for non-small cell lung cancer in never smokers. Cancer research. 2013;73:4028–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rami-Porta R, Crowley JJ, Goldstraw P. The revised TNM staging system for lung cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;15:4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]