Abstract
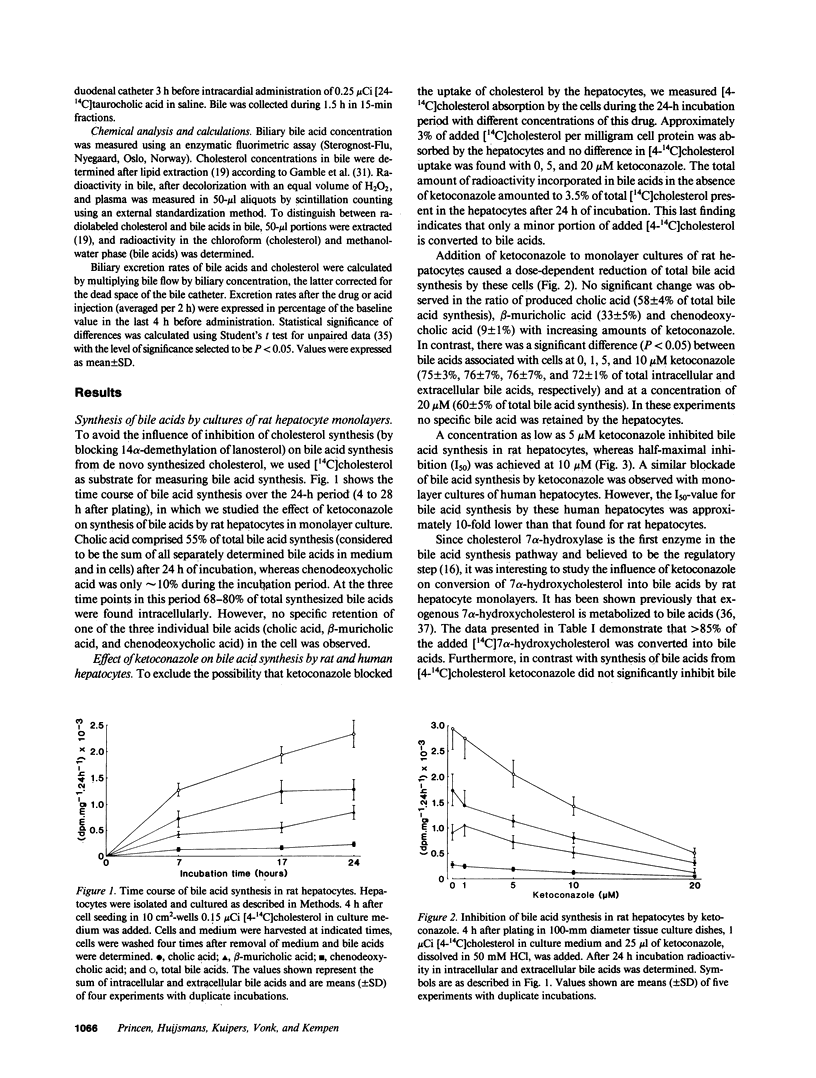
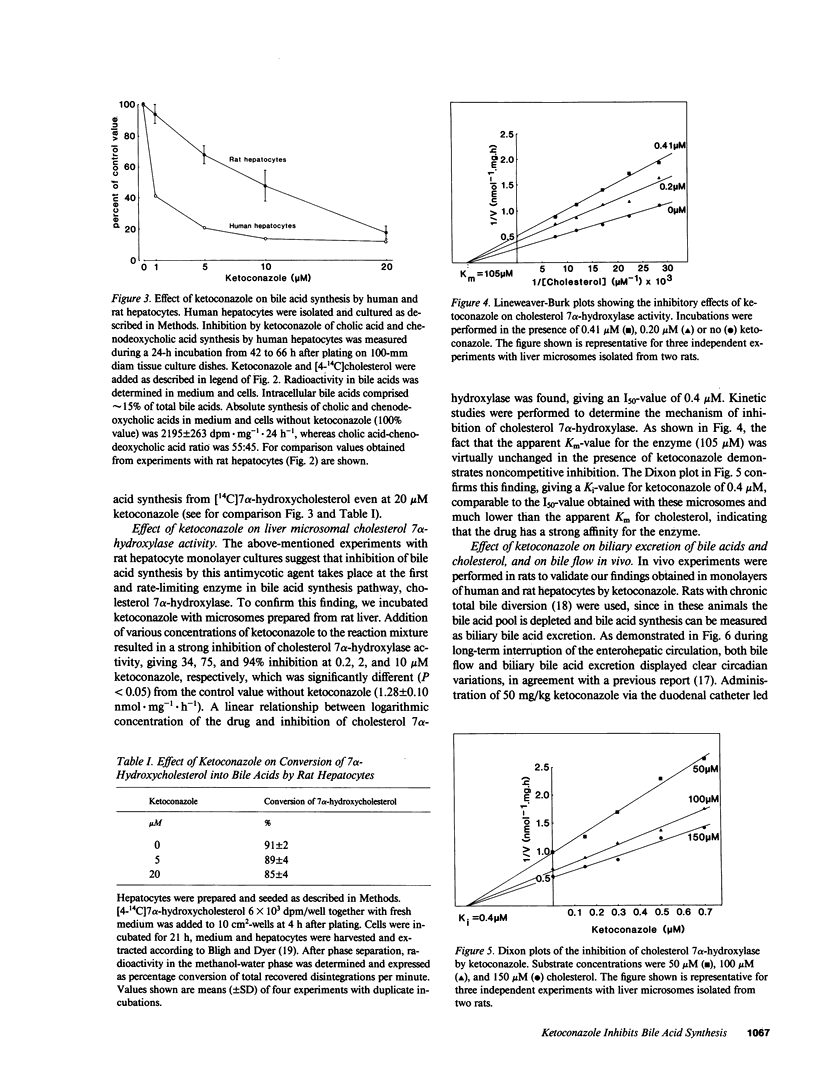
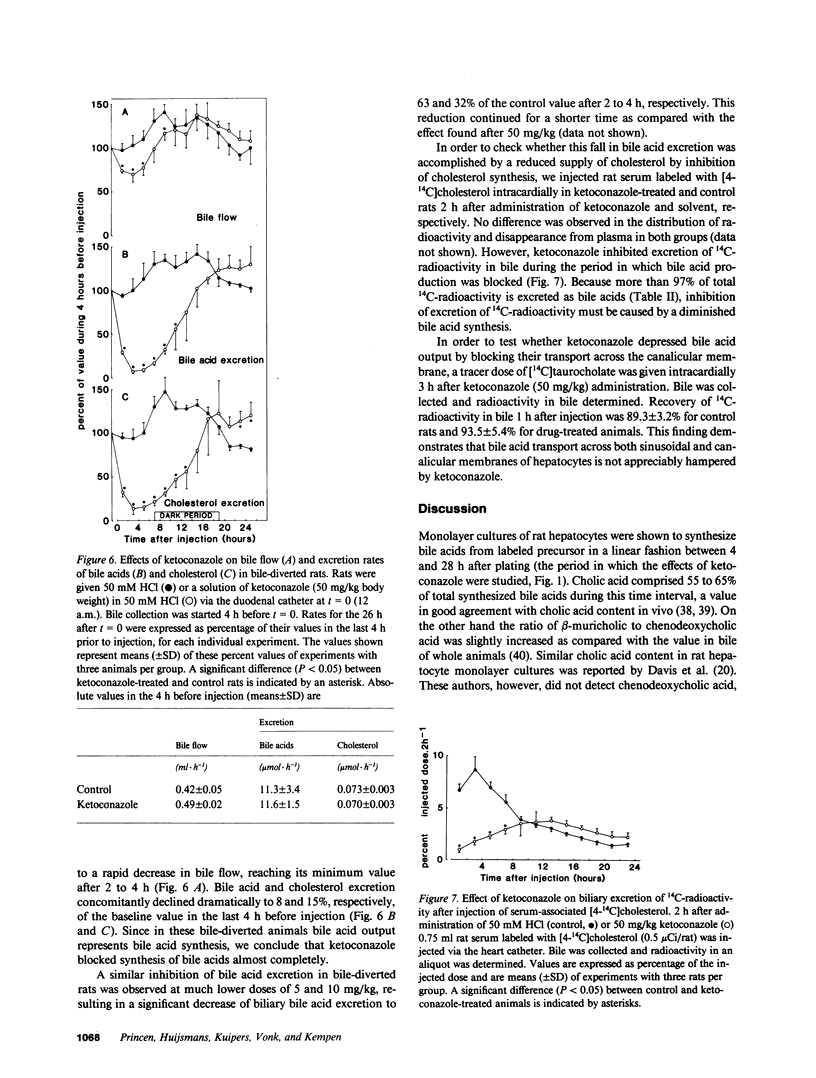
In cultured hepatocytes conversion of [4-14C]cholesterol into bile acids was dose dependently reduced by the antimycotic drug ketoconazole, giving half-maximal inhibition at 10 microM ketoconazole in rat hepatocytes and at 1 microM in human hepatocytes. No change was observed in the ratio of produced cholic, beta-muricholic, and chenodeoxycholic acid with increasing amounts of the drug. Conversion of [4-14C]7 alpha-hydroxycholesterol, an intermediate of bile acid pathway, to bile acids was not affected by ketoconazole. These results together with kinetic studies with rat liver microsomes, demonstrating noncompetitive inhibition (Ki = 0.4 microM), indicate that cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase is the main site of inhibition. In bile-diverted rats a single dose of ketoconazole (50 mg/kg) dramatically impaired bile flow and biliary bile acid output (92% inhibition). A similar blockade was observed using [4-14C]cholesterol as precursor for bile acid synthesis. Therefore, treatment of patients with this drug may inhibit bile acid synthesis, resulting in a reduction of the bile acid pool size after long-term ketoconazole therapy.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayaki Y., Tsuma-Date T., Endo S., Ogura M. Role of endogenous and exogenous cholesterol in liver as the precursor for bile acids in rats. Steroids. 1981 Nov;38(5):495–509. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(81)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Lewenhaupt A. Preferential utilization of newly synthesized cholesterol as substrate for bile acid biosynthesis. An in vivo study using 18O2-inhalation technique. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5252–5256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boström H., Wikvall K. Hydroxylations in biosynthesis of bile acids. Isolation of subfractions with different substrate specificity from cytochrome P-450LM4. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11755–11759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass C., Galgiani J. N., Blaschke T. F., Defelice R., O'Reilly R. A., Stevens D. A. Disposition of ketoconazole, an oral antifungal, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):151–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. W., Maldonado A. L., Meredith C. G., Speeg K. V., Jr Effect of ketoconazole on hepatic oxidative drug metabolism. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Mar;37(3):290–297. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttke T. M., Chapman S. W. Inhibition by ketoconazole of mitogen-induced DNA synthesis and cholesterol biosynthesis in lymphocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):478–485. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronholm T., Einarsson K., Gustafsson J. A. Changes in in vivo metabolism of bile acids in rat after treatment with phenobarbital. Lipids. 1974 Nov;9(11):844–849. doi: 10.1007/BF02532607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Hyde P. M., Kuan J. C., Malone-McNeal M., Archambault-Schexnayder J. Bile acid secretion by cultured rat hepatocytes. Regulation by cholesterol availability. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3661–3667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelice R., Johnson D. G., Galgiani J. N. Gynecomastia with ketoconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1073–1074. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. P., Botham K. M., Suckling K. E., Boyd G. S. Characterisation of rat hepatocyte monolayers for investigation of the metabolism of bile salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 11;836(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble W., Vaughan M., Kruth H. S., Avigan J. Procedure for determination of free and total cholesterol in micro- or nanogram amounts suitable for studies with cultured cells. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1068–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. D., Cooper B. W., Margolis S. Rat liver cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Modulation of enzyme activity by changes in phosphorylation state. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4469–4472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greim H., Trülzsch D., Roboz J., Dressler K., Czygan P., Hutterer F., Schaffner F., Popper H. Mechanism of cholestasis. 5. Bile acids in normal rat livers and in those after bile duct ligation. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):837–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Apter J. T. Micellar theory of biliary cholesterol excretion. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):61–67. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Gurley E. C., Kubaska W. M., Whitehead T. R., Guzelian P. S., Vlahcevic Z. R. Suitability of primary monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes for studies of cholesterol and bile acid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1015–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauregui H. O., Hayner N. T., Driscoll J. L., Williams-Holland R., Lipsky M. H., Galletti P. M. Trypan blue dye uptake and lactate dehydrogenase in adult rat hepatocytes--freshly isolated cells, cell suspensions, and primary monolayer cultures. In Vitro. 1981 Dec;17(12):1100–1110. doi: 10.1007/BF02618612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempen H. J., De Lange J., Vos-Van Holstein M. P., Van Wachem P., Havinga R., Vonk R. J. Effect of ML-236B (compactin) on biliary excretion of bile salts and lipids, and on bile flow, in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 26;794(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempen H. J., Vos-Van Holstein M. P., de Lange J. Bile acids and lipids in isolated rat hepatocytes: content, synthesis, and release, as affected by cholestyramine treatment of the donor rats. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempen H. J., Vos-van Holstein M., de Lange J. Bile acids and lipids in isolated rat hepatocytes. II. Source of cholesterol used for bile acid formation, estimated by incorporation of tritium from tritiated water, and by the effect of ML-236B. J Lipid Res. 1983 Mar;24(3):316–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers F., Havinga R., Bosschieter H., Toorop G. P., Hindriks F. R., Vonk R. J. Enterohepatic circulation in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Feb;88(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Kan P. B., Hirst M. A., Marcus R. A., Feldman D. Ketoconazole blocks adrenal steroidogenesis by inhibiting cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1172/JCI110903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSCHINER J. T., MAHOWALD T. A., ELLIOTT W. H., DOISY E. A., Jr, HSIA S. L., DOISY E. A. Bile acids. I. Two new acids from rat bile. J Biol Chem. 1957 Apr;225(2):771–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith C. G., Maldonado A. L., Speeg K. V., Jr The effect of ketoconazole on hepatic oxidative drug metabolism in the rat in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos. 1985 Mar-Apr;13(2):156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A., Valtonen V. V. Ketoconazole and cholesterol synthesis. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1271–1271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92814-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myant N. B., Mitropoulos K. A. Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):135–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pont A., Williams P. L., Azhar S., Reitz R. E., Bochra C., Smith E. R., Stevens D. A. Ketoconazole blocks testosterone synthesis. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Nov;142(12):2137–2140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pont A., Williams P. L., Loose D. S., Feldman D., Reitz R. E., Bochra C., Stevens D. A. Ketoconazole blocks adrenal steroid synthesis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):370–372. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Princen H. M., Moshage H. J., de Haard H. J., van Gemert P. J., Yap S. H. The influence of glucocorticoid on the fibrinogen messenger RNA content of rat liver in vivo and in hepatocyte suspension culture. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2200631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollman O., Jameson S., Lithell H. Effects of long-term ketoconazole therapy on serum lipid levels. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1985;29(2):241–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00547430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santen R. J., Van den Bossche H., Symoens J., Brugmans J., DeCoster R. Site of action of low dose ketoconazole on androgen biosynthesis in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Oct;57(4):732–736. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-4-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Stephens J. E. Transport of sodium, chloride, and taurocholate by cultured rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Margolis S. Effects of drugs and sterols on cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity in rat liver microsomes. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):28–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz L. R., Burr R., Schwenk M., Pfaff E., Greim H. Uptake of taurocholic acid into isolated rat-liver cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):617–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets J. J., Mason J. I. Ketoconazole: a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P-450-dependent drug metabolism in rat liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984 Sep-Oct;12(5):603–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Biochemical site of regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Princen H. M., Kooistra T., van Hinsbergh V. W. Inhibition of plasminogen activators by conditioned medium of human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hep G2. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jun;105(6):751–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swell L., Entenman C., Leong G. F., Holloway R. J. Bile acids and lipid metabolism. IV. Influence of bile acids on biliary and liver organelle phospholipids and cholesterol. Am J Physiol. 1968 Dec;215(6):1390–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.6.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swell L., Gustafsson J., Schwartz C. C., Halloran L. G., Danielsson H., Vlahcevic Z. R. An in vivo evaluation of the quantitative significance of several potential pathways to cholic and chenodeoxycholic acids from cholesterol in man. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):455–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Regulation of biliary cholesterol output in the rat: dissociation from the rate of hepatic cholesterol synthesis, the size of the hepatic cholesteryl ester pool, and the hepatic uptake of chylomicron cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1979 Nov;20(8):923–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. The contribution of newly synthesized cholesterol to biliary cholesterol in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2438–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Cornelissen F., Lauwers W. F., van Cutsem J. M. In vitro and in vivo effects of the antimycotic drug ketoconazole on sterol synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):922–928. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Bossche H. Biochemical targets for antifungal azole derivatives: hypothesis on the mode of action. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1985;1:313–351. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9547-8_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonk R. J., van Doorn A. B., Strubbe J. H. Bile secretion and bile composition in the freely moving, unanaesthetized rat with a permanent biliary drainage: influence of food intake on bile flow. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1978 Sep;55(3):253–259. doi: 10.1042/cs0550253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M., Gunn J. M. Long-term cell culture of adult rat liver epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Nov;89(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



