Abstract
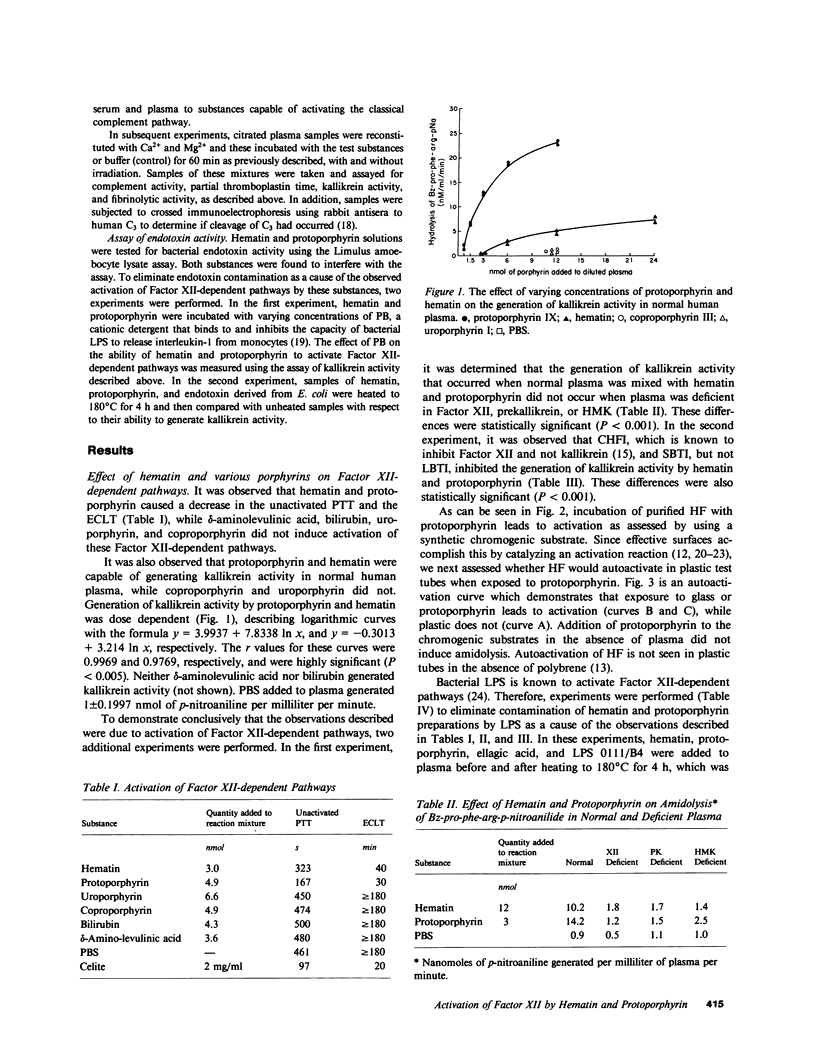
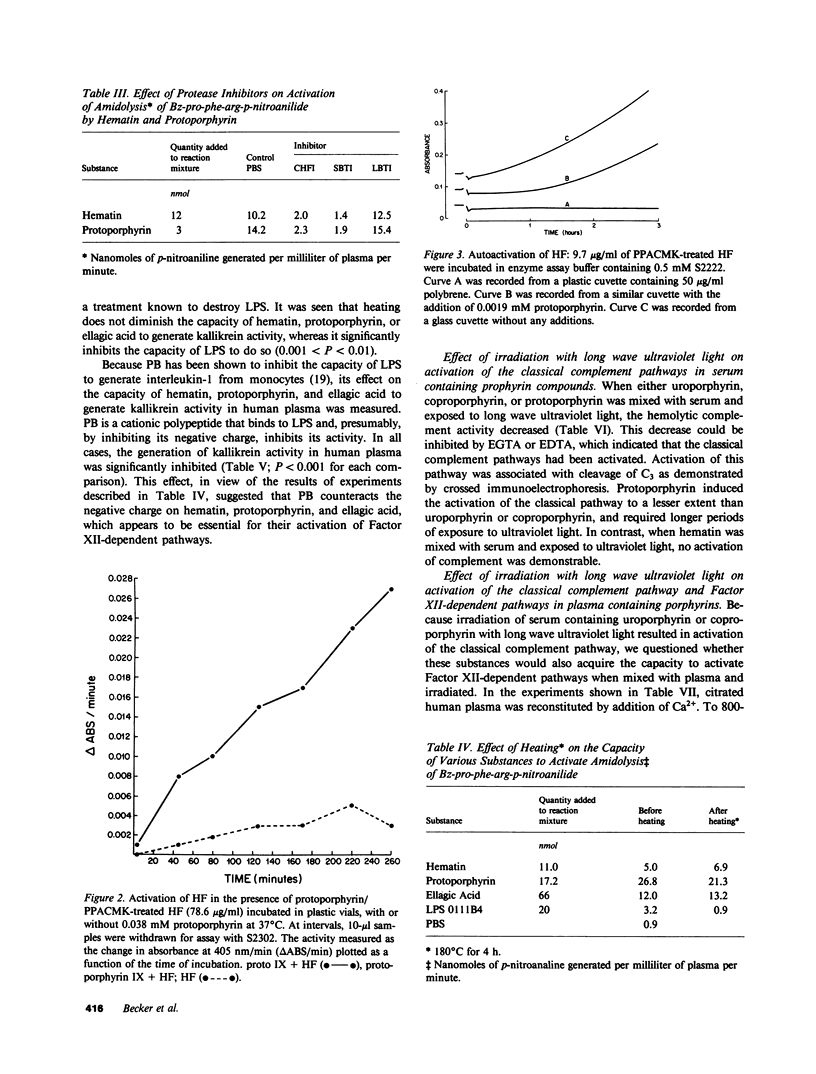
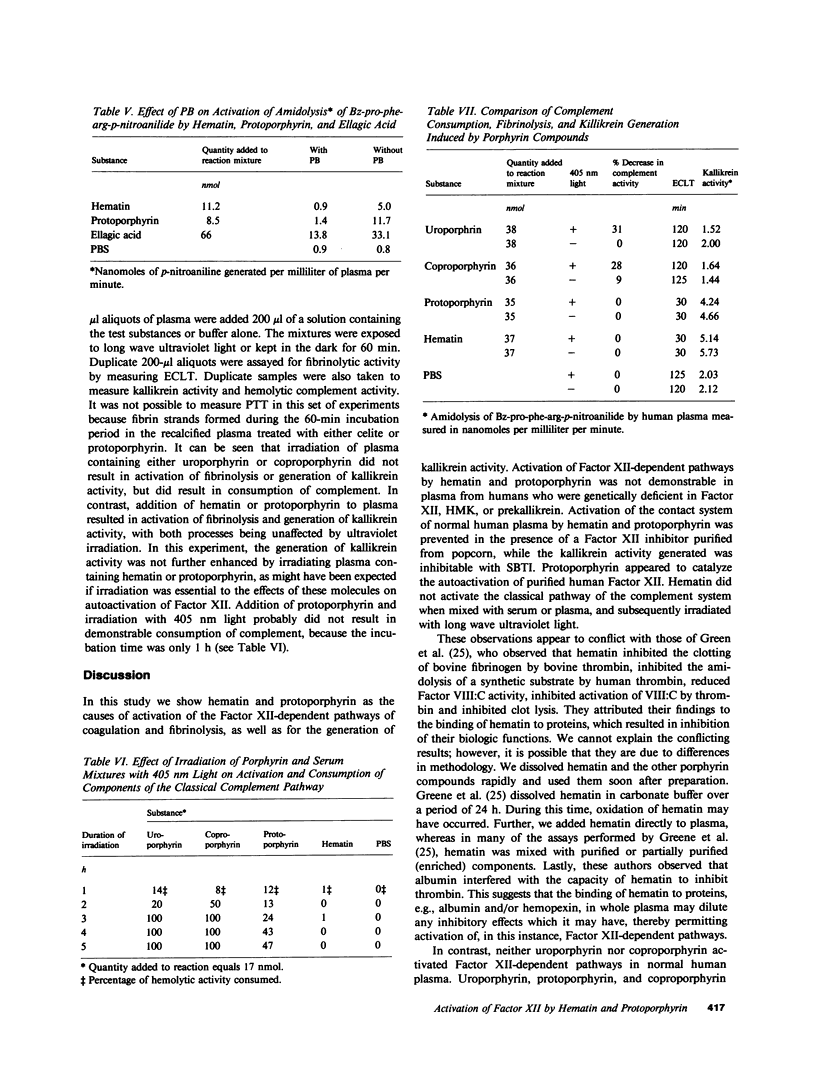
Intravenous administration of hematin is effective in the treatment of acute exacerbations of the inducible porphyrias. In the course of such treatment, coagulopathies have occurred that are characterized by prolongation of prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and formation of fibrin split products. In experiments in vitro with normal human plasma, we observed that hematin and protoporphyrin activated Factor XII-dependent pathways of coagulation and fibrinolysis, and that they generated kallikrein activity. Incubation of protoporphyrin with purified Factor XII resulted in activation as measured by amidolysis of a chromogenic substrate. Neither coproporphyrin, uroporphyrin, delta-aminolevulinic acid, porphobilinogen, or bilirubin activated Factor XII-dependent pathways. Exposure of serum containing added uroporphyrin, coproporphyrin, and protoporphyrin, but not hematin, to ultraviolet light (405 nm) resulted in activation of the classical pathway of the complement system. On the other hand, exposure of plasma containing uroporphyrin or coproporphyrin to ultraviolet light did not result in activation of Factor XII-dependent pathways.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aft R. L., Mueller G. C. Hemin-mediated oxidative degradation of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Dubin T. Activation of factor XII by tobacco glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):457–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Shillcock M., Jones P. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of the aggregation of porphyrins in aqueous solution. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):279–285. doi: 10.1042/bj1530279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claeson G., Friberger P., Knös M., Eriksson E. Methods for determination of prekallikrein in plasma, glandular kallikrein and urokinase. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):76–78. doi: 10.1159/000214238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier G. S., Pratt J. M., De Wet C. R., Tshabalala C. F. Studies on haemin in dimethyl sulphoxide/water mixtures. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj1790281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. H. Enzymatic defects in porphyria: an overview. Semin Liver Dis. 1982 May;2(2):87–99. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Schothorst A. A., Soter N. A., Pathak M. A. Erythropoietic protoporphyria. Photoactivation of the complement system. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):517–522. doi: 10.1172/JCI109883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D., Reynolds N., Klein J., Kohl H., Ts'ao C. H. The inactivation of hemostatic factors by hematin. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Sep;102(3):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H. Role of surface in surface-dependent activation of Hageman factor (blood coagulation factor XII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojima Y., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. Hageman factor fragment inhibitor in corn seeds: purification and characterization. Thromb Res. 1980 Oct 15;20(2):149–162. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90381-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon J. M., Frykholm B. C., Hess R. A., Tschudy D. P. Hematin therapy for acute porphyria. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 May;58(3):252–269. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197905000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim H. W., Novotny H., Gigli I. Role of complement and polymorphonuclear cells in demethylchlortetracycline-induced phototoxicity in guinea pigs. Inhibition by decomplementation in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1326–1335. doi: 10.1172/JCI111088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim H. W., Perez H. D., Goldstein I. M., Gigli I. Complement-derived chemotactic activity is generated in human serum containing uroporphyrin after irradiation with 405 nm light. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1072–1077. doi: 10.1172/JCI110119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim H. W., Perez H. D., Poh-Fitzpatrick M., Goldstein I. M., Gigli I. Generation of chemotactic activity in serum from patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria and porphyria cutanea tarda. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 22;304(4):212–216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101223040406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim H. W., Poh-Fitzpatrick M. B., Gigli I. Activation of the complement system in patients with porphyrias after irradiation in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1961–1965. doi: 10.1172/JCI111616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Autoactivatability of human Hageman factor (factor XII). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):803–810. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90774-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L., Dudley M. D., Pearson R. D. Coagulopathy associated with hematin treatment for acute intermittent porphyria. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Dec;95(6):700–701. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-6-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Cochrane C. G. Direct evidence for Hageman factor (factor XII) activation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins). J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):797–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston D., Bennett N. B., Ogston C. M., Ratnoff O. D. The assay of a plasma component necessary for the generation of a plasminogen activator in the presence of Hageman factor (Hageman factor co-factor). Br J Haematol. 1971 Feb;20(2):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seery V. L., Morgan W. T., Muller-Eberhard U. Interaction of rabbit hemopexin with rose bengal and photooxidation of the rose bengal-hemopexin complex. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6439–6444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Dunn J. T., Garen L., Kaplan A. P. Autoactivation of human Hageman factor. Demonstration utilizing a synthetic substrate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7281–7286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Enzymatic activities of activated and zymogen forms of human Hageman factor (factor XII). Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):64–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tankersley D. L., Finlayson J. S. Kinetics of activation and autoactivation of human factor XII. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):273–279. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truedsson L., Sjöholm A. G., Laurell A. B. Screening for deficiencies in the classical and alternative pathways of complement by hemolysis in gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Jun;89(3):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Cochrane C. G. A protease-like permeability factor in guinea pig skin: immunologic identity with plasma Hageman factor. Am J Pathol. 1982 May;107(2):127–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


